FRM二级模拟题(6)
- 格式:pdf
- 大小:1.85 MB
- 文档页数:9

二级ACCESS分类模拟题选择题(六)选择题1、若窗体Frml中有一个命令按钮Cmd1,则窗体和命令按钮的Click事件过程名分别为______。
A.Form_Click()和Command1_Click() B.Frm1_Click()和Commamd1_Click() C.Form_Click()和Cmd1_Click() D.Frm1_Click()和Cmd1_Click()2、因修改文本框中的数据而触发的事件是______。
A.Change B.Edit C.Getfocus D.LostFocus3、下列关于报表的叙述中,正确的是______。
A.报表只能输入数据 B.报表只能输出数据C.报表可以输入和输出数据 D.报表不能输入和输出数据4、报表的作用不包括______。
A.分组数据 B.汇总数据 C.格式化数据 D.输入数据5、在一份报表中设计内容只出现一次的区域是______。
A.报表页眉 B.页面页眉 C.主体 D.页面页脚6、要指定在报表每一页的底部都输出的内容,需要设置______。
A.报表页脚 B.页面页脚 C.组页脚 D.页面页眉7、下图所示的是报表设计视图,由此可判断该报表的分组字段是______。
A.课程名称 B.学分 C.成绩 D.姓名8、报表的数据源不包括______。
A.表 B.查询 C.SQL语句 D.窗体9、在报表中要显示格式为“共N页,第N页”的页码,正确的页码格式设置是______。
A.="共"+Pages+"页,第"+Page+"页" B.="共"+[Pages]+"页,第"+[Page]+"页"C.="共"&Pages&"页,第"&Page&"页" D.="共"&[Pages]&"页,第"&[Page]&"页"10、要求在页面页脚中显示“第X页,共Y页”,则页脚中的页码“控件来源”应设置为______。

FRM二级模拟题(一)1. Katherine McCollin is a risk manager who has been assigned the task of designing a riskengine for VaR mapping. Which of the following statements accurately describes VaRmapping?a. Beta is an important factor in mapping fixed-income portfolios.b. Duration mapping is an appropriate method for estimating VaR for mapping forwardsand interest-rate swaps.c. VaR mapping involves identifying common risk factors among positions in a portfolioand mapping all positions to an equity index.d. A return-based analysis may fail to spot style drift or hidden risks.Answer: dVaR mapping involves identifying common risk Factors among positions in a portfolioand mapping those positions to risk factors. A return-based analysis may fail to spot style drift or hidden risks. Duration is an important factor in mapping fixed-income portfolios. The delta-normal method is an appropriate method for estimating VaR for mapping forwards and interest-rare swaps.2. A portfolio manager currently holds 20,000 shares of Costiuk Inc. in a particular portfolio.The daily volume of Costiuk shares traded on the stock exchange is 50,000. Additionally, on any given day, the portfolio manager wishes to trade no more than 15% of the daily trading volume of Cosriuk. Which of the following amounts is closest to the liquidity duration of Cosciuk in this portfolio?a. 0.06.b. 0.375.c. 2.67.d. 16.67.Answer: cLiquidity duration is an approximation of the number of days necessary to dispose of aportfolio's holdings (of a particular share in this case) without a significant market impact.It is calculated as: 20,000 / (0.15 x 50,000) = 2.67.3. A firm has determined that the risk-adjusted return on capital (RAROC) for a particularproject is 14%. To evaluate whether the firm should accept the project, an analyst determines that the firm's beta is l.3, the expected market return is 13%, and the risk-free interest rate is5.5%. If the analyst uses the adjusted RAROC (ARAROC) methodology to make anaccept/reject decision, should the project be accepted?a. No, because the computed ARAROC is approximately l% less than the market riskpremiumb. No, because the RAROC is l.25% less than the return predicted by the CAPM.c. Yes, because the computed ARAROC is approximately l% more than the market riskpremium.d. Yes, because the ARAROC is approximately 4% more than the return predicted by theCAPM.Answer: aARAROC = (RAROC – R F) / βE = (0.14 – 0.055) / 1.3 = 0.06538, or 6.54%.The appropriate decision is to accept the project if the ARAROC > R M - R F. 13% - 5.5% =7.5%. The project should not be accepted since the ARA ROC is approximately 1% less than the market risk premium.4. Which of the following statements regarding the marked-to-market value of a credit defaultswap is correct?I. The value of a CDS at inception is zero.II. If the present value of the expected payout is greater than the present value of the expected payments, the CDS has a negative value for the buyer.a. I only.b. II only.c. Both I and II.d. Neither I nor II.Answer: aAt inception, the value of a CDS is zero because the CDS will be priced so that the present value of expected payments made by the swap buyer is exactly equal to the present value of the expected payout in the event of default When the CDS is marked-to-market afterinception, a gain for one counterparty results in an equal loss for the other counterparty,meaning that marking a CDS to marker is a zero-sum game. If the PV of expected payout isgreater than the PV of the expected payments made, the CDS will have a positive value for the buyer since the buyer receives the larger expected payout. If the PV of the expectedpayout is less than the PV of the expected payments, the CDS has a positive value for the seller because the seller receives the expected payments.5. The Basel regulatory framework uses a "building block" approach, whereby a bank'sregulatory capital requirement is the sum of the capital requirements for various riskcategories. Among the risk categories relevant for the banking book and trading book withina financial institution, which of the following risks would be contained within Pillar I on thetrading book side?a. Interest rate risk.b. Business risk.c. Concentration risk.d. Liquidity risk.Answer: aPillar l, on the trading book side, contains counterparty credit risk, interest rate risk, equity risk, foreign exchange risk, commodity risk, and operational risk.。

University of Cambrid g e ESOL ExaminationsWhat does YLE Movers involve?This booklet is a brief introduction to YLE Movers.We show examples from each part of the test,but in some cases we do not show the full text or all of the questions.If you would like to see full sample papers for YLE Movers you can download them from our website at:/support/dloads/yle_downloads.htmThere is a defined set of vocabulary and structures for each level of YLE and you should make sure that you are familiar with the vocabulary and structures you need to know for YLE Movers.This list of grammar and structures and a list of vocabulary (in alphabetical order) is also available from our website.The table below shows the different parts of YLE Movers and how long each paper takes.I Listeningapprox.25 minutes (25 questions)There are five parts in the Listening test.You hear all the parts of the test twice.In the test,all the parts include an example.Information for candidates – YLE MoversDear ParentThank you for encouraging your child to learn English and to take this YLE (Young Learners English) Movers test.We believe that learning English should be fun and stimulating for children and we hope it will also be interesting for you to watch your child grow in confidence as he or she learns more and more English.Taking a test such as YLE Movers is an excellent way of motivating your child to learn and showing how much progress he or she has made.We have prepared this booklet to give you and your child a brief introduction to the different parts of YLE Movers and the type of questions you can expect to find.We hope you will take the time to read the booklet together with your child and that it will give you a clear picture of what we expect children to be able to do in English when taking YLE Movers.Young Learners English tests come to you from Cambridge ESOL (English for Speakers of Other Languages) which is part of Cambridge Assessment,a department of the world-famous University of Cambridge in the UK.So,you can be sure that we have created a test you can trust which will help your child to do his or her very best at English.We hope you enjoy preparing for and taking YLE Movers!With best wishesCambridge ESOLIn Part 1 you see a big picture which shows different people doing different things.There are seven names round the picture.You hear an adult and a child talking about the people in the picture.You have to draw a line from the name you hear to the correct person in the big picture.In the test,there are three more dialogues like the ones to the left of the picture.Part 2 (5 questions)In Part 2 you hear a conversation between two speakers.On the question paper there is a form or a page on a notepad.You have to write a word or a number in five places on the form or notepad.You do not have to spell words perfectly if they are not spelled out for you.In the test,there are three more dialogues and three more questions like the ones below.Peter Jim John SallyJane Daisy AnnaThis is what you hear …Can you see the line? This is an example.Now you listen and draw lines.OneMan:That’s a beautiful rainbow.Girl:Yes,it is.John’s very good at painting.Man:Who’s the girl that’s helping to paint it?Girl:The one who’s standing on a box?Man:Yes.Girl:That’s Sally.T woMan:Who’s the boy that’s painting the leaves?Girl:Which one?Man:The one with jeans and a blue T-shirt.Girl:Oh,he’s called Peter.Man:I love those leaves!This is what you hear …OneWoman:How many different kinds of animals did you see at the zoo?Boy:That’s difficult.Woman:Well,think about it.Boy:Oh … thirty,I think.Woman:Thirty! Good.T woWoman:What were the biggest animals that you saw?Boy:Erm … the giraffes,I think.Woman:Weren’t there any elephants?Boy:Oh yes,that’s right.The elephants were the biggest!In Part 3 you hear a conversation between a child and an adult.The child is telling the adult about what they did on different days during one week.You have to draw a line from the day of the week to the picture which shows what the child did on that day.In the test,there are three more dialogues like the ones below.We have done one example for you.Can you see the line from Sunday?This is what you hear …OneMan:What did you do on Saturday? Girl:I went for a long walk with my mum and dad.We took our dogwith us.Man:Did you enjoy it?Girl:It was OK,but it was verywindy that day.In the evening,we were all tired.T woMan:Did you go shopping last week, Sally?Girl:Yes,we did.We went to theshops in town on Mondayafternoon.I bought a presentfor my grandpa.Man:Did you drive into town?Girl:Yes.The weather was terrible that day and we didn’t want towalk.In Part 3 you hear five little dialogues.There is a question about each dialogue and you have to choose which of three pictures gives the answer to the question.You must put a tick ( ) under the correct picture.In the test,there are three more questions like the ones below.Part 5 (5 questions)In Part 5 you see a big picture.You listen to a dialogue between an adult and a child and must colour specific objects using the colour that you are instructed to use.You will also be asked to draw a simple object or write a short word somewhere in the picture.In the example below,we have already coloured the teacher’s hair for you.In the test,there are three more dialogues to listen to and three more objects to colour.Where did Jim see the film?AB C1 Where did the rabbits in the film go?Z OOA B CWhere did Jim see the film?12This is what you hear …OneBoy:I saw a good film last week.Woman:Oh,did your Mum take you to the cinema?Boy:No …Woman:Was it at your school,then?Boy:No,it was at my birthday party.Woman:Oh,I see!Boy:It was a DVD.T woBoy:The film was about some rabbits.Woman:Oh.I know the one.They have to find a new home.Did they go to live with the animals in a zoo?Boy:No,they didn’t do that!Woman:Oh.Well,did they go to a farm then?Boy:No.They went to live in a big forest.This is what you hear …OneMan:Now,do you want to colour something?Girl:Yes,please.Can I colour the clock?Man:OK,what colour?Girl:Blue is my favourite.Man:OK,that’s a good colour for the clock,then.T woMan:Now,would you like to write something for me?Girl:What? A word?Man:Yes,can you see the map on the wall?Girl:Behind the teacher?Man:That’s right.Can you write the word MAP below it?Girl:OK.I’m writing that now.I Reading and Writing30 minutes/40 questionsThere are six parts in the Reading and Writing test.In the test,all the parts include at least one example.You do not have to write much but you must take care to spell all your answers correctly.Part 1 (6 questions)In Part 1 you look at pictures of objects with their names written under them.You then read some definitions and must decide which picture matches each definition.You must copy that word next to its definition.In the test,there are four more questions like the ones below.Part 2 (6 questions)In Part 2 you look at a big picture and read six sentences about it.Some of the sentences describe the picture correctly and some do not.If the sentence says something true about the picture,then you write ‘yes’ after that sentence.If what the sentence says about the picture is not true,then you write ‘no’ after the sentence.In the test,there areQuestions 1You can eat this from a bowl. Sometimes there are vegetables in it._________________________________2This is the biggest animal in the world. It lives in the sea._________________________________Questions 1A big brown bear is having a shower.______________________________2There are some glasses below the mirror.______________________________3The yellow bear is fatter than the blue bear.