A Fault-Tolerant FPGA Architecture
- 格式:pdf
- 大小:333.87 KB
- 文档页数:8


摘要航天领域技术应用在时刻进步,当前卫星系统的功能呈现出多样性和复杂性的特点,各项性能不断提高,除了对子系统间数据传输的高速率和高可靠性提出要求以外,同时对一体化传输、提高模块复用率、降低开发和制造成本、提高兼容性提出了更高的要求。
这一特点在小卫星平台上的需求尤为迫切,因此需要一种高性能的星上总线网络及对应的多元化架构来满足大数据量传输、实时控制数据传输以及低成本复用与容错的需求。
SpaceWire 技术就是作为下一代星上数据处理系统模型而提出的一种高速率、点对点、全双工、灵活、可定制容错架构的串行总线网络,基于SpaceWire标准设计的星上总线网络的特点,它有望实现上述需求而取代传统星上数据处理系统。
本文在详细分析SpaceWire 路由网络设计需求和深入研究SpaceWire 标准协议的基础上,完成SpaceWire节点接口、路由器设计及路由网络架构的研究。
其中包括SpaceWire节点接口和路由器的硬件设计实现、功能和性能测试以及SpaceWire 路由网络架构性能仿真分析与测试。
设计基于Altra的FPGA 平台使用Verilog HDL硬件描述语言自顶向下地实现,将各个模块按功能划分分别实现验证。
对设计的SpaceWire 总线网络的测试结果和分析证明本设计合理,传输、实时性和容错性能稳定,功能和指标基本符合设计要求,为实际应用设计的总线网络提供了理论和实践的支持。
关键词:SpaceWire标准;总线网络;节点接口;路由器;容错架构;- I -AbstractWith the advances in space technology and space applications, the function of the current satellite system showing the characteristics of diversity and complexity and the performance continues to increase, in addition to the request of the high-speed and high reliability of data transmission between the subsystems.Put forward higher requirements for the integrated transmission module reuse rate, lower development and manufacturing costs, improve compatibility. This feature is particularly urgent demand on the small satellite platform, need a high-performance satellite bus network and the corresponding diversification of structure to meet the large amounts of data, real-time control of data transmission, and demand for low-cost reuse and fault-tolerant . SpaceWire technology is a high rate data processing system model proposed in the next generation on-borad, point-to-point, full duplex, flexible, customizable fault-tolerant architecture serial bus network, based on the SpaceWire standard on-borad bus network characteristics, it is expected to achieve the above requirements and data processing systems replace the traditional star.In the paper, SpaceWire standard protocol of the detailed analysis of the SpaceWire routing network design requirements and in-depth study on the basis of completed SpaceWire node interface router design and routing network architecture are finished. Including SpaceWire node interface and router hardware design and implementation, functionality and performance testing, and SpaceWire routing network architecture performance simulation analysis and testing. Altra's FPGA-based platform, the design using Verilog HDL hardware description language to achieve top-down, the various modules by function, respectively, to achieve validation. Test results and analysis of the SpaceWire bus network designed to prove the rational design, transmission, real-time and fault-tolerant and stable performance, the basic functions and indicators meet the design requirements for the practical application of the design of the bus network to provide the support of the theory and practice.Keywords: SpaceWire standard, bus network, node interface, router, fault-tolerant architecture.目录摘要 (I)ABSTRACT (II)第1章绪论 (1)1.1课题背景及研究的目的和意义 (1)1.2国内外研究现状 (3)1.3本文的主要研究内容 (6)1.4论文章节安排 (7)第2章SPACEWIRE总线网络设计基础 (8)2.1S PACE W IRE标准物理层 (8)2.2S PACE W IRE标准信号层 (9)2.3S PACE W IRE标准字符层 (11)2.4S PACE W IRE标准交换层 (13)2.5S PACE W IRE标准数据包层 (15)2.6S PACE W IRE标准网络层 (15)第3章SPACEWIRE总线节点接口设计 (20)3.1S PACE W IRE总线节点接口整体设计 (20)3.2S PACE W IRE接口主状态机设计 (21)3.3S PACE W IRE接口发送器设计 (23)3.4S PACE W IRE接口接收器设计 (26)3.5流控制模块设计 (31)3.6本章小结 (32)第4章SPACEWIRE总线路由器及容错设计 (33)4.1S PACE W IRE路由器设计需求及整体设计方案 (33)4.2数据包识别模块的设计 (34)4.3路由表及其控制模块设计 (38)4.4裁决器及交换矩阵的设计 (40)4.5S PACE W IRE总线网络容错架构 (42)4.6本章小结 (43)第5章SPACEWIRE总线网络性能测试分析 (44)5.1整体测试方案 (44)5.2S PACE W IRE节点接口测试 (45)5.3S PACE W IRE总线网络路由测试 (48)5.4S PACE W IRE总线容错测试 (50)5.5S PACE W IRE总线网络性能分析 (52)5.6本章小结 (54)结论 (55)参考文献 (56)攻读硕士学位期间发表的论文及其它成果 (61)哈尔滨工业大学学位论文原创性声明及使用授权说明 (62)致谢 (63)第1章绪论1.1 课题背景及研究的目的和意义近年来,随着空间技术的发展和研究的深入,空间任务日益呈现出多样性和复杂性的特点,因而卫星系统的功能也出现了跨越式的发展,这就使得星上各个设备、子系统之间的数据交换、控制信息交换网络变得尤为复杂,性能要求也日益提高,此时,首先需要解决数据量较大、数据环境复杂的情况下星上数据处理系统的可靠性和实时性的问题,从而对负责数据传输的星上总线网络性能有了新的要求[1]。
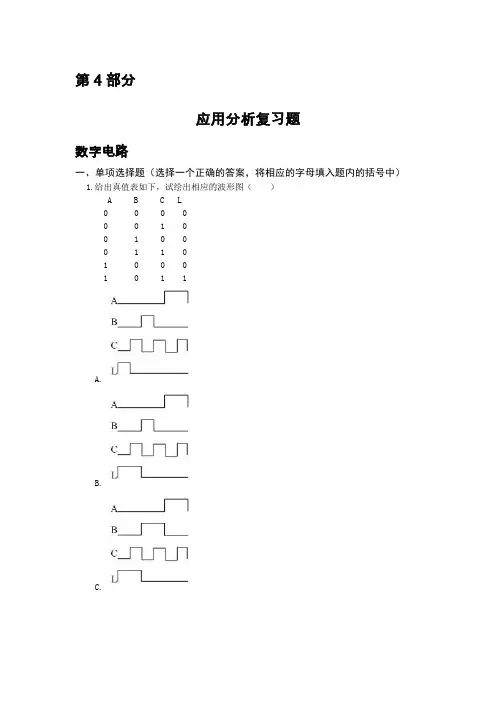
第4部分应用分析复习题数字电路一、单项选择题(选择一个正确的答案,将相应的字母填入题内的括号中)1 .给出真值表如下,试绘出相应的波形图()A B C L0 0 0 00 0 1 00 1 0 00 1 1 01 0 0 01 0 1 1A.B.C.D.2 .题示逻辑图如下,根据逻辑图可得出逻辑表达式为。
()A. L=B. L=C. L=D. L=3 .题示的波形图如下,判断其对应的真值表正确的是()。
A.A B C1 1 10 1 01 0 00 0 1B.A B C1 1 10 1 00 0 11 0 0C.A B C1 1 10 0 11 0 00 0 1D.A B C1 1 10 1 01 0 01 1 14 .A、B、C的真值表如下,试画出A⊙B⊙C的波形图()A B C0 0 00 0 10 1 00 1 1A.B.C.D.5 .A、B、C的真值表如下,试画出,,的波形图。
()A B C1 0 01 0 11 1 01 1 1A.B.C.D.6 .根据题目给出的逻辑图,选择正确的逻辑表达式()。
A. L=B. L=C. L=D. L=7 .题示逻辑图如下,根据逻辑图可得出逻辑表达式为()A.B.C.D.8 .A、B的波形图如下,则其对应的A、B、A+B的真值表是。
()A.A B A+B0 0 00 1 11 0 11 1 1B.A B A+B1 0 00 1 11 0 11 1 1C.A B A+B1 0 10 1 10 0 01 1 1D.A B A+B0 0 00 1 01 0 01 1 19 .已知A、B、C的波形图如下,试画出,,的真值表()。
A., ,1 1 00 1 00 1 00 1 1B., , g”>1 1 00 1 00 1 00 0 1C., , >1 1 00 1 00 1 01 0 1D., ,1 1 00 1 00 1 10 1 1FPGA一、单项选择题(选择一个正确的答案,将相应的字母填入题内的括号中)1 .以下为某FPGA器件的综合分析报告的一部分Selected Device:3s500efg320-4Number of Slices: 4233 of 4656Number of CLBS: 955 of 1164刚其点用的系统资源为()。


FPGA实现实时适应图像阈值Elham Ashari电气与计算机工程系,滑铁卢大学理查德霍恩西计算机科学和工程系,纽约大学摘要:本文提出了一种基于实时阈值的通用FPGA结构。
硬件架构是基于一种加权聚类算法的架构,这种算法的重点就在于聚类的前景和背景像素的阈值问题。
该方法采用聚类的二值加权神经网络法找到两个像素组的质心。
图像的阈值是两个质心的平均值。
因为对于每个输入的像素,选定的最近的权值是用来更新的,因而推荐一种自适应的阈值技术。
更新是基于输入像素的灰度级和相关权值的差额的,通过学习快慢因素来衡量其速率。
硬件系统是在FPGA平台上实现的,它包含两个功能模块。
第一个模块获得图像框架阈值,另一个模块将阈值应用于图像的框架。
两个模块的并行性和简单的硬件组成部分使其适用于实时应用程序,并且,其性能可与经常用于离线阈值技术相媲美。
通过利用FPGA对无数的例子进行模拟和实验,得到该算法的结果。
这项工作的基本应用是确定激光的质心,但接下来将会讨论它在其他方面的应用。
关键词:实时阈值,自适应阈值,FPGA实现、神经网络1 简介图像二值化是图像处理的一个主要问题。
如果要从一张图像上提取有用的信息,我们需要将它分成不同的部分(例如背景色和前景色)来进行更为详细的分析。
一般来说,前景色的像素的灰度级与背景色的灰度级是不同的。
现在已有一些较好的使图像二值化地算法,就性能而不是就速度而言,这些算法的主要目标在于高效率,然而对于一些应用,尤其对是在那些定制的硬件和实时应用程序来说,速度则是最关键的要求。
可实现的快速而简单的阈值技术在实际成像系统中得到广泛应用。
例如,结合了CMOS图像传感器的片上图像处理技术普遍存在于各种各样的成像系统当中。
在这样一个系统当中,图像的实时处理及其得到的相关信息是至关重要的。
实时阈值技术的应用领域包括机器人、汽车、目标追踪以及激光测距。
在激光测距,即确定目标的运动范围的过程中,所捕获的图像为二值图像。

[1] Using FPGA technology towards the design of an adaptive fault tolerant frameworkErdogan, Sevki (University of Hawaii); Gersting, Judith L.; Shaneyfelt, Ted; Duke, Eugene L. Source: Conference Proceedings - IEEE International Conference on Systems, Man and Cybernetics, v 4, IEEE Systems, Man and Cybernetics Society, Proceedings - 2005 International Conference on Systems, Man and Cybernetics, 2005, p 3823-3827ISSN: 1062-922X CODEN: PICYE3Conference: IEEE Systems, Man and Cybernetics Society, Proceedings - 2005 International Conference on Systems, Man and Cybernetics, Oct 10-12 2005, Waikoloa, HI, United States Sponsor: IEEE Systems, Man and Cybernetics Society Publisher: Institute of Electrical and Electronics Engineers Inc.Abstract: In this paper we propose architecture for a Reconfigurable, Adaptive, Fault-Tolerant (RAFT) framework for application in real time systems with require multiple levels of redundancy and protection. Typical application environments include distributed processing, fault-tolerant computation, and mission and safety-critical systems. The framework uses Field Programmable Gate Array (FPGA) technologies with on the fly partial programmability achieving reconfiguration of a system component when the existing components fail or to provide extra reliability as required in the specification. The framework proposes the use an array of FPGA devices to implement a system that, after detecting an error caused by a fault, can adaptively reconfigure itself to achieve fault tolerance. The FPGAs that are becoming widely available at a low cost are exploited by defining a system model that allows the system user to define various levels of reliability choices, providing a monitoring layer for the system engineer. ? 2005 IEEE. (21 refs.)[2]METHOD FOR PROTECTING COMPUTER THROUGH REAL-TIME MONITORING BY PROTECTING EXECUTION FILE, AND COMPUTER AND SYSTEM PROTECTED BY THE SAMEPatent number: KR20040083409Publication date: 2004-10-01Inventor: AHN MU GYEONGApplicant: SAFEI CO LTDClassification:- international: G06F11/30; G06F11/30; (IPC1-7): G06F11/30- european:Application number: KR20040072633 20040910Priority number(s): KR20040072633 20040910View INPADOC patent familyView forward citationsReport a data error hereAbstract of KR20040083409PURPOSE: A method for protecting a computer through real-time monitoring, and the computer and a system protected by the same are provided to safely protect the computer by monitoring an interrupt or an event related to file handling and enable a user to perform setting conveniently. CONSTITUTION: A setting list(50) stores permission for changing an executable file. A detecting module(10) detects/intercepts occurrence of the interrupt or the event related to the file handling. An analysis module(20) checks the permission by comparing the interrupt or the event detected from the detecting module with the setting list after checking that the interrupt or the event is a request for changing the executable file by analyzing the interrupt or the event. A processing module(30) disuses or returns the interrupt or the event depending on an analysis result of the analysis module.[3] Method and system for protecting computer system from malicious software operationPatent number: US2004225877Publication date: 2004-11-11Inventor: HUANG ZEZHEN (US)Applicant:Classification:- International: G06F1/00; G06F11/30; G06F1/00; G06F11/30; (IPC1-7): G06F11/30 - European:Application number: US20040792506 20040303Priority number(s): US20040792506 20040303; US20030469113P 20030509View INPADOC patent familyView forward citationsAlso published as:CN1550950 (A)Report a data error hereAbstract of US2004225877A method and system for protecting a computer system from malicious software operations in real-time is disclosed. The security system combines system and user activity information to derive a user initiation attribute indicating whether or not a system operation is initiated by a computer user, and stop secrete malicious software operations that are not initiated by a computer user. The security system incorporates a plurality of attributes to support flexible security policy design, warn about potentially damaging operations by Trojan programs, and dynamically create security policies to allow trusted programs to perform trusted operations.