Control System Design and Validation for Visual Based Indoor Inspection Helicopter
- 格式:pdf
- 大小:461.45 KB
- 文档页数:8

Optimal Control and Estimation Optimal control and estimation are crucial concepts in the field of engineering and technology. These concepts play a vital role in various applications such as robotics, aerospace systems, autonomous vehicles, and industrial processes. Optimal control refers to the process of finding the best control inputs for a given system to achieve a specific objective, while estimation involves the process of determining the state of a system based on available measurements. Both optimal control and estimation are essential for ensuring the efficient and reliable operation of complex systems. One of the key challenges in optimal control and estimation is the trade-off between performance and computational complexity. In many real-world applications, the system dynamics are nonlinear and the state space is high-dimensional, making it challenging to design optimal control and estimation algorithms that are both computationally efficient and capable of achieving the desired performance. Engineers and researchers often face the dilemma of choosing between computationally intensive algorithms that can achieve near-optimal performance and simpler algorithms that are computationally efficient but may sacrifice performance. Another important consideration in optimal control and estimation is the presence of uncertainties and disturbances in the system. Real-world systems are often subject to various sources of uncertainty, such as sensor noise, modeling errors, and external disturbances. These uncertainties can significantly affect the performance of control and estimation algorithms, making it necessary to develop robust and adaptive techniques that can effectively handle these uncertainties. Robustcontrol and estimation techniques aim to design algorithms that are resilient to uncertainties and disturbances, ensuring the stability and performance of the system under varying operating conditions. From a practical perspective, the successful implementation of optimal control and estimation algorithms also depends on the availability of accurate and reliable sensors for measuring the system state and the effectiveness of the control inputs. In many engineering applications, the design of optimal control and estimation algorithms must take into account the limitations and characteristics of the available sensors, as well as the physical constraints of the system. This often requires a multidisciplinaryapproach that integrates knowledge from control theory, signal processing, and sensor technology to develop practical and effective solutions. Moreover, the integration of optimal control and estimation techniques with modern advancements such as machine learning and artificial intelligence presents both opportunities and challenges. Machine learning algorithms, such as reinforcement learning, have shown promise in learning optimal control policies from data and experience, offering a potential alternative to traditional model-based control approaches. Similarly, data-driven estimation techniques based on machine learning have the potential to improve the accuracy and robustness of state estimation in complex systems. However, the integration of machine learning with optimal control and estimation also raises concerns about the interpretability, safety, andreliability of the resulting control and estimation algorithms, highlighting the need for careful validation and verification processes. In conclusion, optimal control and estimation are fundamental concepts that underpin the design and operation of advanced engineering systems. The challenges and considerations in optimal control and estimation are multifaceted, encompassing issues related to performance, computational complexity, uncertainties, sensor limitations, and the integration of modern technologies. Addressing these challenges requires a holistic and interdisciplinary approach that leverages knowledge from control theory, signal processing, sensor technology, and machine learning. By developing innovative and practical solutions to these challenges, engineers and researchers can advance the state-of-the-art in optimal control and estimation, enabling the efficient and reliable operation of complex engineering systems.。
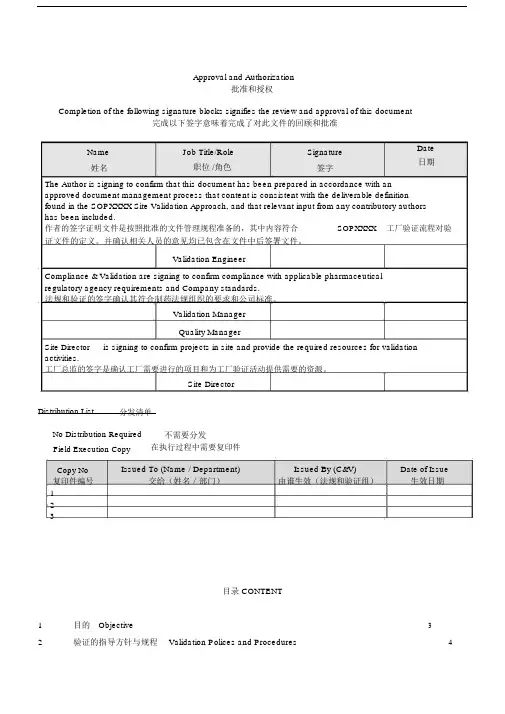
Computerised System Validation计算机系统验证Dept. 部门:Effective Date生效日期:Confidential Level 机密等级:□ Top-secret 绝密 □ Confidential 机密 □ Cryptical 秘密 Distribution List : 分发清单:QA 部、QC 部、OSP 固体制剂部、Lo.物控部、EN 工程部、TD 技术部、EQ 设备部1Objective 目的Year/年Month/月QA 质量保证部Date/日Test and assessment should be taken for URS, design, purchase, installation,function, as well as process adaptability of computerized and PLC control systemrelated to GMP in compliance with this SOP so as to ensure that computerized andPLC are fit for design requirement and stated technical criteria and are able to workstably for a long time.根据本SOP,对URS、设计、采购、安装、功能以及GMP相关的计算机控制和PLC控制系统进行测试评估,以确保计算机和PLC符合设计要求和工艺要求并且能够长时间稳定工作。
2 Scope范围This SOP is fit for the validation management of computerized and PLC controlsystem related to GMP, which apply to material control and management, laboratory equipment control and communication management, manufacturing process control, and utilities control.本SOP适用于GMP相关计算机,PLC控制系统的验证管理,物料控制和管理,实验设备控制和通信管理、生产过程控制、公用设施的控制的验证。

A/D/V Analysis/Development/Validation 分析/发展/验证AA Approve Architecture 审批体系ACD Actual Completion Date 实际完成日期ALBS Assembly Line Balance System 装配线平衡系统ANDON 暗灯AP Advanced Purchasing 提前采购API Advanced Product Information 先进的产品信息APQP Advanced Product Quality Planning 先期产品质量策划ATT Actual Tact Time 实际单件工时BIQ Building in Quality 制造质量BIW Body In White 白车身BOD Bill of Design 设计清单BOE Bill of Equipment 设备清单BOL Bill of Logistic 装载清单BOM Bill of Material 原料清单BOP Bill of Process 过程清单BPD Business Plant Deployment 业务计划实施CAD Computer-Aided Design 计算机辅助设计CAE Computer-Aided Engineering 计算机辅助工程(软件) CARE Customer Acceptance & Review Evaluation 用户接受度和审查评估CIP Continue Improve Process 持续改进CIT Compartment Integration Team 隔间融合为组CKD Complete Knockdown 完全拆缷CMM Coordinate Measuring Machines 坐标测量仪CPV Cost per Vehicle 单车成本CR&W Controls/Robotics & Welding 控制/机器人技术和焊接CS Contract Signing 合同签订CTD Cumulative Trauma Disadjust 累积性外伤失调CTS Component Technical Specification 零件技术规格CVIS Completed Vehicle Inspection Standards 整车检验标准DAP Design Analysis Process 设计分析过程DES Design Center 设计中心DFA Design for Assembly 装配设计DOE Design Of Experiments 试验设计DOL Die Operation Line-Up 冲模业务排行DPV Defect per Vehicle 单车缺陷数DQV Design Quality Verification 设计质量验证DRE Design Release Engineer 设计发布工程师DRL Direct Run Loss 直行损失率DRR Direct Run Run 直行率DSC Decision Support Center 决策支持中心ECD Estimated Completion Date 计划完成日期3 lEGM Engineering Group Manager 工程组经理ENG Engineering 工程技术、工程学EOA End of Acceleration 停止加速EPC&L Engineering Production Control &Logistics 工程生产控制和后勤EQF Early Quality Feedback 早期质量反馈EWO Engineering Work Order 工程工作指令FA Final Approval 最终认可FE Functional Evaluation 功能评估FEDR Functional Evaluation Disposition Report 功能评估部署报告FFF Free Form Fabrication 自由形态制造FIN Financial金融的FPS Fixed Point Stop 定点停FTP File Transfer Protocol 文件传送协议FTQ First Time Quality 一次送检合格率GA General Assembly 总装GA Shop General Assembly Shop 总装车间Paint Shop 涂装车间Body Shop 车身车间Press Shop 冲压车间GCA Global Customer Audit 全球顾客评审GD&T Geometric Dimensioning & Tolerancing 几何尺寸及精度GDS Global Delivery Survey 全球发运检查GM General Motors 通用汽车GMAP GM Asia Pacific 通用亚太GME General Motors Europe 通用汽车欧洲GMIO General Motors International Operations 通用汽车国际运作GMIQ General Motors Initial Quality 通用汽车初始质量GMPTG General Motors Powertrain Group 通用汽车动力组GMS Global Manufacturing System 通用全球制造系统GP General Procedure 通用程序GQTS Global Quality Tracking System 全球质量跟踪系统GSB Global Strategy Board 全球战略部HVAC Heating, Ventilation ,and Air Conditioning 加热、通风及空调IC Initiate Charter 初始租约ICD Interface Control Document 界面控制文件IE Industrial Engineering 工业工程ILRS Indirect Labor Reporting System 间接劳动报告系统IO International Operations 国际业务IOM Inspection Operation Method 检验操作方法IOS Inspection Operation Summary 检验操作概要IPC International Product Center 国际产品中心IPTV Incidents Per Thousand Vehicles 每千辆车的故障率IQS Initial Quality Survey 初始质量调查IR Incident Report 事故报告ISP Integrated Scheduling Project 综合计划ITP Integrated Training Process 综合培训方法ITSD Interior Technical Specification Drawing 内部技术规范图IUVA International Uniform Vehicle Audit 国际统一车辆审核JES Job Element Sheet 工作要素单JIS Job Issue Sheet 工作要素单JIT Just in Time 准时制JPH Job per hour 每小时工作量KCC Key Control Characteristics 关键控制特性KCDS Key Characteristics Designation System 关键特性标识系统KPC Key product Characteristic 关键产品特性LT Look at 看MFD Metal Fabrication Division 金属预制件区MFG Manufacturing Operations 制造过程) MIE Manufacturing Integration Engineer 制造综合工程师MLBS Material Labor Balance System 物化劳动平衡系统MNG Manufacturing Engineering 制造工程MPG Milford Proving Ground 试验场MPI Master Process Index 主程序索引MPL Master Parts List 主零件列表MPS Material Planning System 原料计划系统MRD Material Required Date 物料需求日期MSDS Material Safety Data Sheets 化学品安全数据单MSE Manufacturing System Engineer 制造系统工程MTBF Mean Time Between Failures 平均故障时间MTS Manufacturing Technical Specification 生产技术规范MVSS Motor Vehicle Safety Standards 汽车发动机安全标准NAMA North American Market Analysis 北美市场分析NAO North American Operations 北美业务NAOC NAO Containerization NAO货柜运输NC Numerically Controlled 数字控制NOA Notice of Authorization 授权书NSB NAO Strategy Board 北美业务部OED Organization and Employee Development 组织和员工发展OSH Occupational Safety & Health 职业安全健康TOSHA Occupational Safety & Health Act 职业安全与健康法案OSHMS Occupational Safety & Health Management System职业安全健康管理体系OSHS Occupational Safety & Health Standards 职业安全标准PA Production Achievement 生产结果PAA Product Action Authorization 产品临时授权PAC Performance Assessment Committee 绩效评估委员会PACE Program Assessment and Control Environment 项目评估和控制条件PAD Product Assembly Document 产品装配文件PARTS Part Readiness Tracking System 零件准备跟踪系统PC Problem Communication 问题信息PCL Production Control and Logistics 生产控制和支持PCM Process Control Manager 工艺控制负责人PCR Problem Communication Report 问题交流报告PDM Product Data Management 产品资料管理PDS Product Description System 产品说明系统PDT Product Development Team 产品发展小组PED Production Engineering Department 产品工程部PEP Product Evaluation Program 产品评估程序PER Personnel 人员PET Program Execution Team 项目执行小组PGM Program Management 项目管理PI People Involvement 人员参与PLP Production Launch Process 生产启动程序PMI Process Modeling Integration 加工建模一体化PMM Program Manufacturing Manager 项目制造经理PMR Product Manufacturability Requirements 产品制造能要求POMS Production Order Management System 产品指令管理小组POP Point of Purchase 采购点PP Push Pull 推拉PPAP Production Part Approval Process 生产零部件批准程序PPE Personal Protective Equipment 个人防护用品PPH Problems Per Hundred 百辆车缺陷数PPM Problems Per Million 百万辆车缺陷数PPS Practical Problem Solving 实际问题解决PR Performance Review 绩效评估PR/R Problem Reporting and Resolution 问题报告和PRTS Problem Resolution and Tracking System 问题解决跟踪系统PSC Portfolio Strategy Council 部长职务策略委员会PST Plant Support Team 工厂支持小组PTO Primary Tryout 第一次试验PTR Production Trial Run 生产试运行PUR Purchasing 采购QA Quality Audit 质量评审QAP Quality Assessment Process 质量评估过程QBC Quality Build Concern 质量体系构建关系QC Quality Characteristic 质量特性QCOS Quality Control Operation Sheets 质量风险控制QE Quality Engineer 质量工程师QET Quality Engineering Team 质量工程小组QFD Quality Function Deployment 质量功能配置QRD Quality, Reliability and Durability 质量、可靠性和耐久力QS Quality System 质量体系QUA Quality质量RC Review Charter 评估特许RCD Required Completion Date 必须完成日期RFQ Request For Quotation 报价请求RGM Reliability Growth Management 可靠性增长小组RONA Return on Net Assets 净资产评估RPO Regular Production Option 正式产品选项RQA Routing Quality Assessment 程序安排质量评定RT&TM Rigorous Tracking and Throughout Management 严格跟踪和全SDC Strategic Decision Center 战略决策中心SF Styling Freeze 造型冻结SIL Single Issue List 单一问题清单SIP Standardized Inspection Process 标准化检验过程SL System Layouts 系统规划SLT Short Leading Team 缩短制造周期SMBP Synchronous Math-Based Process 理论同步过程SMT Systems Management Team 系统管理小组SNR 坏路实验SOP Start of Production 生产启动SOP Safe Operating Practice 安全操作规程SOR Statement of Requirements 技术要求SOS Standardization Operation