______________________________In Part 3 you read a short conversation between two people.You have to choose what the second speaker says each time from a set of three choices (A,B or C).There is a picture on the question paper to set the scene.You should put a circle around the correct answer,like this, B .In the test,there are three more questions like the ones below.Part 4 (7 questions)In Part 4 you read a text which has six gaps in it.The missing words may be nouns,adjectives or verbs.Next to the text there is a box with labelled pictures.You choose the correct word from the box and copy it into each gap.Then you must choose the best title for the text from a choice of three possible titles.Jane:What’s the matter? Have you got a headache?Peter: A No, thank you. I don’t want one.B No, I’ve got toothache.C No, I haven’t got it.Jane:Would you like to come to my house?Peter: A Yes, I went home quickly.B No, thanks. I want to go home.C Well, I like my house a lot.3Jane:Have you got a coat?Peter: A Yes, it does.B OK, he’s here.C No, I haven’t.My name is Daisy. I like toys, but I like books and ___________ best. I lovestories about men on the moon and about (1)___________ who live in different countries.I read a good story yesterday. In this story, a boy climbed a(2)___________. At the top, there was a lot of snow. It was evening, but the boy could see the forest below him.He (3)___________ down on a rock to have a drink and to look up at all the (4)___________. But then he (5)___________ something that he didn’t understand. Something very big and round flew quietly and quickly behind a cloud. What was it? The boy didn’t know and he didn’t wait to see it again.He (6)___________ home to his village because he was very afraid. I wasn’t afraid! I enjoyed the story a lot!(7)Now choose the best name for the story.Tick one box.A boy that Daisy knows IA film that Daisy watched A story that Daisy likedcomicsIn Part 5 you read a story which is in three parts.Each part has a picture.There are sentences after each part of the story.You must complete the sentences,using one,twofamily went to the cinema.3Paul didn’t enjoy seeing _____________________ in the film.On Thursday, Paul thought aboutthe film. He didn’t want to swimin the sea. He sat on the beachand watched Sam and Vicky.They played in the water. Mumgave Paul an ice cream but hedidn’t want it. Then Dad said,‘Come on Paul! Let’s go for aswim.’ But Paul didn’t want to.4Sam and Vicky ________________________ in the sea.5Paul didn’t want the ice cream that his _________________________ gave him.6Dad wanted to go for __________________________ with Paul.If you want to read the end of the story,you can download a sample paper from our website at :/support/dloads/yle-downloads.htmIn Part 6 you read a factual text which has five gaps.The gaps are for grammar words like prepositions,pronouns and verbs.You have a choice of three words to fill each gap and must choose the correct word and copy it into the gap.I Speaking5–7 minutes/4 partsIn the Speaking test someone,perhaps your own teacher,will explain the test to you in your own language.That person will then take you into the exam room and will introduce you to the examiner.The examiner will give you marks for understanding what he or she says,for responding appropriately in English and for pronunciation.CatsCatshavegood eyes. They can see verywell at night.cats climb treesand eat meat. They can move very quietly and catch animals. Then they eat them. They have strong teeth.Theresmall cats and big cats like lionsand tigers. Only tigers livethe jungle.Lions don’t. Some people go and see lions and tigers at the zoo.A lot of p eop le have small cats in homes. These cats are pets. People thembecause they are beautiful.Example12345Example 12 34 5had Allam atyour likehave Everyare ontheir likinghas Anyis inour likesPart 1First the examiner will greet you and will ask you your name.Then he or she will show you two pictures which are similar but which have some differences.You must tell the examiner about four of the differences.Part 2In Part 2 the examiner will show you four pictures which tell a story.The examiner tells you about the first picture and then asks you to continue the story.The examiner might say,for example,‘Fred is sad.He can’t play football.His ball is very old.His mum is saying ‘Take the dog to the park’.You must then talk about the other three pictures.Part 3In Part 3 the examiner will show you four sets of four pictures.You must say which picture is the odd one out in each set and explain why.Part 4In Part 4 the examiner will ask you some questions about yourself.He or she might ask you,for example,about school,what you do at the weekends,your hobbies or your friends.Preparing for MoversIf you would like more practice material to help you prepare for the revised YLE Movers exam,past paper packs,including an audio CD of the Listening test (published by Cambridge University Press),will be available in late 2006.You can find more information,prices and details of how to order on our website at:/support/pastpapers.htmNext stepsWe wish you every success in taking Movers and we hope that you will take other Cambridge ESOL exams in future.Flyers is the next level of the Cambridge YLE tests.Youcan find more information about Flyers on our website at:/exams/yle.htmyle movers information for candidates11What do I get after I take the test?When you take a Young Learners English test,you get an award from Cambridge ESOLshowing how well you have done in each part of the test – Listening,Reading andWriting and Speaking.For each part of the test you get one or more Cambridge shields (up to a maximum offive,so you could get a total of 15 shields for the whole test if you do really well!).Belowis a picture of the award which shows you and your family how well you have done./YLEUniversity of CambridgeESOL Examinations1 Hills RoadCambridgeCB1 2EUUnited KingdomTel.+44 1223 553355Fax.+44 1223 460278email ESOL@© UCLES2006 EMC| 3697 | 6Y07 NOT FOR RESALE。

Table of ContentsIntroduction to 2020 FRM Part II Practice Exam (3)2020 FRM Part II Practice Exam – Statistical Reference Table (5)2020 FRM Part II Practice Exam – Special Instructions and Definitions (6)2020 FRM Part II Practice Exam – Candidate Answer Sheet (7)2020 FRM Part II Practice Exam – Questions (8)2020 FRM Part II Practice Exam – Answer Key (44)2020 FRM Part II Practice Exam – Answers & Explanations (45)IntroductionThe FRM Exam is a practice-oriented examination. Its questions are derived from a combination of theory, as set forth in the core readings, and “real-world” work experience. Candidates are expectedto understand risk management concepts and approaches and how they would apply to a risk manager’s day-to-day activities.The FRM Exam is also a comprehensive examination, testing a risk professional on a number of risk management concepts and approaches. It is very rare that a risk manager will be faced with an issue that can immediately be slotted into one category. In the real world, a risk manager must be able to identify any number of risk-related issues and be able to deal with them effectively.The 2020 FRM Part I and Part II Practice Exams have been developed to aid candidates in their preparation for the FRM Exam in May and November 2020. These Practice Exams are based on a sample of questions from prior FRM Exams and are suggestive of the questions that will be on the 2020 FRM Exam.The 2020 FRM Part I Practice Exam contains 100 multiple-choice questions and the 2020 FRM PartII Practice Exam contains 80 multiple-choice questions, the same number of questions that theactual 2020 FRM Exam Part I and 2020 FRM Exam Part II will contain. As such, the Practice Exams were designed to allow candidates to calibrate their preparedness both in terms of material and time.The 2020 FRM Practice Exams do not necessarily cover all topics to be tested in the 2020 FRM Examas any test samples from the universe of testable possible knowledge points. However, the questions selected for inclusion in the Practice Exams were chosen to be broadly reflective of the material assigned for 2020 as well as to represent the style of question that the FRM Committee considers appropriate based on assigned material.For a complete list of current topics, core readings, and key learning objectives, candidatesshould refer to the 2020 FRM Exam Study Guide and 2020 FRM Learning Objectives.Core readings were selected by the FRM Committee to assist candidates in their review of the subjects covered by the Exam. Questions for the FRM Exam are derived from the core readings. It is strongly suggested that candidates study these readings in depth prior to sitting for the Exam.Suggested Use of Practice Exams:To maximize the effectiveness of the practice exams, candidates are encouraged to follow these recommendations:1.Plan a date and time to take the practice exam.•Set dates appropriately to give sufficient study/review time for the practice exam prior to the actual exam.2.Simulate the test environment as closely as possible.•Take the practice exam in a quiet place.•Have only the practice exam, candidate answer sheet, calculator, andwriting instruments (pencils, erasers) a vailable.•Minimize possible distractions from other people, cell phones, televisions,etc.; put away any study material before beginning the practice exam.•Allocate 4 hours to complete FRM Part I Practice Exam and 4 hours to complete FRM Part II Practice Exam and keep track of your time. The actual FRM Exam Part I and FRMExam Part II are 4 hours each.•Complete the entire exam and answer all questions. Points are awarded for correct answers. There is no penalty on the FRM Exam for an incorrect answer.•Follow the FRM calculator policy. Candidates are only allowed to bring certain types of calculators into the exam room. The only calculators authorized for use on the FRMExam in 2020 are listed below; there will be no exceptions to this policy. You will not beallowed into the exam room with a personal calculator other than the following: TexasInstruments BA II Plus (including the BA II Plus Professional), Hewlett Packard 12C(including the HP 12C Platinum and the Anniversary Edition), Hewlett Packard 10B II,Hewlett Packard 10B II+ and Hewlett Packard 20B.3.After completing the FRM Practice Exams•Calculate your score by comparing your answer sheet with the practice exam answer key.•Use the practice exam Answers and Explanations to better understand the correct and incorrect answers and to identify topics that require additional review. Consultreferenced core readings to prepare for the exam.•Remember: pass/fail status for the actual exam is based on the distribution of scores from all candidates, so use your scores only to gauge your ownprogress and level of preparedness.Special Instructions and Definitions1.Unless otherwise indicated, interest rates are assumed to be continuously compounded.2.Unless otherwise indicated, option contracts are assumed to be on one unit of the underlying asset.3.bp(s) = basis point(s)4.CAPM = capital asset pricing modelP = central counterparty or central clearing c ounterparty6.CDO = collateralized debt obligation(s)7.CDS = credit default swap(s)8.CEO, CFO, CIO, and CRO are: chief executive, financial, investment, and risk officers, respectively9.CVA = credit value adjustment10.ERM = enterprise risk management11.ES = expected shortfall12.EWMA = exponentially weighted moving average13.GARCH = generalized auto-regressive conditional heteroskedasticity14.LIBOR = London interbank offered rate15.MBS = mortgage-backed-security(securities)16.OIS = overnight indexed swap17.OTC = over-the-counter18.RAROC = risk-adjusted return on capital19.VaR = value-at-risk20.The following acronyms are used for selected c urrencies:2020 FRM Part II Practice Exam – Candidate Answer Sheet1. A global bank possesses subsidiaries with banking licenses in various countries, including Singapore, Australia,and UK. Regulators in these countries have recently announced their intention to examine the bank’s risk culture framework and its policies regarding conduct and culture. According to best practices described in recent publications, which of the following actions would the regulators most likely perform?A. Increase the bank’s operational risk capital requirementsB.Review the bank’s accountability standards for its senior managementC.Require that the bank implement quantitative approaches to model conduct and cultureD.Recommend that the bank increase the proportion of incentive compensation for its traders andinvestment bankers2. A risk manager is estimating the market risk of a portfolio using both the arithmetic returns with normaldistribution assumptions and the geometric returns with lognormal distribution assumptions. The manager gathers the following data on the portfolio:• Annualized average of arithmetic returns: 12%• Annualized standard deviation of arithmetic returns: 30%• Annualized average of geometric returns: 11%• Annualized standard deviation of geometric returns: 41%• Current portfolio value: EUR 5,200,000• Trading days in a year: 252Assuming both daily arithmetic returns and daily geometric returns are serially independent, which of the following statements is correct?A.1-day normal 95% VaR = 3.06% and 1-day lognormal 95% VaR = 4.12%B.1-day normal 95% VaR = 3.57% and 1-day lognormal 95% VaR = 4.41%C.1-day normal 95% VaR = 4.12% and 1-day lognormal 95% VaR = 3.57%D.1-day normal 95% VaR = 4.46% and 1-day lognormal 95% VaR = 4.49%3. A credit manager in the counterparty risk division of a large bank uses a simplified version of the Mertonmodel to monitor the relative vulnerability