[4]PREBOOT PROTECTION, IDENTIFICATION AND SECURITY OF A COMPUTER SYSTEMPatent number: WO0233522Publication date: 2002-04-25Inventor: TELLO JOSE ALBERTOApplicant: CODEX TECHNOLOGIES INC (CA)Classification:- international: G06F1/00; G06F21/00; G06F1/00; G06F21/00; (IPC1-7): G06F1/00; G06F9/445- european: G06F21/00N5A2D; G06F21/00N1C; G06F21/00N1V; G06F21/00N3P2 Application number: WO2000IB01659 20001017Priority number(s): WO2000IB01659 20001017; US199******** 19990104View INPADOC patent familyView forward citationsAlso published as:US6463537 (B1)Cited documents:WO0048063US5835597WO9613002US5610981WO9839701Report a data error hereAbstract of WO0233522A "personalized" computer with a unique digital signature which will not boot up or recognize any data storage or communication peripheral devices without a matching "personalized" smart card containing a complementary encrypted digital signature. A modified BIOS (Basic Input Output System) replaces the standard BIOS of a motherboard and allows a security engine microprocessor to take over preboot control of the computer from the motherboard CPU (Central Procesisng Unit), configures and operates the encryption-based security system, and enables or disables selected data storage devices and other user selectable peripherals upon start up and shut down of the computer. The enabling or disabling of peripheral devices involves the use of special enabling/disabling circuits. A modified DDL (Device Driver Layer), loaded in the hard drive of the computer as part of the resident O/S (Operating System) of the computer, and memory buffer circuits allows a real time encryption system to be in place for any communication or data storage device. A data encryption engine in the security engine microprocessor allows encryption and decryption of all data stored indata storage devices. Upon power up, reset or interrupt of the computer, the microprocessor looks for, and if present, reads from the smart card in the smart card reader which is logically connected to the security engine microprocessor. This invention can also be used to allow identification and authentication of the computer and its user in networks.[5]Temporarily authorizing the use of a computer programme protected by an electronic cartridgePatent number: GB2302968Publication date: 1997-02-05Inventor: ANTONINI PIERREApplicant: ANTONINI PIERRE (FR)Classification:- international: G06F21/00; G06F21/00; (IPC1-7): G06F1/00- european: G06F21/00N7P5HApplication number: GB199******** 19960701Priority number(s): FR199******** 19950705View INPADOC patent familyView forward citationsAlso published as:US5898778 (A1)FR2736448 (A1)DE19626972 (A1)Report a data error hereAbstract of GB2302968Use of a programme protected by an electronic cartridge in a computer system is authorised for a period limited by a number of hours or a date. So as to extend the use of a protected programme contained in the memory (103) of the computer system (100-106), the user needs to enter by means of the keyboard (105) into this system a password so as to reset the electronic cartridge (107). This electronic cartridge (107) preferably comprises a memory (108), a first counter (110), a second counter (112), a monostable element (113), an adder (114), a real time clock (109) and a cabled logic network (111). This device is connected to the outside of the computer system (100-106) by means of a connector. For renting software, this invention is able to control the use of these programmes.[6] System for computer software protectionPatent number: US5666411Publication date: 1997-09-09Inventor: MCCARTY JOHNNIE C (US)Applicant:Classification:- international: G06F1/00; G06F9/38; G06F21/00; G06F1/00; G06F9/38; G06F21/00; (IPC1-7): H04L9/00- european: G06F21/00N7P5H; G06F9/38S4L; G06F21/00N1C1Application number: US199******** 19940113Priority number(s): US199******** 19940113View INPADOC patent familyView forward citationsReport a data error hereAbstract of US5666411This system protects proprietary software from disclosure and unauthorized use, enforces license limits on number of users of the software, and prevents corruption of protected software by computer viruses. Software protected under this system may execute only on computer systems which incorporate a microprocessor capable of deciphering enciphered instructions in real time. Program files are first enciphered under control of a distribution cipher key. Prior to first use of software, program files must be customized on the user computer system. This customization procedure re-enciphers the programs, so that they are enciphered under a second cipher key. Customized programs may not execute on a computer system other than one constructed with a processor chip which incorporates a crypto microprocessor. The crypto microprocessor is capable of performing this re-encipherment, and of executing both enciphered and unenciphered programs. The customization program runs on user's computer system and normally accesses a remote Exchange database system by means of a modem to accomplish its task. Variations of customization process provide for storage of enciphered software on either a single system, a network server, or a site license repository system.[7]METHOD AND DEVICE FOR PROTECTION OF COMPUTER SYSTEM FROM ILLEGAL DISTRIBUTIONPatent number: BG48653Publication date: 1991-04-15Inventor: KOLEV VLADIMIR N (BG); MARDIROSJAN GARO KH (BG) Applicant: TS LAB KOSM IZSLEDV ANIJAClassification:- international: G06F5/00; G06F5/00; (IPC1-7): G06F5/00- european:Application number: BG198******** 19890712Priority number(s): BG198******** 19890712View INPADOC patent familyView forward citationsReport a data error hereAbstract of BG48653The invention is designed for the production and use of computer systems and their software. It provides complete protection against undesirable unauthorised copying and reproduction. The method of current real time of the computer system serves to establish a protection code combination for the software product currently used by it. The unit consists of a power supply unit (1), a quartz crystal standart (2), a real time register (3), a real time coder (4), a protection code register (5) and an interface package (6)[8]DEVICE FOR PROTECTING INFORMATION BY USING USB SECURITY MODULE ON BASIS OF PC AND CODE CHIPPatent number: KR20010048160Publication date: 2001-06-15Inventor: CHO JIN HO (KR); CHOI KWANG YUN (KR); HAN SEUNG JO (KR) Applicant: CHO JIN HO (KR); CHOI KWANG YUN (KR); HAN SEUNG JO (KR); SOFTPROTEC CO LTD (KR)Classification:- international: H04L9/00; H04L9/00; (IPC1-7): H04L9/00- european:Application number: KR199******** 19991125Priority number(s): KR199******** 19991125View INPADOC patent familyView forward citationsReport a data error hereAbstract of KR2001004816PURPOSE: A device for protecting information by using a USB security module on basis of a PC and a code chip is provided to prevent illegal copy and modification of the software or data by the illegal users on the basis of the PC and to protect the important data and information. CONSTITUTION: The device for protecting information by using a USB(Universal Serial Bus) security module on basis of a PC and a code chip includes a USB controller(10) and a code chip(100). The USB controller(10) is composed of a USB core(11) and an MCU(12). The serial data by the outer input by using the USB port are sent in the USB core(11) and are in/output serially after buffering. If all the input data are the module information request order languages, the module information is read from a PROM(103) of the code chip(100) and is output to the input step of the USB core(11) or the 17 bites are output to the input step of a buffer(101) in the code chip(100) or the 16 bites input from thebuffer(101) are input and output to the input step of the USB core(11) in the MCU(12). The code chip(100) is composed of the buffer(101), a KSE96 block(110), a controlling portion(130), a mode checker(102), a scrambler, the PROM(103) and an RSA calculating portion(140).[9] Security method for protecting a system, e.g. a computer or online system against unauthorized access, whereby a computer is used with a chip card reader, with an additional varying control question used for access authenticationPatent number: DE10218945Publication date: 2003-11-13Inventor: SCHWENK JOERG (DE); SAAR EV A (DE)Applicant: DEUTSCHE TELEKOM AG (DE)Classification:- international: G06F21/00; G07F7/10; G06F21/00; G07F7/10; (IPC1-7): G06F17/60 - european: G06F21/00N5A2D; G07F7/10D6K; G07F7/10D6PApplication number: DE20021018945 20020422Priority number(s): DE20021018945 20020422View INPADOC patent familyView forward citationsReport a data error hereAbstract of DE10218945Method for securing a system against unauthorized access, whereby an input device is used to input a value that is compared with a stored input code in order to provide access to a system. Following input of the code, e.g. a PIN, a further control question is asked via a system output unit, e.g. the monitor. The question includes information for providing the answer and the user must input the correct answer before access is granted. The invention also relates to a system for implementing the method that comprises a computer with a chip card reader. The information displayed in the additional control question changes each time an identification chip card is inserted in the reader.[10]Computer chip heat protection apparatusPatent number: US6496118Publication date: 2002-12-17Inventor: SMITH WARREN L (US)Applicant:Classification:- international: H01L23/34; H01L23/467; H01L23/34; (IPC1-7): G08B17/00- european: H01L23/34; H01L23/467Application number: US20010953001 20010911Priority number(s): US20010953001 20010911View INPADOC patent familyView forward citationsReport a data error hereAbstract of US6496118A heat protection apparatus includes a heat sink adapted for mounting to a computer chip for dissipating heat generated thereby, the heat sink having a base defining a channel peripherally thereabout. A cooling fan is mounted to the heat sink for dispersing the dissipated heat. The apparatus includes a logic circuit capable of evaluating resistance input data and capable of energizing an alarm upon a programmed condition. The apparatus includes a temperature sensitive polymeric tape spanning between a pair of conductors connected to the circuit. The conductors and polymeric tape are mounted in the channel. The circuit energizes the alarm if the resistance data indicates a temperature greater than a predetermined critical temperature parameter or if the data indicates a temperature rate of rise greater than a critical rate of rise parameter. The alarm may be audible or provide a visual indicator to a computer display.