南京理工大学物理光学-1996真题
- 格式:pdf
- 大小:247.40 KB
- 文档页数:2

南京理工大学课程考试试卷(学生考试用)第 1 页共 1 页南京理工大学课程考试答案及评分标准南京理工大学课程考试试卷(学生考试用)6. Suppose we spread white light out into a fan of wavelengths by means of a diffraction grating and then pass a small select region of that spectrum out through a slit. Because of the slit, a band of wavelengths 1.2 nm wide centeredDetermine the frequency bandwidth and the coherence length of this light. (7. What is the general expression for the separation of the fringes of a Fresnel biprism of第 1 页共 1 页08A1. Given the wavefunctions 14sin 2(0.23)x t ψπ=-, and 2[sin(7 3.5)]/2.5x t ψ=+, determine in each case the values of (a) frequency, (b)wavelength, (c) period, (d)amplitude, (e)phase velocity, and (f) direction of motion. Time is in seconds and x is in meters. (12 points)2. Write an expression for the E -and B -fields that constitute a plane harmonic wave traveling in the +z-direction. The wave is linearly polarized with its plane of vibration at 450 to the yz -plane. (8 points)3. A 3.0-V flashlight bulb draws 0.25A, converting about 1.0% of the dissipated power into light(550nm λ≈). If the beam has a cross-sectional area of 10cm 2 and is approximately cylindrical, (a) How many photons are emitted per second? (b) How many photons occupy each meter of the beam? (c) What is the flux density of the beam as it leaves the flashlight? (346.62610h J s -=⨯⋅) (9 points)4. A ray of yellow light from a sodium discharge lamp falls on the surface of a diamond in air at 450. If at that frequency 2.42d n =, compute the angular deviation suffered upon transmission. (8 points)5. A beam of light in air strikes the surface of a smooth piece of plastic having an index of refraction of 1.55 at an angle with the normal of 20.00. The incident light has component E-field amplitudes parallel and perpendicular to the plane-of-incidence of 10.0V/m and 20.0V/m, respectively. Determine the corresponding reflected field amplitudes. (10 points)6. A magnetic-field technique for stabilizing a He-Ne laser to 2 parts in 1010 has been patented. At 632.8nm, what would be the coherence length of a laser with such a frequency stability? (8 points)7. An expanded beam of red light from a He-Ne laser (0632.8nm λ=) is incident on a screen containing two very narrow horizontal slits separated by 0.200mm. A fringe pattern appears on a white screen held 1.00m away. (a) How far (in radians and millimeters) above and below the central axis are the first zeros of irradiance? (b) How far (in mm) from the axis is the fifth bright band? (c) Compare these two results. (12 points)8. One of the mirrors of a Michelson Interferometer is moved, and 1000 fringe-pairs shift past the hairline in a viewing telescope during the process. If the device is illuminated with 500-nm light, how far was the mirror moved? (8 points)9. Suppose that we have a laser emitting a diffraction-limited beam (0632.8nm λ=) with a 2-mm diameter. How big a light spot would be produced on the surface of the Moon a distance of 337610km ⨯ away from such a device? Neglect any effects of the Earth ’s atmosphere. (7 points)10. Sunlight impinges on a transmission grating that is formed with 5000 lines per centimeter. Does the third-order spectrum overlap the second-order spectrum? Take red to be 780nm and violet to be 390 nm. (10 points)11. Imagine that we have randomly polarized room light incident almost normally on the glass surface of a radar screen. A portion of it would be specularly reflected back toward the viewer and would thus tend to obscure the display. Suppose now that we cover the screen with a right-circular polarizer, as shown in the Figure. Trace the incident and reflected beams, indicating their polarization states. What happens to the reflected beam? (8 points)08A答案07a1. Consider a lightwave having a phase velocity of 8310/m s ⨯ and a frequency of14610Hz ⨯. What is the shortest distance along the wave between any two points that have aphase difference of 300? What phase shift occurs at a given point in 10-6s, and how many waves have passed by in that time? (12 points)2. The electric field of an electromagnetic wave traveling in the positive x -direction is given by 00ˆE jsin()cos()E z z kx t πω=-, (a) Describe the field verbally. (b) Determine an expression for k . (c) Find the phase speed of the wave. (7 points)3. How many photons per second are emitted from a 100-W yellow lightbulb if we assume negligible thermal losses and a quasi-monochromatic wavelength of 550nm ? In actuality only about 2.5% of the total dissipated power emerges as visible radiation in an ordinary 100-W lamp. (346.62610h J s -=⨯⋅) (8 points)4. A laserbeam impinges on an air-liquid interface at an angle of 550. The refracted ray is observed to be transmitted at 400. What is the refractive index of the liquid? (7 points)5. Light is incident in air perpendicularly on a sheet of crown glass having an index of refraction of 1.522. Determine both the reflectance and the transmittance. (12 points)6. Imagine that we chop a continuous laserbeam (assumed to be monochromatic at0632.8nm λ=) into 0.1-ns pulses, using some sort of shutter. Compute the resultantlinewidth λ∆, bandwidth, and coherence length. Find the bandwidth and linewidth that would result if we could chop at 1015Hz . (8 points)7. With regard to Young ’s Experiment, derive a general expression for the shift in the vertical position of the m th maximum as a result of placing a thin parallel sheet of glass of index n and thickness d directly over one of the slits. Identify your assumptions. (10 points)8. Suppose we place a chamber 10.0cm long with flat parallel windows in one arm of a Michelson Interferometer that is being illuminated by 600-nm light. If the refractive index of air is 1.00029 and all the air is pumped out of the cell, how many fringe-pairs will shift by in the process? (10 points)9. If you peered through a 0.75-mm hole at an eye chart, you would probably notice a decrease in visual acuity. Compute the angular limit of resolution, assuming that