of its largest counterparties to changes in their valuation andfinancial conditions. To assess the risk of default of three particular counterparties, the manager calculates the distance to default assuming a 1-year horizon (t=1). The counterparties: Company P, Company Q, andCompany R, belong to the same industry, and are non-dividend-paying firms. Selected information on thecompanies is provided in the table below:Using the information above with the assumption that a zero-coupon bond maturing in 1 year is the onlyliability for each company, and the approximation formula of the distance to default, what is the correctranking of the counterparties, from most likely to least likely to default?A. P; R; QB. Q; P; RC.Q; R; PD. R; Q; P4. Bank HJK has written puts on Bank PQR stock to a hedge fund and sold CDS protection on Bank PQR to amanufacturer. Bank HJK and Bank PQR operate in several of the same businesses and geographies and their performances are highly correlated. Many in the market are concerned that rising interest rates couldnegatively impact the credit quality of Bank HJK’s numerous borrowers, which in turn would increase thecredit spread of Bank HJK. From the perspectives of the hedge fund and the manufacturer, which of thefollowing is correct with respect to their counterparty risk exposure to Bank HJK?Hedge Fund ManufacturerA. Right-way risk Wrong-way riskB. Wrong-way risk Right-way riskC.Right-way risk Right-way riskD. Wrong-way risk Wrong-way risk5. A risk consultant has been tasked with assessing a small bank’s liquidity risk profile. While reviewing apresentation produced by the bank, the consultant comes across a list of early warning indicators used to signal potentially heightened liquidity risk. Which of the following trends should the consultant consider as thestrongest warning signal for potential liquidity risk at the bank?A. Decrease in stock price of the bank’s peers but not in the stock price of the bank itselfB. Increase in credit lines received from other financial institutionsC.Widening spreads on the bank’s issued debt and credit default swapD. Significant asset growth funded by an increase in stable liabilities6. An investment bank has a one-way credit support annex (CSA) on a bilateral transaction with a hedge fundcounterparty. Under the terms of the CSA, the mark-to-market value of the transaction forms the basis of the hedge fund’s collateral requirements, which are provided below:Assuming the net exposure increases to CNY 27,000,000 and the mark-to-market value of collateral posted has not changed, how much additional collateral will the hedge fund have to post?A. CNY 0B. CNY 1,990,000C. CNY 2,000,000D. CNY 2,500,0007. The board of directors of an insurance company has identified a number of potential growth opportunities forthe company to consider. To help assess these opportunities and determine an optimal risk structure to use across the organization, the risk committee has recommended that the company implement an ERMprogram. Which of the following would best represent an appropriate goal for the firm to state as part of the ERM program?A. Determine a risk-return trade-off that reflects the company’s target credit rating and ensure that businessunit managers evaluate new projects with this firm-wide target in mind.B. Attempt to eliminate the company’s probability of financial distress t o maximize company value.C. Maximize the firm's leverage ratio within its risk tolerance to ensure the highest expected return on equity.D. Establish a target minimum level of annual earnings and guarantee to shareholders that it will maintain thislevel.8. A US pension fund had assets and liabilities valued at USD 840 million and USD 450 million, respectively, atthe end of 2017. The fund’s assets were fully invested in equities and commodities while its liabilitiesconsisted entirely of fixed-income obligations. The fund reported that by the end of 2018 the value of assets decreased by 14.0% and the value of liabilities increased by 3.5%. Assuming no changes were made to the composition of the assets and liabilities during the yea r, what was the change in the pension fund’s surplus over the 1-year period?A. USD -133.4 millionB. USD -117.6 millionD 256.7 millionD. USD 390.0 million9. A wealth management firm has a portfolio consisting of USD 37 million invested in US equities and USD 48million invested in emerging markets equities. The US equities and emerging markets equities both have a 1-day 95% VaR of USD 1.3 million. The correlation between the returns of the US equities and emergingmarkets equities is 0.25. While rebalancing the portfolio, the manager in charge decides to sell USD 7million of the US equities to buy USD 7 million of the emerging markets equities. At the same time, the CRO of the firm advises the portfolio manager to change the risk measure from 1-day 95% VaR to 10-day 99% VaR. Assuming that returns are normally distributed and that the rebalancing does not affect the volatility of the individual equity positions, by how much will the portfolio VaR increase due to the combined effect of portfolio rebalancing and change in risk measure?A. USD 4.373 millionB. USD 6.428 millionD 7.034 millionD. USD 9.089 million10. An operational risk manager is asked to report a bank’s operational risk capital under the StandardizedMeasurement Approach (SMA) proposed by the Basel Committee in March 2016. The treasury department produces the following data for the bank, calculated according to the SMA guidelines:•Business Indicator (BI): EUR 1,200 million•Internal Loss Multiplier: 1In addition, the manager uses the Business Indicator buckets in the Business Component presented inthe table below:What is the correct operational risk capital that the bank should report under the SMA?A. EUR 120 millionB. EUR 150 millionC.EUR 158 millionD. EUR 180 million11. A credit manager who is well versed in lessons learned from the 2007–2009 subprime mortgage crisis in the USis overseeing the structured credit book of a bank in order to identify potential problems of information flow (frictions) between the parties involved in the securitization process. Which of the following is a correctcombination of a potential friction in the securitization process and an appropriate mechanism to mitigate that friction?A. Friction between the asset manager and the investor: Adverse selection problem. This problem canbe mitigated by the asset manager charging due diligence fees to the investor.B. Friction between the arranger and the originator: Model error problem. This problem can be mitigated bythe arranger providing a credit enhancement to the securitized products with its own funding.C.Friction between the investor and credit rating agencies: Principal-agent conflict. This problem can bemitigated by requiring credit rating agencies to be paid by originators and not by investors for theirrating services.D. Friction between the servicer and the mortgagor: Moral hazard problem. This problem can be mitigatedby requiring the mortgagor to escrow funds for insurance and tax payments.12. A risk manager is backtesting a company’s 1-day 99.5% VaR model over a 10-year horizon at the 95%confidence level. Assuming 250 trading days in a year and the daily returns are independently and identically distributed, which of the following is closest to the maximum number of daily losses exceeding the 1-day99.5% VaR in 10 years that is acceptable to conclude that the model is calibrated correctly?A. 19B. 25C.35D. 3913. A portfolio manager is mapping a fixed-income portfolio into exposures on selected risk factors. The manageris analyzing the comparable mechanics and risk measurement outputs of principal mapping, durationmapping, and cash-flow mapping. Which of the following is correct?A. Cash-flow mapping groups cash flows into buckets based on their size.B. Cash-flow mapping uses the average rates in each risk group as a discount factor.C.Principal mapping incorporates correlations among zero-coupon bonds.D. Duration mapping replaces the portfolio with a zero-coupon bond with maturity equal to the duration of theportfolio.14. A CRO of a hedge fund is asking the risk team to develop a term-structure model that is appropriate for fittinginterest rates for use in the fund’s options pricing practice. The risk team is evaluating several interest rate models with time-dependent drift and time-dependent volatility functions. Which of the following is a correct description of the specified model?A. In the Ho-Lee model, the drift of the interest rate process is presumed to be constant.B. In the Ho-Lee model, when the short-term rate is above its long-run equilibrium value, the drift ispresumed to be negative.C.In the Cox-Ingersoll-Ross model, the basis-point volatility of the short-term rate is presumed to beproportional to the square root of the rate, and short-term rates cannot be negative.D. In the Cox-Ingersoll-Ross model, the volatility of the short-term rate is presumed to decline exponentiallyto a constant long-run level.15.Due to lack of available investment opportunities in public markets, a pension fund decided to hire aninvestment consultant to assess the potential for investing in illiquid markets in the US. Which of the following characteristics of illiquid markets in the US should the consultant present to the pension managers?A. Municipal bonds are usually more liquid than pink-sheet over-the-counter equitiesB. The traditional public, liquid markets of stocks and bonds are larger than the total wealth held in illiquidassets.C. The share of illiquid assets in institutional portfolios has generally gone up in the past 2 decades.D. During the 2008-2009 Financial Crisis, liquidity dried up in repo markets but not in commercial papermarkets.16. A mid-size investment bank conducts several trades. As part of its risk control, it has entered into nettingagreements on 8 equity trade positions with an average correlation of 0.28. The firm believes that it canimprove upon the diversification benefit of netting by revising the current agreement. Assuming values of future trade positions are normally distributed, which of the following trade combinations would increase the firm’s expected netting benefit the most from the current level?A. Trade combination ABCB. Trade combination LMNC. Trade combination PQRD. Trade combination TUV17. A regional bank wants to improve its operational resilience to help keep pace with emerging best practices inthis area. A consultant hired by the bank recommends that it establish a set of impact tolerances to improve its resilience. Which of the following correctly describes a potential benefit to the bank of establishing an impact tolerance?A.It will enhance the bank’s ability to identify and limit concentration risk.B.It will accurately estimate the severity of a potential disruption to an operational process and the amountof downtime that would result.C.It will help the bank optimize its allocation of resources to its most important business services.D.It will prevent failures of critical operational processes and the systems that support these processes.18. A manager is evaluating the risks of a portfolio of stocks. Currently, the portfolio is valued at CNY 124 millionand contains CNY 14 million in stock Y. The annualized standard deviations of returns of the overall portfolio and of stock Y are 16% and 12%, respectively. The correlation of returns between the portfolio and stock Y is0.52. Assuming the risk analyst uses a 1-year 95% VaR and the returns are normally distributed, what is thecomponent VaR of stock Y?A. CNY 0.103 millionB. CNY 1.437 millionY 2.032 millionD. CNY 3.685 millionQUESTIONS 19 AND 20 REFER TO THE FOLLOWING INFORMATION:XYZ, a small investment management firm, specializes in structuring small business loans and selling the government guaranteed portion to other institutional investors while retaining the riskier portions for high net worth investors. XYZ funds its operations by engaging in overnight repurchase agreements (repos) with three firms, but primarily with ABC, a firm that XYZ also has a large line of credit with. ABC specializes in pooling funds from community banks and local government agencies and investing them in short-term, high-quality, government-secured investments.Last week, XYZ was informed by ABC that its line of credit had been frozen. XYZ learned that ABC had been defrauded by Repo Co., another of its repo borrowers, who had provided false documentation of non-existent collateral of government-guaranteed loans. ABC feared a run by its investors as news of the fraud spread.The diagram below illustrates the parties involved:19.The use of a central clearinghouse to handle the transactions executed between XYZ's main funding source,ABC and ABC's client, Repo Co., would likely have resulted in a reduction in:A. ABC's funding liquidity riskB. Repo Co.'s default riskC.XYZ's lending riskD. ABC's operational risk20.By using a clearinghouse to handle the repo transactions between ABC Co. and Repo Co., obligations owedbetween the two could have been netted once the fraudulent documentation was discovered. Which of the following is the most appropriate type of netting to use in this situation and what would be a likely