[11] Protection device for portable computersPatent number: US2005039502Publication date: 2005-02-24Inventor: A VGANIM MAIR (IL)Applicant:Classification:- international: G06F1/00; G06F21/00; G06F1/00; G06F21/00; (IPC1-7): E05B73/00 - european: G06F21/00N5A2D; G06F21/00N1Z; G06F21/00N5A2BApplication number: US20040497635 20040602Priority number(s): IL20010146897 20011204; WO2002IL00965 20021202View INPADOC patent familyView forward citationsAlso published as:WO03048907 (A3)WO03048907 (A2)AU2002365735 (A1)Report a data error hereAbstract of US2005039502A protection device (16) particularly for portable computers (10) having a Universal Serial Bus (USB) socket (12) and a standardized dedicated slot (14) formed in vicinityof the socket (12). A key or the like operable mechanism (18) is provided for rotatinga T-shaped tip member (20) which is adapted to be inserted into and locked by the slot(14). Plug (22) may be either a "demo" or part of an active device, which functions to enable/disable the operation of the computer. The device (16) may further be provided with arresting means in the form of a cable (24), which can be tied to an immovable object such as table leg (26) for protecting the computer (10) against theft.[12] Electronic system and corresponding method for protecting an access gate of a computerPatent number: EP1429226Publication date: 2004-06-16Inventor: NICCOLINI MARCELLO (IT)Applicant: INFOTRONIC SPA (IT)Classification:- international: G06F21/00; G06F21/00; (IPC1-7): G06F1/00- european: G06F21/00N1V3Application number: EP20020425770 20021213Priority number(s): EP20020425770 20021213View INPADOC patent familyView forward citationsView document in the European RegisterCited documents:EP1248179WO9743716US6009527Report a data error hereAbstract of EP1429226The invention relates to a system and a method for protected access to an input/output gate (2) of an electronic processor equipped with conventional microprocessor units, volatile and mass memory units, at least one display unit, and an operating system (4) arranged to handle the several processor units, said access gate (2) being a USB gate allowing connenction at fast receptacle to predetermined peripheral units (3) of the electronic processor that are entitled to accede to be plugged in. The method comprises the following steps: detecting, through the operating system (4), the type of any unit coupled to said USB gate (2); comparing the detected type with a stored list of the predetermined units (3) entitled to accede; disabling the USB gate (2) if the comparison gives negative result.[13]APPARATUS FOR PROTECTING COMPUTER USING FUNCTIONAL CHARACTERPatent number: WO03072451Publication date: 2003-09-04Inventor: LEE IN JA (KR)Applicant: LEE IN JA (KR)Classification:- international: B65D41/26; B65D51/24; B65D81/36; B65D41/02; B65D51/24; B65D81/00; (IPC1-7): B65D41/26- european: B65D41/26; B65D51/24L; B65D81/36D2Application number: WO2002KR00432 20020313Priority number(s): KR20020005975U 20020228View INPADOC patent familyView forward citationsAlso published as:AU2002239122 (A1)Cited documents:KR890016287UKR880016247UReport a data error hereAbstract of WO03072451The present invention relates to a apparatus for protecting computer for notifying the outside of each of operation state of virus inspection using the character apparatus connected to the computer. The present invention includes computer for generating and transmitting the USB code value corresponding to registry value inspected from each of operation state of vaccine engine, and character apparatus for inquiring and outputting the voice data corresponding to the USB code value received from the computer. Hence, the present invention has an effect on not only hearing the information to virus inspection through the voice irrespective of the time as it always surveys the vaccine engine, but also presenting a fine view around the computer and increasing the effective value of the character by forming the character apparatus as the character including a doll.[14] Multiple protecting system to protect personal computer data from burglary utilized flash memory drivePatent number: US2003079140Publication date: 2003-04-24Inventor: URA YOSUKE (JP)Applicant:Classification:- international: G06F21/00; G06F21/00; (IPC1-7): H04L9/00- european: G06F21/00N1D1; G06F21/00N1V3Application number: US20010002501 20011024Priority number(s): US20010002501 20011024View INPADOC patent familyView forward citationsReport a data error hereAbstract of US2003079140This invention provides the system to protect the data stored in personal computer from burglary. This invention features providing method to protect the data stored in personal computer from easy burglary by combining several types of protecting method in the system that data is input and output inserting flash memory drive into USB port on personal computer.[15]Secure general purpose input/output pins for protecting computer system resourcesPatent number: US6138240Publication date: 2000-10-24Inventor: TRAN ROBIN T (US); SIMONICH CHRISTOPHER E (US) Applicant: COMPAQ COMPUTER CORP (US)Classification:- international: G06F21/00; G06F21/00; (IPC1-7): G06F11/00- european: G06F21/00N1VApplication number: US199******** 19980619Priority number(s): US199******** 19980619View INPADOC patent familyView forward citationsReport a data error hereAbstract of US6138240A security device and methodology that prevents unauthorized access to general purpose I/O pins in a computer system. In a system according to the invention, secure general purpose I/O pins are utilized as enable signals for data transfer devices such as Universal Serial Port (USB) ports. In one embodiment of the invention, access to the secure general purpose I/O pins is governed by an administrator password that is protected by a memory slot in a security device. When an administrator (or other authorized user) desires access to the general purpose I/O register that controls the secure general purpose I/O pins, the administrator enters the administrator password. If the password is correct, the relevant slot of the security device is unlocked, thereby permitting completion of write cycles to the secure general purpose I/O register. If a write cycle to the secure general purpose I/O register is attempted while the relevantslot in the security device is locked, the write cycle is ignored. Control and monitoring of various system resources in a secure manner is thereby permitted via use of the secure general purpose I/O pins.[16] SECRECY-PROTECTING COMPUTER AND PROGRAMPatent number: JP2006338136Publication date: 2006-12-14Inventor: KANEUCHI HIDEApplicant: MITSUBISHI ELECTRIC INF TECHClassification:- international: G06F21/24; H04L9/32; G06F21/00; H04L9/32;- european:Application number: JP20050159474 20050531Priority number(s): JP20050159474 20050531View INPADOC patent familyView forward citationsReport a data error hereAbstract of JP2006338136PROBLEM TO BE SOLVED: To provide a secrecy-protecting computer which prevents a file from being operated in a computer except the computer from which the file is taken away.SOLUTION: When a file is closed by a filter driver provided between an I/O manager and a device driver, plain-sentence data 100 to be stored are encrypted, and the file is stored in a form of mixed data 130 which include the encrypted data and a MAC address 120 unique to the computer. When the file is opened, the encrypted data included in the mixed data are decrypted only when the MAC address included in the mixed data 130 accords with a MAC address 130 unique to the computer which opens the file.[17] ACCESS PROTECTION FOR A COMPUTER BY MEANS OF A PORTABLE STORAGE MEDIUMPatent number: WO2006074490Publication date: 2006-07-13Inventor: FUCHS HJALMAR DOUGLAS (ZA)Applicant: FUCHS HJALMAR DOUGLAS (ZA)Classification:- international: G06F21/20; G06F21/20;- european:Application number: WO2005ZA00176 20051130Priority number(s): ZA20040009657 20041130View INPADOC patent familyView forward citationsCited documents:WO03079163US6401205DE19508288NL9101506FR2783943Report a data error hereAbstract of WO2006074490This Invention relates to a memory device such as a memory stick with a unique identifier or ID to be used in conduction with an electronic device such as a Personal Computer as to enable a user to gain access or operate or control devices or services associated with the electronic device for example a PC or Laptop. The systems software running or operational on the electronic device and/or memory device will search and read a unique identifier on the memory device such as a serial number or code. Should the serial number or code not be Read operation of the electronic device is seized.[18]METHOD AND SYSTEM FOR PROTECTING AGAINST COMPUTER VIRUSESPatent number: WO2005008417Publication date: 2005-01-27Inventor: KWAN TONY (AU)Applicant: COMPUTER ASS THINK INC (US); KWAN TONY (AU) Classification:- international: G06F21/00; G06F21/00; (IPC1-7): G06F- european: G06F21/00N3P; G06F21/00N3V6; H04L29/06C6HApplication number: WO2004US22216 20040709Priority number(s): US20030486754P 20030711View INPADOC patent familyView forward citationsView document in the European RegisterAlso published as:WO2005008417 (A3)EP1644859 (A3)EP1644859 (A2)EP1644859 (A0)Cited documents:US5956408US6049671US2003084322US5948104US2003065926more >>Report a data error hereAbstract of WO2005008417A method for delivering an update to at least one user including creating an electronic communication including an update and a unique signature identifying, the electronic communication as including the update and sending the electronic communication to the user..