会计chap2
- 格式:ppt
- 大小:1.06 MB
- 文档页数:38





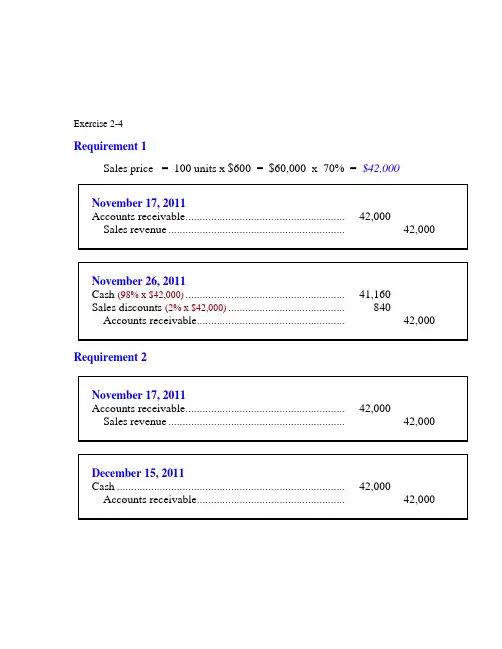
Exercise 2-4Requirement 1Sales price = 100 units x $600 = $60,000 x 70% = $42,000Requirement 2Exercise 7-4 (concluded)Requirement 3Requirement 1, using the net method:Requirement 2, using the net method:Exercise 2-7Requirement 1Estimated returns = 4% x $11,500,000 = $460,000Less: Actual returns (450,000)Remaining estimated returns $10,000Note: another series of journal entries that produce the same end result would be:Exercise 2-7 (continued)Requirement 2Beginning balance in allowance account $300,000 Add: Year-end estimate 460,000 Less: Actual returns (450,000) Ending balance in allowance account $310,000Exercise 2-8Requirement 1Bad debt expense = $67,500 (1.5% x $4,500,000)Requirement 2Allowance for uncollectible accountsBalance, beginning of year $42,000 Add: Bad debt expense for 2011 (1.5% x $4,500,000) 67,500 Less: End-of-year balance (40,000) Accounts receivable written off $69,500 Requirement 3$69,500 — the amount of accounts receivable written off.Exercise 2-9Requirement 1To record the write-off of receivables.To reinstate an account previously written off and to record the collection.Allowance for uncollectible accounts:Balance, beginning of year $32,000Deduct: Receivables written off (21,000) Add: Collection of receivable previously written off 1,200Balance, before adjusting entry for 2011 bad debts 12,200Required allowance: 10% x $625,000 (62,500) Bad debt expense $50,300 To record bad debt expense for the year.Requirement 2Current assets:Accounts receivable, net of $62,500 allowancefor uncollectible accounts $562,500Exercise 2-10Using the direct write-off method, bad debt expense is equal to actual write-offs. Collections of previously written-off receivables are recorded as revenue.Allowance for uncollectible accounts:Balance, beginning of year $17,280Deduct: Receivables written off (17,100)Add: Collection of receivables previously written off 2,200Less: End of year balance (22,410)Bad debt expense for the year 2011 $20,030 Exercise 2-11($ in millions)Allowance for uncollectible accounts:Balance, beginning of year $16Add: Bad debt expense 14Less: End of year balance (18)Write-offs during the year $ 12*Accounts receivable analysis:Balance, beginning of year ($1,084 + 16)$ 1,100Add: Credit sales 4,271Less: Write-offs* (12)Less: Balance end of year ($953 + 18) (971)Cash collections $4,388Exercise 2-12Requirement 1Requirement 22011 income before income taxes would be understated by $900 2012 income before income taxes would be overstated by $900.Exercise2-13Requirement 1Requirement 2$ 1,800 interest for 9 months÷ $28,200 sales price= 6.383% rate for 9 monthsx 12/9to annualize the rate_______= 8.511% effective interest rateExercise 2-14Requirement 1Book value of stock $16,000Plus gain on sale of stock 6,000= Note receivable $22,000Interest reported for the year $ 2,200= 10% rate Divided by value of note $ 22,000 Requirement 2To record sale of stock in exchange for note receivable.To accrue interest on note receivable for twelve months.Exercise 2-15Exercise 2-16Exercise 2-17Exercise 2-18Mountain High retains significant risks and rewards and therefore must treat the transfer as a secured borrowing. The accounts receivable stay on the balance sheet of Mountain High, and they must record a liability.Exercise 2-19Step 1: Accrue interest earned.Step 2: Add interest to maturity to calculate maturity value.Step 3: Deduct discount to calculate cash proceeds.Step 4: To record a loss for the difference between the cash proceeds and the note’s book value.Exercise 2-21Requirement 1Step 1: To accrue interest earned for two months on note receivableStep 2: Add interest to maturity to calculate maturity value.Step 3: Deduct discount to calculate cash proceeds.Exercise 7-21 (continued)Step 4: To record a loss for the difference between the cash proceeds and the note’s book value.Exercise 2-21 (concluded)Requirement 2To accrue interest earned on note receivable.。