additional impact from using this netting?A. Payment netting would be used, which would reduce ABC's counterparty risk, but this risk would betransferred to other creditors outside the clearinghouse.B. Payment netting would be used, which would reduce Repo Co.'s counterparty risk, but ABC's counterpartyrisk would be increased.C.Closeout netting would be used, which would reduce ABC's counterparty risk, but this risk would betransferred to other creditors outside the clearinghouse.D. Closeout netting would be used, which would reduce Repo Co.'s counterparty risk, but ABC's counterpartyrisk would be increased.21.The CRO at a bank wants to strengthen the bank’s capability to defend itself against emerging cyber-threats. Tohelp achieve this goal, the CRO is assessing the current range of practices regarding the sharing ofcybersecurity information between different types of institutions, as well as the potential benefits from sharing information. Which of the following statements would be most appropriate for the CRO to make?A. The sharing of cybersecurity information among banks is less frequently observed and generally consideredto be less effective than other cyber-security information-sharing practices.B. The scope and depth of information-sharing practices among banks may significantly vary between financialmarkets, depending on the level of trust among participating banks.rmation-sharing among different national regulators has evolved significantly over the past several yearsand is now a widespread practice at a large majority of jurisdictions.D. Existing peer-sharing mechanisms among banks focus on the exchange of information related to cyber-security incidents, but such information is generally not shared from banks to regulators.22.A risk manager is training junior risk analysts at an international bank. The manager is instructing them about thedifference between repurchase agreements (repos) and reverse repurchase agreements (reverse repos), as well as the relevant market participants. Which of the following is a correct statement for the manager to present to the class?A. A trader who would like to short a bond could enter into a repo to borrow the bond.B. Haircuts on collateral are typically charged to those who lend collateral in repo transactions, but margin callsare usually not made.C.When financing a purchase of securities, financial institutions often sell the repo to avoid putting up fullpurchase price for the securities.D. Money market mutual funds tend to enter into a repo to invest short-term liquid instruments.23.The risk audit committee of an equity mutual fund is reviewing a portfolio construction technique proposed by anew portfolio manager who has recently been allocated capital to manage. The fund typically grants its portfolio managers flexibility in selecting and implementing appropriate portfolio construction procedures but requires that any methodology adopted fulfills key risk control objectives set by the firm. Which of the following portfolio construction techniques and its capability for risk control in portfolio construction is correct?A. Quadratic programming allows for risk control through parameter estimation but generally requires manymore inputs estimated from market data than other portfolio construction techniques require.B. The screening technique provides superior risk control by concentrating stocks in selected sectors based onexpected alpha.C.When using the stratification technique, risk control is implemented by overweighting the categories withlower risks and underweighting the categories with higher risks.D. When using the linear programming technique, risk is controlled by selecting the portfolio with the lowestlevel of active risk.24.An analyst reports the following fund information to the advisor of a pension fund that currently invests ingovernment and corporate bonds and carries a surplus of USD 40 million:To evaluate the sufficiency of the fund's surplus, the advisor estimates the possible surplus values at the end of 1 year. The advisor assumes that annual returns on assets and the annual growth of the liabilities are jointly normally distributed and their correlation coefficient is 0.68. Assuming that the volatility of surplus is USD35.76 million, what is the lower bound of the 95% confidence interval for the expected end-of-year surplusthat the advisor can report?A. USD -76.4B. USD -58.2D -33.3D. USD -22.025. A treasurer at a small regional bank is assessing the bank’s liquidity position. The treasurer estimates that thefollowing cash inflows and outflows will occur in the next week:Which of the following is the correct amount, at the week’s end, for the bank’s net liquidity position?A. -80B. -20C.40D. 10026. A packaging materials manufacturer is considering a project that has an estimated risk-adjusted return oncapital (RAROC) of 15%. Suppose that the risk-free rate is 3% per year, the expected market rate of return is 11% per year, and the company's equity beta is 1.8. Using the criterion of adjusted risk-adjusted return on capital (ARAROC), the company should:A. Reject the project because the ARAROC is higher than the market expected excess return.B. Accept the project because the ARAROC is higher than the market expected excess return.C.Reject the project because the ARAROC is lower than the risk-free rate.D. Accept the project because the ARAROC is lower than the risk-free rate.27. A derivative trading firm only trades derivatives on rare commodities. The company and a handful of otherfirms, all of whom have large notional outstanding contracts with the company, dominate the market for such derivatives. The company’s management would like to mitigate its overall counter party exposure, with the goal of reducing it to almost zero. Which of the following methods, if implemented, could best achieve this goal?A. Ensuring that sufficient collateral is posted by counterpartiesB. Diversifying among counterpartiesC.Cross-product netting on a single counterparty basisD. Purchasing credit derivatives, such as credit default swaps28.HIP Bank (HIP) often enters into interest rate swaps with ADB Banking Corporation (ADB) on terms that reflectappropriate counterparty risk. Earlier in the year, HIP and ADB entered into a 3-year swap in which ADBagreed to pay HIP a fixed rate of 5% in return for 6-month LIBOR plus a spread. Since the swap was entered into, both banks were downgraded. As a result of the ratings changes, the credit spread for HIP has increased from 36 bps to 144 bps, while the credit spread for ADB has increased from 114 bps to 156 bps. Assuming no change in the LIBOR curve, if an identical 3-year swap was entered into today, which of the following is the most likely to be correct?A. Since HIP’s spread increased more than ADB’s spread, HIP’s DVA will increase and ADB’s DVA willdecrease.B. Since HIP’s spread increased more than ADB’s spread, HIP’s CVA will increase and ADB’s CVA willdecrease.C.Since both banks’ spreads increased, the CVA on both sides of the contract will be higher.D. Since both banks’ spreads increased, the DVA on both sides of the contract will be lower.。

FRM二级常见易错题1.For banks that use the advanced internal ratings-based(advanced IRB) approach to credit risk,the primary inputs to the capital calculations are:(保留)A.Credit assessments of external rating agencies.B.The banks'internal assessments ofkey risk drivers.C.Mandated by bank supervisors.D.Interest rates.2.The cumulative probability of default for a note over tvvo years is3.8%. If the probability of default during the first year is1.5%,the probability of default during the second year is closest to:(保留)A.2.96%B.2.34%C.3.17%D.3.28%3.Pillar III of the Basel II accord includes all ofthe following requirements for internationally active banks except:(保留)A.A formal disclosure policy should be established,and supported by a bank's board of directors.B.Banks should operate above minimum regulatory capital ratios.C.Financial statements that fairly retlect financial condition should be Pllblished reglllarly.D.There should be specific remedial actions in the event of nondisclosure.Answer:1.BUnder the advanced IRB approach,the bank uses its own intβmal measures of credit risk andexposure in capital calculations2.BThe cumulative probability of default is equal to one minus the probabiJity of surviving to the endofthe period without default:C2=1-(1-p1)(1-P2)0.038=1-(1-0.015)(1-P2)=>P2= 0.02343.BThe requirement to operate above minimum regulatory capital ratios is a requirement laid out in Pillar II regarding the interaction of supervisors and internationally active banks. Note that PillarIII relates to market discipline and disclosure.4.How many of the following statements concerning the capital structure in a securitization are most likely correct?(保留)I.The mezzanine tranche is typically the smallest tranche size.II.The mezzanine and equity tranches typicaUy offer fixed coupons.III.The senior tranche typically receives the lowest coupon.A.No statements are correct.B.One statement is correct.C.Two statements are correct.D.Three statements are correct.5.Identify the risks in a convertible arbitrage strategy that takes long positions in convertible bonds hedged with short positions in treasuries and the underlying stock.(保留)A.short implied volatilityB.long durationC.long stock deltaD.positive gamma6.A pool of high yield bonds is placed in an SPV and three tranches (including the equity tranche)of bonds are issued collateralized by the bondsto create a Collateralized Bond Obligation(CBO).Which of the following is true? (保留)A.At fair value,the value of the issued bonds should be less than the collateralB.At fair value,the total default probability,weighted by size of issue,of the issued bonds should equal the default probability of the collateral poolC.The equity tranche of the CBO has the least risk of defaultD.The yield on the low risk tranche must be greater than the yield on the collateral poolAnswer:4.BSenior tranches are perceived to be the safest,so they receive the lowest coupon.The equity tranche receives residual cash flows and no explicit coupon.Although the rnezzanine tranche is often thin,the equity tranche is typically the thinnest slice.5.DThis position is hedged against interest rate risk,so B is wrong.It is also hedged against directional movements in the stock,so C is wrong.The position is long an option (option to convert the bond into the stock)and so is long implied volatility,so A is wrong. Long options positions have positive gamma.6.BA Collateralized Bond Obligation and the underlying securities must have equal market value,similar cash flow pattern and identical risk,which eliminate choice A in favor of B. The equity tranche has the greatest risk of default;the yield on the low risk tranche must be less than the yield on the collateral pool.7.A risk analyst in a fund of funds is gauging the liquidity risk exposure of a hedge fund by examining the autocorrelation in the fund's returns.If found,a significant first-order autocorrelation coefficient of0.5for the monthly historical returns can be seen as an indicator of all of the following except: (保留)A.High market frictions.B.Historical return smoothing.C.Engaging in a managed futures strategy.D.Investments in the equity of non-public firms.Answer:7.CAutocorrelation(自相关):残差项之间存在correlation,市场越有效,自相关发生的可能性越小。