[19] Systems, methods, and computer program products for privacy protection Patent number: US2003130893Publication date: 2003-07-10Inventor: FARMER BENNIE L (US)Applicant: TELANON INC (US)Classification:- international: (IPC1-7): G06F17/60- european: G06F21/00N9A2P1Application number: US20020291196 20021108Priority number(s): US20020291196 20021108; US20000638177 20000811; US20010337827P 20011108View INPADOC patent familyView forward citationsReport a data error hereAbstract of US2003130893A systems and method of transmitting or communicating unique data from a unique user through a communications and/or computer network to a third party, wherein the third party has no method of determining the personal-identifying information (PII) of the unique user upon receiving the data. The invention provides privacy protection and location for communication of data, voice orOther information via a communications network, for providing various services related to telemetric communications and other location-based services.[20]Method and apparatus for establishing computer configuration protection passwords for protecting computer configurationsPatent number: US6470454Publication date: 2002-10-22Inventor: CHALLENER DA VID CARROLL (US); ATKINS BARRY DOUGLAS (US); ARNOLD TODD W (US)Applicant: IBM (US)Classification:- international: G06F21/00; G06F21/00; (IPC1-7): G06F11/30; H04L9/00; H04L12/14- european: G06F21/00N5A2Application number: US199******** 19980331Priority number(s): US199******** 19980331View INPADOC patent familyView forward citationsReport a data error hereAbstract of US6470454A method and apparatus is provided for facilitating the generation and use of computer system configuration passwords which can be utilized in an enterprise or organization to allow authorized users having knowledge of the password associated with a particular data processing system to make and change configuration decisions, but which prevents unauthorized users from making and changing such configuration decisions. In the preferred embodiment, a unique identifier (such as a serial number) and an enterprise secret key are supplied to a one-way cryptographic hash function in order to generate the configuration passwords which are unique to each data processing system of the plurality of data processing system of the enterprise or organization.。

引言随着卫星技术的不断发展,卫星的功能越来越复杂。
卫星的功能离不开FPGA 技术的支持。
然而,卫星运转的环境非常苛刻,容易受到辐射颗粒的影响,进而导致单粒子翻转(Single Event Upset ,SEU)现象的发生。
针对这一问题,本文提出采用SRAM 型FPGA 抗单粒子翻转可靠性设计的方法,以提高卫星的可靠性。
FPGA 的原理FPGA(Field-Programmable Gate Array)是一种采用可编程门电路实现的集成电路。
通过FPGA,开发人员可以自由编程,将其变为自行制定的特定电路或处理器。
若干个可编程逻辑单元(Programmable Logic Block ,PLB)、一些时钟管理模块、存储器、和输入/输出模块等构成了FPGA 的架构。
各种模块间的连接通过可编程的路由器实现。
FPGA 的可编程性是其最大的特点之一,这一特性使FPGA 比前面的ASIC (Application Specific Integrated Circuit)更加灵活。
FPGA 的SEU 问题FPGA 在卫星中的应用已经变得非常广泛。
然而,卫星在轨运行的环境却非常恶劣,包括极端的温度、空气和重力等,其中最大的问题是粒子辐射。
在高能脉冲射线的辐射下,晶体管容易发生单粒子翻转,即SEU。
单粒子翻转有可能导致电路故障,进而产生错误的计算结果。
这种问题的出现会严重影响卫星的正常运转。
在FPGA 中,存储在SRAM 中的开关逻辑电路众多,这意味着FPGA 中存在着大量的SEU 敏感电路。
一旦发生单粒子翻转,存放在SRAM 中的状态就会被改变,从而导致计算结果的变化。
大多数FPGA 供应商都采用种种技术来加强FPGA 的SEU 抵御能力,而SRAM 型FPGA 对于单粒子翻转的敏感性也较高。
因此,加强SRAM 型FPGA 的抗SEU 能力尤为重要。
SRAM 型FPGA 抗SEU 技术目前,针对SRAM 型FPGA 的抗SEU 技术可以归纳为以下几种。


fault-tolerant的中文-回复题目:faulttolerant的中文意思及其应用领域的探讨引言:现如今,随着信息技术的高速发展,各行各业对于系统的可靠性要求越来越高。
而faulttolerant作为一种重要的技术手段,在信息领域扮演着重要的角色。
本文将着重探讨faulttolerant的中文意思以及其在不同领域的应用。
第一部分:faulttolerant的中文意思faulttolerant一词源于英文,fault意为“故障”,tolerant则是“容忍”的意思。
结合起来,faulttolerant可以翻译为“容错”或者“故障容忍”。
它指的是一种系统或设备在发生故障时,仍然保持运行,并且不会对整体系统的正常工作产生影响。
第二部分:faulttolerant的应用领域1.计算机科学领域:在计算机科学领域,faulttolerant技术被广泛应用于操作系统、数据库系统、网络通信等方面。
一些关键性的任务,比如银行交易、航空航天系统和核能系统等都需要高度的容错性,以确保任何故障都不会导致系统瘫痪或数据损失。
2.云计算与大数据领域:随着云计算和大数据应用的迅速发展,对于系统的可靠性要求也越来越高。
在这些领域中,faulttolerant被广泛使用以确保系统的高可用性。
例如,分布式存储系统和分布式计算框架通常采用冗余数据和备份策略,以应对节点故障和数据丢失的情况。
3.网络和通信领域:在网络和通信领域,faulttolerant技术用于保证数据的可靠传输。
例如,通过使用冗余的网络链路或路由协议,可以避免单个链路或节点的故障对整个网络的影响。
此外,还有许多基于容错技术的通信协议被应用于提高通信的可靠性。
4.工业自动化领域:在工业自动化领域,faulttolerant技术可应用于保证生产过程的持续运行。
通过使用冗余的传感器、执行器和数据采集设备,可以在故障发生时快速切换到备用设备,避免生产中断和设备损坏。

HMI—Human Machine Interface(人机界面)HTML—Hyper Text Markup Language(超文本链接标示语言)CM——Control Module控制模块SCM——Sequential Control Module顺序控制模块CPM——Control Processing Module控制处理模块CEE——Control Execution Environment控制执行环境CNI——Control Net Interface控制网络接口C200——Control processor控制处理器RM——Redundancy Module冗余模块IOMs——input/output Modules输入/输出模块SCE——Simulation Control Module模拟控制模块ACE——Application Control Module应用控制模块IOLIM——IO Link Interface Module接口模块FIM——Fieldbus Inerface Module现场总线模块PMIO—Process Manager Input/Output流程管理器输入/输出FTA-Field Termination AssembliesIOP——Input/Output Processor (card)输入/输出处理器(卡)ERDB——Engineering Repository Database工程数据库EMDB—Enterprise model database企业模型数据库RTDB—Real Time Database实时数据库ODBC—Open Database Connectivity开放式数据库连接SQL—Structured Query Language结构化查询语言PV—Process Value工艺价值SCADA—Supervisory control and data acquisition监督控制和数据采集FTE-fault tolerant Ethernet容错以太网CP-control processor控制处理器CNI-control net interface控制网接口FTEB-fault tolerant Ethernet bridge容错以太网桥RM-redundancy module冗余模块FIM-fieldbus interface module现场总线接口模块OPC-OLE for process control用于过程控制ACE-application control environment(应用控制环境)DSA-distributed system architecture分布式系统架构CEE-control execute environment控制执行环境ES-CE --Console Extension Station控制扩展控制站ES-F --Experion Flex StationES-C --Experion Console StationFTA--Field Termination Assembly (for Serial Interface) CDA server :Contorl Data Access Server 控制数据接入服务器OPC:OLE for process controlDSA:disbuted system Architecture 分布式系统结构FTE:fault tolerant Ethernet 容错以太网RTD:热电阻T/C:热电偶PIM:pulse Input Module 脉冲输入模块SIM:Serial Interface Module 串口接口模块SIEMENS PLC常用英语缩写表集散控制系统——Distributed Control System(DCS)现场总线控制系统——Fieldbus Control System(FCS)监控及数据采集系统——Supervisory Control And Data Acqusition(SCADA)可编程序控制器——Programmable Logic Controller(PLC)可编程计算机控制器——Programmable Computer Controller(PCC)工厂自动化——Factory Automation(FA)过程自动化——Process Automation(PA)办公自动化——Office Automation(OA)管理信息系统——Management Information System(MIS)楼宇自动化系统——Building Automation System人机界面——Human Machine Interface(HMI)工控机——Industrial Personal Computer(IPC)单片机——Single Chip Microprocessor计算机数控(CNC)远程测控终端——Remote Terminal Unit(RTU)上位机——Supervisory Computer图形用户界面(GUI)人工智能——Artificial Intelligent(AI)智能终端——Intelligent Terminal模糊控制——Fuzzy Control组态——Configuration仿真——Simulation冗余——Redundant客户/服务器——Client/Server网络——Network设备网——DeviceNET基金会现场总线——foundation fieldbus(FF)现场总线——Fieldbus以太网——Ethernet变频器——Inverter脉宽调制——Pulse Width Modulation(PWM)伺服驱动器——Servo Driver软起动器——Soft Starter步进——Step-by-Step控制阀——Control Valver流量计——Flowmeter仪表——Instrument记录仪—— Recorder传感器——Sensor智能传感器——Smart Sensor智能变送器——Smart Transducer虚拟仪器——Virtual Instrument主站/从站——Master Station/Slave station操作员站/工程师站/管理员站——Operator Station/Engineer Station/Manager StationDCS画面常用常用缩写词语1ST1级FRQ频率A报警FSH末级过热器ADS自动调度系统FSSS炉膛安全监测系统AGC自动发电机控制FW给水AH空气预热器FWP给水泵AS轴向位移GC高压调门控制ATC汽轮机自动控制GEN发电机AUTO自动GV(高压)调节汽门AUX辅助的HH高高BASE基本HAV暖通BCP炉水循环泵HDR联箱,集箱BD排污HP高压缸BF锅炉跟随HTR加热器BFP锅炉给水泵IC中压调门控制BMCR锅炉最大连续出力ID标志,标识BMP燃烧器管理系统IDF引风机BOP轴承油泵IMP冲动式(级)BP旁路INCR提高,增加BRG轴承INTERM定期,间断BTG锅炉-汽机-发电机IV中压调门C切换LL低低CAF冷却风机LDC负荷指令计算机CAMP控制+报警+监测+保护LOP顶轴油泵CCCW闭式循环冷却水Lp低压CCS协调控制系统LSH低温过热器CDSR凝汽器LUB润滑油COND凝结MANU手动(方式)CON连续的MCR最大连续出力COOR连续的MCS模拟量控制系统CORR校正,修正MEH小型汽轮机电液调节CRT显示器MFT主燃料失去保护CRH低温再热器MIN最小CSH包覆过热器MS主蒸汽CW循环水MW兆瓦D NO编号,第。

ISO 26262-1 词汇表ISO26262是基于IEC61508标准演化而来的一项标准,旨在满足道路车辆电子电气系统领域的特定需求。
这种改编适用于由电子电气元件和软件组件组成的安全系统的整个生命周期内的所有活动。
安全是未来汽车发展的关键问题之一。
一些新的功能,在驾驶员辅助、动力、车内动态控制和主动&被动安全系统等方面日益牵涉到越来越多的系统安全工程。
这些功能的开发和集成会增加对安全系统开发流程、并证明所有合理的系统安全目标都得到满足的证据的需求程度。
随着技术复杂度、软件内容和机电一体化程度的不断提高,系统失效和随机硬件失效的风险也越来越大。
ISO 26262会提供适当的要求和流程来避免这些风险。
系统安全是通过一系列安全措施来实现的,通过应用各种技术(例如机械、液压、气动、电气、电子、可编程电子),并在开发过程的各个层面上应用。
尽管ISO26262涉及到电子电气系统的功能安全,但是它也会提供其他系统常用安全技术的框架。
ISO26262可以:a)提供车辆安全生命周期的支持(管理、开发、生产、操作、服务、报废);b)提供车辆专用的风险评估方法(ASIL,Automotive Safety Integrity Levels,汽车安全完整性等级);c)使用ASIL评级提出可实施的功能安全需求,来避免不合理的剩余风险;d)向供应商提供功能安全需求。
功能安全受到开发流程(需求规范、设计、实现、集成、验证、确认和配置)、生产和服务流程、管理流程的影响。
安全问题与以功能为导向、以质量为导向的开发活动和工作产品交织在一起。
ISO 26262阐述了开发活动和工作产品等安全相关的内容。
1 名称解释:1.1allocation:分配;将需求分配给架构级元件。
1.2anomaly:异常;指偏离期望的一些条件,这些条件包括需求、说明书、设计文档、用户文档、标准或者经验。
1.3architecture:架构;代表相关项/功能/系统/元件的构造块及构造块的边界和接口,且相关的功能已经分配给了硬件/软件元件。
基于VC33主动磁轴承控制系统的设计1尹国华,徐龙祥南京航空航天大学机械设计及理论系,南京(210016)E-mail:yinguohua@摘要:基于美国TI公司推出的浮点DSP芯片TMS320VC33设计了磁悬浮轴承系统的数字控制器,并运用可编程逻辑器件(CPLD)实现了DSP对A/D和D/A的逻辑操作。
采用嵌入式C语言和汇编语言混合编写了磁悬浮轴承数字控制器的PID控制算法。
成功实现了五自由度磁悬浮轴承系统的稳定悬浮。
静态悬浮试验结果表明设计的磁悬浮轴承系统控制器稳定性好、可靠性好、其控制精度达到了预期的效果。
为进一步实现先进的控制算法提供了硬件平台。
关键词:磁悬浮轴承;TMS320VC33;PID控制;稳定悬浮中图分类号:TP332.31.引言磁悬浮轴承是一种利用电磁场力将转子悬浮于空间,不需要任何介质而实现承载的非接触式支承装置,与传统的滚动轴承和滑动轴承相比,磁悬浮轴承明显的特点在于没有机械接触,而且其支承力可控[1]。
由此而具有传统轴承无法比拟的优越性能:由于没有机械摩擦和磨损,所以降低了工作能耗和噪声,延长了使用寿命[2];动力损失小,便于应用在高速运转场合;由于不需要润滑和密封系统,排除了污染,可应用于真空超净,腐蚀性介质以及极端温度和压力等特殊工作环境[3]。
TMS320C3X是TI推出的第三代产品,也是第一代浮点DSP芯片。
TMS320VC33是最新的一款32位高性能数字信号处理器。
指令周期分13ns和17ns两种,单周期完成32位整数、40位浮点乘法运算,DSP工作在75MHz主频时,其浮点运算能力可达150MFLOPS(Million Floating-Point Operations Per Second[6]。
TMS320信号处理器家族具有特别适合信号处理的硬件结构和指令系统, 而该信号处理器家族的高性能浮点处理器系列TMS320C3X又增加了许多浮点处理功能,因此在信号处理的各个应用领域都得到了广泛应用。
一种针对COTS器件的抗辐射加固方法梁健;张润宁;赵帅【摘要】随着商用现货(COTS)器件在空间任务中的广泛应用,COTS器件的抗辐射加固显得尤为重要,针对COTS器件在空间环境下易受宇宙射线和高能粒子冲击而产生辐射效应的特点,文章结合三模冗余(TMR)技术与现场可编程门阵列(FPGA)的重构技术,提出了一种基于TMR的可重构星载处理单元抗辐射加固方法.通过基于Markov过程的可靠度分析可知,冗余和重构技术相结合可以使处理单元具有更强的容错能力.文章利用实验模拟验证了该星载处理单元的各项关键技术,结果表明:此处理单元能够屏蔽单模故障,并能够定位和修复由空间复杂环境引发的软错误.【期刊名称】《航天器工程》【年(卷),期】2016(025)004【总页数】6页(P81-86)【关键词】星载处理单元;冗余;可重构;商用现货【作者】梁健;张润宁;赵帅【作者单位】航天东方红卫星有限公司,北京 100094;航天东方红卫星有限公司,北京 100094;西北工业大学,西安710072【正文语种】中文【中图分类】V473空间环境中存在较多的宇宙射线和高能粒子,运行在这种复杂环境下的航天器的计算系统很容易受到这些粒子和射线的冲击而产生辐射效应。
当前,在空间处理系统中,现场可编程门阵列(FPGA)以其低功耗、灵活性、通用性、高集成性等优点获得了广泛的应用。
基于静态随机存储器(SRAM)型的商用现货(COTS)FPGA器件很容易受到高能粒子的影响而产生辐射效应[1-3]。
而基于Flash架构的FPGA器件有较强的抗辐射性能,对由空间高能粒子引发的固件错误具有免疫能力,但是基于Flash架构的FPGA器件逻辑资源有限,不具备嵌入式软处理器的能力,故运算和处理能力受限,直接应用于复杂的星务管理和运算具有一定的局限性[4-5]。
传统的三模冗余(TMR)技术可以有效屏蔽单模故障,但表决器本身并不具备抗辐射能力,或者表决器由简单的逻辑开关组成,控制与协调能力不足[6-7]。