Sheet 标准化工作操作单SOW Statement of Work 工作说明SPA Shipping Priority Audit 发运优先级审计SPC Statistical Process Control 统计过程控制SPE Surface and Prototype Engineering 表面及原型工程SPO Service Parts Operations 配件组织SPT Single Point Team 专一任务小组SQA Supplier Quality Assurance 供应商质量保证(供应商现场工程师)SQC Supplier Quality Control 供方质量控制SQD Supplier Quality Development 供应方质量开发SQE Supplier Quality Engineer 供方质量工程师SQIP Supplier Quality Improvement Process 供应商质量改进程序SSLT Subsystem Leadership Team 子系统领导组SSTS Subsystem Technical Specification 技术参数子系统STD Standardization 标准化STO Secondary Tryout 二级试验SUI 安全作业指导书SUW Standard Unit of Work 标准工作单位SWE Simulated Work Environment 模拟工作环境TAG Timing Analysis Group 定时分析组TBD To Be Determined 下决定TCS Traction Control System 牵引控制系统TDC Technology Development Centre 技术中心TDMF Text Data Management Facility 文本数据管理设备TG Tooling 工具TIMS Test Incident Management System 试验事件管理系统TIR Test Incident Report 试验事件报告TMIE Total Manufacturing Integration Engineer 总的制造综合工程TOE Total Ownership Experience 总的物主体验TPM Total Production Maintenance 全员生产维护TSM Trade Study Methodology 贸易研究方法TT Tact Time 单件工时TVDE Total Vehicle Dimensional Engineer 整车外型尺寸工程师TVIE Total Vehicle Integration Engineer 整车综合工程师TWS Tire and Wheel System 轮胎和车轮系统UAW United Auto Workers 班组UCL Uniform Criteria List 统一的标准表UDR Unverified Data Release 未经核对的资料发布UPC Uniform Parts Classification 统一零件分级VAE Vehicle Assembly Engineer 车辆装配工程师VCD Vehicle Chief Designer 汽车首席设计师VCE Vehicle Chief Engineer 汽车总工程师CVCRI Validation Cross-Reference Index 确认交叉引用索引VDR Verified Data Release 核实数据发布VDS Vehicle Description Summary 汽车描述概要VDT Vehicle Development Team 汽车发展组VEC Vehicle Engineering Center 汽车工程中心VIE Vehicle Integration Engineer 汽车综合工程师VIN Vehicle Identification Number 车辆识别代码VIS Vehicle Information System 汽车信息系统VLE Vehicle Line Executive 总装线主管VLM Vehicle Launch Manager 汽车创办经理VOC Voice of Customer 顾客的意见VOD Voice of Design 设计意见VS Validation Station 确认站VSAS Vehicle Synthesis Analysis and Simulation 汽车综合、分析和仿真VSE Vehicle System Engineer 汽车系统工程师VTS Vehicle Technical Specification 汽车技术说明书WOT Wide Open Throttle 压制广泛开放WPO Work Place Organization 工作场地布置WWP Worldwide Purchasing 全球采购COMMWIP Correction 纠错浪费。

33.28 Engine control systems.(a) Applicability. These requirements are applicable to any system or device that is part of engine type design, that controls, limits, or monitors engine operation, and is necessary for the continued airworthiness of the engine.(a)适用。
这些规定适用於任何系统或设备,一部分是引擎型式的设计,控制、限制、或监测引擎运作,则必须为继续适航的引擎。
(b) Validation —(1) Functional aspects. The applicant must substantiate by tests, analysis, or a combination thereof, that the engine control system performs the intended functions in a manner which:(b)审定-(1)功能方面。
申请人必须证明的测试,分析,或两者结合,引擎控制制度发挥了预期功能的方式:(i) Enables selected values of relevant control parameters to be maintained and the engine kept within the approved operating limits over changing atmospheric conditions in the declared flight envelope;(i)使选定的数值的有关管制参数的引擎要维持和保持在经批准的营运限制在改变大气状况的飞行信封的宣布;(ii) Complies with the operability requirements of §§33.51, 33.65 and 33.73, as appropriate, under all likely system inputs and allowable engine power or thrust demands, unless it can be demonstrated that failure of the control function results in a non-dispatchable condition in the intended application;(ii)符合要求的可操作性的第33.51、33.65及二○○八年首,酌情根据所有可能系统的投入和允许发动机功率或主旨要求,除非可以表明,管制措施的失败函数的结果非dispatchable条件在拟提出申请;(iii) Allows modulation of engine power or thrust with adequate sensitivity over the declared range of engine operating conditions; and(iii)允许调制的引擎动力或目标,充分认识在宣布系列发动机经营情况; 和(iv) Does not create unacceptable power or thrust oscillations.(㈣)并不造成不能接受权力或主旨振荡。

Robust Control and Estimation Robust control and estimation are essential concepts in the field of engineering, particularly in the design and implementation of control systems for various applications. These concepts are crucial for ensuring that control systems can effectively handle uncertainties and disturbances, leading to stable and reliable performance. In this response, I will explore the significance of robust control and estimation from different perspectives, highlighting their importancein engineering and the challenges associated with their implementation. From an engineering perspective, robust control and estimation play a vital role in ensuring the stability and performance of control systems in the presence of uncertainties and variations in system dynamics. These uncertainties can arisefrom various sources, such as modeling errors, external disturbances, andvariations in system parameters. Robust control techniques, such as H-infinity control and mu-synthesis, are designed to address these uncertainties and provide guarantees on the performance and stability of control systems. Similarly, robust estimation techniques, such as Kalman filtering and robust observers, are used to accurately estimate the state of a system in the presence of uncertainties and disturbances. By incorporating these techniques into the design of control systems, engineers can ensure that the systems can effectively operate in real-world environments where uncertainties are inevitable. In addition to theirsignificance in engineering, robust control and estimation also present several challenges in their implementation. One of the primary challenges is thecomplexity of designing robust control and estimation algorithms that can effectively handle a wide range of uncertainties and variations in system dynamics. This often requires a deep understanding of system modeling and analysis techniques, as well as advanced mathematical tools for robust controller and observer design. Furthermore, the implementation of robust control and estimation techniques often involves trade-offs between performance, robustness, and computational complexity, requiring engineers to carefully balance these factorsto achieve an optimal solution. Moreover, the validation and testing of robust control and estimation algorithms can be challenging, as it requires the consideration of a wide range of operating conditions and uncertainties to ensurethe robustness and reliability of the designed control systems. From a practical perspective, the significance of robust control and estimation becomes evident in various engineering applications, such as aerospace, automotive, robotics, and process control. In these applications, the ability to effectively handle uncertainties and disturbances is crucial for ensuring the safety, reliability, and performance of control systems. For example, in aerospace applications, robust control techniques are used to design flight control systems that can operate in the presence of aerodynamic uncertainties and external disturbances. Similarly, in automotive applications, robust estimation techniques are used for state estimation in vehicle navigation and control systems, where uncertainties in sensor measurements and environmental conditions can affect the system's performance. By incorporating robust control and estimation techniques into these applications, engineers can ensure that the control systems can operate safely and effectively in real-world scenarios. Furthermore, the significance of robust control and estimation extends beyond engineering applications, as these concepts also have implications for broader societal and economic challenges. For instance, in the context of autonomous systems and artificial intelligence, robust control and estimation are essential for ensuring the safety and reliability of autonomous vehicles, drones, and robotic systems. The ability to effectively handle uncertainties and disturbances is critical for the widespread adoption of these technologies, as it directly impacts their ability to operate safely in dynamic and unpredictable environments. Moreover, in the context of industrial automation and process control, robust control and estimation techniques are essential for optimizing the performance and efficiency of manufacturing processes, leading to economic benefits and environmental sustainability. In conclusion, robust control and estimation are essential concepts in the field of engineering, withsignificant implications for various applications and societal challenges. Despite the challenges associated with their implementation, these concepts play a crucial role in ensuring the stability, reliability, and performance of control systems in the presence of uncertainties and disturbances. By addressing these challenges and incorporating robust control and estimation techniques into engineering applications, engineers can ensure the safe and effective operation of controlsystems in real-world environments, leading to technological advancements and societal benefits.。

第28卷㊀第3期2024年3月㊀电㊀机㊀与㊀控㊀制㊀学㊀报Electri c ㊀Machines ㊀and ㊀Control㊀Vol.28No.3Mar.2024㊀㊀㊀㊀㊀㊀基于特征模型的永磁同步直线电机自适应控制曹阳,㊀郭健(南京理工大学自动化学院,江苏南京210094)摘㊀要:为了解决永磁同步直线电机系统的参数不确定性㊁建模不确定性及饱和非线性等问题,提出一种基于特征模型的自适应控制器㊂依据特征模型理论描述永磁同步直线电机系统,采用自适应和鲁棒控制方法设计控制器㊂建立永磁同步直线电机的特征模型,并给出具体建立步骤,使得控制器设计变得简单,易于工程实现㊂通过设计参数自适应律对系统未知特征参数进行估计,可实现对系统模型的精确补偿,同时在控制器中添加带有误差积分的鲁棒控制项,提高系统对不确定参数及未知干扰的鲁棒性㊂此外,由于饱和特性的存在,导致控制器产生windup 问题,给系统的控制性能和稳定性造成不利影响㊂因此,该控制器中还带有抗饱和控制项,能够提升系统的抗饱和能力㊂最后,通过对比实验验证了所提控制器的有效性㊂关键词:永磁同步直线电机;参数不确定性;建模不确定性;饱和非线性;特征模型;自适应控制;抗饱和DOI :10.15938/j.emc.2024.03.013中图分类号:TM351文献标志码:A文章编号:1007-449X(2024)03-0131-10㊀㊀㊀㊀㊀㊀㊀㊀㊀㊀㊀㊀㊀㊀㊀㊀㊀㊀㊀㊀㊀㊀㊀㊀㊀㊀㊀㊀㊀㊀㊀㊀㊀㊀㊀㊀㊀㊀㊀㊀㊀㊀㊀㊀㊀㊀㊀㊀㊀㊀㊀㊀㊀㊀㊀㊀㊀㊀㊀㊀㊀㊀㊀㊀㊀㊀㊀㊀㊀㊀㊀㊀㊀㊀㊀㊀㊀㊀㊀㊀㊀㊀㊀㊀㊀㊀㊀㊀㊀㊀㊀㊀㊀㊀㊀㊀㊀㊀㊀㊀㊀㊀㊀㊀㊀㊀收稿日期:2022-07-04基金项目:国家自然科学基金(61673219)作者简介:曹㊀阳(1993 ),男,博士研究生,研究方向为电机系统分析与控制;郭㊀健(1974 ),男,博士,教授,博士生导师,研究方向为智能系统与智能控制㊁机器人系统㊁高精度电机控制等㊂通信作者:郭㊀健Adaptive control of permanent magnet synchronous linear motorbased on characteristic modelCAO Yang,㊀GUO Jian(School of Automation,Nanjing University of Science and Technology,Nanjing 210094,China)Abstract :To address the problems of parameter uncertainty,modeling uncertainty and saturation nonlin-earity in the permanent magnet synchronous linear motor system,an adaptive controller based on charac-teristic model was proposed.A characteristic model was used to describe the permanent magnet synchro-nous linear motor system,and the controller was designed using adaptive and robust control methods.The characteristic model was established based on the system dynamics and parameters,and the specific steps were presented.This simplifies the controller design and facilitates the engineering implementation.An online parameter adaptation law was employed to estimate the unknown characteristic parameters of the system and achieve accurate compensation for the system model.Furthermore,an integral-type robust control term was incorporated into the controller,which improves the robustness of the system against un-certain parameters and unknown disturbances.In addition,the saturation nonlinearity leads to the windup problem in the controller,which has adverse effects on the control performance and stability of the sys-tem.Therefore,an anti-windup control scheme was devised for the controller,which can enhance the an-ti-saturation ability of the system.Finally,comparative experiments with other control methods were con-ducted to verify effectiveness of the proposed controller.Keywords:permanent magnet synchronous linear motor;friction nonlinearity;saturation nonlinearity;ar-mature mass variation;characteristic model;adaptive control;anti-windup0㊀引㊀言相比于旋转同步电机,永磁同步直线电机(per-manent magnet synchronous linear motor,PMSLM)具有更高的推力密度和更快的动态响应,特别适用于对速度和精度要求较高的场合,已被广泛应用在高精密加工㊁轨道交通传输等现代工业领域[1-2]㊂但是由于采用直接驱动方式,PMSLM控制系统对参数摄动及扰动等因素变得更加敏感[3],这会严重影响系统的控制性能㊂因此,保证PMSLM系统的高精度跟踪性能与抗扰动能力十分重要,对提高机床加工精度㊁提升交通传输效率具有重要的意义㊂针对PMSLM系统的高精度跟踪问题,国内外已有众多学者对其进行了研究㊂文献[4]设计了一种带模型参考自适应观测器的预测电流控制策略,经过实验验证该控制策略可以实现对速度进行在线准确辨识,进而提高电流的跟踪性能㊂文献[5]利用扩张状态观测器和非线性状态误差反馈对PMSLM的自抗扰控制器进行优化,提高了系统的动态响应性能和抗干扰能力㊂文献[6]提出一种基于周期性扰动学习的自适应滑模控制方法,采用滑模控制确保PMSLM系统对不确定性因素具有较强的鲁棒性㊂文献[7]在系统模型反馈线性化的基础上,将Hɕ鲁棒控制方法与D-K迭代法相结合,提高了系统对不确定性因素影响的抑制能力㊂姚斌等[8]提出一种自适应鲁棒控制方法,所开发的控制器成功应用在多种控制系统中[9-11]㊂为了解决非光滑饱和非线性的影响,文献[12]构造了一种新的近似饱和模型,该模型能够以任意规定的精度平滑地逼近实际饱和㊂此外,通过添加积分器技术,使得控制器可以消除与表面误差和边界层误差有关的耦合项㊂但是该方法在控制器的设计中需要对虚拟控制量重复微分,如果系统模型阶数高,会增加设计的复杂性㊂文献[13]提出一种考虑LuGre 