FRM二级习题1. After estimating the 99%, l-day VaR of a bank's portfolio to be USD l,484 using historicalsimulation with 1000 past trading days, you are concerned that the VaR measure is notproviding enough information about tail losses. You decide to re-examine the simulation results and sort the simulated daily P&L from worst to best giving the following worst 15 scenarios:Scenario Rank Daily P/L1 USD -2,8332 USD -2,3333 USD -2.2284 USD -2.0845 USD -1,9606 USD -1,7517 USD -1,6798 USD -1,5589 USD -1,54210 USD -1,48411 USD -1,45012 USD -1,42813 USD -1,36814 USD -1,34715 USD -1.319What is the 99Vo, l-day expected shortfall of the portfolio?A. USD 433B. USD l,285C. USD l,945D. USD 2.833Answer: CExplanation:Expected Shortfall = Average of the worst 10 daily P&L = USD 1945.2. Which of following statement about mortgage-backed securities (MBS) is correct?I The price of a MBS is more sensitive to yield curve twists than zero-coupon bonds.II When the yield is higher than the coupon rate of a MBS, the MBS behaves similar to corporate bonds as interest rates change.A. I onlyB. II onlyC. BothD. NeitherAnswer: CExplanation:I. This statement is correct. MBS' cash flows are like annuities, which are more sensitive toyield curve twist because of reinvestment risk. Normal bond has a lump sum payment atmaturity, which implies less reinvestment risk.II. This statement is correct. When yield is higher than MBSJ coupon rate, the embedded call option is out of the money. It is much the same as a normal bond.3. A fixed-income portfolio with market value of USD 60 million, modified duration of 2.53years and yielding 4.7Vo compounded semiannually. What would be the change in the value of this portfolio after a parallel rate decline of 20 basis points in the yield curve?A. A loss of USD 607,200B. A loss of USD 303,600C. A gain of USD 303,600D. A gain of USD 607,200Answer: CExplanation:By definition, D mod = (-l/P) * (dP/dy). So as a linear approximationAP = -l * Ay * D mod * P = -l * -0.0020 * 2.53 * 60 = 0.3036 million4. Assuming equal strike prices and expiration dates, which of the following options should bethe least expensive?A. American call optionB. Shout call optionC. European call optionD. Lookback call optionAnswer: CExplanation:C is correct. The shout call option and lookback call option are clearly wrong, since theygrant more rights to the buyer than the European call option. American calls also offer more to the buyer than the European calls.5. Edward Art, a CFO of Bank of Mitsubishi, has recently proposed to increase the bank'sliquidity by securitizing existing credit card receivables. Edward's proposed securitization includes tranches with multiple internal credit enhancements as shown in Exhibit l below.The total value of the collateral for the structure is USD 680 million, the lockout period is two years, and the subordinated tranche B bond class is the first loss piece:Exhibit l. Proposed ABS StructureBond Class Par ValueSenior tranche USD 270 millionJunior tranche A USD 230 millionJunior tranche B USD 80 millionSubordinated tranche A USD 60 millionSubordinated tranche B USD 40 millionTotal USD 680 million At the end of the fourteenth month after the securities were issued, the underlying credit card Accounts have prepaid USD 300 million in principal in addition to regularly scheduledprincipal and interest payments.What is the amount of the prepaid principal paid out to the holders of the junior tranche A bond class?A. USD 0 millionB. USD 30 millionC. USD 120 millionD. USD 230 millionAnswer: AExplanation:d: is correct. The securities have a two-year lockout period; all principal prepayments withinthe first two years will be used to fund new loans. No security tranche will receive principal prepayments until after the 24 months lockout period. Credit card prepayments are usually just rolled into new loans (not repaid to bondholders).。

FRM二级模拟题(二)1. Kate Harrison, FRM, is the risk manager for a medium-sized, regional depository institutionwith significant concentration risk in outstanding loans. She is trying to estimate and hedge the banks' exposure to credit losses. First, Kate has decided to estimate credit VaR usingCreditPortfolio View because of its use of macroeconomic transition matrices. She decided not to use the CreditRisk+ approach because of its reliance on non-parametric methods.Lastly, she is concerned that the proposed hedge bears counterparty risk and proposes avulnerable option calculation to evaluate this risk. Which of Kate's conclusions are accurate?a. Her statement about CreditPortfolioView and CreditRisk+ are correct, but her statementabout vulnerable options is not.b. Her statement about CreditPortfolioView is correct, but her statements about CreditRisk+and vulnerable options are not.c. Her statement about CreditRisk+ and vulnerable options are correct, but her statementabout CreditPortfolio View is not.d. Her statements about CreditPortfolioView and vulnerable options are correct, but herstatement about CreditRisk十 is not.Answer: dVulnerable options are options with positive probability of default. CreditRisk + assumes a specific functional Form and does not use non-parametric methods. CreditPortfolio View incorporates macroeconomic transition matrices since macro factors are the principal drivers of default.2. In determining thar prior capital asset pricing model (CAPM) tests of validity were flawed,Richard Roll and other researchers tried to correct for flawed security market line (SML) estimates by using portfolios rather than individual securities. How would the results of their first-pass and second-pass regression estimates be best described when the portfolio approach was used?a. The first-pass regression and second-pass regression were equally accurate.b. The second-pass regression was more accurate, improved by the portfolio approach.c. There were more observations in the second-pass regression, so portfolios wereconstructed with the smallest possible dispersion of beta coefficients.d. There were fewer observations in the second-pass regression, so portfolios wereconstructed with the greatest possible dispersion of beta coefficients.Answer: dAlthough the first-pass regression was estimated more accurately, it was at the expense of the second-pass regression due to fewer observations from the grouping of portfolios. To adjust, portfolios were constructed with the highest possible dispersion of beta coefficients.3. In Basel II, the foundation and advanced IRB approaches differ primarily in terms of theinputs that are provided by the bank based on its own estimates and those that have beenspecified by the supervisor. For the foundation approach, the inputs provided by the bank are the:a. probability of default.b. loss given default and exposure at default.c. probability of default and loss given default.d. probability of loss given default and maturity.Answer: aIn the foundation approach, only the probability of default is based on the bank's ownestimate.4. Trader A purchased a 3-month floating lookback call option on ABA stock three months ago.Trader B purchased a 3-month fixed lookback call option on the same stock during the same time period as Trader A. ABA stock finished at $50 at the end of the three-month option term, and the initial strike price was equal to $40. The minimum stock price over the investment horizon was $35, and the maximum stock price over the investment horizon was $53. The payoff difference between the floating lookback call and the fixed lookback call is closest to:a. $2.b. $3.c. $8.d. $10.Answer: aA floating lookback call pays the difference between the expiration price and the minimumprice of the stock over the horizon of the option. Therefore, its payoff is equal to: $50 - $35 = $15. A fixed lookback call has a payoff function equal to the difference between themaximum price during the option's life and the strike price. Therefore, its payoff is equal to: $53 - $40 = $13. The payoff difference between the two exotic options is equal to $2.5. An analyst has the following .information pertaining to Portfolio x:. Risk-free rate = 2%.. Actual portfolio return = 10% .. Relevant benchmark return - 8%.. Portfolio standard deviarion = 5%.. Observed tracking error = 3%.Which of the following statements regarding Portfolio X is correct?a. The information ratio is 0.67.b. The information ratio is l.60.c. The Sharpe ratio is 0.40.d. The Sharpe ratio is 2.67.Answer: aThe information ratio is calculated as: (10% - 8%) / 3% = 0.67The Sharpe ratio is calculated as: (l0% - 2%) / 5% = 1.60。

frm考试题及答案FRM(Financial Risk Manager)考试是由全球风险管理专业人士协会(GARP)提供的金融风险管理领域的专业认证考试。
以下是一份模拟的FRM考试题目及其答案:FRM考试模拟题一、单项选择题1. 在现代投资组合理论中,哪一项是投资组合风险的主要来源?A. 系统性风险B. 非系统性风险C. 利率变动D. 汇率波动答案:A2. 以下哪个不是信用评级机构?A. 标准普尔B. 穆迪C. 惠誉D. 花旗银行答案:D3. 风险价值(VaR)是一种衡量投资组合在一定置信水平下,一定时间内可能遭受的最大损失的方法。
它属于哪种风险管理技术?A. 敏感性分析B. 压力测试C. 极值理论D. 统计风险管理答案:D二、多项选择题4. 以下哪些因素会影响期权的时间价值?A. 期权的执行价格B. 期权到期前的时间长度C. 标的资产的波动性D. 无风险利率答案:B, C, D5. 在进行市场风险管理时,以下哪些措施是有效的?A. 多元化投资B. 风险对冲C. 增加杠杆D. 风险转移答案:A, B, D三、简答题6. 描述一下什么是流动性风险,并给出一个金融机构可能面临的流动性风险的例子。
答案:流动性风险是指金融机构在需要时无法以合理成本迅速出售资产或获得资金的风险。
一个例子是银行在金融危机期间面临大量客户同时提取存款,导致银行流动性枯竭。
四、计算题7. 假设一个投资组合由两种资产组成,资产A和资产B。
资产A的预期收益率为10%,标准差为15%,资产B的预期收益率为8%,标准差为10%。
如果投资组合由60%的资产A和40%的资产B组成,且两种资产的相关系数为0.5,请计算投资组合的预期收益率和标准差。
答案:预期收益率 = 0.6 * 10% + 0.4 * 8% = 9.2%标准差= √(0.6^2 * 15%^2 + 0.4^2 * 10%^2 + 2 * 0.6 * 0.4 * 0.5 * 15% * 10%) = √(10.125% + 4% + 6%) = √20.125% ≈ 14.17%结束语:以上题目仅供参考,实际FRM考试内容和难度可能会有所不同。

试卷:FRM 诺曼底PART 2-201905操作风险测量与管理(40道题)第1题(单选题)Leopard Zhang, CFA, is the top trader in Huangpu Asset Manager. As the most profitable trader, Zhang is profit-oriented, defiant and unruly. In this investment bank, board of directors and senior executives acquiesce some of Zhang’s behaviors, despite these behaviors have violated bank’s rule. Furthermore, it makes a very bad example for other traders, even other employees in this bank. Zhang has begun to hide some of his major deals recently. However, nobody has found these severe problems. Which of the following pairs of the 11 principles of risk management has Huangpu Asset Manager most clearly violated?• A. Principle 1 (a strong risk management culture) and Principle 2 (develop an integrated approach to operational risk management).• B. Principle 1 (a strong risk management culture) and Principle 6 (understand the risk and incentives related to risk inherent in the banks business lines andprocesses).• C. Principle 6 (understand the risk and incentives related to risk inherent in the banks business lines and processes) and Principle 7 (establish a rigorous approval process for new lines of business).• D. Principle 2 (develop an integrated approach to operational risk management) and Principle 7 (establish a rigorous approval process for new lines of business).第2题(单选题)Tse Group is a large banking holding company (BHC). It is constructed by some majorM&As primarily. Because of the reason, this group still has five independent risk management and reporting lines, and the heads of the five risk management offices rarely share information. Besides that, mandatory vacation system still stays on paper. Furthermore, public relation office of Tse Group has very limited information, so it is the convention for them to supply biased information to the public. Which of the following 11 fundamental principles of risk management has the bank most clearly violated? (1 )I. Principle 2 (risk management integrated into the bank’s overall risk management processes).II. Principle 3 (approve and review the operational risk framework)III. Principle 9 (strong control environment that utilizes policies, processes and systems; appropriate internal controls; and appropriate risk mitigation and transfer strategies). IV. Principle 11 (public disclosures should allow stakeholders to assess its approach to operational risk management).• A. I & II• B. I & III• C. II & III• D. I & III & IV.第3题(单选题)The members of the board of directors should have which of the following responsibilities related to risk management:I. The board must approve the firm's risk management policies and procedures.II. The board must be able to evaluate the performance of risk management activities. III. The board must maintain oversight of risk management activities.• A. I and II only• B. II and III only• C. I and III only• D. I, II, and III第4题(单选题)If the target of using scorecards is acquiring a high-level understanding of risks in data, which of the following viewpoints is the most appropriate one?• A. Data quality issues view.• B. Data process issues view.• C. Business impact view.• D. Business process view.第5题(单选题)There are no conflicts in data sets is necessary before we analyze data. If the cash distribution value in transaction book is different with that in reconciliation book, which of the following kinds of data consistency violates?• A. Record level.• B. Temporal level.• C. Cross-record level.• D. Infinite level.第6题(单选题)Risk control self-assessment (RCSA) program includes several steps. Which statement is least likely a step in RCSA?• A. Reports to the Central Bank should be prepared, and the reports should include the degree of OpRisk.• B. Risk metrics and other OpRisk initiatives should be prepared and linked to the RCSA program.• C. Control effect are considered and added to RCSA, then risk self-assessment (RSA) could consider risk mitigation.• D. Risks associated with each business unit’s and line’s activities should be identified and assessed thoroughly.第7题(单选题)Mrs. Zhao is a famous expert in Chinese A Stock Market, and she has 20-year experience in investing stocks. Recently, she has been promoted to the managing director of OTC Option Department. Based on her experience, the maximum loss of her portfolio is limited to 20% in a single month. Besides that, she ignores the obvious difference between listed stock market and OTC option. So she significantly under-estimates the maximum loss in OTC option market. Which is the most appropriate statement on the type of bias in this context?• A. Huddle bias.• B. Context bias.• C. Availability bias.• D. Anchoring bias.第8题(单选题)Compared with the IBM Algo FIRST database, which event type accounts for the most risk events in Operational Riskdata eXchange Association (ORX)?• A. Business Disruptions and Systems Failures.• B. Execution, Delivery, and Process Management.• C. Clients, Products, and Business Practices.• D. Internal Fraud.第9题(单选题)B ay Consolidation Bank (Bay) only has two commercial banking lines. In three consecutive years, commercial banking realized 100 million, -50 million and 120 million revenue separately, while the revenue for retail banking would be -80 million, 60 million and 100 million separately. Which is the closest value (in million) of the operational risk capital requirement under the standardized approach (SA)?• A. 12.5• B. 19• C. 11.8• D. 11.7第10题(单选题)Which of following statements is least likely correct?• A. Compared with the standardized approach, the alternative standardized approach (ASA) uses loans and advances plus a multiplier to replace revenue in commercial and retail banking lines.