it ’s determined only by diffraction; take 0550nm λ=. Compare your results with the value of41.710rad -⨯, which corresponds to a 4.0-mm pupil. (10 points)10. Light having a frequency of 144.010Hz ⨯ is incident on a grating formed with 10000 lines per centimeter. What is the highestorder spectrum that can be seen with this device? Explain. (8 points)11. A Babinet compensator is positioned at 450 between crossed linear polarizers and is being illuminated with sodium light. When a thin sheet of mica (indices 1.599 and 1.594) is placed on the compensator, the black bands all shift by 1/4 of the space separating them. Compute the retardance of the sheet and its thickness. (8 points)1. Solution:814/310/5100.6c m λνμ==⨯⨯= 83/310/60510c km λν==⨯=⨯2. Solution:The number of waves is 0/AB λ. With the glass in place, there are 0()/AB L λ- waves in vacuum and an additional /L λwaves in glass for a total of 00(/)(1/1/)AB L λλλ-. The difference in number is 0(1/1/)L λλ-, giving a phase shift of φ∆ of 2π for each wave; hence , 0002(1/1/)2(/1/)2/22000L L n L πλλπλλπλπ-=-==.3. Solution:(a) The phase angle is retarded by an amount (2/)2/n y y πλπλ∆-∆ or (1)/n y c ω-∆. Thus0exp [(1)//]p E E i t n y c y c ω=--∆- or 0exp[(1)/]exp (/)p E E i n y c i t y c ωω=--∆- (b) Since 1x e x ≈+ for small x, if 1n ≈ of 1y ∆ , exp[(1)/]1(1)/i n y c i n y c ωω--∆≈--∆ and since exp(/2)i i π-=-, (1)(/)exp(/2)p u u E E n y E c i ωπ=+-∆-4. Solution:/t i t i r n n n n -+ . Air-water: 4/311/70.144/31r -===+. Air-crown glass:3/211/50.203/21r -===+.More reflectance for glass. 2/r i I I R r ==.Air-water: 2(1/7)0.02R ==. Air-crown glass: 2(1/5)0.04R ==5. Solution:/21sin sin it ti n n θθθθ==/2/1sin sin t i n n θθ=/21sin sin t i n n θθ= and /t i i θθ=__/cos AB d t =θ ___/)sin(AB a t i =-θθ t t i daθθθcos )sin(=- a d t t i =-θθθcos )sin(6. Solution:99//(1.210)/(50010)0.0024m m ννλλ--∆=∆=⨯⨯=c νλ=, so 8914/(310/)/(50010) 6.0010c m s m Hz νλ-==⨯⨯=⨯1412(0.0024)(6.0010) 1.4410Hz ν∆=⨯=⨯131/ 6.9410c t s ν-∆∆=⨯8134(310/)(6.9410) 2.0810c c l c t m s s m --∆∆=⨯⨯=⨯7. Solution:)(2//0n n d s y -=∆αλ8.Solution :λ=nd 2m nd 71084.12-⨯==λ9. Solution:θαsin 2k a =,θβsin 2k b=,mb a =,πβαm m 2==N=number of fringes=m m a 2/2/==πππ10. Solution:sin m a m θλ=sin /m m Y R θ6(/)10,000/10/m Y m a R lines cm lines m λ=== So 610a m -=761(589.5923)[1(5.89592310)/10](1.00)0.5895923Y nm m m m m--=⨯='761(588.9953)[1(5.88955310)/10](1.00)0.5889953Y nm m m m m--=⨯='411 5.9710Separation Y Y m -=-=⨯11. Solutionsin /sin i t ti n θθ=; sin sin /sin(40)/1.5t i ti n θθ== ; 25.4t θ= .2222tan ()/tan ()tan (14.6)/tan (65.4)0.014i t i t R θθθθ=-+=-=2222sin ()/sin ()sin (14.6)/sin (65.4)0.077i t i t R θθθθ⊥=-+=-=1()0.04552R R R ⊥=+= /()()/()67%p p n V I I I R R R R R ⊥⊥=+=+++=。
![2020年南京理工大学819光学工程[物理光学(75分)、应用光学(75分)]考研真题汇编](https://uimg.taocdn.com/d3700222844769eae009edd7.webp)
2020年南京理工大学819光学工程[物理光学(75分)、应用光学(75分)]考研真题汇编
说明:本套考研资料由本机构多位高分研究生潜心整理编写,2020年考研初试首选资料。
一、南京理工大学819光学工程[物理光学(75分)、应用光学(75分)]考研真题汇编
1.南京理工大学819光学工程[物理光学(75分)、应用光学(75分)]2010-2015年考研真题,暂无答案。