Abound v.大量存在Accelerate v.加速Access v.存取,接近Accommodate v.容纳,使适应Acousticadj. 听觉的Acousticsensor声传感器,声敏原件Acronym n.首字母缩写词Active adj.主动的,有源的Active network有源网络Actuator n.执行器Ad hoc 尤其,特定地Address n.寻址Addressgenerators 地址发生器Adjoint n. , adj. 伴随(的),共轭(的)Admissible adj. 可采纳的,允许的Advent n.出现Aerodynamic adj. 空气动力学的Aerodynamic n. 空气动力学,气体力学Aesthetically adv. 美术地,美学地Aforementioned adj. 上述的,前面提到的Agility n.灵活,便捷Ai 人工智能Air gap 气隙Aircraft n.飞行器Airgap=air gap 气隙Air-to-close ( AC ) adj.气关的Air-to-open ( AO ) adj.气开的Albeit conj.虽然Algebraic equation代数方程Alignment n.组合All-electricrange全电动行驶里程Alleviate v.减轻,缓和Allowance for finish 加工余量Alloy n.合金Alnico n.铝镍钴合金,铝镍钴永磁合金Aloft adv.高高地Alphanumeric adj. 字母数字混合的Alternative n. 可供选择的办法Altitude n.海拔Aluminum n.铝Amortisseur n.阻尼器Amplifier n.放大器Amplify v.放大Amplitude n.振幅Answeringmachine 电话答录机Anthropomorphically adv.拟人的Anti-aliasfilter 抗混叠滤波器Antilockbrakingsystem防抱死系统APICS=AmericanProductionandInventoryControlSociety 美国生产与库存管理学会Apparatus n.一套仪器,装置Application n. 应用(程序)Approach n.途径,方法;研究Aptness n.恰当Arbitrary adj.任意的Arbitrary adj.任意的Architecture n.架构Architecture n.体系结构Archive v.存档Argument n.辐角,相位Arithmetic-logic unit算术逻辑部件Armature n.电枢,衔铁,加固Arrival angle入射角Arrival point汇合点Artificial intelligence人工智能Artillery shell炮弹ASIC=ApplicationSpecificIntegratedCircuit 特定用途集成电路Assembly n.装置,构件Assemblyline 装配生产线Assumption n.假设Asymmetric adj. 不对称的Asymptote n.渐近线Asymptotically stable渐近稳定Asynchronous adj. 异步的At rest 处于平衡状态At the most 至多Attached adj.附加的Attain v.达到,实现Attenuate v.减弱Attenuation n.衰减Attitude n.姿态Attribute n.品质,特征Audioadj. 音频的 Auto-isolation n.自动隔离Automatictellermachine自动柜员机Autonomous adj. 自治的Autonomous adj. 自治的,自激的Auto-restoration n.自动恢复供电Auto-sectionalizing n.自动分段Auxiliary material 辅助材料Axon n.轴突Backlash n.齿隙游移Bandwidth n.带宽Bar code scanner 条码扫描仪Baud n.波特Become adept in 熟练Bench mark 基准点Biasn.偏压Bi-directional adj. 双向的Binaryadj.二进制的Binary-coded adj. 二进制编码的Biomassn.生物质Biopsyn.活体检查Bipolaradj. 双向的Bjt 双极结型晶体管Blackout n.(大区域的)停电Bldm 无刷直流电动机Block diagram algebra方块图计算(代数)Boilern.汽锅,锅炉Boolean algebra 布尔代数Boost chopper升压式变压器Bound v.限制Bracket v.加括号Break frequency转折频率Breakaway point分离点Breakdown n.击穿,雪崩Breakover n.导通Brush n.电刷Buck chopper 降压式变压器Building blocks 积木Buildingautomation 楼宇自动化Bulkyadj.大的,笨重的Bus-compatibleadj. 兼容的Bypass n.旁路;v.旁路By-productn.副品CAD=Computer-aidedDesign 算机助CAE=Computer-aideden gineering 算机助工程Cage n.子,形Calibrate v.校准Calibrationn.校准,度Calibrationn.校准,CAM=Computer-aidedM anufacturing算机助制造Can n.密封外壳Can 控制器局域网,一种Capacitorn.容器Carbohydrate n. 碳水化合物Carrier n.波,体Cascaden.,v.串; adj.串的Cellulartelephones蜂Census n.人口Central processing unit (cpu )中央理器CEO=ChiefExecutiveOfficer 行裁,首席行官Ceramic adj. 陶瓷的 Chain n.串Channeln.信道Characteristic adj. 特性(的); n.特性曲Characteristic equation 特征方程Characterrecognition 文字C i r c u i t r y n .路C i r c u m s t a n c e n .状况,境C l a m p v .箝位,定位C l o c k -d r i v e n a d j . 的Closed-loop n.Close-knit adj. 密的CNC=ComputerNumericalControl 算机数字控制Cockpit n.座Coefficient n.系数Coil n.,圈; v.Coincide v.一致Combustible adj. 易燃的,可燃的Combustion n.燃Commercial off the shelf( cots)商Commercially adv. 工地,商地Commissioningn.,运Commit v.保Common logarithm 常数Commutator n.向器,整流器Complement v.充,求Complex adj.复数的; n.复数Compound-wound dcmotor复励直流机Comprehensive adj.合(性)的Comprise v.包含Computer simulation算机仿真Concentrated coil 集中Concurrent adj. 并的Conduction n.,Configuration n.构造,构Configuration n.廓,格局Confinev.限制(在⋯⋯范内)Conjugate adj. 共的Conjunction n.合Conjunction n.合Consecutiveadj. 的Console n.控制台Constancy n.恒定Constant matrix 常数矩Constant-speed adj.恒速的Constitute v.构造,Constraint n.迫Constraint n.束条件Consuming adj.控制的Continuity n.性Continuum n.Contour n.廓,外形Controllability n.能控性Control-oriented adj.面向控制的Controlpanel 控制Converge v.集中,聚,收Convergev.合Converter n.逆器,整流器Converter n.器,流器,流器Conveyorn.送送机Convolution nCoordinate nCopper-cladCore n.心Correspondin的Cost-effective价格比(高)的Coulomb fri摩擦Counterclock的Counterpart配物Criteria n.准Criteria n.判据Critically da阻尼CRM=CustomshipManagem关系管理Crossover fre越率CRT阴极射管Crustn.外壳Crystal n.晶体CSMA/BA波/ 位仲裁CSMA/CD 波路 / 冲突Culmination点Cumbersome的Cumulative aCurbsiden.路Current-fed流源型逆器Cycloconvert--2器Cycloconverter n.周波器Cylindrical adj. 柱形的Cylindricaladj. 柱(形)的Damper winding 阻尼Damping n.阻尼; adj. 阻尼的Dampv.阻尼,减幅,衰减Data acquisition 数据采集Data filtering数字波Data logging 数据Dataencryption数字加密Datafusion 数据融合Datatype n.数据型Datawarehouse 数据Dead substationtransfer 故障站移Deadband n.死区Deadlock n.死,僵局Debugging n.Decay v.衰减Decibel n.分Decimal adj. 十制的Decode v.解,Decompose v.分解Decouple v.解耦,退耦Decrement n.减少量Deduce v.演 De-facto adj.事上的,的Deferment n.延期,Deflection n.偏(离,差)Defrost v.除霜Delta n. 希腊字母δ(δ),三角形(物)Demagnetization n. 去磁,退磁Dendrite n.突Denominator n.分子Deodorize v.除⋯⋯臭Departure angle 出射角Dependent variable 量Depict v.描述Deplete v.耗尽,使衰竭Derivation n.数Derivation n.起源,得来Destabilizev. 使打破平衡,使不定Detector n.探器Deteriorate v.化,化Determinant n.行列式Determinism n.确定性Determinism n.决定Deterministic adj. 确定的Deterministic adj. 确定的Deterministic n. 确定性的Detractor n.批者Detrimental adj. 不利的Develop v.出,引入Development system 开系Deviation n.偏差Diagnosis n.断Dial-out 叫 Dictate v.命令,要求Dieseln.柴油机Difference equation 差分方程Differential adj.差的,差的Differential adj. 微分的 n.微分Differential equation 微分方程Differentiate v.微分Digit n.位数Diminish v.(使)减少,Direct memory accessl a c e v .移D i s p l a ys c r e e n示屏D i s r u p tv .干,D i s t o r t i o nn .失真D i s t r i b u t e da d j .分散的,分布的D i s t r i b u t e dp a r a m e t e r--3Ensuingadj. 相继的Entail v., n.负担,需要Entryn.入口Equivalent adj.等价的;n.等价Equivalent adj.同等的,等效的; n.同等,等效Equivalentadj. 相等的,相当的Erasable adj.可擦除的ERO=EnterpriseResource optimization企业资源优化ERP=EnterpriseResource sPlanning 企业资源计划Estimation n.预测,估计Ethanoln.乙醇Evaluation n.估计Evaporatev.(使)蒸发,(使)变为气体Even adj.偶数的 Even multiple 偶数倍 Event-drivenadj. 事件驱动的Evolvev.开展,进化,逐渐形成Excitation n.激励Expert system 专家系统Expertise n.专门知识Exploit v.开发Exponential adj.指数的;n.指数Exponential adj. 指数的Extreme adj.极端的; n.极端的事情 / 情况Fabrication n.构成,组成,制作Facilitate v.使容易,促进Factor n.因子; v.分解因式Factored adj.可分解的Factory floor 工厂车间Fail-closed( FC) adj. 无信号则关的Fail-open( FO)adj. 无信号则开的Faraday n.法拉第FastFouriertransforms 快速傅里叶变换Fault-tolerant adj.容错的Faulttolerant 容错Feedbackn.反馈Ferromagnetic adj. 铁磁性的,铁磁体的Fetch v.,n.取来Fictitious adj.假想的Field n.域,字段Field winding n. 励磁绕组Field n.字段Field-weakening n.弱磁Filter v.滤波Filtering technique滤波技术Final value 终值 Firingangle 触发角 Flashconverter 闪速转换器Fleetn.车队; adj.快速的Flextime n. 灵活定时上班制Flip-flop n.触发器Floating-point adj. 浮点的Fluxn.磁通Force commutated 强制换向Force-commutation n. 强制换向Forcing frequency 强制频率Foregoingadj.前面的,以上的Formulation n. 公式化(表达)Forward biased 正向偏置Foulingn.阻塞Fourier series 傅里叶级数Fractional adj. 分数的Fractional adj. 小数的Fractionn.分数,小数Frame n.机壳,机座Framework n.构架,结构Freewheeling n. 单向传动Fuelcell 燃料电池Full-scall adj. 满量程的Functionality n.功能性Fundamental n. 基本原理Fusionn.融合Fuzzy adj.模糊的Fuzzyadj.模糊的Gainn.增益Galvanometer n.电流计,安培计Gate n.门,门电路General form一般形式Generalize v.概括,一般化,普及Generalize v.一般化,普及Generator n.发生器,发电机Geologicallyadv. 地质学地,地质地Geometry n.几何学,几何形状Geothermal adj. 地热的Geothermal adj.地热的Germanium n.锗Get around 回避,躲开Globally stable 全局稳定Gouge v.挖Graphicaluserinterface( GUI)图形用户界面Graphicequalizer 图像均精选文库衡器Greenhousen.温室Grid n.格子,网格Gripper n.抓手,夹持器Gross national product国民生产总值Groundsourceheatpump地源热泵Group control system 群控系统Gto 门极可关断晶闸管Guarantee v.;n.保证,担保Guidance system引导(导航)系统Habitat n.栖息地,居留地Hairline n.游丝,细测量线Hamiltonian哈密尔顿的Handheld terminal手持终端Handshaking n.握手Hardware n.硬件Hard-wired n.硬接线Hardwired adj. 电路的,硬件连线实现的Harmonics n.谐波Harmonics n.谐波Harmonicsn.谐波Harmonize v.协调Harnessv.利用Harnessv.利用(河流,瀑布等)产生动力(尤指电力)Harshadj.苛刻的Hexadecimal adj.十六进制的Hierarchical adj. 分级的Hierarchicaladj. 分级的,分层的Hierarchyv.层次,级别High end 高端--4High-end n.高端Hilberttransforms n.希伯特Holding current保持流Homogeneous solution 通解Homomorphicprocessin g同理Horizontally adv.水平地Horsepower n.力,功率Horsepower n.功率Hotexchanger 交器Housekeeping n.常事物Hub height 塔杆高度Humanoidrobot 人机Igbt 双极型晶体管Igct 集成极向晶管Imaginary axis 虚Immerse v.沉浸,浸入Imperfection n.不完全,不足,缺点Implement v.Implementation n.,履行Imply v.包含Improper integral奇异(无理)分Impulse v.冲激In series 串Inactive n.不活,停止Incidentally adv.偶然地精选文库Instruction set指令集Isocline n.等Instruction set指令集Isoscelesadj. 等腰的Instrument n.器,工具IT=InformationTechnoloInstrument transformer gy 信息技表(用)互感器Iterative adj. 重复的,反Integer n.整数复的Integral n.分Jacobian matrix雅戈比Integrated circuit 集成矩路Jargonn.行Integrate v.分JIT=Just-in-time 即(生Integro-differential)equation 微分方程Jittern.抖(),Interactive adj. 交互式的簸Interactive adj. 交互式的Justify v.明Interchangeably adv. 可Kinematicsn.力学交地Kirchhoff’first law 基Interconnect v.互相接霍夫第一定律Interdisciplinary adj. 跨Knowledge base知器人Hurwitz criterion赫茨判据Hybrid adj.混合的Hybrid n.混合 Hybridadj. 混合的 Hydraulic adj. 水力的,液的Hydraulic adj.水的Hydrauliccylinder 液缸Hydroadj. 水的 Hydro-electric adj. 水力的Inclineto 向于Incorporation n.合并Increment n.增量Incur v.招致Indentation n.缺口Independent variable自量In-depth adv.深入地Induction machine感机Inductor n.感器Inertial guidancesystems性航系Infeasible adj.不可行的学科的Interface n.界面Interpret v.解,解析Intersect v.相交Intersection n.相交,乘法Interval n.隔Intrinsic adj. 内在的Intrinsic adj. 固有的,体内的,体征Intrusive adj. 侵入的Intuition n.直Intuitively adv.直地Inventory n.管理Knowledge engineering知工程Knowledge-basedadj. 基知的Lag v., n.延Lagging n.滞后Lagging n.滞后,滞Lagn.滞后Lagrangian 拉格朗日的Laminated adj. 分的,叠片的Landsliden.泥石流Laplace transformation拉普拉斯Hydroelectric adj.水的Hydrogen n. Hysteresis n.滞回I/o-mapped adj. 入 /出映射的(独址)Infinitesimal adj.无限小的Infrared adj. 外的Inherent adj.固有的Inhibit v.抑制Inverse n.反,逆,倒数Lapsen.(等)流逝Inverse transform反Latch v.抓住,占有;n.(逆)寄存器Inverter n.逆器Latching currentIrrelevancen.不相干,不流Identification n.辨,Identify v.确,,辨Identifyoneselfwith ( in)参与,和⋯⋯打成一片Identity n.一致性,等式Initial condition 初始条件Initial value 初 Inputdevice 入Insensitive adj. 不敏感的Insofar as 到的程度,在⋯⋯范内切Irrespective adj. 不考的ISDN=IntegrateServiceDigitalNetwork合数据网Latentheat 潜伏Latticework n.格子Layoutn.布置,划,,敷Lead n.Lead n.引Leading adj. 超前的--5Leadn.超前Leakagecurrent 漏流Leakage n.漏Lease v.出租Least-significant bit (msb)最低有效位Liapunov 李普夫Limit cycle极限Line to line voltage Linearvectorspace性矢量空Linearization n.性化Linearization n.性化Linearization n.性化Load flow潮流Load tapchanger抽开关器Localco mmunicationnetworks 局域网Localizationn.定位Locallystable 局域定 Locationn.(存)元Look-uptable 表Loopcurrent 回路流 Lumpedadj. 集中的Lumped parameter 集中参数Lumpedadj. 集的 Machine tool 机床Magnetic tape drive 磁机Magnitude n.幅 Mammography n.胸部透Mandatory adj.命令的,制的,托管的Manipulate v.理Manipulatedvariable 操量Manipulator n.操型机器人,机器手Marshaled n.整,配置 Matrix algebra 矩代数MatrixMatrixMatricMct mMecha(制),MechaMediu( MAC器映射MeniaMeritMeshMetadMethaMicro/米机器Micro-操作MillenMimic化MinimMirrorMisint解,Mislea致的MissilModeModeModeModifi改ModuMoment e r i n d i c a to r式表M o v e a b l e -s c a l e i n d i c a t o r圈式表M R A C模型参考自适控制M R P= M a t e r i a l R e q u i r e m e n t sp l a n n i n g制--6Output device 出Overdamped adj.阻尼的Overlap v., n.重叠Overridev., n.超,倒Overshoot n.超Overshoot n.超量Overwhelming adj. 倒一切的Package n.包Parallel n.似Parameter n.参数Partial differential equation偏微分方程Partial fraction expansion 部分分式展开式Particular solution特解Passionate adj.激烈的Passive adj. 被的,无源的Passive network 无源网Patch v.修Patternrecognition模式Patternrecognition模式Peak time 峰Pedaln.踏板Performance criteria性能指Performance index性能指Periodic adj. 周期性的Peripheral n.外,外Periphery n.外Permanent-magnet dc motor 永磁直流机Personnel n.人,Phase controlled相控的Phase n.状,相位Phase sequence 相序Phase-lag n.相位滞后Phase-lead n.相位超前Phase-lockedloops 相Phase-plane equation 相平面方程Philosophy n.原理,原Photosynthesisn.光合作用Photovoltaic adj. 光的Piecewiseadj. 分段的Piecewisecontinuous 分段Piggy-back adj. 背式的Pilot n.行Planningapplication划申Plant n.