• B. Basic indicator approach (BA) could calculate operational risk capital requirements. In this approach, the calculated required capital might be greatlyaffected by a single year’s extraordin ary revenue.• C. The advanced measurement approach (AMA) require banks to set model with99.9% confidence level in one year.• D. A qualified model in advanced measurement approach (AMA) might use both internal loss data and external loss data.第11题(单选题)A bank uses the standardized approach to determine their capital charge for operational risk under Basel II (or Basel III). The bank has three business lines and each business line contributes one-third toward the total gross income. For a given total gross income, which business mix will produce the largest capital charge?• A. Corporate finance, trading and sales, payment and settlement• B. Retail banking, retail brokerage, and asset management• C. Commercial banking, agency services, asset management• D. Retail banking, commercial banking, and payment and settlement第12题(单选题)There two main EVT approaches: peaks-over-threshold (POT) and block-maxima.POT is characterized by a generalized Pareto (GP) distribution while block-maxima is characterized by a generalized extreme-value (GEV) distribution. Which of the following describes the necessary parameters for the POT GP distribution?• A. Only scale and tail/shape index parameters• B. Scale and tail/shape plus threshold (u) must be specified• C. Only scale, location, and tail/shape index parameters• D. Scale, location, and tail/shape index parameters plus threshold (u) must be specified第13题(单选题)Your assignment is to configure a model for financial market (price-based) losses at your bank. For the extreme tail, you want to fit an EVT distribution, either GPD or GEV, to your internal historical loss dataset. However, your bank’s loss data exhibits a high degree of clustering; i.e., time dependency which violates an assumption that the losses are independent and identically distributed (i.i.d.). Which is the best approach, POT or GEV? • A. The clustering is not relevant and you can use either POT or GEV: unlike CLT, neither EVT distribution requires an assumption that the underlying losses are i.i.d. • B. Use the POT (GPD) approach: GEV (block maxima) requires i.i.d. but POT does not, and in fact, anticipates clustering.• C. Use the GEV (block maxima) approach: with long enough time blocks, the clustering effect should be mitigated.• D. Neither GEV nor POT can be used; there is no currently known method for dealing with non-i.i.d. data under EVT.第14题(单选题)You are quantitative analyst at an insurance company. Given some large losses incurred by the company recently, your boss is interested in determining the expected number of extreme losses per year. As well, your boss is quite certain that the company is now more likely to experience an extreme event than before. Based on the information provided by your boss, to model the frequency and severity of extreme events, which of the following distributions would be most appropriate to use?Frequency Severity• A. Poisson distribution Frechet distribution• B. Poisson distribution Gumbel distribution• C. Weibull distribution Frechet distribution• D. Weibull distribution Gumbel distribution第15题(单选题)The RAROC is 15%, the risk-free rate is 3%, the market return is 16%, and the equity beta is 1.50. What is the adjusted RAROC (ARAROC), and should the project be accepted?• A. The ARAROC is 8.0%, and the project should be rejected.• B. The ARAROC is 8.0%, and the project should be accepted.• C. The ARAROC is 12.0%, and the project should be rejected.• D. The ARAROC is 12.0%, and the project should be accepted.第16题(单选题)The risk-free rate is 2% and the expected rate of return on the market is 8%. A bank figures that the risk-adjusted return on capital of a risky project with a beta of 1.6 is 11%. Is the project advisable if the bank uses adjusted RAROC?• A. Not advisable, ARAROC is negative at 0.6%.• B. Not advisable, ARAROC is only 5.625%.• C. Advisable, ARAROC of 5.625% is greater than 3.75%.• D. Advisable, ARAROC is positive at 0.6%.第17题(单选题)Banking holding companies (BHCs) should have comprehensive risk identification processes, which should include evaluation process on:I. On- and off-balance sheet positions.II. Risk transfer and/or risk mitigation techniques.III. Changes in institutions’ risk profile due to portfolio quality.IV. Reputational risk.How many of the following statements is most likely correct?• A. One statement.• B. Two statements.• C. Three statements.• D. Four statements.第18题(单选题)In recent year, large dealer banks financed significant fractions of their assets using short-term, often overnight, repurchase (repo) agreements in which creditors held bank securities as collateral against default losses. The table below shows the quarter-end financing of four broker-dealer banks. All values are in USD billions.If repo creditors become nervous about a bank’s solvency, which bank is least vulnerable to a liquidity crisis?• A. Bank A• B. Bank B• C. Bank C• D. Bank D第19题(单选题)How many of the following statements is most likely correct?I . The special spreads usually derives from the difference between the general collateral rate and the repo rate if the collateral securities are on-the-run (OTR) T-bonds.II. An important reason that special trade usually uses on-the-run (OTR) bonds is the brilliant liquidity involved in new-issued T-bonds, and the liquidity has been cherished by both investors who hold long positions and short sellers.I II. Special spread would usually become largest immediately after auctions and smallest before auctions.• A. Zero• B. One• C. Two• D. Three第20题(单选题)Consider a holding of $10,000 in a stock that has a VaR of $1,000. The current constant bid-ask spread for the stock is 2%. The liquidity-adjusted VaR (LVaR) for a 1-day holding period at the 99% confidence level is closest to:• A. $800.• B. $1,000.• C. $1,100.• D. $2,330.第21题(单选题)Each of the following is true about the foundation/advanced internal ratings-based (IRB) approach to credit risk in Basel II and Basel III, except:• A. The risk weight function estimates a 99.9% confident one-year horizon credit value-at-risk.• B. The capital charge intends to cover unexpected losses and not expected losses with UL = WCL – EL• C. The risk weight function includes PD, LGD, EAD and asset correlations but does not include a maturity adjustment.• D. Asset correlations are included in the risk weight function but cannot be specified by the banks’ own internal estimates.第22题(单选题)A bank wants to estimate its total capital charge using the least sophisticated set of Basel II approaches (i.e., SA for credit and market risk, BIA for operational risk). With respect to its Standardized Approach (SA) to Market Risk, the bank has already determined that its market risk charge is $40 million. With respect to its Basic Indicator Approach (BIA) to operational risk, the bank’s three-year average annual gross income was $80 million per year. With respect to its Standardized Approach (SA) to Credit Risk, the bank’s credit assets (aka, credit exposures) total $650 million with a weighted-average risk weight of 75%. Which is nearest to the bank’s total capital charge?• A. $43.16 million• B. $72.80 million• C. $91 million• D. $104 million第23题(单选题)Small Bank is attempting to transition to the new Basel III standards. Specifically, they are wondering if their liquidity and funding ratios meet the updated requirements as specified by the Basel Committee. Given the following information, what is the bank’s net stable funding ratio?l High-quality liquidity assets $300l Marketable securities $125l Required amount of stable funding $250l Cash inflows over the next 30 days $214l Net cash outflows over the next 30 days $285l Long-Term economic capital $500l Available amount of stable funding $255• A. 89%• B. 98%• C. 102%• D. 196%第24题(单选题)In October 2007, the Basel Committee released guidelines for treating incremental default risk in the trading book. Later, in light of the global financial crisis (GFC), the Committee expanded the scope of the capital charge into the more encompassing incremental risk charge (IRC). Which of the following was most nearly the motivation for the expanded coverage of the IRC?• A. Losses due to idiosyncratic factors, not systematic factors, including basis risk and event risk.• B. Unanticipated losses during a period of stress.• C. Losses in the trading book not necessarily due to default but due to credit migrations, widening spreads and/or loss of liquidity.• D. Losses on securitized products due to operational risk including legal and contract risk.第25题(单选题)Each of the following was both a deficiency and omission of Basel II but is, at the same time, explicitly a 5 ddressed by new requirement in Basel III except for:• A. Basel II did not formally include liquidity risk, but Basel III explicitly covers liquidity risk.• B. Basel II could arguably create a procyclical effect, but Basel III explicitly adds a buffer to address this.• C. Basel II did not require external credit ratings, but Basel III seeks to increase the reliance on external ratings.• D. Basel II allowed many banks to show strong risk-based regulatory capital ratios despite high on- and off-balance sheet leverage; Basel III adds a simple leverage ratio to act as a backstop (增援) to the risk-based capital ratio.第26题(单选题)The capital conservation buffer:• A. Will provide an extra 2.5% Common Equity Tier 1 capital buffer in times of stress. • B. Will be used exclusively to protect banks from the losses garnered from OTC derivatives trading.• C. Is required only for banks with inadequate liquidity coverage and net stable funding source ratios.• D. Is covered in the increased Common Equity Tier 1 capital to risk-weighted assets ratio that will increase to 4.5% from the current 2% over the next few years.第27题(单选题)Basel II/III contains capital rules for the banking industry, while Solvency II looks at the regulatory framework and quantifiable risks in the insurance industry. Comparing Solvency II and Basel II/III, which statement best characterizes the Basel II/III approach? • A. Basel II/III does not try to achieve safety for the entire company, but rather focuses on asset-specific risks (market, credit, and operational).• B. Basel II/III requires a more holistic perspective than Solvency II.• C. Basel II/III does not take in consideration pro-cyclical effects.• D. The goal of Basel II/III is to operate under no supervisory authority.第28题(单选题)Afte r the review of Basel III, which of the following statements on OTC derivatives is most likely incorrect?• A. The rule of non-standard OTC derivatives has been tightened, and both initial and variation margin must be posted by both sides.• B. The amount of initial margin would be calculated by Standard Initial Margin Model (SIMM), which is approved by regulators.• C. The global systematic risk of financial market could be only from big banks, but not big CCPs.• D. Rehypothecation will be restricted, and liquidity pressure becomes clear.第29题(单选题)Which of the following statements on s ummary of Basel III Reform is least likely correct? • A. For measuring credit risk, internal ratings based (IRB) approach has been greatly restricted.• B. Standardized approach for credit risk would not involve specific provisions for real estate exposure.• C. Standardized approach for credit risk highlights subordinated debt and equity exposure.• D. For measuring operational risk, basic indicator approach, standardized approach, and advanced measurement approach have been abandoned.第30题(单选题)Which of the following statements best identify a difference between the SMA and other older operational risk capital approaches?• A. The standardized measurement approach (SMA) uses a model-based methodology, while the advanced measurement approach (AMA) was more flexible and principles-based.• B. The standardized approach (SA) and the alternative standardized approach (ASA) were variations of the standardized measurement approach (SMA).• C. The advanced measurement approach (AMA) was more flexible in its application than the standardized measurement approach (SMA).• D. The standardized measurement approach (SMA) accounts for internal loss experiences that were not factored into the advanced measurement approach(AMA).第31题(单选题)Each of the following is generally true about bid-ask spreads except:• A. The bid-ask spread is a measure of “tightness” and a good but basic and imperfect measure of market (asset) liquidity risk.• B. In a crash, bid-ask spreads tend to widen.• C. The bid-ask spread can incorporate both endogenous and exogenous liquidity risks.• D. A key weakness of the bid-ask spread is that it is not simple-to-implement in the VaR approach.第32题(单选题)Major Investments is an asset management firm with USD 25 billion under management. It owns 20% of the stock of a company. Major Investment’s risk manager is concerned that, in the event the entire position needs to be sold, it size would affect the market price. His estimate of the price elasticity of demand is -0.5. What is the increase in Major Investments’ Value-at-Risk estimate for this position if a liquidity adjustment is made? • A. 4%• B. 10%• C. 15%• D. 20%第33题(单选题)Niu’s Funds tries to use leverage to increase the returns on a long-only equity strategy. The return on assets (ROA) of the strategy is 12%, while the fund plans to finance the investment with 60% borrowed funds. The cost of borrowing is 5%. The return on equity (ROE) is closest to:• A. 5%.