Exercise 2-4Requirement 1Sales price = 100 units x $600 = $60,000 x 70% = $42,000Requirement 2Exercise 7-4 (concluded)Requirement 3Requirement 1, using the net method:Requirement 2, using the net method:Exercise 2-7Requirement 1Estimated returns = 4% x $11,500,000 = $460,000Less: Actual returns (450,000)Remaining estimated returns $10,000Note: another series of journal entries that produce the same end result would be:Exercise 2-7 (continued)Requirement 2Beginning balance in allowance account $300,000 Add: Year-end estimate 460,000 Less: Actual returns (450,000) Ending balance in allowance account $310,000Exercise 2-8Requirement 1Bad debt expense = $67,500 (1.5% x $4,500,000)Requirement 2Allowance for uncollectible accountsBalance, beginning of year $42,000 Add: Bad debt expense for 2011 (1.5% x $4,500,000) 67,500 Less: End-of-year balance (40,000) Accounts receivable written off $69,500 Requirement 3$69,500 — the amount of accounts receivable written off.Exercise 2-9Requirement 1To record the write-off of receivables.To reinstate an account previously written off and to record the collection.Allowance for uncollectible accounts:Balance, beginning of year $32,000Deduct: Receivables written off (21,000) Add: Collection of receivable previously written off 1,200Balance, before adjusting entry for 2011 bad debts 12,200Required allowance: 10% x $625,000 (62,500) Bad debt expense $50,300 To record bad debt expense for the year.Requirement 2Current assets:Accounts receivable, net of $62,500 allowancefor uncollectible accounts $562,500Exercise 2-10Using the direct write-off method, bad debt expense is equal to actual write-offs. Collections of previously written-off receivables are recorded as revenue.Allowance for uncollectible accounts:Balance, beginning of year $17,280Deduct: Receivables written off (17,100)Add: Collection of receivables previously written off 2,200Less: End of year balance (22,410)Bad debt expense for the year 2011 $20,030 Exercise 2-11($ in millions)Allowance for uncollectible accounts:Balance, beginning of year $16Add: Bad debt expense 14Less: End of year balance (18)Write-offs during the year $ 12*Accounts receivable analysis:Balance, beginning of year ($1,084 + 16)$ 1,100Add: Credit sales 4,271Less: Write-offs* (12)Less: Balance end of year ($953 + 18) (971)Cash collections $4,388Exercise 2-12Requirement 1Requirement 22011 income before income taxes would be understated by $900 2012 income before income taxes would be overstated by $900.Exercise2-13Requirement 1Requirement 2$ 1,800 interest for 9 months÷ $28,200 sales price= 6.383% rate for 9 monthsx 12/9to annualize the rate_______= 8.511% effective interest rateExercise 2-14Requirement 1Book value of stock $16,000Plus gain on sale of stock 6,000= Note receivable $22,000Interest reported for the year $ 2,200= 10% rate Divided by value of note $ 22,000 Requirement 2To record sale of stock in exchange for note receivable.To accrue interest on note receivable for twelve months.Exercise 2-15Exercise 2-16Exercise 2-17Exercise 2-18Mountain High retains significant risks and rewards and therefore must treat the transfer as a secured borrowing. The accounts receivable stay on the balance sheet of Mountain High, and they must record a liability.Exercise 2-19Step 1: Accrue interest earned.Step 2: Add interest to maturity to calculate maturity value.Step 3: Deduct discount to calculate cash proceeds.Step 4: To record a loss for the difference between the cash proceeds and the note’s book value.Exercise 2-21Requirement 1Step 1: To accrue interest earned for two months on note receivableStep 2: Add interest to maturity to calculate maturity value.Step 3: Deduct discount to calculate cash proceeds.Exercise 7-21 (continued)Step 4: To record a loss for the difference between the cash proceeds and the note’s book value.Exercise 2-21 (concluded)Requirement 2To accrue interest earned on note receivable.。