摩擦的自适应鲁棒控制方法,针对陀螺框架伺服系统未知惯量和阻尼系数㊁LuGre摩擦参数不确定性及未知外部干扰上界,设计参数更新律对其进行估计,该控制律提高了系统的跟踪精度并通过仿真结果验证了所提方法的有效性㊂但该方法需要被控对象的精确数学模型,另外估计的未知参数过多,多个自适应参数需要反复调试,增加了实际应用时的难度㊂自适应鲁棒控制可以估计系统未知参数,但如果系统模型复杂㊁未知参数多㊁某些状态不可测时,控制器的设计将面临巨大挑战㊂针对这些问题,吴宏鑫院士等[14-15]提出特征建模的思想,特征模型一般用一阶或二阶差分方程/微分方程来描述,有关信息都压缩到几个特征参数中,并不丢失原有的信息㊂特征模型建立的形式比原对象动力学方程简单,为实际复杂系统的建模问题提供了一条途径㊂文献[16]基于永磁同步电机的特征模型,设计一个以非线性黄金分割自适应控制为主的控制方案㊂通过安排过渡过程和特征模型参数的在线辨识,该控制方案实现了控制器参数的在线自适应调节㊂文献[17]将特征建模方法推广到具有惯性变化的齿轮传动伺服系统中,设计了一个自适应二阶离散终端滑模控制器,并实现了有限时间有界性㊂然而上述基于特征模型所设计的控制器没有进行抗饱和(anti-windup)研究㊂windup现象是指由于被控对象的输入限制,使得被控对象的实际输入与控制器的输出不等,引起系统闭环响应变差(如超调变大,调节时间变长,甚至使系统失去稳定)的现象㊂实际的PMSLM是个物理限制系统,转速控制器的输出必须限定在一定的范围内,使得实际电机的控制输入量不能大于一个预先设定值㊂当控制器输出受到饱和限制时,特别是含有积分项的控制信号仍然增加时,就会出现windup现象,使实际闭环系统的性能下降,因此对PMSLM系统设计抗饱和控制是有必要的[18-19]㊂基于上述分析,针对PMSLM系统存在的参数不确定性㊁建模不确定性及饱和非线性等问题,提出一种基于特征模型的抗饱和自适应鲁棒控制器(an-ti-windup adaptive robust control based on characteris-tic model,AARC)㊂利用特征模型简化PMSLM系统的描述,并对其进行验证㊂然后,设计一种基于参数投影的自适应律,实现对系统模型的在线补偿㊂同时,将系统的不确定参数和未知干扰视为集总的干231电㊀机㊀与㊀控㊀制㊀学㊀报㊀㊀㊀㊀㊀㊀㊀㊀㊀㊀㊀㊀㊀第28卷㊀扰项,引入误差积分的鲁棒控制项进行抑制㊂此外,为了解决积分环节可能引起的windup 现象,加入抗饱和控制项,提高系统的抗饱和能力㊂最后,基于Lyapunov 函数证明闭环系统的稳定性,并通过实验验证所提控制器的有效性和鲁棒性㊂1㊀PMSLM 的特征建模与验证1.1㊀PMSLM 模型PMSLM 的运动方程为m d y d t =3π2τn p i q [ψf+(L d -L q )i d ]-F fric (y )㊂(1)式中:m 为等效质量;ψf 为磁链;y 为动子速度;i d ㊁i q 分别为d㊁q 轴电流;τ为极距;n p 为极对数;L d ㊁L q 分别为d㊁q 轴电感;F fric (y )为摩擦力㊂由式(1)可得y ㊃㊃=1.5πn p mτ[ψf i ㊃q +(L d -L q )(i ㊃d i q +i ㊃q i d )]- F fric y㊃m y㊂(2)设PMSLM 的采样周期为T ,将式(2)离散化可得㊀y (k +1)-2y (k )+y (k -1)T 2=[1.5πmTτn p ψf +1.5n p (L d -L q )i d (k )mTτ]i q (k )-[1.5πmTτn p ψf +1.5n p (L d -L q )i d (k )mTτ]i q (k -1)+1.5πn p (L d -L q )i q (k )mTτ[i d (k )-i d (k -1)]-1mT F firc (y (k )-y (k -1))y ㊂(3)在式(3)两边同乘T 2,可以重新写为y (k +1)=[1.5πmτn p ψfT +1.5n p (L d -L q )i d (k )Tmτ]i q (k )+[2-1m F firc T v ]y (k )+[1m F firc T v-1]y (k -1)+[1.5n p (L d -L q )i d (k )T mτ-1.5πmτn p ψfT ]i q (k -1)+1.5πn p (L d -L q )i q (k )Tmτˑ[i d (k )-i d (k -1)]=β1(k )i q (k )+α1(k )y (k )+α2(k )y (k -1)+Δ(k )㊂(4)式中:y (k )为系统输出;i q (k )为系统输入;α1㊁α2㊁β1为系统的特征参数,定义为:α1(k )=[2-1m F firc Tv];α2(k )=[1m F firc Tv -1];β1(k )=[1.5πmτn p ψf T +1.5n p (L d -L q )i d (k )T mτ]㊂üþýïïïïïïï(5)Δ(k )表示集总未知非线性函数,包括建模误差和未知扰动,定义为Δ(k )=[1.5n p (L d -L q )i d (k )Tmτ-1.5πmτn p ψfT ]i q (k -1)+1.5πn p (L d -L q )i q (k )Tmτˑ[i d (k )-i d (k -1)]㊂(6)通过式(4)可以看出,特征模型是将模型结构的模型不确定性和参数摄动等不确定信息压缩成几个未知的特征参数,使其与实际模型等价而不是近似㊂使用特征建模不仅能简化控制器设计,而且更利于工程应用㊂1.2㊀特征模型验证特征模型验证过程如图1所示㊂首先,分别给予PMSLM 系统和特征模型相同的输入信号u ㊂然后,采样PMSLM 的输入输出信号,采用传统投影梯算法[16]在线辨识特征参数,并计算特征模型输出㊂最后,通过比较特征模型输出y ^与PMSLM 系统输出y ,得到误差e 0㊂将输入设为1sin(2.09t )A 的正弦信号,并且设PMSLM 的采样频率为80μs㊂特征模型验证结果如图2所示㊂实验结果表明,在相同的控制输入作用下,特性模型输出与实际系统输出的误差很小,说明特征模型可以很好地描述PMSLM 系统的输入输出特征,可以利用该特征模型来设计控制器㊂331第3期曹㊀阳等:基于特征模型的永磁同步直线电机自适应控制图1㊀特征模型验证Fig.1㊀Verification block diagram of characteristicmodel图2㊀特征模型验证结果Fig.2㊀Verification results of characteristic model2㊀非线性自适应控制器设计2.1㊀自适应控制设计针对PMSLM 系统中存在的参数不确定㊁饱和非线性以及外界干扰,设计基于特征模型的自适应鲁棒控制律,对系统的不确定性和干扰进行估计和补偿,实现PMSLM 的速度跟踪控制㊂设计的自适应控制结构如图3所示,控制器包括模型补偿项u a ㊁线性反馈项u s1㊁积分鲁棒控制律u s2和抗饱和控制律k cw η,i qmax =0.03㊁i qmin =-0.03为饱和限制上下界㊂图3㊀自适应抗饱和控制结构框图Fig.3㊀Structure diagram of adaptive anti-windupcontroller将特征模型写成如下二阶时变辨识模型:y (k +1)=φ(k )T θ(k )㊂(7)式中:φ(k )=[y (k )y (k -1)u (k )]T ;θ(k )=[α1(k )α2(k )β1(k )]T ㊂在下面的部分中,㊃j 表示向量㊃的第j 个分量,并且针对2个向量的运算 < 是根据向量的相应元素来执行的㊂用θ^表示θ的估计值,θ~表示估计误差(θ~=θ^-θ)㊂结合式(7),一种不连续投影可以定义为proj θ^j {㊃j }=0,if θ^j =θj max and㊃j >0;0,if θ^j =θj min and㊃j <0;㊃j ,otherwise㊂ìîíïïïï(8)式中:j =1,2,3;proj θ^j{㊃j }可以保证估计参数在有界凸闭集D s 内㊂为保证参数估计值的有界性,设计未知参数估计自适应律为:θn (k )=θ^(k -1)+Γτλ+φT(k -1)φ(k -1);θ^(k )=proj θ^(θn(k ))㊂}(9)式中:Γ>0,λ>0为待设计的可调参数;τ为待合成的自适应函数;θ^(k )为系统参数θ(k )的估计值,利用基于不连续投影的参数自适应律可以估计出未知的特征参数α1㊁α2㊁β1㊂特征模型式(4)可被重写为y (k +1)=[α^1(k )-α~1(k )]y (k )+[α^2(k )-α~2(k )]y (k -1)+[β^1(k )-β~1(k )]u (k )+β1η(k )+Δ(k )㊂(10)式中α~1(k )=α^1(k )-α1(k ),α~2(k )=α^2(k )-α2(k ),β~1(k )=β^1(k )-β1(k )为辨识误差㊂所以式(10)可以改写为431电㊀机㊀与㊀控㊀制㊀学㊀报㊀㊀㊀㊀㊀㊀㊀㊀㊀㊀㊀㊀㊀第28卷㊀y(k+1)=α^1(k)y(k)+α^2(k)y(k-1)+β^1(k)u(k)+β1η+Δ(k)-θ~(k)φ(k)㊂(11)其中θ~(k)φ(k)=α~1(k)y(k)+α~2(k)y(k)+β~1(k)u(k)表示模型估计误差㊂假设1:从工程实践中可知,对于稳定对象,参数不确定性和不确定非线性的程度已知,即θɪΩθ {θ:θminɤθɤθmax};ΔɪΩd {Δ:|Δ(k)-Δ(k-1)|ɤδd(k)}㊂}(12)式中:θmin=[θ1min, ,θ3min]T;θmax=[θ1max, ,θ3max]T;δd是已知的㊂控制目标是设计自适应控制器使得系统的输出y(k)跟踪期望输出y d(k),定义跟踪误差函数为e(k)=y(k)-y d(k)㊂(13)定义s(k)为s(k)=e(k)-k1e(k-1)㊂(14)其中0<k1<1为待设计的可调参数㊂所以有s(k+1)=e(k+1)-k1e(k)㊂(15)自适应抗饱和控制律可以设计为:u(k)=1β^1(k)[u a(k)+u s1(k)+u s2(k)];u a(k)=-α^1(k)y(k)-α^2(k)y(k-1)+ y d(k+1)+k1e(k)-k cwη;u s1(k)=k s s(k);u s2(k)=-E1(k)㊂üþýïïïïïïïï(16)式中:k cwȡ β1 max为抗饱和反馈增益;|k s|<1是待设计的可调参数;E1(k)表达式为E1(k)=E1(k-1)+k s k2s(k-1)+βsat(s(k-1))㊂(17)式中:k2>0为可调系数;sat(㊃)为饱和函数㊂设计参数自适应律τ=s(k)φ(k-1),将式(9)改写为:θn(k)=θ^(k-1)+Γs(k)φ(k-1)λ+φT(k-1)φ(k-1);θ^(k)=projθ^(θn(k))㊂üþýïïï(18) 2.2㊀稳定性分析定理1:对于特征模型式(10)所描述的PMSLM,所有信号都是有界的㊂采用自适应控制律式(16)和参数更新规律式(18),能使闭环系统的跟踪误差渐近收敛至0㊂证明:将式(16)代入式(10)中,并结合式(18)可得s(k+1)=[y(k+1)-y d(k+1)]-k1e(k)=α^1(k)y(k)+α^2(k)y(k-1)+β^1(k)u(k)-α~1(k)y(k)-α~2(k)y(k-1)-β~1(k)u(k)+Δ(k)=-θ~T(k)φ(k)+β1η(k)-k cwη(k)+k s s(k)-E1(k)+Δ(k)㊂(19)取k cwȡ β1 max,然后对式(19)进行差分可得s(k+1)-s(k)=-(θ~T(k)φ(k)-θ~T(k-1)φ(k-1))+k s(s(k)-s(k-1))-(E1(k)-E1(k-1))+Δ(k)-Δ(k-1)㊂(20)考虑到采样周期很小,通过线性外推法预测可知s(k+1)=2s(k)-s(k-1)㊂(21)构建Lyapunov函数为V(k)=s(k)λ+φT(k-1)φ(k-1)+θ~(k) 2Γ㊂(22)首先考虑式(22)的第2项,根据投影参数自适应律式(18)可得θ~(k) 2ɤ θn(k)-θ(k) 2= θ~(k-1) 2+2Γs(k)φT(k-1)θ~(k-1)λ+ φ(k-1)Tφ(k-1) +(Γs(k))2 φ(k-1) 2(λ+ φ(k-1) 2)2ɤ2Γs(k)φT(k-1)θ~(k-1)λ+ φ(k-1) 2+Γ2s2(k)λ+ φ(k-1) 2+ θ~(k-1) 2㊂(23)将式(16)㊁式(20)和式(21)代入式(23)可得 θ~(k) 2- θ~(k-1) 2ɤ2Γs(k)[-(s(k)-s(k-1))+k s(s(k-1)-s(k-2))]λ+ φ(k-1) 2+ 2Γs(k)[-θ~T(k-2)φ(k-2)+k s k2s(k-1)-βsign(s(k-1))]λ+ φ(k-1) 2+531第3期曹㊀阳等:基于特征模型的永磁同步直线电机自适应控制2Γs (k )[(Δ(k -1)-Δ(k -2)]λ+ φ(k -1) 2+Γ2s 2(k )λ+ φ(k -1) 2㊂(24)选取βȡ| θM φmax +δd |,进一步可得 θ~(k ) 2- θ~(k -1) 2ɤ2Γs (k )(k s -1)(s (k )-s (k -1))+2Γk s k 2s (k )s (k -1)λ+ φ(k -1) 2+Γ2s 2(k )λ+ φ(k -1) 2㊂(25)引理1[20]:(Young 不等式)假设a ㊁b 为非负实数,P >1,1p +1q =1,那么ab ɤa p p +b pq ,当且仅当a p=b q时,等号成立㊂根据引理1可得:2s (k )s (k -1)ɤ s (k ) 2+ s (k -1) 2; θ~(k ) 2- θ~(k -1) 2ɤ-Γ(3-3k s -k s k 2)s 2(k )λ+ φ(k -1) 2+Γ(k s +k s k 2-1)s 2(k -1)λ+ φT (k -1) 2㊂üþýïïïïïï(26)对Lyapunov 函数式(22)进行差分,并联立式(26)可得ΔV (k )=V (k )-V (k -1)ɤs 2(k )λ+ φT (k -1) 2-s 2(k -1)λ+ φT (k -2) 2+-(3-3k s -k s k 2)s 2(k )λ+ φ(k -1) 2+(k s +k s k 2-1)s 2(k -1)λ+ φT (k -1) 2+Γs 2(k )λ+ φT (k -1) 2ɤ-(2-3k s -k s k 2-Γ)s 2(k )λ+ φT (k -1) 2+(k s +k s k 2-1)s 2(k -1)λ+ φT (k -1) 2-s 2(k -1)λ+ φT (k -2) 2ɤ-As 2(k )-Bs 2(k -1)㊂(27)式中:A =2-3k s -k s k 2-Γλ+ φT (k -1) 2;B =1λ+ φT (k -2) 2-1-k s -k s k 2λ+ φT (k -1) 2㊂通过选取合适的参数k s ㊁k 2㊁Γ㊁λ使得A >0,B >0㊂根据式(27),对Δ(k )从1到k 求和可得ðki =1[As 2(k )+Bs 2(k -1)]ɤV (1)-V (k )ɤV (1)㊂(28)当k ңɕ时,As 2(k )+Bs 2(k -1)ȡ0,由于φ(k ) 有界,可知lim k ңɕ|s (k )|=0㊂(29)根据式(29)可知,∃N ,当k >N 时,有|s (k )|ɤ0㊂(30)由式(15)可得|e (k )|ɤ|k 1||e (k -1)|+|s (k )|ɤ|k 1|k -N|e (N )|+|k 1|k -N -1|s (N +1)|+ +s (k )ɤ|k 1|k -N|e (N )|+0㊂(31)因为|k s |<1,所以有lim k ңɕsup |e (k )|=0㊂(32)3㊀实验结果比较为了说明上述方法的可行性和有效性,在实验室建立一个验证平台如图4所示,PMSLM 的基本参数列于表1㊂该平台由MOSFET 三相逆变桥㊁磁栅尺㊁相电流采样电路㊁TMS320F28062(DSP)及外围电路㊁IR2181S 驱动电路㊁系统电源电路组成㊂此外,为了模拟不同的工作条件,对直线电机的动子进行了调整㊂通过直接在动子上安装标准化铁块,准确地改变其质量m ,以模拟不同的惯性效应㊂图4㊀PMSLM 实验平台Fig.4㊀PMSLM experimental platform631电㊀机㊀与㊀控㊀制㊀学㊀报㊀㊀㊀㊀㊀㊀㊀㊀㊀㊀㊀㊀㊀第28卷㊀表1㊀PMSLM 的基本参数Table 1㊀Parameters of PMSLM㊀㊀参数数值极对数n p7极距τ/mm(180ʎ)12d 轴电感L d /mH 8q 轴电感L q /mH 8永磁体磁链ψf /Wb0.61PMSLM 矢量控制系统框架如图5所示㊂它由PMSLM㊁空间矢量脉宽调制(space vector pulse widthmodulation,SVPWM)模块㊁Park 和Clark 坐标变换㊁电压源逆变器㊁电流调节器和速度控制器组成㊂本文设计一种速度控制器,电流控制器采用PI 控制㊂图5㊀矢量控制总体结构框图Fig.5㊀Overall structure diagram of vector control为了验证所提控制器的可行性和有效性,本文对以下3种控制器进行比较㊂1)AARC㊂本文设计的抗饱和自适应鲁棒控制器参数设置如下:k 1=0.15,k 2=0.0006,k s =0.1,β=0.04,k cw =0.1,Γ=0.05,λ=0.995,θ^(0)=[1.9,-0.9,0.00001]T ㊂2)抗饱和自适应控制器(anti-windup adaptivecontrol based on characteristic model,AAC)㊂未添加鲁棒项u s2的抗饱和自适应控制器,其他参数与AARC 一致㊂3)抗饱和PID 控制器(anti-windup proportional-integral-differential,APID)㊂控制器的增益设置为k p =150,k i =1,k d =0,k cw =0.1㊂此外,将使用跟踪误差的最大值㊁平均值和标准差来衡量每个控制算法的质量,定义如下:1)最大跟踪误差的绝对值为M e =max i =1, ,N{|e (i )|}㊂(33)2)平均跟踪误差定义为μ=1N ðNi =1|e (i )|㊂(34)3)跟踪误差的标准差为δ=1N ðNi =1[|e (i )|-μ]2㊂(35)其中N 是所记录的数字信号的个数㊂首先将给定速度设置为y d =0.56sin(3.14t)m/s㊂系统跟踪结果如图6所示,性能指标如表2所示㊂从这些实验结果可以看出,所提出的AARC 控制器在瞬态和最终跟踪误差方面优于其他两种控制器,因为AARC 采用了基于参数自适应的补偿和鲁棒控制项,可以同时处理参数和未建模不确定性㊂虽然AAC 中也包含参数自适应,但对于建模的不确定性和未知扰动的抑制效果不佳㊂通过表2可以看出,AARC 添加鲁棒项后各种误差指标会比AAC 小,验证了鲁棒控制项u s2的有效性㊂在3种控制器中,线性抗饱和PID 的误差指标最差,达到了AARC 的2倍以上,这说明基于非线性模型的控制器设计方法具有更大的优势㊂图6㊀无铁块情况下PMSLM 的跟踪结果Fig.6㊀Tracking results of PMSLM without iron表2㊀最后两个周期的性能指标Table 2㊀Performance indexes during the last two cycles控制方法M e /(m /s)μ/(m /s)δ/(m /s)APID 0.055420.013360.00971AAC0.026890.008100.00572AARC 0.025220.006000.00490731第3期曹㊀阳等:基于特征模型的永磁同步直线电机自适应控制为了进一步验证控制器对参数变化的自适应能力,设定了不同的动子质量来进行实验㊂给PMSLM 的动子上添加1.33kg 的铁块㊂系统跟踪结果如图7所示,表3列出了最后两个周期的性能指标㊂从图7可以看出,使用AARC 控制方法的控制系统,在面对动子质量变化时,其反应速度快,并且波动较小㊂从表3可知,APID 的最大跟踪误差没有增大,意味着APID 中存在大的积分增益对该扰动也有一定的抑制效果㊂但与上一个实验情况相比,APID 的μ和δ指标增大明显,仍然比其他2个控制器差㊂适当的参数自适应在一定程度上也可以削弱动子质量变化给系统带来的参数不确定性影响,就像AAC 那样㊂AARC 的各项误差指标是3个控制器中最好的,再次证明了该控制器的有效性㊂图7㊀铁块质量为1.33kg 时PMSLM 的跟踪结果Fig.7㊀Tracking results of PMSLM when iron massis 1.33kg表3㊀最后两个周期的性能指标Table 3㊀Performance indexes during the last two cycles控制方法M e /(m /s)μ/(m /s)δ/(m /s)APID 0.043890.015370.01061AAC0.029620.008440.00605AARC 0.025320.005980.00496最后将动子上的铁块增加到2.64kg,此时PMSLM 受到的摩擦非线性和扰动进一步增大,3个控制器的跟踪性能都有所变差㊂实验结果如图8所示,误差指标见表4㊂在这个测试用例中,APID 中的跟踪误差抖动变大,而AARC 的跟踪误差则相当平滑㊂APID 控制器表现出最差的跟踪性能,最大跟踪误差为0.094,表明APID 在该跟踪任务中已经达到了其局限性㊂另外,即使在增大动子质量情况下,所提出的AARC 控制器仍然可以对模型进行补偿并衰减未建模的扰动,从而在所有比较的控制器中达到最好的跟踪性能㊂图8㊀铁块质量增加到2.64kg 情况下PMSLM 的跟踪结果Fig.8㊀Tracking results of PMSLM when the mass ofiron is increased to 2.64kg 表4㊀最后两个周期的性能指标Table 4㊀Performance indexes during the last two cycles控制方法M e /(m /s)μ/(m /s)δ/(m /s)APID 0.093700.027090.01934AAC0.034620.008410.00643AARC 0.028870.005860.005054㊀结㊀论本文针对PMSLM 系统提出一种基于特征模型的自适应控制方法,该方法能够有效地解决PMSLM 系统的参数不确定性㊁建模误差和外部干扰等问题㊂首先利用二阶变差分方程对PMSLM 系统进行简化831电㊀机㊀与㊀控㊀制㊀学㊀报㊀㊀㊀㊀㊀㊀㊀㊀㊀㊀㊀㊀㊀第28卷㊀建模,然后设计了一种基于特征模型的自适应控制器,仅利用系统的输入和输出信号,实现了对PMSLM系统的精确速度跟踪控制㊂为了提高系统的鲁棒性和抗饱和能力,还引入了鲁棒补偿项和抗饱和控制项,并严格证明了闭环系统的稳定性㊂最后,通过实验结果验证了所提控制方法的有效性㊂本文控制器的参数是固定的,需要通过反复调试来确认㊂当实验条件和环境发生改变时,可能导致参数不一定是最优的㊂因此,在未来工作中将考虑进一步研究控制器参数的自动调整技术[21],采用自学习的方法来替代控制器中参数的人工调整部分㊂参考文献:[1]㊀龚夕霞,李焱鑫,卢琴芬.模块化永磁直线同步电机考虑制造公差的推力鲁棒性优化[J].电工技术学报,2024,39(2):465.GONG Xixia,LI Yanxin,LU Qinfen.Thrust robustness optimiza-tion of modular permanent magnet linear synchronous motor ac-counting for manufacture tolerance[J].Transactions of China Electrotechnical Society,2024,39(2):465.[2]㊀张春雷,张辉,叶佩青.高霍尔位置检测精度的圆筒型永磁同步直线电机设计[J].电工技术学报,2022,37(10):2481.ZHANG Chunlei,ZHANG Hui,YE Peiqing.Design of tubular permanent magnet synchronous linear motor by reliability-based ro-bust design optimization[J].Transactions of China Electrotechni-cal Society,2022,37(10):2481.[3]㊀缪仲翠,苏乙,张磊,等.梯形Halbach交替极无铁心永磁同步直线电机特性分析与优化设计[J].电机与控制学报, 2024,28(1):164.MIAO Zhongcui,SU Yi,ZHANG Lei,et al.Characteristic analy-sis and optimization design of air-core permanent magnet linear synchronous motor with trapezoidal Halbach array consequent-pole [J].Electric Machines and Control,2024,28(1):164. [4]㊀李争,安金峰,肖宇,等.基于自适应观测器的永磁同步直线电机模型预测控制系统设计[J].电工技术学报,2021,36(6):1190.LI Zheng,AN Jinfeng,XIAO Yu,et al.Design of model predic-tive control system for permanent magnet synchronous linear motor based on adaptive observer[J].Transactions of China Electrotech-nical Society,2021,36(6):1190.[5]㊀李争,张梓豪,王康涛,等.基于无模型的PMLSM改进自适应滑模自抗扰控制[J].电机与控制学报,2024,28(1):142.LI Zheng,ZHANG Zihao,WANG Kangtao,et al.Improved adap-tive sliding mode active disturbance rejection control for PMLSM based on model-free theory[J].Electric Machines and Control, 2024,28(1):142.[6]㊀张康,王丽梅.基于周期性扰动学习的永磁直线电机自适应滑模位置控制[J].电机与控制学报,2021,25(8):132.ZHANG Kang,WANG Limei.Adaptive sliding mode position con-trol for permanent magnet linear motor based on periodic disturb-ance learning[J].Electric Machines and Control,2021,25(8): 132.[7]㊀孙宜标,毛爽,夏加宽.直线电机悬浮平台的μ-Hɕ鲁棒控制[J].沈阳工业大学学报,2014,36(1):7.SUN Yibiao,MAO Shuang,XIA Jiakuan.μ-Hɕrobust control for linear motor levitation platform[J].Journal of Shenyang Uni-versity of Technology,2014,36(1):7.[8]㊀YAO B,BU F,REEDY J,et al.Adaptive robust control of sin-glerod hydraulic actuators:theory and experiments[J].IEEE/ ASME Transactions on Mechatronics,2000,5(1):79. [9]㊀CHEN S,CHEN Z,YAO B,et al.Adaptive robust cascade forcecontrol of1-DOF hydraulic exoskeleton for human performance augmentation[J].IEEE/ASME Transactions on Mechatronics, 2017,22(2):589.