机器,被控象Plot v.; n.曲Pneumatic adj. 气的Pneumatic adj. 气的Polar plot极坐Polarity n.极性Polarity n.极性Pole-top n.杆Poll v.登,通信,定Polling n.Pollutant n.染物Polymer n.聚合物Polynomial n.多式Porcelain adj. 陶制的Portability n.便Portrait n.描述Portrait n.肖像,描写,型式Positive definite 正定Postindustrial adj. 后工的Potassiumn.Potential n.() Powerboost 功率推助装置Power factor 功率因数Power mosfet 力 mosfet效晶体管 Powerplant厂Preactv.; n.超前;提前修正量Precursorn.先Predictable adj. 可断定的Prediction n.矛盾Predominance n.Predominantly adv. 卓越地,突出地Preferencesn.参数Preloadable adj. 的Preset adj. 事先整的Prevalent adj. 流行的Prevent ⋯ From doing 使⋯⋯不⋯⋯Primary storage(memory )主存器Prime mover 原机Principal adj.主要的Private lan 用局域网Probability theory 概率Procedure n.程序,程Processor n.理器Product n.乘Proliferate v.激增Prominent adj. 卓越的,突出的Property n.性Proponent n.提倡者Proportional to 与⋯⋯成正比Propulsion n.推,推力Protocol n.Protocol n.Prototype n.原型(机)PP感PP振P脉PP的QQnQQ交QQvRoRaR的R家RRRR的R述RR性RRRRRRechargeableadj.可再充电的Recloser n.自动重合闸装置(开关)Recognition n.认识Recovery n.恢复Rectification n.整流Rectifier n.整流器Recurrent adj. 再发生的,循环的Redundancyn.冗余Redundancyn.冗余Regulatev.调整Regulatorycontrol调节控制Reinventv.彻底改造Relay n.继电器Relayn.继电器Relentlessly adv. 无情地,残酷地Relevance n.关联Remainder n.余数Renewable adj. 可再生的Represent v.代表,表示,阐明Representation n.表示符号Request n.请求Reserve capacity储备功率Resetrate 复位速率Resettime 复位时间Residentialproperty 住宅物业Resistance n.阻抗Resistor n.电阻器Resolution n.分辨率Resonance n.共振,共鸣Responsiveness n.响应Retrievaln.取回Retrievaln.取回,补偿,提取Retrieve v.检索Retrofit v.更新,改进Retrospectively adv.回顾地Reusability n.可用性Reveal v.显现,揭示Reverse biased 反向偏置Reversev., n.反转; adj.变换极性的Revolution n.旋转Rheostat n.变阻器Rigidity n.严格Rigorous adj.严密的,精确的Rimn.边,轮缘Ripplen.波纹,波动RISC=ReductionInstructionSetComputer精简指令集计算机Rise time 上升时间Rms=root-mean-square有效值,方均根Roboticsn.机器人学,机器人技术Root locus gain 根轨迹增益Rotating-dialindicator旋盘式仪表Rotating-drumindicator旋鼓式仪表Rotor n.转子Routh criterion劳斯判据Routines n.程序Rugged adj. 结实的,耐用的Sabotage n.破坏Salient adj.凸起的,突出的Sample v.采样Sample-and-hold n.采样保存Sampled-data n.采样数据Saturation n.饱和Saturation n.饱和Saturation n.饱和Scalabilityn.可测量性Scalar adj. 数量的,标量的; n.数量,标量Scalen.刻度Schedule v.调度Schemen.方法,形式,示意图Schottky diode 肖基特二极管SCM=SupplyChainManagement 供应链管理Seamless adj.无缝的Secondary storage(memory )辅助存储器Secureadj. 可靠的,放心的,无虑的Semicircle n.半圆形Semiconductor n.半导体Semigraphicadj. 半图解的Semilog paper半对数坐标(纸)Sensorn.传感器Sensorn.传感器Series-wound dc motor串励直流电动机Servo control system 伺服控制系统Servocontrol 伺服控制Servon.伺服Settling time 调节时间Shaft n.转轴Shared resource 共享资源Shifting theorem 平移定理Shunt-wound dc motor并励直流电动机Shutdown v.关闭Sign n.符号Signal-precision adj. 单精度的Significance n.意义Silicon n.硅Simplicity n.简单Simulation n.仿真Simultaneously adv. 同时地Sinusoidal adj. 正弦的Sit 静态感应晶体管 Sketchv.,n.(绘)草图,素描Slew rate 转换速度Slip n.转差(率)Slop n.斜率Slotn.槽Sluggish adj. 惰性的,缓慢的Smps 开关电流Snubbern.缓冲器,减震器Socket n.插座Socket n.插座Solarcollector 太阳能集热器Solidoutput 可靠输出Soma n.体细胞Sophisticated adj. 非常复杂的、精密或尖端的Sophisticated adj. 复杂精密的Spann.测量范围 Spatialadj. 空间的 Specificationn.(复)规格Spectrum n.(光)谱,领域,范围Speechrecognition语音识别Spilln.溢出Split adj. 分离的Spool v.绕; n.卷筒,线圈,阀柱Spring n.弹簧Sprinklern.洒水车,洒水装置Spur v.刺激Sql 构化言Squarerootextractor开方器Square-wave n.方波Startup n.启State variable 状量State-controllable adj. 状可控(制)的Stationary adj. 静的Stator n.定子Statusquon.状Steady-state n.Steady-stateStep motor n.步机Step n.(信号) Stepper motor 步机Stereotyped adj. 僵化的Stiff current source 恒流源Stiff voltage source 恒源Stimulus n.刺激,鼓励Stochastic adj. 随机的Stored program 存程序Straight-forward adj. 直截了当的,的Strategicadj. 略的Strategy n.方法Strobe v.通,通脉冲Subharmonics n.次波Suboptimal adj. 次的Subscriptn.下,脚注,索引Subsequent adj. 后序的Substation load transfer 站荷移Substation n.站Substitute n.代替Substitution n.代替Succeedv.⋯⋯之后,接替Successiveapproximation逐次逼近Superconductive adj. 超的Superimposed adj. 有次的Superposition n.叠加Superposition n.叠加Supersede v.取代Supervision n.督,管理Supervision n.Supplementary adj. 助的Suppressv.抑制Susceptiveadj. ⋯⋯敏感的;易受⋯⋯影响的Suspend v.挂Sustain v.持Switched reluctancemachine 开关磁阻机Symbolic adj.符号的,号的Symmetric adj. 称的Symmetrical adj. 称的Synapse n.神Synchronous condenser同步相机Synchronous machine 同步机Synchronous speed 同步速Synthesis n.合 Systemcrash 系崩Tacklev.理Tacticn.策略Tactilesensor 触感器Tangent adj. 切的,正切的; n.切,正切Tectonicadj. 构造的,建筑的Temperaturedrift 温度漂移Temporal adj.的Tenantn.承租人Terminal n.端Terminal n.端(机)Terminology n.Terminology n.主流The theory of residues 余数定理Theme n.目,主,文Theoretically adv. 理上的Thereof adv.将它()Thermocouple n.偶Thermodynamics n.力学Thermostat n.恒温器Thermostat n. 自温器Thevenin impedance 隔离器Threshold n.极,限,极限Thresholdn.Throttle v.()Throttle v.(),用()Thyratron n.流管Thyristor n.晶管Time-invariant adj. 不的Time-of-day n.日 Tipn.端Tolerant adj. 容忍的,容忍的Topology n.拓扑Topology n.拓扑构Touchsensor 接触感器Trade deficit 易赤字Trade off 取 Trail-and-error n.凑法Trajectories n.迹,道Trajectory n.迹Trajectory n.迹Trajectory n.迹,道Trajectory n.迹Transducer n.感器,器Transducern.感器Transfer function 函数Transformer n.器Transient adj.的,瞬的,渡的Transistorn.晶体管Transmitter n.敏阻Transparencyn.透明Transputern.晶片机Trapezoidaladj. 梯形的 Tray n.子Trench n.沟Triac n.三端双向晶管Triangular adj. 三角的Turbine n.Turbinen.Turn n.匝数Tutorial adj. 指性的Tutorial n.个人Ultimate adj. 界的Unauthorized adj. 未授的,未批准的Underdamped adj. 欠阻尼的Undergo v. Underlyingadj. 根本的Uniform adj. 一致的Uniform adj. 一致的Unilateral fourierintegral 傅里叶分Unity feedback system位反系Unparalleled adj. 无比的,空前的Upsetn.干Uranium n.Utility n.公用事 Vague adj. 含糊的,不清楚的Valid adj. 有效力的Valve n.Var 静无功功率 Variablen.量 Variableadj. 化的,可的; n.量 Variable-speed adj. 速的Variant adj. 不同的,替的Variational adj.化的,种的Vector n.矢量Vendor n.主,供商Versus prep.⋯⋯⋯⋯Vertically adv.垂直地Very large scaleintegrated circuits ( vlsi)超大模集成路Via prep. 由Vice versa 反之亦然VideoCassetteRecorder (VCR)像机Violently adv.激烈地VIP=veryimportantpersonVirtual reality虚Vista n.展望Volatile adj. 易的Volcanon.火山Voltage drop 降Voltage-fed inverter源型逆器Vortices n. Vortex 的复数,旋体(面)Vrm 磁阻机VSS构系精选文库Vulnerability n.弱点Weight n.Whiskv.奔White paper白皮Winding adj.的; n.圈,Wiring n.配With respect to相于Word length字Words and termsWorkhorse n.重,重荷Workstation n.工作站Wound-rotor n.子Wye n. Y 形,星形,三通Xml 可展言Yaw n.偏航Yield v.推出,得出Yoghurtn.乳酸酪。
故障注入及故障状态实时观测的多总线测试系统张智慧,王志超,林岩(北京航空航天大学自动化科学与电气工程学院,北京100191)摘要:武器系统对可靠性要求较高,这就意味着系统本身要对各种突发故障具有一定的容错能力㊂为了检测并提升系统容错能力,需要在总线测试过程中加速系统故障生成,因此故障注入系统的设计尤为关键㊂本文旨在设计这样一套系统,该系统将武器领域中使用较为广泛的1553B总线以及R S422总线进行集成,具备更广泛的适用性㊂系统包含上位机软件以及故障注入模块,两者间利用以太网通信能够实现人工设定的故障注入以及故障状态的实时观测㊂最后,故障注入系统的有效性得到了验证㊂关键词:容错;故障注入;多类型总线;以太网通信中图分类号:T P29文献标识码:AD e s i g n o f M u l t i-t y p e B u s T e s t i n g S y s t e m B a s e d o n F a u l t I n j e c t i o na n d R e a l-t i m e M o n i t o r i n g o f F a u l t S t a t u sZ h a n g Z h i h u i,W a n g Z h i c h a o,L i n Y a n(S c h o o l o f A u t o m a t i o n,B e i h a n g U n i v e r s i t y,B e i j i n g100191,C h i n a)A b s t r a c t:T h e w e a p o n s y s t e m r e q u i r e s h i g h r e l i a b i l i t y,w h i c h m e a n s t h a t t h e s y s t e m i t s e l f s h o u l d h a v e c e r t a i n f a u l t t o l e r a n c e a b i l i t y f o r a l l k i n d s o f s u d d e n f a u l t.I n o r d e r t o d e t e c t a n d i m p r o v e t h e f a u l t t o l e r a n c e a b i l i t y o f t h e s y s t e m,w e h a v e t o a c c e l e r a t e t h e g e n e r a t i o n o f s y s t e m f a u l t d u r i n g t h e s y s t e m t e s t,s o t h e d e s i g n o f f a u l t i n j e c t i o n s y s t e m i s p a r t i c u l a r l y c r i t i c a l.T h e p u r p o s e o f t h i s p a p e r i s t o d e s i g n a s y s t e m,w h i c h i n t e g r a t e s t h e1553B b u s a n d R S422b u s w h i c h a r e w i d e l y u s e d i n t h e w e a p o n f i e l d.T h i s k i n d o f f a u l t i n j e c t i o n s y s t e m h a s a w i d e r a p p l i c a b i l i t y.T h e s y s t e m c o n s i s t s o f h o s t c o m p u t e s o f t w a r e a n d f a u l t i n j e c t i o n m o d u l e.T h e t w o m o d u l e s c o mm u n i c a t e w i t h e a c h o t h e r t h r o u g h E t h e r n e t,w h i c h c a n r e a l i z e f a u l t i n j e c t i o n a n d r e a l-t i m e o b s e r v a t i o n o f f a u l t s t a t e.F i n a l l y,t h e a u t h e n t i c i t y o f f a u l t i n j e c t i o n s y s t e m i s v e r i f i e d.K e y w o r d s:f a u l t t o l e r a n t;f a u l t i n j e c t i o n;m u l t i-t y p e b u s;E t h e r n e t c o mm u n i c a t i o n0引言武器系统对可靠性要求较高,因此必须在测试过程中尽可能真实地模拟实际工作中发生的各种故障㊂之前研究中的故障注入工具大多是针对1553B或R S422两种总线中的一种类型,联盟在文章中提出了对1553总线的故障注入测试方法[1],荆广等人提出了多总线故障注入设计思路,但不包含1553总线[2]㊂杨森斌提出了多总线故障注入测试方法,但系统实现功能较少,无法满足多层次㊁多模式的故障注入[3]㊂本文在前人的基础上设计了基于故障注入的多总线测试系统,能够实现对1553B总线和R S422总线标准的物理层㊁电气层和协议层三个层级的故障模拟,具体包括物理断路㊁噪声干扰和数据替换取反等多种故障㊂本系统由软件和硬件混合实现,既能够实现软件层级的人工操控,也可以实现硬件层级的真实故障模拟㊂整套系统易于操作,更能满足操作人员在实际测试中的要求㊂1原理简介1.11553B总线简介1553B总线全称为飞机内部十分制指令响应式多路传输数据总线㊂1553B通信系统通常由4部分构成:传输媒介㊁总线控制器(B u s C o n t r o l l e r,B C)㊁远端(R e m o t e T e r m i n a l,R T)㊁总线监视器(B u s M o n i t o r,B M)[4]㊂1553B总线消息传输机制:①首先B C向R T下发命令指令,指令内容为使R T保持接收或传输状态㊂②为表示应答,R T向B C返回一个状态字并执行B C发送的命令指令㊂③B C通过判断R T返回的状态字来判断消息是否传输成功㊂如图1所示,当B C下发接收数据指令到R T 时,给予应答向返回状态字并执行接收命令㊂如图2所示,当B C 下发传输数据指令到R T 时,R T 给予应答向B C 返回状态字并执行数据传输指令㊂图1 R T接收数据过程图2 R T 传输数据过程1.2 R S 422总线简介R S 422是一种串行总线接口标准,全称是 平衡电压数字接口电路的电气特性 ,由美国电子工业协会(E A )发布㊂该标准在R S 232上发展而来,弥补了R S 232通信距离短㊁传输速率低的缺陷㊂该标准只对接口的电气特性做出规定,而在协议层上无明确约束,因此用户可建立自己的通信协议[5]㊂1.3 故障注入原理介绍故障注入一词最早于20世纪70年代被提出,通常用来对一个容错系统所采用的容错方法进行有效性验证,进而提高容错系统的故障处理效率㊂本文的设计方法建立在硬件故障注入基础上,且故障注入单元采用的是对系统结构损伤较小的嵌入式方式㊂其中上位机软件实现故障注入命令的发布和故障状态的监视,下位机(故障注入单元)实现对上位机的命令解析与执行㊂2 总体设计本文设计的多总线故障注入系统集合了1553B 及R S 422总线,实现了物理层㊁电气层㊁协议层的故障注入㊂设计的核心在于软件层级,具体包含上位机软件(即故障注入控制注入软件)设计和核心板卡中的以太网通信逻辑设计㊂总体流程为上位机软件将人为设定的故障模式经由以太网下发至核心板卡,核心板卡中的A R M 接收指令后将其解析后下发至F P G A ,在此过程中A R M 一直对F P G A 实行端口状态监测,将信息返回至上位机,实现下位机状态显示㊂F P -G A 执行A R M 解析后的指令,使得目标故障在板卡中发生,在此过程中F P G A 持续读取寄存器状态并返回给A R M ㊂图3所示为故障注入系统总体设计流程㊂3 上位机软件设计3.1 软件架构本文设计了这样一套上位机软件,它界面清晰明了且图3 总体设计流程图内容丰富,能够实现多总线多故障模式的故障注入任务,易于操作和监视㊂软件使用Q T 与V i s u a l S t u d i o 2015联合编写,编程语言为C ++㊂软件中主要包含4个区域:菜单栏区㊁故障选择区㊁状态显示区和故障操作区㊂软件框架如图4所示,各区域功能如下:①菜单栏区:主要包括文件㊁测试㊁视图㊁网络配置功能㊂具体包含软件退出㊁文件保存㊁故障参数配置㊁故障注入等功能㊂②故障选择区:在该软件中故障模式采用树状结构,使菜单分级㊂一级菜单的设立主要为了区分板卡类型:1553B 和R S 422两类㊂以1553B 为例,将故障层级分为物理层㊁电气层和协议层,将此三类故障层级设置为二级菜单㊂第三层级为具体故障类型,如物理层下的断路㊁短路等,电气层下的噪声叠加㊁斜率调节等,以及协议层下的数据替换取反等㊂以及协议R S 422具有与协议1553B 相同的故障层级㊂③状态显示区:本区域主要用来进行信息(状态)显示,即显示当前连接板卡类型㊁板卡I P 以及当前故障状态,使得操作者能够更容易实现对故障注入的控制及监控㊂④故障操作区:这个区域是为了实现故障流程的设置以及故障参数的设置㊂图4 软件框架3.2 接口(逻辑)设计表1中的5类实现了软件整体框架的搭建㊂T r e e -w i d ge t 类实现对故障模式的整理,按照多级菜单的设计使故障分层,并使得故障按照树状图在软件界面中呈现㊂N o d e I c o n 类用以实现界面中(故障选择区以及操作区)的图标显示㊂A r r o w I c o n 类在软件界面中以箭头形式出现,用以实现故障流程的设计,使故障按照流程图的先后顺序依次执行㊂D e v i c e 类不呈现在界面中,但界面中的1553B以及R S 