• B. 12%.• C. 22.5%.• D. 30%.第34题(单选题)An inves tment bank finds that current market has been highly volatile but its own capital base is large enough. However, the counterparty of this bank asks for higher and higher collateral for the bank’s repo and repo rollover. This phenomenon shows:• A. balance sheet risk.• B. transactions liquidity risk.• C. systematic risk.• D. maturity transformation risk.第35题(单选题)Each of the following is true about the liquidity risk typology except which is false?• A. Liquidity risk has three major types: 1. Transaction (aka, asset, market); 2.Funding (aka, cash flow, balance sheet); and 3. Systemic (aka, crisis)• B. Transaction liquidity risk (aka, asset or market liquidity risk) can be modeled by either or both of an exogenous-spread approach or/and an endogenous priceapproach• C. A key example of funding (aka, cash flow or balance sheet) liquidity risk is the rollover risk created by the maturity transformation function in a traditional depository institution• D. The liquidity risk typology is well-defined into three buckets because the three major liquidity risk types do not interrelate; e.g., funding risk is not due to systemic causes; transaction risk does not constrain funding liquidity第36题(单选题)Some large bank holding companies (BHC) is regarded as diseconomies of scope. Based on recent history, the primary part in diseconomies of scope most probably refers to:• A. risk management.• B. technology.• C. marketing.• D. financial innovation.第37题(单选题)One of the key differences between the 2011 CCAR stress test and the 2011 EBA Irish stress test is that:• A. the CCAR did not require banks to provide results from their own stress scenarios.• B. the EBA Irish did not find any banks in violation of capital adequacy requirements. • C. the CCAR required disclosure of macro-level, not bank level, scenario results.• D. the EBA Irish allowed for 1-year stress horizons.第38题(单选题)Niu’s Funds (Niu) operates in Shanghai and plans to expand its sales out of China. For this purpose, Niu hires a sales and marketing company in Indonesia named Jakarta International Business Service Co. (Jakarta). However, Jakarta reveals detailed sensitive and confidential information on customers unintentionally. Because of the severe data breach, which of the following risks is Niu least likely to face?• A. Compliance risk.• B. Country risk.• C. Legal risk.• D. Operational risk.第39题(单选题)Basel’s 1996 Amendment allows more sophisticated banks with well-established risk management functions to use an internal model-based approach (IMA) for setting market risk capital. Most large banks preferred to use the internal model-based approach because it better reflected the benefits of diversification and led to lower capital requirements. About this capital charge for market risk under the internal models approach (IMA), including 2009 revisions to the original Amendment, each of the following is true except which is not?• A. The value-at-risk (VaR) measure used in the internal model-based approach is calculated with a 10-day time horizon and a 99.0% confidence level; and regulators explicitly stated that the 10-day 99.0% VaR can be calculated as the one-day 99.0% VaR multiplied by the square root of ten; i.e., 10-day 99.0% VaR = one-day 99.0% VaR×sqrt• B. The capital requirement is equal to max[VaR(t – 1), m(c) ×VaR(avg)] + SRC, where m(c) is a multiplicative factor with a minimum value of 3, SRC is a specific risk charge, VaR(t – 1) is the previous day’s value at risk, and VaR(avg) is the average value at risk over the past 60 days• C. The capital requirement adds two terms: value-at-risk (VaR) and specific risk charge (SCR). In a corporate bond security, for example, the credit risk is captured by the VaR term and the interest rate risk is captures by the SRC term.• D. The bank’s VaR risk model must contain a “sufficient” number of risk factors and the bank must justify the omission of any risk factors that are otherwise used inpricing (valuation).第40题(单选题)Griffin Riehl is a risk manager at Bluegrass Bank and Trust, a small, independent commercial bank in Kentucky. Riehl has recently read the Basel Committee on Banking Supervision’s recommendations for sound operational management and would like to put several controls in place. He would like to start with the three lines of defense suggested by the committee. Which of the following is not one of the three common “lines of defense” suggested by the Basel Committee for operational risk governance?• A. Business line management.• B. Board of directors and senior management risk training programs.• C. Creating an independent operational risk management function in the bank.• D. Conducting independent reviews of operational risks and risk management operations.。

I.Liquidity and Treasury Risk Measurement andManagementThe Investment Function in Financial Services Management1.The Acme Investment Firm wants to re-position one of its bond portfolios.Based onits in-house expertise,for the portfolio,it can select from among the following maturity strategies:Ladder Policy,Front-end Load Maturity Policy,Back-end Load Maturity Policy,Barbell Strategy,or Rate Expectations Approach.The firm's goal for the portfolio is NEITHER to maximize income NOR to seek to maximize the upside potential for earnings.Instead,the goal is to use the portfolio primarily as a source of liquidity.Given that goal,which strategy is BEST?dder PolicyB.Front-end Load Maturity PolicyC.Back-end Load Maturity PolicyD.Rate Expectations Approach2.Over the next24hours,Greenlux State Bank estimates that the following cashinflows and outflows(all figures in millions)will occur:What is the bank's projected net liquidity position?A.-30.0millionB.+10.0millionC.+40.0millionD.+90.0million3.Kingstreet Savings is attempting to determine its liquidity requirement.The bank hasclassified its checking,savings,and nonperson time deposits(which total$380.0 million in deposits)into three categories:hot money,vulnerable,and stable(aka,core)funds:The total liquidity requirement is the sum of the liability and loan requirements,but we are here ignoring the loan liquidity requirement;further,the reserve requirements are not necessarily realistic but instead are rounded for the sake of more convenient calculations.Management has elected to hold an80.0%reserve in liquid assets or borrowing capacity for each dollar of hot money deposits,a50.0%reserve behind vulnerable deposits,and a20.0%reserve for its holdings of core funds.The legal reserve requirement is10.0%for both checkable and savings deposits;nonpersonal time deposits have zero legal reserve requirements.Kingstreet Savings is using the Structure of Funds approach to estimating its liquidity requirement.What is Kingstreet's net deposit liquidity requirement for the(total of)vulnerable funds?A.$13.0millionB.$30.0millionC.$62.0millionD.$177.0million4.Below are five of the ten liquidity indicators defined in Rose and Hudgins(the otherfive are Cash position,Liquid securities,Net federal funds and repurchase agreements position,Deposit brokerage index,and Loan commitments ratio).●Capacity ratio=Net loans and leases divided by Total assets(-)●Pledged securities ratio=Pledged securities divided by Total Assets(-)●Hot money ratio=Money market assets divided by Volatile liabilities(+)●Core deposit ratio=Core deposits divided by Total assets(+)●Deposit composition ratio=Demand deposits divided by Time deposits(-)If the Core deposit ratio unexpectedly dropped,this might be a red flag liquidity indicator.Put another way,the Core deposit ratio is a positive liquidity indicator such that its increase is generally favorable or indicative of a safer situation for the firm with respect to its liquidity needs.Negative liquidity indicators go in the opposite direction: their decrease is favorable while their increase might be cause for concern.Among the five liquidity indicators listed above,in addition to the Core deposit ratio, which is a POSITIVE liquidity indicator;for which would an unexpected drop maybe be a yellow-or red-flag cause for concern?A.Capacity ratioB.Hot money ratioC.Pledged securities ratioD.Deposit composition ratio⏹Liquidity Risk5.An investor holds two positions:●Long shares worth$25,000where the bid-offer spread has a mean and standarddeviation of0.050●Long shares worth$40,000where the bid-offer spread has a mean and standarddeviation of0.030If we assume the bid-offer spreads are normally distributed,then which is nearest to the worst expected cost of unwinding with95.0%confidence?A.$1,730B.$2,950C.$3,240D.$6,5006.Liquidity funding risk refers to the firm's ability to meet its cash needs.About liquidityfunding risk,which of the following statements is TRUE?A.Wholesale deposits are the most stable source of fundingB.A lack of confidence can contribute to an institution's liquidity funding problemsC.A solvent firm cannot experience a liquidity funding problem;i.e.,only aninsolvent firm can experience a liquidity problemD.Case studies such as Northern Rock and Ashanti Goldfields demonstrate that ahedged position is the best protection against liquidity funding problems⏹Liquidity and Leverage7.Suppose a firm with a simple capital structure has assets of$20.0million and debt of$10.0million.Return on assets(ROA)is9.0%and cost of debt is4.0%,such that the firm's leverage is2.0and its return on equity(ROE)is14.0%.If the firm borrows an additional$6.0million at the same cost of4.0%,and asset returns are fixed,what is the firm's new leverage and return on equity(ROE)?A.Leverage=1.7and ROE=13.3%B.Leverage=2.0and ROE=15.7%C.Leverage=2.3and ROE=23.5%D.Leverage=2.6and ROE=17.0%8.On opening day,Lever Brothers Multistrategy Master Fund LP has the followingeconomic balance sheet:$100in Cash,$20in Debt,and Equity of$80.Assume Lever Brothers creates a short position in a stock,borrowing$100of the security and selling it.It has thus created a liability equal to the value of the borrowed stock,and an asset,equal in value,consisting of the cash proceeds from the short sale.The cash cannot be used to fund other investments,as it is collateral;the broker uses it to ensure that the short stock can be repurchased and returned to the stock lender.It remains in a segregated short account,offset by the value of the borrowed stock.The stock might rise in price,in which case the$100of proceeds would not suffice to cover its return to the borrower.Lever Brothers must therefore in addition put up margin of$50.After the trade,what is the leverage in the firm's economic balance sheet?A. 1.25B. 1.50C. 1.75D. 2.50⏹Failure Mechanics of Dealer Banks9.Duffie examines several policy measures that might alleviate firm-specific andsystemic risks related to large dealer banks.He would tend to agree with each of the following EXCEPT to which statement would he most DISAGREE?A.The threat posed by the flight of over-the-counter derivatives counterparties canbe lowered by central clearingB.Distress-contingent convertible debt is an innovation that is likely to bedestabilizing during periods of financial distress,and regulators should considercurtailing their usageC.Short-term tri-party repos are a particularly unstable source of financing;potential remedies to their risk include a tri-party repo utility,central-bankinsurance of tri-party repo transactions,or an emergency bank to be financed byrepo market participantsD.The most important source of systemic risk is the potential impact of dealer-bankfire sales on market prices and investor portfolio;during the financial crisis,therisk of fire sales was significantly mitigated by lender-of-last resort financing bycentral banks and by capital injections into dealer banks⏹Early Warning Indicators10.Venkat writes that"The EWI framework can be summarized as M.E.R.I.T"where the(M)refers to measures.Which of the following is a TRUE characteristic(or feature)of good Early Warning Indicator(EWI)measures?A.Only internal but not external measuresB.Forward-looking and not too coarse(i.e.,granular)measuresC.Measures are disassociated(aka,de-linked)from the escalation processD.Measures are tracked during business-as-usual environments but should not beaffected by stressed environments⏹Intraday Liquidity Risk Management11.Each of the following is a measure for quantifying and/or monitoring risk levelsEXCEPT which is a measure for understanding intraday flows?A.Total paymentsB.Client intraday credit usageC.Intraday credit relative to tier1capitalD.Daily maximum intraday liquidity usageRepurchase Agreements and Financing12.Pasquini Investments(Pasquini)is a private brokerage looking for30-day financing of$25million of its accounts payable but is unsure whether the appropriate investment is a term repurchase agreement(repo)or a term reverse repo agreement.Pasquini is willing to post AAA-rated government bonds as collateral.The bonds have a face value of$27million and a market value of$25million.The firm is quoted a rate of0.5%for the transaction.Which of the following choices most accurately reflects thecontract type and the contract price needed by Pasquini?Contract Type Contract PriceA.Repo$27,011,250B.Reverse Repo$25,010,417C.Repo$25,010,417D.Reverse Repo$27,011,25013.Posting collateral and requiring collateral haircuts are important risk mitigants in repotransactions with respect to which of the following risks?Posting Collateral Collateral haircutsA.Market risk Interest rate riskB.Credit risk Interest rate riskC.Market risk Liquidity riskD.Credit risk Liquidity risk14.In a presentation to management,a bond trader makes the following statementsabout repo collateral:Statement1:The difference between the federal funds rate and the general collateral rate is the special spread.Statement2:During times of financial crises,the spread between the federal funds rate and the general collateral rate widens.Which of the trader’s statements are accurate?A.Both statements are incorrect.B.Only statement1is correct.C.Only statement2is correct.D.Both statement are correct.15.Rankcon is a repo investor in the money market mutual fund industry with theexclusive motive of cash management.As Fabozzi explains,"Investors holding cash for liquidity or safekeeping purposes often find investing in repo to be an ideal solution.The most significant example of this is the money market mutual fund industry,which invests on behalf of investors willing to accept relatively low returns in exchange for liquidity and safety.