[10]㊀HELIAN B,CHEN Z,YAO B.Adaptive robust motion control ofa pump direct drive electro-hydraulic system with meter-out pres-sure regulation[J].IFAC-Papers OnLine,2020,53(2):9005.[11]㊀HAN J,YANG S,XIA L,et al.Deterministic adaptive robustcontrol with a novel optimal gain design approach for a fuzzy2doflower limb exoskeleton robot system[J].IEEE Transactions onFuzzy Systems,2020,29(8):2373.[12]㊀LIU Y.Saturated robust adaptive control for uncertain nonlinearsystems using a new approximate model[J].IET Control Theoryand Applications,2017,11(6):870.[13]㊀王璐,郭毓,钟晨星,等.控制力矩陀螺框架伺服系统期望补偿自适应鲁棒控制[J].控制理论与应用,2017,34(9):1143.WANG Lu,GUO Yu,ZHONG Chenxing,et al.Desired com-pensation adaptive robust control for control moment gyroscopesgimbal servo system[J].Control Theory and Applications,2017,34(9):1143.[14]㊀CHANG Y,JIANG T,PU Z.Adaptive control of hypersonic ve-hicles based on characteristic models with fuzzy neural networkestimators[J].Aerospace Science and Technology,2017,68:475.[15]㊀常亚菲.一类不确定非线性系统基于特征模型的复合自适应控制[J].控制理论与应用,2019,36(7):1137.CHANG Yafei.Characteristic model-based composite adaptivecontrol for a class of uncertain nonlinear systems[J].ControlTheory and Applications,2019,36(7):1137. [16]㊀王永,窦晓华,方浩,等.永磁同步电机非线性黄金分割自适应转速控制[J].电机与控制学报,2017,21(10):23.WANG Yong,DOU Xiaohua,FANG Hao,et al.Nonlineargolden-section adaptive speed control of permanent magnet syn-chronous motor[J].Electric Machines and Control,2017,21(10):23.931第3期曹㊀阳等:基于特征模型的永磁同步直线电机自适应控制[17]㊀WANG X,WU Y,ZHANG E,et al.Adaptive terminal sliding-mode controller based on characteristic model for gear transmis-sion servo systems[J].Transactions of the Institute of Measure-ment and Control,2019,41(1):219.[18]㊀QI L,BAO S,SHI H.Permanent-magnet synchronous motor ve-locity control based on second-order integral sliding mode controlalgorithm[J].Transactions of the Institute of Measurement andControl,2015,37(7):875.[19]㊀张兴华,姚丹.感应电机直接转矩控制系统的 抗饱和 控制器设计[J].电工技术学报,2014,29(5):181.ZHANG Xinghua,YAO Dan.Anti-windup speed controller de-sign for direct torque controlled induction motor drives[J].Trans-actions of China Electrotechnical Society,2014,29(5):181.[20]㊀IGHACHANE M A,AKKOUCHI M.Further refinements ofYoung's type inequality for positive linear maps[J].Revista de laReal Academia de Ciencias Exactas,Físicas y Naturales.SerieA.Matemáticas,2021,115(2):10.[21]㊀BENOSMAN M.Learning-based adaptive control for nonlinearsystems[C]//European Control Conference(ECC),June24-27,2014,Strasbourg,France.2014:920-925.(编辑:邱赫男)041电㊀机㊀与㊀控㊀制㊀学㊀报㊀㊀㊀㊀㊀㊀㊀㊀㊀㊀㊀㊀㊀第28卷㊀。

电控开发v流程The development of electronic control systems is an essential part of the automotive industry. 电子控制系统的开发是汽车行业的重要组成部分。
It involves the design and implementation of electronic systems that control various functions in a vehicle, such as the engine, transmission, and braking. 它涉及设计和实施控制车辆各种功能的电子系统,如发动机、变速器和制动系统。
The development process for these systems is complex and requires a thorough understanding of both hardware and software. 这些系统的开发过程复杂,需要对硬件和软件都有透彻的理解。
From concept to production, there are multiple stages and factors to consider when developing electronic control systems for vehicles. 从概念到生产,开发车辆电子控制系统涉及多个阶段和因素。
The first stage in the development of electronic control systems for vehicles is the conceptualization phase. 车辆电子控制系统开发的第一阶段是概念化阶段。
During this phase, engineers and designers brainstorm ideas and concepts for the electronic control system based on the requirements and specifications provided by the vehicle manufacturer. 在这个阶段,工程师和设计师根据车辆制造商提供的要求和规格,对电子控制系统的想法和概念进行头脑风暴。

Automotive Systems and Control As an AI language model, I will address the problem of automotive systems and control from multiple perspectives, aiming to provide a human-like response with emotional elements. When it comes to automotive systems and control, there are various aspects to consider, including safety, performance, and efficiency. One of the key challenges in this field is ensuring that the different systems within a vehicle work together seamlessly to provide a safe and enjoyable driving experience. This requires advanced control systems that can monitor and adjust various parameters in real-time, such as engine performance, braking, andstability control. From an engineering perspective, developing these control systems requires a deep understanding of mechanical, electrical, and software engineering. Engineers must consider factors such as vehicle dynamics, powertrain design, and sensor integration to create a comprehensive control system that can adapt to different driving conditions. This involves extensive testing and validation to ensure that the control systems are reliable and effective in real-world scenarios. In addition to the technical challenges, there are also regulatory and safety considerations that must be taken into account. Automotive control systems must comply with strict safety standards and regulations, which can vary by region. This adds another layer of complexity to the development process, as engineers must navigate a complex web of legal and regulatory requirements to bring their products to market. From a consumer perspective, automotive control systems play a crucial role in the overall driving experience. Modern vehicles are equipped with a wide range of advanced control systems, such as adaptive cruise control, lane-keeping assist, and automatic emergency braking. These systems not only enhance safety but also contribute to a more comfortable and enjoyable driving experience. As a result, consumers have come to expect these features in new vehicles, putting pressure on automakers to continually innovate and improve their control systems. Furthermore, the rise of electric and autonomous vehicles has introduced new challenges and opportunities in automotive control systems. Electric vehicles require sophisticated battery management and power distribution systems, while autonomous vehicles rely on advanced sensor fusion and decision-making algorithms. These developments are reshaping theautomotive industry and pushing control system engineers to rethink traditional approaches to vehicle design and operation. In conclusion, automotive systems and control present a complex and multifaceted challenge that requires expertise in engineering, regulation, and consumer experience. As the automotive industry continues to evolve, control system engineers will play a crucial role in shaping the future of transportation, ensuring that vehicles are not only safe andefficient but also enjoyable to drive. This field will continue to demand innovation and creativity as new technologies and trends emerge, making it an exciting and dynamic area of engineering.。

System Identification and Control System identification and control are essential components in the field of engineering and technology. They involve the process of building mathematical models of dynamic systems and using these models to design controllers that can manipulate the system to achieve desired outcomes. This process is crucial in various industries, including aerospace, automotive, robotics, and more. One of the key aspects of system identification is collecting data from the system to understand its behavior. This data can be obtained through experiments, simulations, or real-time monitoring. By analyzing this data, engineers can develop mathematical models that represent the system's dynamics accurately. These models can then be used to design controllers that can regulate the system's behavior and achieve specific objectives. Control systems play a crucial role in ensuring that a system behaves in a desired manner. These systems use feedback mechanisms to monitor the system's output and adjust the input to maintainstability and performance. By implementing control strategies, engineers can optimize the system's performance, improve efficiency, and enhance safety. In the field of autonomous vehicles, system identification and control are vital for ensuring safe and efficient operation. By accurately modeling the vehicle's dynamics and designing robust control systems, engineers can develop autonomous vehicles that can navigate complex environments, avoid obstacles, and respond to changing conditions in real-time. These technologies have the potential to revolutionize transportation and improve road safety. In industrial automation, system identification and control are used to optimize manufacturing processes, increase productivity, and reduce costs. By accurately modeling production systems and implementing advanced control strategies, engineers can improve product quality, minimize waste, and enhance overall efficiency. These technologies are essential for modern manufacturing facilities to stay competitive in today's global market. Overall, system identification and control are fundamental concepts in engineering that enable us to understand and manipulate complex systems effectively. By developing accurate mathematical models and implementing robust control strategies, engineers can design systems that meet specific performance requirements and achieve desired outcomes. These technologies have awide range of applications in various industries and play a crucial role in advancing technological innovation and improving quality of life.。
design of temperature controlsystemDesign of Temperature Control SystemThe design of a temperature control system involves several key components and considerations to ensure accurate and efficient temperature regulation. Here is a general overview of the design process:1. Define Requirements: Determine the temperature range, accuracy, response time, and other specifications required for the system. This will help in selecting appropriate sensors, actuators, and control algorithms.2. Sensor Selection: Select temperature sensors that are suitable for the operating range and accuracy requirements. Common types include thermistors, resistance temperature detectors (RTDs), and thermocouples.3. Actuator Selection: Choose actuators, such as heating elements or cooling devices, that can be controlled to achieve the desired temperature setpoint. Consider factors like power requirements, efficiency, and response time.4. Control Algorithm: Select a control algorithm, such as proportional-integral-derivative (PID), to regulate the temperature. The PID controller adjusts the actuator based on the measured temperature and the desired setpoint.5. Microcontroller or PLC: A microcontroller or programmable logic controller (PLC) is used to implement the control algorithm and interface with the sensors and actuators. It receives temperature measurements, calculates the control output, and sends commands to the actuator.6. User Interface: Design a user interface, such as a graphical display or a keypad, to allow operators to monitor and adjust temperature settings.7. Safety Features: Incorporate safety features, such as over-temperature alarms and shut-off mechanisms, to protect the system and personnel from potentialhazards.8. Testing and Calibration: Perform comprehensive testing and calibration of the temperature control system to ensure its accuracy and reliability. This may involve calibration of sensors, fine-tuning of the control algorithm, and validation of temperature stability.9. Integration and Optimization: Integrate the various components of the system, including hardware, firmware, and software. Optimize the system performance by considering factors like energy efficiency, response time, and noise immunity.The design of a temperature control system requires a careful consideration of the application requirements, selection of suitable components, and implementation of an effective control algorithm. By following these steps, you can develop a reliable and efficient temperature control system tailored to your specific needs.。