422全都是D e v i c e 的子类,用以对板卡任务进行集中管理㊂G r a p h i c s V i e w 类负责主显示区域的显示任务,显示人为设置的故障流程㊂表1 软件框架接口设计序 号类 名描 述1T r e e W i d g e t 管理设备类型及其故障类型2N o d e I c o n管理界面中的图标类型3A r r o w I c o n 表示故障流程先后关系4D e v i c e 所有板卡设备的父类5G r a ph i c s V i e w 主显示区显示故障连接流程表2中的6类实现了软件层级上故障注入任务的实现,由表1中的类派生而成㊂D e v i c e R S 422类与D e -v i c e 1553B 类是表1中D e v i c e 类的子类,具体负责1553B 板卡与R S 422板卡故障注入相关事务㊂N e t W o r k 类实现对板卡以及本地的网络I P 设置,以实现上位机与板卡通信㊂U d p N e t W o r k 主要负责整体通信进程,包括协议报文的收发㊁监听等,考虑到测试系统对信息实时性要求较高,在此处选择通信速度快的U D P 通信协议㊂B u g I t e m 类用来实现对多种故障的集中控制,在该控制下每种故障实现对B u g I t e m 类的继承,以实现自己的报文协议㊂P a r a m e t e r D l g类用来实现对多种故障参数设置的集中控制,在该控制下每种故障实现对P a r a m e t e r D l g 类的继承,以实现对自己的故障参数设置㊂B u g I t e m 与P a r a m e t e r D l g 两者共同实现故障参数的设置与存放㊂表2 故障注入任务接口设计序 号类 名描 述1D e v i c e R S 422R S 422板卡类处理板卡事务2D e v i c e 1553B 1553B 板卡类处理板卡事务3N e t W o r k 载入网络配置4U d p N e t W o r k 处理网络通信任务5B u gI t e m 用于管理故障信息6P a r a m e t e r D l g故障参数设置4 通信设计本文主要设计思想在于,上位机针对不同的待注入故障将对应的协议报文以U D P 传输模式发送至下位机(F P G A ),对指定I P 和端口始终保持监听状态的下位机接收协议报文并对其进行解析与执行㊂协议报文有两种,分别为请求帧(上位机下发至下位机的报文)和响应帧(下位机下发至上位机的报文)㊂4.1 请求帧设计上位机下发指令报文(即请求帧)到下位机(F P G A ),在此处设计请求帧格式为:帧头㊁帧长度㊁帧计数㊁设备信息㊁数据㊁累加和校验,共计6部分㊂各字段含义如下:①帧头:依照通信原理,采用固定网络传输帧头格式,即0x 55和0x A A 两个字节㊂②帧长度是指设备类型位和数据位两部分所占字节数总和,不包含帧头㊁帧长度㊁帧计数㊁累加校验和字节㊂③帧计数是一个帧的轮询计数,提供给上位机使用,F P G A 应答时需要返回此字节㊂④设备信息是设备的类型码,用于判断命令信息是否为发送给当前设备㊂这里将1553B 板卡设备设定为01㊂⑤数据位包含故障码和故障参数值㊂由于需要考虑故障注入分物理层㊁电气层㊁协议层,且每层中又有若干故障,因此这里对每一种故障用一个故障码表示,以便所有设备统一㊂故障参数值是针对具体的某种故障,长度依据注入故障类型的变化而变化㊂⑥累加和校验:除本身外所有字段的字节累加㊂4.2 响应帧设计下位机(F P G A )发送指令报文(即响应帧)到上位机,在此处设计响应帧格式为:帧头㊁帧计数㊁设备信息㊁故障码㊁状态,共计5部分㊂各字段含义同请求帧相同㊂5 测试结果5.1 上位机通信测试利用串口网络数据调试器验证上位机发送数据报文㊂图5所示为上位机故障参数配置界面,在状态显示区中可以看出,1553B 设备板卡以及R S 422设备板卡已与上位机建立连接,此外还可获知当前待注入故障设备信息和注入故障类型㊂连接设置电气层斜率调节故障,设置边沿斜率为4(下降沿),故障持续时间为10s㊂图5 1553B 设备电气层斜率调节故障参数设置图图6所示为上位机注入故障后下位机接收到的报文协议,协议共两条,第一条为故障插入命令,第二条为超出设定的故障注入持续时间后上位机下发清零协议,使得下位机清除故障,恢复至正常模态㊂其中第一条 55A A 000400012410043C 中 55A A 为帧头, 0004为帧长度, 00 为帧计数,即第一条报文, 01241004是数据段, 01 对应设备为1553B 板卡, 24 为斜率调节对应的故障码, 10 为模式码, 04 对应斜度4, 3C 为数据校验位㊂第二条指令是 55A A 00030101F F 1013,与之前不同的是清零报文中数据段为 F F 10,即全部层级无故障命令㊂两条数据报文与待注入故障目标的报文协议一致,由此可见通信部分设计的有效性㊂图6 1553B 设备注入电气层斜率调节故障数据接收图5.2 故障注入测试上位机下发故障注入指令,在下位机端连接示波器观察㊂如图7所示,I 区域为故障注入之前示波器波形输出效果,I I 区域为电气层注入4级斜率故障之后示波器波形输出效果,对比效果明显,完成既定目标㊂6 结 语本文设计的多总线故障注入系统包含1553B 及R S 422两种总线标准,解决了传统设计方式中总线模式单图7 斜率调节故障注入前后示波器波形对照图一㊁故障类型少的问题㊂文中通过对总体设计方法㊁软件层级的设计方法㊁通信逻辑的实现多方面进行阐述,验证了此种方法的正确性与可行性㊂此外,由于设计中采用了故障分层的方式,使得系统可模拟的故障模式在实际应用中易于扩展,对实际需求的适应性更强㊂该平台系统已通过测试验证,稳定可靠,已成功应用于工程项目中㊂参考文献[1]连盟,李学锋.1553B 总线故障注入测试方法研究[J ].航天控制,2012(2):8488.[2]荆广,徐宏伟,黎玉刚,等.一种多类型总线故障注入系统设计[J ].弹箭与制导学报,2018,38(2):129132,136.[3]杨森彬.航天总线容错性能测试平台的研究与实现[D ].哈尔滨:哈尔滨工业大学,2013.[4]戴虹.1553b 数据总线协议分析[J ].科学技术与工程,2008(13):35363538.[5]郑国灿.R S 232㊁R S 422与R S 485标准及应用技术[C]//中国电影电视技术学会影视科技论文集,2002:8287.张智慧(硕士),主要研究方向为控制工程;王志超(博士),主要研究方向为控制理论与控制工程;林岩(教授),主要研究方向为自适应控制㊁容错控制理论及应用㊂(责任编辑:薛士然 收修改稿日期:2020-11-16)莱迪思F P G A 助力玩视科技实现S D I 转H D M I 解决方案莱迪思半导体有限公司宣布:深圳玩视科技有限公司(H D C V T )采用莱迪思F P G A 器件提供的丰富高速S E R D E S 资源和灵活的I /O 接口,实现双通道3G S D I 转H D M I /V G A /R G B 桥接,适用于专业音视频传输㊁处理及控制类设备㊂莱迪思中国销售副总裁王诚先生表示: 玩视科技有限公司作为本地领军企业,专注音频和视频设备的设计㊁制造和销售㊂我们很高兴看到他们的产品选用我们的F P G A 器件,莱迪思F P G A 可实现各类灵活的桥接解决方案,并且通过我们资深的研发和应用工程方面的经验,满足他们的各类需求,帮助他们缩短产品上市时间㊂L a t t i c e F P G A 系列具备高性能特性,如增强的D S P 架构㊁高速S E R D E S 和高速源同步接口㊂该器件的查找表(L U T )高达149K 逻辑单元,支持最多486个用户I /O ,提供高达320个18ˑ18乘法器和各种并行I /O 标准支持,完美契合了要求低功耗㊁高容量㊁高速度和小尺寸的解决方案㊂。
Chapter1Hume:aFunctionally-Inspired Language for Safety-Critical SystemsKevin Hammond1and Greg Michaelson2Abstract:Hume is a novel functionally-based language that targets safety-critical applications.The language is designed to support rigorous cost and space anal-yses,whilst providing a high level of abstraction including polymorphic type inference,automatic memory management,higher-order functions,exception-handling and a good range of primitive types.1.1INTRODUCTIONThis paper describes the Hume programming language.Hume(Higher-order Unified Meta-Environment)is a strongly typed,mostly-functional language with an integrated tool set for developing,proving and assessing concurrent,safety-critical systems.Hume aims to extend the frontiers of safety-critical language design,introducing new levels of abstraction and provability.A full description of Hume including a formal dynamic semantics and a partially completed static semantics can be found at /hume. We anticipate publishing this material as a formal language definition in the near future.1.1.1BackgroundHume is named for the Scottish Enlightenment sceptical philosopher David Hume (1711-1776),who counseled that:To begin with clear and self-evident principles,to advance by timorous and sure steps,to review frequently our conclusions,and examine accurately all their consequences;though by these means we shall make both a slow and a short progress in our systems;are the only methods,by which we can ever hope to reach truth,and attain a proper stability and certainty in our determinations.D.Hume,An Enquiry Concerning Human Understanding,1748These sentiments epitomise the philosophy of programming language design that we have followed in constructing Hume.1.2MOTIV ATION AND OBJECTIVESSince the focus of the Hume design is on safety critical applications,it is paramount that Hume programs have predictable and,preferably,provable properties.How-ever,the strong properties of program equivalence,termination and time and space use are undecidable for Turing complete languages.Conversely,languages in which such properties are decidable(i.e.finite state machines)lack expressive-ness.The goal of the Hume language design is to support a high level of expres-sive power,whilst providing strong guarantees of dynamic behavioural properties such as execution time and space usage.Hume reflects these considerations in: the separation of the expression and coordination aspects of the language;and the provision of an integrated tool set,spanning both static and dynamic pro-gram analysis and manipulation.1.2.1Important Design CharacteristicsAny system that is aimed at safety critical applications must meet a number of stringent criteria if it is to be used with confidence.Hume has been designed to support Leveson’s guidelines for Safeware—software intended for safety critical applications[11],as well as similar guidelines provided by other authors[2].In general,safety critical systems must meet both strong correctness criteria and strict performance criteria.The latter are most easily attained by working at a low level,whereas the former are most easily attained by working at a high level.A primary objective of the Hume design is to allow both types of criteria to be met while working at a high level of abstraction.The Hume language has been designed to allow relatively simple formal cost models to be developed,capable of costing both space and time usage.This re-quires some restrictions on the expression language in cases which are cost or2space critical.Thisfirst version of the language design is deliberately rather spar-tan,allowing experimentation with essential features but omitting some desirable syntax or other language features,such as type classes.Future versions of the language should address these omissions.The language definition does support a wide range of(particularly numeric)basic types.This is because issues of type coercion and type safety are fundamental to ensuring both correctness and safety.Both system level and process level exceptions are supported,including the ability to set timeouts for expression computations.Exceptions may be raised from within the expression language but can only be handled by the process lan-guage.This reduces the cost of handling exceptions and maintains a pure expres-sion language,as well as simplifying the expression cost calculus.A radical design decision for safety critical systems is the use of automatic memory management techniques.Automatic memory management has the ad-vantage of reducing errors due to poor manual management of memory.The disadvantage lies in terms of excessive time or space usage.Hume implementa-tions will use static analysis tools to limit space usage,and will incorporate recent developments in bounded-time memory management techniques[3].1.3THE HUME LANGUAGEThis section introduces the Hume language informally.A full description,from which this section is abstracted,can be found in the Hume language definition[13].1.3.1Structure of the LanguageIn common with other coordination language approaches such as Linda[4],Hume takes a layered approach.The outermost layer is a static declaration language that provides definitions of types,streams etc.to be used in the dynamic parts of the language.The innermost layer is a fairly conventional expression language which is used to define values and(potentially higher-order)functions using purely func-tional expressions.Finally,the middle layer is a coordination language that links functions into possibly concurrent processes.Exceptions transcend the layers.They are declared by exception<id> <type>within declarations,raised by raise<id><expr>within expres-sions and handled by boxes.1.3.2The Hume Expression LanguageThe Hume expression language is a purely functional language with a strict se-mantics.It is intended to be used for the description of single,one-shot,non-reentrant processes.It is deterministic,and has statically bounded time and space behaviour.In order to achieve this,expressions that are not the target of dynamic timeouts must be restricted to statically-checkable primitive recursive forms.This allows the construction of verifiable static cost analyses.Dynamically bounded time and space expressions(within-expressions)specify that evaluation of the3associated expression must complete within the specified constant time or space. Failure to do so causes the Timeout or HeapOverflow exception to be raised.Note that the expression language has no concept of external,imperative state. Such state considerations are encapsulated entirely within the coordination lan-guage.1.3.3The Hume Coordination LanguageThe Hume coordination language is afinite state language for the description of multiple,interacting,re-entrant processes built from the purely functional ex-pression layer.The coordination language is designed to have statically provable properties that include both process equivalence and safety properties such as the absence of deadlock,livelock