说明:分析历年考研真题可以把握出题脉络,了解考题难度、风格,侧重点等,为考研复习指明方向。
二、资料全国统一零售价
2.本套考研资料全国统一零售价:[¥120.00]
三、2020年研究生入学考试指定/推荐参考书目(资料不包括教材)
3.南京理工大学819光学工程考研初试参考书
《物理光学》(修订本)机械工业出版社,梁铨廷(浙大)
《应用光学》机械工业出版社,张以漠
《应用光学与光学设计基础》东南大学出版社,迟泽英、陈文建。


2011级大物试卷及答案一、选择题(每题2分,共20分)1、一质点从静止出发绕半径为R 的圆周作匀变速圆周运动,角加速度为α,当该质点走完一圈回到出发点时,所经历的时间为 ( B )(A )R 221α; (B )απ4; (C )απ2; (D )条件不够不能确定。
2、有一个小球,置于一个光滑的水平桌面上,有一绳其一端连接此小球,另一端穿过桌面中心的小孔,该小球原以角速度ω在距孔为r 的圆周上转动,今将绳从小孔缓慢往下拉的过程中,则对小球下列叙述正确的是 ( C ) (A )角动量、动能、动量都不变; (B )角动量、动能、动量都改变; (C )角动量不变,动能、动量都改变; (D )角动量和动量不变,动能改变。
3、均匀细棒OA 可绕通过其一端O 而与棒垂直的水平固定光滑轴转动,如图1。
今使棒从水平位置由静止开始下落。
在棒摆动到竖直位置的过程中,则应 ( A ) (A )角速度从小到大,角加速度从大到小; (B )角速度从小到大,角加速度从小到大; (C )角速度从大到小,角加速度从大到小; (D )角速度从大到小,角加速度从小到大。
4、一简谐振动曲线如图2所示,则振动周期为 ( D ) (A )2.62s ; (B )0.42s ; (C )0.38s ; (D )2.40s5、传播速度为100m/s ,频率为50Hz 的平面简谐波,在波线上相距为0.5m 的两点之间的位相差为 ( C )(A )3π; (B )6π; (C )2π; (D )4π。
6、如图3所示,设某热力学系统经历一个准静态过程b →c →a ,a ,b 两点在同一条绝热线上,则该系统在b →c →a 过程中 ( D ) (A )只吸热,不放热; (B )只放热,不吸热;(C )有的阶段吸热,有的阶段放热,吸收的热量等于放出的热量; (D )有的阶段吸热,有的阶段放热,吸收的热量大于放出的热量; (E )有的阶段吸热,有的阶段放热,吸收的热量小于放出的热量。




南 京 理 工 大 学 考 试 卷课程名称 大学物理 姓 名 学 号适用专业考试形式闭卷考试时间 120分钟一、选择题(每题3分,共30分) 1、下列各种说法正确的是( )(A )作用力的冲量与反作用力的冲量总是等值反向的; (B )系统的内力可以改变系统的总动量; (C )冲量的方向与物体动量的方向相同;(D )以恒力作用于物体,时间越长,物体的动量越大。
2、一炮弹由于特殊原因在飞行过程中突然炸裂成两块,其中一块作自由下落,另一块的着地点( )(A )比原来更远; (B )比原来更近; (C )和原来一样; (D )无法判断。
3、两个匀质圆盘A 和B 的密度分别为A ρ和B ρ。
若B A ρρ>,但两圆盘质量和厚度相同,若两盘对通过盘心垂直于盘面的轴的转动惯量分别为A J 和B J ,则 ( ) (A )B J J >A ; (B )B J J <A ; (C )B J J =A ; (D )不能确定哪个大。
4、任何一个实际弹簧都是有质量的,若考虑其质量,则弹簧振子振动周期将:( ) (A )不变; (B )变小; (C )变大; (D )无法确定。
5、机械波在弹性媒质中传播时,若媒质中媒质元刚好经过平衡位置,则它的能量为( ) (A )动能最大,势能也最大; (B )动能最小,势能也最小; (C )动能最大,势能最小; (D )动能最小,势能最大。
6、某容器种有理想气体,若绝对温度提高为原来的2倍,用P 和k ε分别表示气体的压强和气体分子的平均动能,则: ( ) (A )k P ε,均提高为原来的2倍; (B )k P ε,均提高为原来的4倍; (C )P 提高为原来的2倍,k ε提高为原来的4倍; (D )k P ε,均不变。
7、关于热力学过程,下列说法正确的是: ( ) (A )准静态过程一定是可逆过程;(B )非准静态过程不一定是不可逆过程; (C )可逆过程一定是准静态过程; (D )不可逆过程一定是非准静态过程。
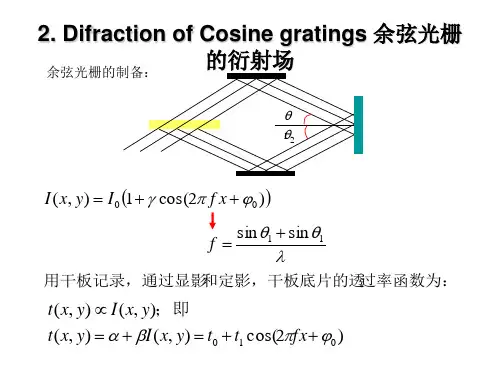

2017版南京理工大学《819光学工程》全套考研资料我们是布丁考研网南理工考研团队,是在读学长。
我们亲身经历过南理工考研,录取后把自己当年考研时用过的资料重新整理,从本校的研招办拿到了最新的真题,同时新添加很多高参考价值的内部复习资料,保证资料的真实性,希望能帮助大家成功考入南理工。
此外,我们还提供学长一对一个性化辅导服务,适合二战、在职、基础或本科不好的同学,可在短时间内快速把握重点和考点。
有任何考南理工相关的疑问,也可以咨询我们,学长会提供免费的解答。
更多信息,请关注布丁考研网。
以下为本科目的资料清单(有实物图及预览,货真价实):南京理工大学《光学工程》全套考研资料包含:一、南京理工大学《光学工程》历年考研真题及答案解析2016年南京理工大学《光学工程》考研真题(含答案解析)(11月份统一更新)2015年南京理工大学《光学工程》考研真题2012年南京理工大学《光学工程》考研真题2011年南京理工大学《光学工程》考研真题2010年南京理工大学《光学工程》考研真题2009年南京理工大学《光学工程》考研真题2008年南京理工大学《光学工程》考研真题2007年南京理工大学《光学工程》考研真题2006年南京理工大学《光学工程》考研真题(含答案解析)2005年南京理工大学《光学工程》考研真题(含答案解析)2004年南京理工大学《光学工程》考研真题(含答案解析)2003年南京理工大学《光学工程》考研真题2002年南京理工大学《物理光学》考研真题2001年南京理工大学《物理光学》考研真题2000年南京理工大学《物理光学》考研真题1999年南京理工大学《物理光学》考研真题1998年南京理工大学《物理光学》考研真题2002年南京理工大学《应用光学》考研真题2001年南京理工大学《应用光学》考研真题2000年南京理工大学《应用光学》考研真题1999年南京理工大学《应用光学》考研真题1998年南京理工大学《应用光学》考研真题1997年南京理工大学《应用光学》考研真题1996年南京理工大学《应用光学》考研真题1995年南京理工大学《应用光学》考研真题二、南京理工大学《光学工程》期中期末试题汇编三、南京理工大学《光学工程》考研复习笔记1、《光学工程》公式定律总结四、南京理工大学《光学工程》考研复习题1、《光学工程》重难点例题解析2、《光学工程》考研练习题3、《光学工程》核心模拟题4、《光学工程》历年模拟题与答案5、《光学工程》模拟题库6、《光学工程》考研本校各章节练习题(英语版)以下为截图及预览2015年考研真题公式定律总结模拟题库重难点例题解析。