整车开发过程中的英文缩写-汽车行业的你一定要知道的小编整理的一份超级全面的整车开发过程中用到的英语,供大家参考整车开发通用英文缩写(按首字母排序)英文缩写英文全称中文含义(按首字母排序)100% Cal 100% Calibration 100%标定100% IVER 100% Integration Vehicle EngineeringRelease100%集成车工程发布100% PPAP All parts at full PPAP for Vehicleprogram为了整车项目,所有零件PPAP100% SVER 100% Structure Vehicle EngineeringRelease100%结构车工程发布65% Cal 65% Calibration 65%的动力总成标定80% Cal 80% Calibration 80%的动力总成标定8D 8 Disciplines 问题解决8步法A Alpha Alpha阶段(动力总成产品阶段)A MRD Alpha Material Required Date Alpha样件需求日期A/T Automatic Transmission 自动变速器A/T Automatic Transmission 自动变速器AA Architecture Approval 架构批准AAM Alliance of Automobile Manufactures 汽车制造商联盟ABS Anti-lock Brake System or Anti-BlockSteering防抱死制动系统AC Architecture Confirmation 架构确认ACE Assistant Chief Engineer 总工助理ACT Activity 工艺路线ACT BOM Assembly Component Tree BOM 总成件树形BOMAD Alternatives Development 主题开发ADV Analysis / Development / Validation 分析/开发/验证ADV Analysis, Development and Validation 分析,开发和认证AE Application Engineer 应用工程师AE Application Engineer 应用工程师AEM Assimilability evaluation method 可装配性评估方法AFI Architecture Framing Initiation 架构框架启动AIAC Automotive Industry Action Group 美国汽车工业行动集团ALY Alloy 铝合金AMT Automatic Machincal Transmission 机械式自动变速器ANSI American National Standards Institute 美国国家标准协会AP Advanced Purchasing 提前采购AP Assembly Plant 总装厂APB Automotive Product Board 汽车产品委员会APD Approved Product Description 批准的产品描述APE Annual Program Execution 年度项目执行APEC Asia Pacific Economic Cooperation 亚太经济联盟APQP/CP Advanced Product Quality Planning andControl Plan先期产品质量规划和控制计APSB Asia Pacific Strategy Board 亚太战略委员会(通用汽理组织)AR Appropriation Request 项目预算ARC Architecture Refinement Complete 架构优化完成ASB Automotive Strategy Board 汽车战略委员会(通用汽理组织)ASC 经销商售后管理系统ASE Automotive Safety Engineering 汽车安全工程ASE Aftersales Engineering 售后工程ASN Advanced shipping notice 发货通知单ASSI Architecture Statement of StrategicIntent战略意向的架构陈述Assy Check-in Assembly Line Check-in 装配线进场启动现场安调Assy PPAP Assembly Line PPAP 装配线通过PPAPAssy PPAP Assembly Line PPAP 装配线通过PPAPAssy PPV Assembly Line Products and ProcessValidation装配线交付后的产品工艺验Assy PPV Assembly Line Production and ProcessValidation装配线交付后产品工艺验证Assy Run-Off Assembly Line Run-Off 装配线试装交样日期Assy Run-off Assembly Line RUN-Off 装配线整线打通,启动试工装配Assy Run-off MRD Assembly Line RUN-Off Material RequiedDate装配线ATC Auto Temperature Controller 自动空调控制器ATF Automatic Transmission Fluid 自动变速箱油ATT Attachment 附件ATT Actual takt time 实际单件工时AVD Advanced Vehicle Development 先期车辆开发AVDC Advance Vehicle Development Center 先期车辆开发中心AVD-LT Advanced Vehicle Development-LeadershipTeam前期整车开发-领导小组AVDP Advanced Vehicle Development Process(Time between DSI and VPI)先期车辆开发流程(在DS间)AVPM Advanced Vehicle Planning Manager 先期车辆计划经理B Beta Beta阶段(动力总成产品阶段)B Build 制造B MRD Beta Material Required Date Beta样件需求日期B+U Building and Utility 土建公用BAD Build Authorization Document 试制授权文档BC Business Case 业务计划BCM Body Control Module 车身控制器BDC Body Distributon Central 车辆调配中心BESC Base Engine Steering Committee 发动机总成战略转向委员会BIQ Building in Quality 制造质量BIR Prototype Build Issue Report 试制问题报告BIR Build Issues Resolution 试制问题BIR Build Incident Report 装车问题报告BIR Bulding issue report 造车问题报告BIW Body-In-White 白车身BIW Body in White 白车身BOD Bill of Design 设计清单BOE Bill of Equipment 设备清单BOM Bill of Material 物料清单BOM Bill of Material 物料清单BOM Bill of Material 物料清单BOM Bill Of Material 物料清单BOM Bill Of Material 物料清单BOM Bill of Material 物料清单BOP Bill of Process 工艺清单BOP Bill Of Process 工艺清单BP Break Point 断点BPD Business Plant Deployment 业务计划实施BPP Best people practices 最佳人员准则BPR Business plan recompose 业务流程重组BS Body Shop 车身车间BSD Build Site Direction 试制现场指导书BUFFER Buffer 线边缓存区C/CAP Construction/Conversionand Acceleration Plan土建/改造和生产提速计划CAB Change Approval Board 更改审批会CAC 服务热线专员CAFE Corporate Average Fuel Economy 公司平均油耗Cal Calibration 动力总成标定CARE Customer acceptance review evaluation 整车报交检查CARE Customer Acceptance & Review Evaluation 用户接受度和审查评估CC Concept Confirmation 验证概念CC Consolidation Center 集散中心CC Confirmation Clinic 确认临床Cert LSO Certification Lift Stop Order 通过排放认证通知CET Cold Environment Test 寒区试验CH Chassis Department 底盘部CI Concept Initiation 提出项目概念CIM Customer Interface Manager 客户服务经理CIP Continue Improve Process 持续改进CIP Continue Improve Process 持续改进CIT Continuous Improvement Team 不断改进小组CIT Compartment Integration Team 车厢集成小组CMC Container Management Center 空箱管理中心CME Change Management Engineer 更改管理工程师Cmk N/A 临界机器能力指数Cmk Capability Machine Index 机器设备能力CMM 三坐标测量C-NCAP China New CAR Assessment Process 中国标准新车评估体系COC Centre of Competence 能力中心COE Center of Expertise 经验总结中心CP Control Plan 控制计划CPIT Current Product Improvement Team 现有产品改进小组Cpk Complex Process Capability 过程能力指数Cpk Process Capability Index 稳定过程的能力指数CPQE Current Product Quality Engineer 现有产品质量工程师CPV Cost per Vehicle 单车成本CR/DN Change Request / Decision Notice 更改决议CR/DN Change Request/Decision Notice 变更申请/决议通知CRB Change Review Board 更改评审小组CS Contract Signing 动力总成签署项目合同CS Contract Signing 合同签订CS1 Controled Shipping 1 一级受控发运CS2 Controled Shipping 2 二级受控发运CSC Controls Steering Committee 控制模块战略转向委员会CSI Customer Satisfaction Index 用户满意度指标CSI Customer Satisfaction Index 售后满意度CSN Current Sequence Number 流水号CSO Contract Sign-Off 合同签署CSO Contract Sign-Off (VDP) 整车签署项目合同(VDP术CSO HC Contract Sign-Off Health Check 合同签署健康检查CSO HC Contract Sign-Off Health Check 合同签署健康检查CT Cycle Time 制程周期CT Cycle time 周期时间CT Creativity Teams 创造性工作小组CT Critical Test 关键试验CTS Component Technical Specification 零部件技术标准CTT Common Timing Template 标准2级进度模板CVER Concept Vehicle Engineering Release 概念车工程发布CVER LL Concept Vehicle Engineering ReleaseLong Lead概念车工程发布--长周期CVIS Completed Vehicle Inspection Standards 整车检验标准CVQC Completed vehicle quality ceter 整车质量中心CVQCB Completed vehicle quality ceter board 整车质量目视板CVT Continuously Variable Transmission 无级变速器D.Q.R 合格率概况DAS Design & Analysis Section 设计分析科DC Deliver Charter 递交项目章程DCN Design Change Notice 设计更改通知DCN Design Change Notice 设计更改通知DCP Dimension Control Plan 尺寸控制计划DCS Design Concept Sheet 概念设计表DCT Double Clutch Transmission 双离合器变速箱DD Direct Delivery 直接投线DDSP Driver Door Switch Pack 驾驶席门控开关DEI Die Engineering Integration 模具工程集成DFA Design for Assembly 装配工艺性设计DFM Design for Manufacturability 制造工艺性设计DFMEA Design failure mode and effects analysis 设计失效模式和效果分析DFMEA Design FMEA 设计失效模式分析DIFF Differential 差速器DL 3b Design Level 3b 设计阶段3bDMS Dealer Manage System 经销商管理系统DOL Dealer On Line 经销商在线系统DP Demand Plan 需求计划DPV Defects per vehicle 单车缺陷数DPV Defect per Vehicle 单车缺陷数DQ&V Design Quality & Validation 设计质量和验证DR Direct run 直接通过率DRC Design Review Committee 设计评审委员会DRE Design Responsible Engineer 设计和发布工程师DRE Design Release Engineer 设计发布工程师DRE Design release engineer 设计发布工程师DRL Direct run loss 直接通过损失率Drop Off Drop Off 停产DS44 HIGH SPEED DURABILITY TEST 高速耐久试验(MGRES 标准DSG Direct shift gearbox 双离合器变速箱DSI Document of Strategic Intent 战略意向书DSM Driver Seat Module 驾驶席座椅控制模块DSO Design Sign Off 设计签署DTA Design Theme Alternatives 设计主题选项DTC Diagnostic Trouble Code 诊断故障码DV Design Validation 设计验证DV Design Validation 产品设计验证DVP Design Validation Plan 设计验证计划DVT Dynamic vehicle test 整车综合动态测试E/T/C Engine/Transmission/Controller 发动机/变速器/控制模块EBA Emergency Brake Assistant 紧急制动辅助系统EBD Electronical Brake Distribute 电子制动力分配系统EBOM Engineering BOM 工程BOMEC Embedded Controller 控制模块ECC ERP Central Component ERP核心组建ECR Engineering Change Request 工程更改请求ECR Engineering Change Request 工程更改请求ECR Engineering Change Request 工程更改申请ECR Engineering Change Request 工程项目变更申请ECS Engineering Change Summary 工程变更摘要ECT Emission Control System 电子控制自动变速器EDS Electronic Data Systems 电子数据系统EEVC European Enhanced Vehicle-Safety Committee欧洲提高车辆安全性委员会EFEO Emissions & Fuel Economy 排放和燃料经济EGM Engineering Group Manager 产品工程小组经理EI&S Electronics Integration & Software 电器零件集成和软件ELV End of life vehicle 整车寿命结束EMlS Emission 排放EMS Engine Management System 发动机管理系统ENB Build-Test Section 试制试验科E-NCAP Euro New Car Assessment Process 欧洲标准新车评估体系ENG Engineer 工程师EOA End of Acceleration 生产提速的完成EOLT End of Line Test 生产线试验结束EP Engineering Prototype 工程样车(件)EPA Environmental Protection Agency 环境保护厅EPC Engineering Program Committee 工程项目委员会EPN Engineering Project Number 工程项目数目ERD Early Requirement Document 早期的要求文件ESB European Strategy Board 欧洲战略委员会(通用汽理组织)ESO Engineering Sign Off 发动机整机工程签署ESO Engineering Sign Off 工程签署ESO Engineering Sign-off 工程签署ET Engineering Technology 工程技术EV Engineering Vehicle 工程样车EWO Engineering Work Order 工程工作指令EWO Engineering Work Order 工程更改号EWO Engineering workorder 工程更改流程Exp Cal Experimental Calibration 尝试性标定FA Final Approval 批准正式生产FAC 集团销售经理FATG Final Approval to Grain 生产最终批准FBIW First Body in White Complete 第一轮白车身完成FE Functional Evaluation 功能评估FE LSO Fuel Economy Label Lift Stop Order 通过油耗认证的通知FIVC First Integration Vehicle Complete 第1辆集成车制造完毕FIVC First Integration Vehicle Complete 第一轮集成车完成FLO Factory Layout 工厂布局FM 功能尺寸FM Finance Manager 财务经理FMC First Mule Complete 第一轮骡子车完成FMC 区域售后支持FMEA Failure model effectiveness analysis 失效模式分析FMEA Failure model effectiveness analysis 失效模式分析FMEA Failure Mode and Effects Analysis 潜在失效模式及后果分析FMEA Failure mode and effects analysis 失效模式和后果分析FMEA Failure Mode and Effect Analysis 失效模式和影响分析FMS Flexible manufacturing systems 柔性制造系统FMVSS Federal Motor Vehicle Safety Standards 联邦汽车安全标准FPPV BIW First Product/Process Body in WhiteComplete第一轮产品/工艺白车身完FPPVC First Product/ProcessValidation Vehicle Complete第一轮产品/工艺验证车辆FPS Fixed Point Stop 固定停止位置FTC First Time Capability 首次能力FTP/FTQ First time pass/quality 一次通过合格率FTQ First time quality 下线合格率FWD Four Wheel Drive 四轮驱动G Gamma Gamma阶段(动力总成产品阶段)G MRD Gamma Material Required Date Gamma样件需求日期G/L Group leader 工段长GA General Assembly 总装GA General Assembly 总装GADT Global Architecture Development Team 全球架构开发小组GBOM Global Bill of Material 全球物料清单GMNA General Motors North America 通用汽车北美分部GMPT General Motors Powertrain 通用汽车动力总成分部GPDC Global Product Development Council 全球产品开发理事会GPDP Global Powertrain Development Process 全球动力总成开发流程GPDS Global Product Description System 全球产品管理系统GSD Global Segment Director 全球细分主管GSS Global Sales and Service 全球销售和服务GVDP Global Vehicle Development Process 全球整车开发流程GVDP Global Vehicle Development Process 整车开发流程GVDP Global Vehicle Development Process 整车开发流程GVDP Global Vehicle Development Process 全球汽车开发流程GVDP Global Vehicle Development Process 全球整车开发流程GVDP Global Vehicle Development Process 整车开发流程GVLE Global Vehicle Line Executive 整车平台执行GVW Gross Vehicle Weight 车辆总重GW Gateway 网关HET Hot Environment Test 热带试验HRC Hardware Release Center 硬件发布中心ICD Interface Control Document 接口控制文件IDR Initial Data Release 初始数据发布IDSR Integration DrivenSubsystem Requirement集成驱动子系统要求ILP Inbound Logistic Planning 入厂物流规划IMES Integration Manufacturing ExecutiveSystem生产执行系统Initial Cal Initial Calibration 初始标定IOM Inspection operator method 检验操作方法IOS Inspection operator summary 检验操作概要IPPE integrated Product andProcess Engineering集成产品与工艺工程IPTV Incident per Thousand Vehicles 每千辆车的故障率IPTV Incidents Per Thousand Vehicles 每一千台车事故率IPTV Incidents Per Thousand Vehicles 每千辆车的故障率IPTV Incidents Per Thousand Vehicles 千辆车故障率IR Incident Report 事故报告IRP Issue Resolution Process 问题解决流程IRR Internal Rate of Return 内含报酬率ISO International Standard Organization 国际标准化组织IV Integration Vehicle 集成车IV MRD Integration Vehicle Material RequiredDate集成车的物料需求日期IVBR Integration Vehicle Build ReadinessReview集成车制造准备评审IVER Integration Vehicle Engineering Release 集成车工程发布JIS Just In Sequence 排序供货JIS Just In Sort 供应商排序供货方式JIS Job Instruction Sheet 岗位指导书JIT Just In Time 及时供货JIT Just In Time 供应商及时供货方式JPH Job per Hour 生产节拍JRS Joint Ride Session 联合评审JSC 生产采购委员会JSC-GP Joint Sourcing Committee - Generalpurchase联合采购委员会-一般采购Kcc Key Control Characteristic 关键过程控制特性KCC Key Control Character 关键控制特性KCDS Key Characteristic Designation System 产品关键特性定义系统KO Kick-Off 启动Kpc Key Product Characteristic 关键产品特性KPC Key Product Characteristic 关键产品特性KPC Key product characteristic 主要产品特性KPC Key product characteristic 主要产品特性KPC Key process control 关键过程控制KPC Key process control 关键过程控制LAAMSB Latin America, Africa, Middle EastStrategy Board通用的拉美,非洲,中东战LCL Lower Control Limit 管制下限LCS Logistic Confirmation Sheet 物流确认单LL Learning Loop 学习周期LL Long Lead 长周期LLPR Long Lead Production Release 长周期的产品发布LM Launch Manager 启动经理LOU Line of Usage BOM 整车BOM行LSL Lower Specification Limit 规格下限LSP Lean sales and marketing prograne 精宜营销LTR Launch Team Release 启动小组释放LWO Logistic Work Order 物流属性更改号M+E Machine & Equipment 机器设备MAC 区域经理MBOM Manufacturing BOM 制造BOMMDS Materiel Data Sheet 物料数据单ME Manufacture Engineer 样车试制工程师或生产线制ME