or resource starvation.The coordination language also inherits properties from the expression language that is embedded within it.The basic unit of coordination is the box,an abstract notion of a process that specifies the links between its input and output channels in terms of functional expressions,and which provides exception handling facilities including timeouts and system exceptions The coordination language is responsible for interaction with external,imperative state through streams and ports that are ultimately con-nected to external devices.1.3.4The Hume Declaration LanguageThe declaration language introduces types and values that scope over either or both the coordination and expression languages.The coordination language is embedded in the declaration language through box and wiring declarations while the expression language is embedded through function and value declarations. While it is possible to define recursive and mutually recursive functions,it is not possible to do the same for simple values.1.4EXAMPLE PROGRAMS1.4.1Parity CheckingOurfirst example is a simple even parity checker whose input is wired to a com-munications port(comm1),and whose output is wired to its second input.The initial parity value is defined to be true.box even_parityin(b::word1,p::bool)out(p’::bool)match(0,true)->true|(1,true)->false|(0,false)->false4|(1,false)->true;wire even_parity(comm1,even_parity.p’initially true)(even_parity.p);1.4.2ChecksumThe second example calculates the checksum of256input numbers.It returns a string which is either"OK"or an error message.This example illustrates(some-what artificially)the use of exceptions and handlers.type short=int16;type long=int32;box checksumin(n::short,sum::long,count::short)out(sum’::long,count’::short,message::string)handles CheckSumErrormatch(n,sum,256)->(0,0,if n=sum then"OK"else raise CheckSumError())|(n,sum,count)->(sum+n,count+1,"")handleCheckSumError_->(0,0,"Checksum error:sum="+tostring(sum)+"checksum="+tostring(n));wire checksum(comm1,checksum.sum’initially0,checksum.count’initially0)(checksum.sum,checksum.count,stdout); 1.5COSTING HUME PROGRAMSFigures1.1–1.6give rules that can be used to statically derive a bounded time cost forfirst-order Hume programs(we are independently working on time sys-tems for higher-order programs[12]).The rules are a simple big-step operational semantics,with extensions to timeouts and exceptions.We have deliberately used a very simple cost semantics here rather than the more general form that we are developing as part of our work in parallel computation[12].The latter is intended for arbitrary recursion and requires the use of a constraint solving engine,whereas Hume is restricted to primitive recursive forms.It would be straightforward to al-ter these rules to cover space rather than time cost,as required.The cost rules specified here derive notation from the Hume static and dynamic semantics,which is in turn derived from that used for Haskell and Standard ML.5E decls E Costni1i n EE’j decl i E i c ij1E var exp cE var∞matches c cE body CostE matches c c E handlers cE matches time handles min t c c cFIGURE1.2.Cost axioms for boxesOnly two forms of declaration are interesting.Variable declarations are evaluatedat the start of a declaration block.They therefore have afixed dynamic cost.The cost of a function(of the form var matches)is defined as the cost of matching allpatterns in the set of matches,plus the cost of the most expensive expression on the right-hand-sides of the matches.This therefore computes an upper bound on the cost of evaluating a function body.Recursive definitions are assigned infinitecost.The cost is bound to the function name in the environment so that the cost of each and every function call is correctly calculated.The result of a declaration sequence is the union of the environment recording function costsFigure1.2gives the cost of a single box iteration.This is defined similarly to the cost of a function definition,but including the upper bound of the exceptionhandling cost.There are two cases.If no timeout clause is given,then the matches must befinite.Otherwise the cost is the lesser of the timeout and the actual execution cost plus the handler cost.Figures1.3–1.4give cost rules for expressions.The cost of a function ap-plication is the cost of evaluating the body of the function plus the cost of each argument.The cost of building a new constructor such as a list or tuple is thecost of evaluating the arguments to that constructor plus one for each argument (representing the cost of building each heap cell).Note that the cost of a non-nulllist exp1exp n includes the cost of thefinal,and is therefore greater than the equivalently sized tuple exp1exp n or vector exp1exp n.The cost of a coercing an expression to a given type using an as-expression dependson the original type of the expression and the one that it is coerced to.There is,of course,no cost for a simple type cast.The cost of raising an exception is the cost of the enclosed expression plus one(representing the cost of actually throwing that exception).Finally the cost of an expression enclosed within a timeout is the minimum of the expression cost and the specified timeout.Figure1.5gives costs for pattern matches.Two values are returned from a match sequence.Thefirst is the total cost of matching all the patterns in the match sequence.This places an upper bound on the match cost.The second is the cost of evaluating the most expensive right-hand-side.This places an upper7E exp Costn0E var exp1exp n∑n i1c i cE con exp1exp n∑n i1c i1E exp1exp n∑n i1c i n1E exp1exp n∑n i1c i nE exp1exp n∑n i1c i nFIGURE 1.3.Cost axioms for expressions(variables,applications and construc-tors)bound on the expression cost.The cost of matching multiple patterns in a single match is the sum of matching each pattern.Wildcard patterns(E exp Cost E exp c E match cE if exp1then exp2else exp3c1max c2c3E decls E’c E E’exp cE exnid exp c1value exp2t E exp1cE Matches Cost CostE match c c E matches c cE pat1pat n exp∑n i1c i cE pat CostE con pat1pat n∑n i1c i1i1i n E pat i c iE0i1i n E pat i c iE0i1i n E pat i c iE1FIGURE1.5.Cost axioms for pattern matchesapproach separatesfinite data structures such as tuples from potentially infinite structures such as streams.This allows the definition of functions that are guar-anteed to be primitive recursive.In contrast with Hume,it is necessary to identify functions that may be more generally recursive.Ada is widely used for embedded systems,and many tools have been con-structed to assist the understanding of space and time behaviour[2].Compared with ANSI standard Ada,Hume provides much higher level of abstraction with a far more rigorously defined semantics,which is specifically designed to support cost semantics.Finally,there has been recent interest in using variants of Java as the ba-sis for embedded systems,though to our knowledge there is as yet no specif-ically safety-critical design.Two interesting variants are Embedded Java[17]10E Handlers CostE pat c E exp cE handler handlers max c cFIGURE1.6.Cost axioms for exception handlersand RTJava[9],for soft real-time applications.Like Hume,both languages sup-port dynamic memory allocation with automatic garbage collection and provide strong exception handling mechanism.The primary differences from Hume are the incorporation of arbitrary recursion in all cases,an absence of formal design principles,the use of a single-layered approach in which coordination is merged with computation,and of course the use of an object-oriented expression language rather than one that is purely functional.We believe that the design choices made here are more suitable for applications where safety is paramount.For example, the use of purely functional rather than dynamically-linked object-oriented design allows straightforward static reasoning about the meaning of programs,at the cost of convenience in modifying a running system.1.7CONCLUSIONThis paper has introduced the Hume language,a novel functionally-inspired lan-guage that is geared towards safety critical applications.A key feature of the design is the incorporation of a purely functional expression language that pro-vides strong guarantees of functional correctness with equally strong guarantees of time and space behaviour.To our knowledge,this is thefirst fully-featured functional language that supports such guarantees.To illustrate the key features of our language design,we have produced a sim-ple boundedfirst-order time cost analysis.The analysis makes a number of sim-plifying assumptions,such as costing all heap allocations,exception raises and variable bindings identically(as1in this set of definitions).It would,however, be straightforward to parameterise the analysis on more realistic costs,or even to modify it so as to calculate space rather than time costs.Clearly,Hume is still at an early stage of development.None of our language tools has yet been constructed and important design details are still to be resolved. We feel,however,that the properties designed into the language should yield long-term benefits in the safety-critical arena.11REFERENCES[1]W.Ackermann,Solvable Cases of the Decision Problem,North Holland,1954.[2]J.G.P.Barnes,High Integrity Ada:the Spark Approach,Addison-Wesley,1997.[3]C.Clack,“The Demense Model for Bounded Automatic Memory Management”,Un-published Report,University College,London,2000.[4]D.Gelernter,and N.Carriero,“Coordination Languages and Their Significance”,CACM,32(2),February,1992,pp.97–107.[5]A.D.Gordon,S.Marlow and S.L.Peyton Jones,“A Semantics for Imprecise Excep-tions”,Proc.Symposium on Principles of Programming Languages(POPL2000), January2000.[6]M.G.Hinchey and J.P.Bowen,Applications of Formal Methods,Prentice-Hall,1995.[7]International Organisation for Standardisation,“ISO:Information Processing Sys-tems—Open Systems Interconnection—LOTOS,A Formal Description Technique based on the Temporal Ordering of Observational Behaviour”,ISO8807,Geneva, August1988.[8]International Organisation for Standardisation,“ISO:Information Processing Sys-tems—Open Systems Interconnection—Estelle,A Formal Description Technique based on an Extended State Transition Model”,ISO9074,Geneva,May1989. [9]D.Jensen,“‘Real-time Java’.What could and what should it mean?”URL:/carnahan/real-time/vocab/ rt-java。