Machine and Electronic 电器设备ME Manufacturing Engineering 制造工程ME Manufacturing Engineering 制造工程MEC 区域市场支持MEIS Manufacturing Engineering Info System 制造工程信息系统MES Manufacturing Execution System 制造执行系统MES Manufacturing Execution System 制造执行系统MFG Site Dec Manufacturing Site Decision 确定生产厂址MIC Marketing Information Center 市场信息中心MILKRUN Milkrun 循环取货MKT Marketing 营销MMR Manufacturable Math Release 制造数模发布MO Manufacturing Operations 生产管理部门MP OTS 100% 100% Made Parts in OTS 100%自制件达到OTS状态MP OTS 100%100% Made Parts in OTS 100%自制件达到OTS状态MP PPAP Made Parts PPAP 自制件通过PPAPMP PPAP Made Parts PPAP 自制件通过PPAPMP PPV Made Parts Production and ProcessValidation自制件生产线交付后的产品MP PPV Made Parts Production and ProcessValidation自制件生产线交付后的产品MPS Master Planning System 主计划系统MPV Multi-Purpose Vehicle 多用途轿车MR Manufacturing Requirements 制造要求MRD Material Required Date 交样日期MRD Material Requirement Date 物料需求日期MRD Material Required Date (for physicalbuilds)物料需求日期(用于制造样MRD Math Required Date (for virtual builds) 数模需求日期(用于虚拟制MRE Manufacturing Responsible Engineer 制造工程师MS Manufacturing Studies 制造车间MSA Measurement System Analysis 测量系统分析手册MSA Measurement System Analysis 测量系统分析MSA Measure System Analyse 测量系统分析MSA Measurement system analysis 测量系统分析MSS Market Segment Specification 市场细分规范MSS 区域销售支持MSS Market Segment Specification 市场分割规范MT Manual Transmission 手动变速箱MT&E Machines, Tools and Equipment 机床,工装和设备MTS Manufacturing Technical Specification 制造技术标准MVB Manufacturing Validation Build 用于认证制造工艺的整车制MVB Manufacturing Validation Build 制造验证造车MVB (ns) Manufacturing Validation Build (nonsaleable)用于认证制造工艺的整车销售的)MVB (s) Manufacturing ValidationBuild (saleable)用于认证制造工艺的整车售的)MVBns Manufacturing Validation Build Non-Salable非销售制造验证造车MVBs Manufacturing Validation Build Salable 销售制造验证造车MVSS Motor Vehicle Safety Standards 汽车安全标准MWO Manufacture Work Order 制造属性更改号MY Model Year年度款 MYM Model Year Manager车型年经理 NAO North American Operations 通用的北美分部 NEO New Employee Orientation 新员工培训 NOA Notice of Authorization 授权书 NOD Notice of Decision 决议 NOD Notice of Decision 决议通知 NPV Net Present Value 净现值 NRD Normal Road一般公路NSB North American Strategy Board通用的北美传略委员会(管理组织)OBD On Board Diagnostics 车载诊断系统 OEMOriginal Equipment manufacturers 原始设备制造商(主机厂)OEM Run-Off Original Equipment Manufacturer Run-Off零件供应商工装设备具备试生产条件OEM Run-off Original Equipment Manufacturer Run-off 零件供应商工装设备具备试OJT On Job Training 在岗培训 OPO Office of Product Operations 产品高层管理组织 ORS Occupant Restraint System 乘员约束系统 OT Overtime 加班 OTD Order to Delivery 订单到货时间 OTP On Time Performance 及时性能 OTS 装车评审 OTS Off-tool Sample 工装样件 OTS Off-tool Sample 工装样件 OTS Off-tool Sample 工装样件 OTS OFF-TOOL-SAMPLE 工装样件OTS QV OTS Quality ValveOTS 质量阀OTS 交付状态满足质保的开OTS QV OTS Quality ValveOTS 质量阀,OTS 交付状态开阀要求OTS TG2 Off Tooling Samples Tooling Go Level 2OTS 设计达到TG2阶段,发供应商启动工装和设备投入OTS TGL2 Off Tooling Samples Tooling Go Level 2 OTS 设计达到TG2阶段 P Pilot 批量试生产 P Pilot 小批量生产 PA Production Approval 批准正式生产 PA Program Administrator 项目管理专员 PaC Physical Alpha for Customer 提交客户的Alpha 样机 PACK Packaging 包装规划 PAD Product Assembly Documentation 产品装配文件 PAM Product Assemble Manual 样车装配指南 PAM Product Assemble Manual 产品装配手册PAPIRProduct and Process Integration Review 产品和工艺集成会议PAS Packaging Approval Sheet 包装确认单PAS Parking Aid System 泊车辅助系统PAS Parking Aid System 泊车辅助系统PbC Physical Beta for Customer 提交客户的Beta样机PBS Painted Body Store 油漆车身存储区PC Deliver Pilot to Customer 向客户提交Pilot产品PC Pullcord 拉环PC Problem Communication 问题信息PC&L Production Control and Logistics PC&L部门(GM的一个部门PCL Production Control Manager 生产控制与支持PCM Powertrain Control Module 动力总成控制模块PCM Process Control Manager 工艺控制负责人PCN Project Cost Change Notice 项目更改通知单PCN Project Costbook Change Notice 项目Costbook更改通知单PCR Problem communication report 问题交流报告PCR Problem communication report 问题交流报告PCR Problem Communication Report 问题交流报告PCR Problem Communication Report 问题交流报告PDC Parking Distance Control 泊车距离控制PDC Parking Distance Control 泊车距离控制PDCA Plan、Do、Check、Action 计划、实施、检查、行动PDCA Plan-Do-Check-Action 计划,实施,检查,行动PDI Product delivery inspection 产品交付检查PDI Preliminary Data Indicator 初步数据指示器PDI Pre-delivery Inspection 车辆行运“零公里”检查报PDS Product Data Structure 产品数据结构,在SCM中用象,集成了BOM、工艺和工PDT Product Development Team 产品开发组PDT Product Development Team 产品开发小组PDT Product Development Team 产品开发小组PDT Product Development Team 产品开发小组PDT Product Development Team 产品开发小组PE Product Engineering 产品工程PET Program Executive Team 项目执行小组PET Program Execution Team 项目组PET Program Execution Team 项目执行小组PFI Program Framing Initiated 项目框架启动PFMEA Process failure modeand effectsanalysis过程失效模式和后果分析PFMEA Process FMEA 工艺失效模式分析PFMEA Process failure mode & effects analysis 过程失效模式分析PFSE Product Focus Systems Engineer 产品系统工程师PG3 Powertrain Gateway 关键里程碑节点PgC Physical Gamma for Customer 向客户发运Gamma样机PGM Program Management / Project Management 项目管理PGM Program Management 项目管理PGM Program Management 项目管理Pilot Pilot 试生产Pilot Pilot 试生产Pilot QV Pilot Quality Valve 试生产质量阀满足启动试要球Pilot MRD Pilot Material Requied Date Pilot交样日期Pilot MRD Pilot Material Required Date Pilot的物料需求日期Pilot QV Pilot Quality Valve 试生产质量阀满足启动试生产的开阀要求PIM Powertrain Interface Manager 动力总成接口经理PLM Production Launch Manager 生产启动经理PLP 单车利润表PM Programme Manager 项目工程经理PM Program Manager 项目经理PM Program Manager 项目经理PM Plan maintain 计划维护PM Prevention Maintenance 预防性维护PM Program Manager 项目经理PMO Program Management Office 项目管理办公室(通用的一PMP 常规尺寸PMT Product Management Team 产品管理小组PN Part NO. 零件号PP Pre-pilot 前期试生产PP Pre-Pilot 预试生产PP Pre-pilot 试生产P-P Pre-Pilot 试生产PP PPAP Purchased Parts ProductionParts Approval Process外购件完成生产件批准程序PP Appr. Purchased Parts Approved 外购件批准SQE开具入库许可单PP ESO Purchased Parts Engineering Sign Off 外购件工程签署,完成OT 认可PP OTS 100%100% Purchased Parts in OTS 外购件的OTS交样率达到PP OTS 80% 80% Purchased Parts in OTS 外购件的OTS交样率达到PP OTS 80%80% Purchased Parts in OTS 外购件的OTS交样率达到PP PPAP Purchased Parts PPAP 外购件完成PPAPPPA Product Planning Approval 产品规划批准PPAP Production Parts Approval Process 生产件批准程序PPAP Production Part Approval Process 生产零部件批准程序PPAP Production Part Approval Process 生产件批准程序PPAP Production Part Approval Process 生产件批准程序PPAP Production Parts Approval Process 生产件批准程序PPAP Production Part Approval Process 生产件批准流程PPAP PPAP Production Part Approval Process 产品零部件批准流程PPAP Production Part Approval Process 生产零部件批准程序PPC Deliver Pre-Pilot to Customer 向客户发运Pre-pilot动力PPC Product Program Content 项目任务书。
Process control solutionsFesto is a leading global manufacturer of pneumatic and electromechanical systems, components, and controls for process control and factory automation solutions. Celebrating more than 40 years of innovation in U.S., and over 80 years globally, Festo continuously elevates the state of manufacturing with innovations and optimizedmotion control solutions.1925Year foundedCompanies in61countriesBranch offices3billionEurosgroup turnoveremployees>300,000Industrial customersper year8%Of turnover spent on R&D33,000componentsSales engineersaround the worldFesto figures, facts & dataThe company at a glanceControl cabinet solutions from Festo almost completely eliminate the complex working processes involved in the construction of a pneumatic sub-system. We construct, bolt, test and deliver pre-assembled control cabinets for the pneumatic actuation of your plant.Concentrate on your core business while saving time and money by as much as 50% while Festo builds your customized control cabinet. Utilizing one order and one contact person, you can reduce purchasing costs, enhance process reliability and boost productivity.Constructing and building production plants is highly complicated and can include many sub-contractors often working closely together. We coordinate all the partners who contribute to planning and building the pneumatic control cabinets for your project, thus relieving a lot of the pressure.All advantages included – with control cabinet solutionsfrom FestoAdditional benefits include:•From pre-assembled to integration to customsolutions, we can provide standard or custom control panels that help to meet your objectives.•Whether you need one or several hundred control cabinets, Festo is punctual and reliable.•The uniform design of the control cabinet throughout the entire plant makes it easier to troubleshoot in the event of a problem.Control cabinetsElectric controlsDigital I/OAnalog I/OLab automationsolutionsFesto offers control panels pre-assembled on a flat plate or custom designedmounting structure to facilitate pneumatic and electric components from bothFesto and third party manufacturers. The assemblies are function specificbased on a customer’s requirements, and require minimum effort to integratethe complete assembly into the customer’s system.• Pre-assembled solution to mount directly into the customer’s machine• Flat mounting panel or custom designed structure to fit available footprint• Pre-wired and pneumatically connected• Easy integration including interconnect documentation• A single part number of simple ordering and vendor reductionAir supplypreparationE2M Smartair monitoringDrivesActuatorsFieldbus protocolsFielddevices/sensorsMotorsProcess control valve solutionsMPANEMA 4/4XClass 1 Div 2VTEM Smart terminalVTUG MultipoleCPV MultipolePneumatic controlsFesto: A global manufacturer of process control and factory automation solutionsFesto is a leading global manufacturer of automation technology including systems, components and controls for process control and factory automation solutions. Festo Didactic provides industrial training and education programs aimed to maximize the productivity and competitiveness of its customers.Our objective is to provide innovative solutions to solve the most challenging automation problems.Working with designers and manufacturers to increase manufacturing productivity, we continue to advance the state of industrial automation with proven innovations, customized design solutions and exceptional service worldwide.At the control level, Festo manufactures pneumatic pilot valves, valve terminals, I/O systems and HMIs which integrate seamlessly with leading DCS and controllers.This reduces risk and cost by simplifying integration and providing a singlesource supplier. The ability to incorporate standard diagnostic features into solenoid valves and I/O systems helps accurately diagnose problems which reduce downtime and field service calls.With the comprehensive range of products, engineering competencies and strong design experience. Festo is uniquely positioned to be your complete automationsolutions partner.1. Consultation and design• Pneumatic, servopneumatic, electrical and mechatronic technologies• Application and industry specific• Consideration of application specific requirements • Systematic support right from the start2. Quotation and orders• Design review of engineering concept including 2D/3D model and scope of services • Detailed proposal• Single point of contact for pricing and order fulfillment3. Engineering• Complete engineering solution • Technology and component selection• Solutions based on the latest technological standards • NEMA, UL and IEC standards • UL & CE certifications1.2.3.4.Consultation and designDesignReview/ProposalEngineeringProcurement and logisticsProgr5.From initial design to commissioning, Festo will take care of it for you. This allows you to ...Make the most of it at every stage ...4. Procurement and logistics • Procurement of all Festo and third-party components• Single point of contact for PM execution5. Programming • Software suppor within Rockwell,Emerson environProduction and assembly Testing andvalidationDocumentationramming 6.7.8.9.Delivery andcommissioning ... significantly shorten the individual process solution steps and save up to 50% of total costs... by providing value and flexibility along the entire project life cycle planrt for integration , Siemens and nments 6. Production and assembly• Application specific fabricationand assembly of all solenoidpanel components7. Testing and validation• 100% functional testing• F.A.T. & validation protocolexecution• Certifications, e.g. EN 60204-1,ATEX, UL-508A8. Documentation• Detailed system documentation:- Assembly drawing- Parts list- Circuit diagrams- Operating instructions- User manual9. Delivery and commissioning• Commissioning and startupservices• We provide solutions that havebeen assembled and tested fora ready-to-install systemThe quick and easy steps to your ready-to-install solutionExcellence in automation Our engineers are backed by over 80 years of industry experience in building advanced pneumatic and electromechanical control systems and components for OEM’s and end-users around the world.Custom systems and components, from concept to completionOur project teams will work with you every step of the way,from concept through system design and delivery of a completeautomated system.• You contact us and describe your task to us.• We design your system and develop your ready-to-install solutionin close consultation with you.• We produce a customized quotation for you.• We procure the components.• We build, test and document your solution.• We deliver the ready-to-install system.• If desired, we will also commission the system.Total quality assuranceFesto established a certifiedmanagement system as a basisfor implementing, maintainingand continuously improvingquality, safety and environmentpractices. This is applied to allproduction and design facilitiesglobally. We adhere to thefollowing standards:• ISO 9001• ISO 14001Solenoid panel overview• Materials: 316SS & 304SS Cabinet • Rating: NEMA 4X & UL rated• Standard Sizes: 16, 32 and 48 solenoids• Filtration: Ultra low particle filters (01um)• I/O: Analog and discreteISO Clean RoomMechanical RoomSolenoid control cabinetSolenoid panel overview• Materials: Painted steel or 304SS cabinet• Rating: NEMA 4/12 & UL rated• Standard Sizes: 16, 32 and 48solenoids• I/O: Analog and discreteHazardous areaSolenoid panel overview• Materials: Painted steel or 316SS cabinet• Rating: NEMA 4X & CD12 & UL rated • Standard Sizes: 16, 32 and 48solenoids• I/O:Intrinsically safe I/OBenefits from innovative products, services and best practicesReduce field service costsEnergy efficient & increased uptimeHot swap valve replacementDiagnostic information from Festo valves and I/O can be extracted by DCS/PLC over fieldbus. Information such as shorted wire, failed solenoid valve or number of cycles can pinpoint issues quickly and help diagnose issues remotely.Utilization of flow sensors can provide real time usage and volumetric consumption, both of which can be used as a benchmark to market your equipmentimprovements. Measuring flow at FAT and monitoring it over the lifetime of the equipment is an excellent and cost effective diagnostic tool. An increase in air consumption is an early indication of a leak or component breakdown.At times valve replacement is necessary while parts of the skid remain active. Utilization of a hot swappable valve provides the ability to isolate and replace a single valve while the manifold stays pressurized and operational. Helpful forpreventative maintenance of valvescontrolling reactor processes.Improve image supportSingle source supplierFesto offers complete range of regulators, filters and dryers to ensure equipment uptime and a safe quality air supply for all applications. Contact a local Festo sales representative or refer to our Air Quality Guide to ensure air quality at your facility meets FDA requirements.Partnering with a manufacturer located in 176 countries improves market acceptance and ensures global support for you and your customers.Festo is recognized as thetechnology leader in automation solutions within the life science industry.Reduce costs with a single partner for process control and automation.Festo is the leading supplier of valves,I/O, air preparation, fittings, tubing,sensors, process valves andadditionally manufacturers a completerange of handling and motion control solutions.Ensure clean airServices and supportOnline Shop 24hName:Date:OVERVIEW Brief Description:Supply Pressure:(psi)No. of Systems: Avg. Temperature(°C or °F)Quote Needed By: EnvironmentBACKGROUNDSystem New Design Retrofit Customer Design ComponentsCPX/MPA ManifoldVTUG ManifoldCPV Manifold3/2 valve5/2 valveTotal valves: QuoteBudgetary QuoteFormal QuotePreliminary Drawings Certification UL C1D2 ATEX OTHERENCLOSURE Enclosure TypeGeneral PurposeHazardous AreaISO Clean Room304 SS316L SSFiberglassWhiteGrayCustom NEMA Rating NEMA 4X NEMA 4 NEMA 12 OTHERDoor & FrameRight TopLeft BottomSloped Special FrameWindow LabelsSize (WxHxD)CONNECTIONS & OPTIONSWorking PortsConnection Port Size Mounting SpecialQuick ConnectCompressionMultipole Plate1/4 in5/16 in6 mmBottomRight SideLeft SideConduitCable TrayOther Air PrepRegulator Filtration Valve Location7 bar12 bar40 Microns5 MicronsHandAutoIn LeftOut RT Other (specify)ElectricalDI 8 pt 16 ptDO 8 pt 16 ptAI 4 pt 8 ptAC In 110VDC In 24VFuses Cir Breaker CommunicationEthernet IP Profinet Profibus Multipin IO-LinkOther (specify)OptionsTurnover (TOP) Package Startup Support FAT SupportOther (specify)Solenoid cabinet checklist1123314213 12.2019 S u b j e c t t o c h a n geFesto: Your partner in automationConnect with us/socialmedia 1Festo Inc.2Festo Pneumatic3Festo Corporation4Regional Service Center5300 Explorer DriveMississauga, ON L4W 5G4CanadaAv. Ceylán 3,Col. Tequesquináhuac 54020 Tlalnepantla, Estado de México1377 Motor Parkway Suite 310Islandia, NY 117497777 Columbia Road Mason, OH 45040Festo Customer Interaction CenterTel:187****3786Fax:187****3786Email:*****************************Multinational Contact Center 01 800 337 8669***********************Festo Customer Interaction Center180****3786180****3786*****************************。
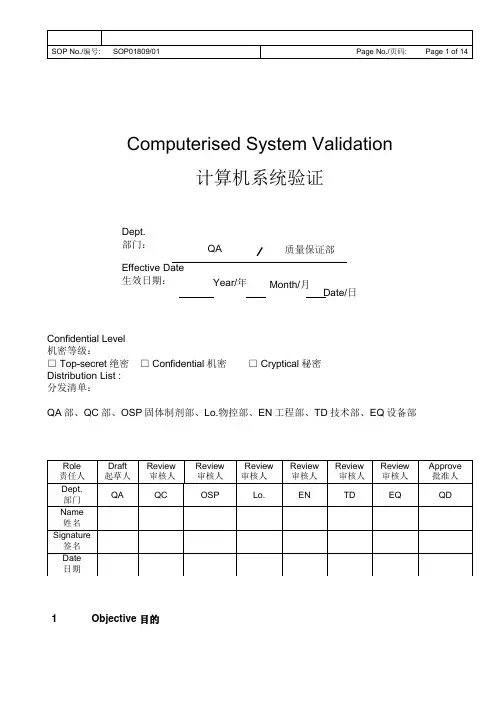
Computerised System Validation计算机系统验证Dept. 部门:Effective Date生效日期:Confidential Level 机密等级:□ Top-secret 绝密 □ Confidential 机密 □ Cryptical 秘密 Distribution List : 分发清单:QA 部、QC 部、OSP 固体制剂部、Lo.物控部、EN 工程部、TD 技术部、EQ 设备部Year/Month/月QA质量保证部Date/日1Objective 目的Test and assessment should be taken for URS, design, purchase,installation, function, as well as process adaptability of computerized and PLC control system related to GMP in compliance with this SOP so as toensure that computerized and PLC are fit for design requirement and statedtechnical criteria and are able to work stably for a long time.测试、评估采取的URS、设计、采购、安装、功能以及计算机控制和PLC控制系统符合GMP,以确保计算机和PLC符合设计要求和工艺要求并且能够稳定工作很长时间。
2Scope范围This SOP is fit for the validation management of computerized and PLCcontrol system related to GMP, which apply to material control andmanagement, laboratory equipment control and communication management,manufacturing process control, and utilities control.本SOP适用于电脑,PLC控制系统的管理是否符合GMP,物料控制和管理,实验设备控制和通信管理、生产过程控制、公用设施的控制的验证。
制药工程常用英文缩写,缩略语1GMP Good Manufacturing Practices药品生产质量管理规范2GxP各种药品规范的统称3GCP Good Clinical Practice药物临床试验质量管理规范4GLP Good Laboratory Practice药物非临床试验(实验室)质量管理规范5GSPGDPGood Supplg practiceGood Distribute Practice(美)药品经营质量管理规范6GDP Good Dossier practice申报资料质量管理规范7GPP Good Pharmacy practice药房质量管理规范8GQP Good Quality Practice 药品质量管理规范9GRP Good Rearch Practice药品研究质量管理规范10GUPGPPGood Use PracticeGood Preparation Practice(欧美)药品使用质量管理规范11GVP Good Validation Practice验证管理规范12GAP Good Agricultural Practice中药材生产质量管理规范13GEP Good Engineering Practice工程管理规范14GWP Good Warehousing Practice药品仓储规范15GMPC Good Manufacture Practice of Cosmetic Products 化学品生产质量管理规范16cGMP Current Good Manufacturing Practice现行药品生产质量管理规范17EU-GMP European –Good Manufacturing Practice欧洲GMP18CFR Code of Federal Regulations美国联邦法规19ChP Chinese Pharmacopoeia中国药典20USP United States Pharmacopoeia美国药典21EP European Pharmacopoeia欧洲药典22JP Japanese Pharmacopoeia日本药典23BP British Pharmacopoeia英国药典24IP Indian Pharmacopoeia印度药典25EN European Norm欧洲规范,欧洲标准26ANSI American National Standards Institute美国国家标准学会27ASME American Society of Mechanical Engineers美国机械工程师学会28ASTM American Society for Testing and Materials美国材料实验学会29ISPE International Society for Pharmaceutical Engineering 国际制药工程学会30WHO World Health Organization世界卫生组织31ISO International Standards Organization国际标准组织32EEC European Economic Community欧洲共同体、欧共体33EU European Union欧盟34ES European Commission欧洲委员会35CFDA China Food and Drug Administration中国食品和药品监督管理局36FDA Food and Drug Administration(美国)食品和药品管理局37MHRA Medicines & Healthcare Products Regulatory Agency(英国)药品和健康产品管理局38EHX Environment Health Safety环境、职业健康、安全管理体系39BPE Bioprocessing Equipment生物处理设备403A美国卫生行业协会、美国卫生论证标识41NBST National Bureau of Standards and Technology美国国家标准研究院42EMA European Medicines Agency欧洲药监局43EMEA European Agency for the evaluationof medicinal欧洲药品评价局44EDQM European Directorate for the Quality of Medicines 欧洲药品理事会45EQDM European Directorate for the Quality of Medicines & Healthcare欧洲药品与健康理事会46EHEDG European Hygienic Equipment Design Group欧洲卫生设备设计组织47ICH International Conference on Harmonization of TechnicalRequirements for Registration of Pharmaceuticals for Human 人用药物注册技术要求国际协调会议48IEC International Electrotechnical Commission国际电工委员会通用及组织49NEMA National Electrical Manufacturers Association美国电器制造商协会50CEP Certificate of Suitability for European Pharmacopeia欧洲药典适用性证书51CE Conformite Europeenne 欧洲电气安全论证52PIC/S Pharmaceutical Inspection ConventionPharmaceutical Inspection Cooperation Scheme国际医药品稽查协约组织53HHS United States Department of Health and Human Services美国卫生及公共服务部、美国卫生部54PDA Parenteral Drug Association(美国)注射剂协会55EPA Environmental Protection Agency(美国国家)环境保护局56CDER Center for Drug Evaluation and Research药物评价与研究中心57MHWMHLWMinistry of Health and WelfareMinistry of Health, Labor and Welfare(日本)厚生省(日本)厚生劳动省5821 CFR Title 21―Food and Drugs美国联邦法规,第21篇,食品与药品59Part11Electronic Records; Electronic Signatures第11节,电子记录与电子签名60Part210Current Good Manufacturing Practice in Manufacturing,Processing,Packing,or Holding of Drugs;General第210节,药品生产、加工、包装、储存质量规范部分61Part211Current Good Manufacturing Practice for Finished 第211节,制剂药物生产质量规范部分62Part314Applications for FDA Approval to Market a New Drug第314节,新药上市申请部分63Part320Bioavailability and Bioequivalence Requirements 第320节,生物利用度和等效性要求1QMS Quality Management System质量管理体系2QRS Quality Regulation System质量控制体系3QA Quality Assurance质量保证4QC Quality Control质量控制5QM Quality Management质量管理6QI Quality Inspection质量检验7QP Quality Plan质量计划8QRM Quality Risk Management质量风险管理9URS User Requirement Specification用户需求10DQ Design Qualification设计确认11IQ Installation Qualification安装确认12OQ Operational Qualification操作确认13PQ Performance Qualification性能确认14VIT Vendor Internal Test供应商内部测试15FAT Factory Acceptance Test工厂验收测试16SAT Site Acceptance Test现场验收测试17SOP Standard of Operation标准操作规程18FDS Functional and Design Specifications功能设计说明、功能设计规范19FS Functional Specifications功能说明20DS Design Specifications设计说明21TS Technical Specification技术说明、技术规范22RTM(TM)Requirement Traceability Matrix需求追溯矩阵23ITR Inspection T est Reports检查测试报告24QOR Quality Observation Report质量检查报告25QR Quality Requirements质量要求26QR Quality Records质量记录27RA Risk Assessment风险评估28SIA System Impact Assessment系统影响性评估29CCA CriticalComponents Assessment部件关键性评估30PV Process Validation工艺验证31CV Cleaning Validation清洁验证32CSV Computer System Validation计算机验证33VMP Validation Master Plan 验证主计划质量、验证34VP Validation Plan 验证计划35VP Validation Protocol验证方案36VR Validation Report验证报告37PVP Project Validation Plan项目验证计划38PVR Project Validation Report项目验证报告39QbD Quality by Design质量源于设计40DMF Drug Master File药品主文件、药物管理档案41FMEA Failure Mode and Effects Analysis失效模式和效果分析42SST System Suitability Test系统适应性测试43CAL Calibration校验、校准44CAPA Corrective Action and Preventive Action纠正预防措施45RCA Root Cause Analysis根本原因分析46ERES Electronic Record and Electronic Signature电子记录与电子签名47AQL Acceptable Quality Level可接受质量水平48CQA Critical Quality Attribut关键质量属性49CPP Critical Process Pararneter关键工艺参数50CTD Common T echnical Document通用技术文件51IA Impact Assessment影响评估52PQR Procut Quality Review产品质量回顾53COA Certification of Analysis分析合格证书、检验报告54BPR Batch Production Records批生产记录55BR Batch Records批记录56CC Change Control变更控制57DR Deviation Records偏差记录58COM Commissioning试车59BAR Batch Analysis Record批检验记录60PP Process Procedure工艺规程61OOS Out of Specification超出标准(限度)62LAL Limulus Smoebocyte Lysate鲎试剂63AQL Acceptable Quality Level可接受质量水平64SMF Site Master File工厂主文件65PM Preventive Maintenance预防性维修66QP Qualified Person质量授权人67R&D Research and Development研发部门68NDA New Drug Application新药申请电气及自控1GAMP Good Automated Manufacturing Practices设备自动化生产管理规范2HMI Human Machine Interface人机界面3OIT Operator Interface Terminals操作员界面终端4OIP Operator Interface Panel操作员界面面板5PLC Programmable Logic Controller可编程序控制器6PCS Process Control System过程控制系统7DCS Distributed Control System集散控制系统8PCS Process Control System工艺控制系统9DDC Direct Digital Controller直接数字控制器10IPC Industrial Personal Computer工业控制计算机,工控机11PAC Programmable Automation Controller可编程自动化控制器12PCC programmable computer controller可编程计算机控制器13MCU Microcontroller Unit单片机14CPU Central Process Unit中央处理器15PC Personal Computer个人电脑16SCADA Supervisory Control And Data Acquisition监控及数据采集17SDS Software design specification软件设计说明18HDS Hardware Design Specification硬件设计说明19FL Functional Logic功能逻辑说明20I/O Input / Output输入/输出21AI Analog Input模拟量输入22AO Analog Output模拟量输出23DI Digital Input数字量输入24DO Digital Output数字量输出25RTD Resistance Temperature Detector热电阻26T/C Thermocouple热电偶27RTU Remote Terminal Unit远程终端单元28ARS Automation Requirement Specification自动化需求规范29VFD Variable Frequency Drive变频驱动30EMC Electromagnetic Compatibility电磁兼容31UPS Uninterrupted Power supply不间断电源32EPS Emergency Power supply应急电源33FL Functional Logic功能逻辑说明34ER and Electronic Signature电子记录35ES Electronic Signature电子签名36AT Audit Trail审计踪迹37NO Normally Open常开38NC Normally Close常关39FO Fault Open故障开40FC Fault Close故障关41AC Alternating Current交流42DC Direct Current直流43PID Proportional Integral Derivative比例积分微分44LED Light Emitting Diode发光二极管45LCD Liquid Crystal Display液晶显示器46LIMS Laboratory Information Management System实验室信息管理系统 47LECP Laboratory Equipment Calibration Program 实验室仪器校准程序48WMS Warehouse Management System仓库管理系统49MES Manufacturing Execution System制造执行系统50ERP Enterprise Resource Planning企业资源计划其它1N/A Not Applicable不适用2NLT Not Less Than不少于3NMT Not More Than不多于4NB Nominal Bore公称管径5PED Pressure Equipment Directive压力设备指令(欧洲) 6PW Purified Water纯化水7WFI Water for Injections注射用水8PS Pure Steam纯蒸汽发生器9PWG PW Generator Unit纯化水制备机组10WFIG WFI Generator注射用水制备机组11MEWD Multi-effect Water Distillator 多效蒸馏水机12PSG PS Generator纯蒸汽发生器13PAC Poly Alumina Chlorine聚合氯化铝14DW Demineralized Water脱盐水,去离子水15MF Micro-Filter微滤16UF Ultra-Filter 超滤17NF Nano-Filter纳滤18MMF Multi-Media Filter多介质过滤器19ACF Activated Carbon Filter活性炭过滤器20SF Softener软化器21DG Degasifier脱气塔22RO Reverse Osmosis 反渗透23EDI Electrodeionization电法去离子24MB Mixed Bed混床25MDG Membrane Degasifier膜脱气26COP Clean out Place离线清洗27CEB Chemical Enhanced Backwash化学增强反冲洗28CIP Clean In Place在线清洗29SIP Sterilization in Place在线灭菌30POU Point Of Use使用点31PH Potential of Hydrogen酸碱度32TOC Total Organic Carbon总有机碳33ORP Oxidation-Reduction Potential氧化还原电位34COD Chemical Oxygen Demand化学耗氧量35BOD Biological Oxygen Demand生物耗氧量36SDI Silt Density Index污染密度指数37TUB Turbidity浊度38TSS Suspended Solid总悬浮固体39DO Dissoved Cxygn溶解氧40TDS Total dissolved solids总溶解固体41TH Total Hardness总硬度42PAT Process Analytical & Measurement T echnology过程分析技术43IRS Installation Requirement Specification安装要求说明44OEM Original Equipment Manufacturer 原始设备制造商45GDS General Design Specification总体设计说明46DDS Detailed Design Specification详细设计说明47PCP Preparation of Construction Plan施工组织设计48WMS Work Method Statement施工方案49BOQ Bill of Quantities工程量清单50BOM Bill of Material材料清单51P&ID Process and Instrumentation Diagram工艺与仪表流程图52PFD Process Flow Diagram工艺流程示意图53ANDA Abbreviation New Drug Application仿制药或仿制新药申请54OPQ Operational Personnel Qualification操作人员资格鉴定55MBT Microbiologic Test微生物测定56ADR Adverse Drug Reaction药物副作用报告,药品不良报告57OMM Operating and Maintenance Manual操作和维护保养手册58HACCP Hazard Analysis and Critical Control Point危害分析及关键环节控制点59CCP Critical Control Point关键环节控制点60IPC In Process Control过程控制61IPC Intermediate Production Control中间生产控制62CIPC Critical In-Process Control关键中间控制点63MBR Master Batch Record主生产批记录64PPM Parts Per Million百万分之一65OC Organizational Charts组织结构图66FIT Filter Integrity Test过滤器完整性测试67WIT Water Intergrity Test水侵入测试68GA General Arrangement总平面图69RPM Rotations per minute转/分70PD Prescription Drug处方药71Rx Receptor x处方药72NPD Nonprescription Drug非处方药73OTC Over The Counter非处方药74API Active Pharmaceutical Ingredient原料药、活性药75BPC Bulk Pharmaceutical Chemical原料药(原简称)76DS Drug Substance原料药77DP Drug Product成品药78RO Restriction orifice限流孔板79SG Sight Glass视镜80LG Lamp Glass,Light Glass灯镜81RD Rupture Disk爆破片材料1MOC Material Of Construction建造材质2SS Stainless Steel不锈钢3CI Cast iron铸铁4NCI Nodular east iron球墨铸铁5CS Carbon Steel碳钢6 C.Stl Cast Steel铸钢7 F.Stl Freezing Steel锻钢8PA Polyamide聚酰胺9PB Polybutylene聚丁烯10PC Polycarbonate聚碳酸酯11PE Polyethylene聚乙烯12PEX Cross-linked PolyEthylene交联聚乙烯13HDPE High-density polyethylene plastics高密度聚乙烯14MDPE Medium-density polyethylene plastics中密度聚乙烯15PO Polyolefin聚烯烃16PP Polypropylens聚丙烯17FRPP Polypropylens玻纤增强聚丙烯18PPR Polypropyla无规共聚聚丙烯19PPS PolyPhenylene Sulfide聚苯硫醚20PS Polystrene聚苯乙烯21PU Polyurethane,或者缩写为PUR聚氨酯22POM PolyOxyMethylene or Polyacetal聚甲醛,聚氧化亚甲基23HIPS High impact polystyrene高抗冲聚苯乙烯26PFA Polyfluoroalkoxy四氟乙烯—全氟烷氧基乙烯基醚共聚物27PTFE Polytetrafluoroethylene聚四氟乙烯28PVDF Poly vinylidene fluofide聚偏二氟乙烯29PVC Polyvinyl chloride聚氯乙烯30UPVC Unplasticised Polyvinyl Chloride硬聚氯乙烯,增强聚氯乙烯31CPVC Chlorinated polyvinyl chloride,或者缩写为PVCC氯化聚氯乙烯32PA Nylon,Polyamide尼龙,聚酰胺33PES PolyEtherSulfone聚醚砜,聚酯34AAS Acrylonirile butadiene styrene丙烯腈-丙烯酸酌-苯乙烯35ABS Acrylonitrile-Butadiene-Styrene丙烯腈-丁二烯-苯乙烯共聚物36ACS Acrylonitrile Chlorinated polyethylene Styrene丙烯胯-氯化聚乙烯-苯乙烯37ASB Asbestos石棉38PMMA Polymethel methacrylate聚甲基丙烯酸甲酯39SR Styrene-rubber苯乙烯橡胶24EPDM Ethylene Propylene Diene Monomer三元乙丙橡胶25EPM Ethylene Propylene Methylene乙丙橡胶,乙烯/丙烯共聚物40SR Silicone rubber硅橡胶40HTV High Temperature Vulcanization高温硫化(硅橡胶)40RTV Room Temperature Vulcanization室温硫化(硅橡胶)40MQ Silicone rubber甲基硅橡胶40VMQ Silicone rubber甲基乙烯基硅橡胶40PVMQ Silicone rubber甲基乙烯基苯基硅橡胶41FPMFKMFluororubberFluorocarbon Rubber氟橡胶42NBR Vulcanized nitrile rubber丁腈橡胶43FRP Glass Fibre Reinforced Plastic玻璃钢,玻璃纤维增强塑料1HVAC Heating Ventilation and Conditioning供热通风空调2AC Air Conditioner空调3AHU Air Handling Unit空气处理单元4BMS Building Monitoring System建筑管理系统、楼宇检测系统5CFU Colony Forming Unit菌落形成单位6CNC Controlled Non-Classified控制但未分级7FFU Fan Filter Unit风机过滤单元8FMS Factory Monitoring System车间监控系统9HEPA High Efficiency Particulate Air高效空气过滤器10LAF Laminar Air Flow层流、单向流11UDF Unidirectional Flow单向流12RABS Restricted Access Barrier Systems限制通过隔离系统13DP Differential Pressure压差14SDP Static Differential Pressure静压差15RH Relative Humidity相对湿度16CHWs Chilled Water (Supply)冷冻水(供给)17CWr Cooling Water (Return)冷却水(回流)18HW Hot Water热水19FS Factory Steam工厂蒸汽20SC Steam Condensate蒸汽冷凝水21WD Waste Drain废水排放22PWW Process Wastewater工艺污水23CA Compressed Air压缩空气24PA Process Air工艺压缩空气25IA Instrument Air仪表压缩空气26RW Raw Water原水27SW Soft Water软水28MW Middle Water中水29DW Domestic Water生活用水30CW City Water市政供水、自来水31DK Drinking Wat 饮用水32LPG Liquefied Petroleum Gas液化石油气33LNG Liquefied Natural Gas液化天然气34CNG Compressed natural gas压缩天然气35VE Visual Examination外观检查36UT Ultrasonic inspection Test超声探伤37RT Radiographic inspection Test射线探伤38MT Magnetic particle inspection Test磁粉探伤39PT liquid Penterant inspection Test液体渗透探伤40AutoclaveSterilizer灭菌柜公用工程41FBD Fluid Bed Dryer流化床42BFS Blowing Filling and Sealing吹灌封43HPLC High Pressure Liquid Chromatograph高效液相色谱44TLC Thin Layer Chromatograph薄层色谱45GC Gas Chromatograph气相色谱46UV Ultra-Violet紫外线47IR InfraRed红外线48RFQ Request for Quotations报价征询书49NPT American standard taper pipe thread美国标准锥管螺纹50NPS American standard straight pipe thread美国标准直管螺纹51NF American national fine thread美国标准细牙螺纹52NC American national coarse thread美国标准粗牙螺纹53Union Union 活接头,由宁。
Robust ControlRobust control is a critical concept in the field of engineering and automation. It refers to the ability of a control system to maintain stable and satisfactory performance in the presence of various uncertainties and disturbances. This is particularly important in real-world applications where external factors can impact the performance of a control system. In this response, I will discuss the importance of robust control, its applications, and the challenges associated with implementing robust control systems. One of the key reasons why robustcontrol is essential is its ability to ensure stability and performance in theface of uncertainties. In many engineering applications, it is impossible to accurately model all the factors that can affect the behavior of a system. Thiscan include variations in parameters, external disturbances, and modeling errors. Robust control techniques provide a way to design control systems that can accommodate these uncertainties and still deliver satisfactory performance. Thisis particularly important in safety-critical applications such as aerospace, automotive, and medical devices, where the consequences of control system failure can be catastrophic. Another important aspect of robust control is its ability to handle disturbances and variations in the system. In many real-world applications, the environment in which a control system operates can change over time. This can be due to factors such as temperature variations, changes in load, or wear andtear of components. Robust control techniques allow for the design of control systems that can adapt to these changes and maintain their performance over time. This is particularly important in industrial automation and manufacturing, where the ability to maintain consistent performance in the face of changing conditionsis crucial for efficiency and productivity. In addition to stability and adaptability, robust control also plays a crucial role in ensuring the safety and reliability of control systems. In safety-critical applications such as autonomous vehicles or medical devices, the ability of a control system to handle unexpected events or failures is of paramount importance. Robust control techniques can help to design control systems that can detect and recover from faults, ensuring the safety of both the system and its surroundings. This is particularly important in applications where the consequences of failure can be severe, such as in nuclearpower plants or chemical processing facilities. Despite its numerous benefits, implementing robust control systems comes with its own set of challenges. One of the main challenges is the complexity of designing and implementing robust control techniques. Unlike traditional control design, robust control requires a deep understanding of system uncertainties and their impact on performance. This often involves advanced mathematical techniques such as robust optimization, H-infinity control, and mu-synthesis, which can be complex and difficult to implement in practice. Additionally, the design of robust control systems often requires a trade-off between performance and robustness, making it a challenging task for control engineers. Another challenge in implementing robust control systems is the validation and testing of the designed controllers. Unlike traditional control systems, which can often be validated through simulation and testing, robust control systems require more rigorous validation due to their ability to handle uncertainties. This often involves extensive testing under various operating conditions and disturbances to ensure that the control system can maintain its performance in the presence of uncertainties. This can be time-consuming and resource-intensive, making it a significant challenge for the implementation of robust control systems in real-world applications. In conclusion, robust control is a critical concept in the field of engineering and automation, with numerous benefits and challenges. Its ability to ensure stability, adaptability, and safety in the face of uncertainties makes it essential for a wide range of applications, from aerospace and automotive to industrial automation and medical devices. However, the complexity of designing robust control systems and the challenges associated with their validation and testing make it a challenging task forcontrol engineers. Despite these challenges, the importance of robust control in ensuring the performance and safety of control systems cannot be overstated, making it an essential area of research and development in the field of control engineering.。