[A money market fund would lend money while taking collateral and then,at maturity,collect the loan plus interest and return the collateral.]Holding collateral makes the lender less vulnerable to the creditworthiness of a counterparty because,in the event of a default by the counterparty,the investor(e.g., the money market fund)can sell the repo collateral to recover any amounts owed.In summary,relative to super-safe and liquid non-interest-bearing bank deposits,repo investments pay a short-term rate without sacrificing much liquidity or incurring significant default risk."Given this motivation,Rankcon understandably employs each of the following criteria(or preference)with respect to its repo investments EXCEPT which is the LEAST likely preference?A.Rankcon insists on a sufficient(i.e.,greater rather than lesser)collateral haircutB.Rankcon only accept securities with the highest credit quality;e.g.,debt ofgovernment-sponsored entities(GSEs)C.Rankcon refuses to accept general collateral(at general collateral repo rates)and instead insists on particular securities with delineated asset classesD.Rankcon places a premium on liquidity so tends to lend overnight rather than forterm;or,if it wants to lend cash for an extended period,engages in an open repo16.Consider the following illustration of a simplified repurchase agreement(repo)tradebetween generic Counterparty A and Counterparty B.Please note this illustration refers to the initiation of the repo trade,not the unwinding.Consider the three primary motivations for a repo trade:I.Lend funds short-term on a secured basis:A money market mutual fund whoholds cash for liquidity or safekeeping purposes but who wants to lend the cashsafely would BUY the repo as Counterparty B;because the fund is investingcash,the mutual fund is willing to accept general collateralII.Finance the long position in a security:The trading desk at a financial institution who wants to finance the purchase of a security would sell the repo(aka,repoout)as Counterparty A using the purchased security as collateral III.Borrow a security in order to sell it short:A hedge fund that wants to short a security but needs to borrow the security in order to sell it would do a reverserepo(aka,buy the repo)as Counterparty B;because the hedge fund isborrowing a bond,it does not accept a general collateral and instead requiresdelivery of a particular securityWhich of the above is ACCURATE(true)?A.None are accurateB.I.only is accurate(II.and III.are mistaken)C.III.only is accurate(I.and II.are mistaken)D.All are accurate17.At the time of the Bear Stern's demise in March2008,Paul Friedman was a SeniorManaging Director at the firm with responsibility for its fixed income repo desk.About the repo market's role in the collapse of Bear Sterns,he said in testimony before the Financial Crisis Inquiry Commission,"During the week of March10,2008,Bear Stearns suffered from a run on the bank that resulted,in my view,from an unwarranted loss of confidence in the firm by certain of its customers,lenders,and counterparties.In part,this loss of confidence was prompted by market rumors,whichI believe were unsubstantiated and untrue,about Bear Stearns’liquidity position.Nevertheless,the loss of confidence had three related consequences."Each of the following was one of his cited three consequences EXCEPT which was not?A.Prime brokerage clients withdrew their cash and unencumbered securities at arapid and increasing rateB.Repo market lenders declined to roll over or renew repo loans,even when theloans were supported by high-quality collateral such as agency securitiesC.Counterpart to non-simultaneous settlements of foreign exchange trades refusedto pay until Bear Stearns paid firstD.Short sellers seized on the panic and drove the stock price down which reducedequity capital available,and equity capital was already the least stable source offunds18.In contrast to general collateral(CG)repo rates,which of the following is TRUE aboutspecial repo rates?A.Special rates are typically less than general collateral ratesB.If the counterparty's primary motivation is to lend cash rather than borrow asecurity,the special rate appliesC.Special rates are well-suited to repo investors who are looking to obtain thehighest rate for the collateral they are willing to acceptD.The most commonly cited special rates are for overnight repos where any U.S.Treasury collateral is acceptable19.In regard to special spreads,each of the following is true EXCEPT which is false?A.On-the-run(OTR)issues tend to trade"more special"than off-the-run(OFR;i.e.,old or double-old)issues,where"more special"refers to special spreads that arelargerB.The special spread equals the general collateral(GC)repo rate minus thespecial collateral(aka,specifically requested collateral)repo rateC.On-the-run special spreads peak immediately after an auction,and tend todecrease over the cycle,reaching their lowest level immediately before the nextauctionD.Special spreads tend to be volatile on a daily basis(reflecting supply anddemand for special collateral)and special spreads can be quite large(e.g.,hundreds of basis points)⏹Monitoring Liquidity20.Geofinancial Bank currently has the following(very)simplified balance sheet:Further,the maturities of these accounts are as follows:●Assets:The bonds($30.0million)expire in one year.In regard to the loans($70.0),$40.0million expire in five(5)years,$10.0million expire in seven(7)years,and$20.0million expire in ten(10)years.●Liabilities:In regard to the deposits($20.0million),$10.0million expire in one(1)year,and$20.0million expire in two(2)years.In regard to the bonds($50.0million),$10.0million expire in five(5)years,$30.0million expire in seven(7)years,and$10.0million expire in beyond ten(>10)years.Equity($20.0million)is presumed to expire in ten(10)yearsWhich term structure of expected cash flows is accurate for Geofinancial Bank?E.Series AF.Series BG.Series CH.Series D21.Which of the following best describes the term structure of expected liquidity,TSL(e)?A.TLS(e)is the cumulative change in the term structure of available assets(TSAA)B.TLS(e)is a combination of the term structures of cash flow at risk(CFaR)andliquidity at risk(LaR)C.TLS(e)is a combination of the term structure of expected cash(TSEC),changein working capital(CIWC),and change in deposits(CID)D.TLS(e)is a combination of the term structures of cumulative expected cash flows(TSECCF)and liquidity generation capacity(TSCLGC)22.Consider the following four definitions related to liquidity risk:●Liquidity risk:The event that in the future the bank receives smaller thanexpected amounts of cash flows to meet its payment obligations.●Funding cost risk:The event that in the future the bank has to pay greater thanexpected cost(spread)above the risk-free rate to receive funds from sources ofliquidity that are available●Liquidity generation capacity:The ability of a bank to generate positive cashflows,beyond contractual ones,from the sources of liquidity available in thebalance sheet and off the balance sheet at a given date.●Cash flow at Risk(CFaR):The amount of economic losses due to the fact that ona given date the algebraic sum of positive and negative cash flows and ofexisting cash available at that date,is different from some(desired)expectedlevel.About these definitions,which of the following statements is TRUE?A.Liquidity risk is inaccurate,but the other three are correctB.Funding cost risk is inaccurate,but the other three are correctC.Cash risk at Risk(CFaR)is inaccurate,but the other three are correctD.All four definitions are correct⏹Illiquid Asset23.Illiquidity can arise due to the following market imperfections:Clientèle effects andparticipation costs,transaction costs,search frictions,asymmetric information,price impact or funding constraints.He characterizes the effects of these imperfections as "illiquidity."In regard to the CHARACTERISTICS of illiquid markets,which of the following statements is TRUE(such that the other statements are generally false)?A.Normally liquid markets periodically become illiquidB.Most individuals hold the majority of their wealth in liquid or highly liquid assetsC.Most asset classes are liquid such that genuinely illiquid markets tend to besmall and temporaryD.Technology has virtually eliminated the following frictions:transaction costs,search friction,asymmetric information,price impact,and funding constraints24.Each of the following is a bias that overstates the expected returns(and/orunderstates the risk)of illiquid assets EXCEPT which is not accurate?A.Survivorship bias can inflate returns by4.0%or moreB.Infrequent sampling(aka,infrequent trading)artificially reduces risk andrisk-related metrics such as volatility,correlation and betaC.Turnover bias decreases the typical time between transactions and tends toartificially increase the expected return by5.0%or moreD.Selection bias(aka,reporting bias)is a distortion of the sample that artificiallyincreases(ie,overestimates)alpha and artificially decreases(ie,underestimates)betaI.ANSWERS AND EXPLANATIONThe Investment Function in Financial Services Management1.Answer:B.The Front-end Load Maturity Policy purchases short-term securities that mature within ashort time interval.Its primary goal is liquidity rather than income or maxim upside.2.Answer:B.Inflows include:Deposit inflows=100+Scheduled loan repayments=60+Borrowings from the money market=80+Sales of bank assets=30+Revenues from sale of nondeposit services=10;for total inflows of$100+$60+$80+$30+$10=280.0million.Outflows include:Deposit withdrawals=70+Acceptable loan requests=90+Stockholder dividend payments=20+Repayment of bank borrowings=50+Operating expenses=40;for total outflows of$70+$90+$20+$50+$40=$270.0millionTherefore,the projected net liquidity position=$280-270=+10.0million.3.Answer:C.Because50.0%*[$20.0*(1-0.10)+$40.0*(1-0.10)+$70.0]=$62.0million4.Answer:B.The Hot money ratio is a positive liquidity indicator.Hot money ratio=Money market assets divided by Volatile liabilities.It indicates whether the firm has balanced the volatile liabilities with the money market funds it could sell quickly to cover those liabilities.The money market assets comprise cash plus cash due from other depository institutions plus short-term securities plus federal funds loans plus reverse repurchase agreements (repos).The volatile liabilities include large certificates of deposit(CDs)plus eurocurrency deposits plus federal funds borrowings plus repos.In regard to Capacity ratio(ie,Net loans and leases divided by Total assets);Pledgedsecurities ratio(ie,Pledged securities divided by Total Assets);and Deposit composition ratio(ie,Demand deposits divided by Time deposits),these are negative liquidity indicators.⏹Liquidity Risk5.Answer:C.The95.0%confident worst expected spread for each position is given by:●$25,000*(0.050+0.050*1.645)=$3,306.25;●$40,000*(0.030+0.030*1.645)=$3,174.00Total cost of unwinding with95.0%confidence is therefore(3,306.25+3,174.00)/2= $3,240.13,or about$3,240.6.Answer:B.A lack of confidence can contribute to an institution's liquidity funding problems⏹Liquidity and Leverage7.Answer:D.Leverage=2.6and ROE=17.0%Given new assets of26.0and new debt of16.0,new equity is unchanged at10.0=26.0-16.0.New leverage=26.0/10.0=2.60and new ROE=(26.0*9%-16.0*4%)/10.0=17.0%.8.Answer:D.After the trade,Assets=$200=$50cash+$150Due from broker(i.e.,$100short sale proceeds+$50margin)After the trade,Liabilities=$120=$20debt+$100Borrowed Stock,such that Equity =$80=$200-$120;Therefore,Leverage=200/80=2.50.⏹Failure Mechanics of Dealer Banks9.Answer:B.Duffie actually proposed(in a paper)"that distress-contingent convertible debt be complemented with regulations favoring mandatory rights offerings of equity that,similarly, are automatically triggered by leverage or liquidity thresholds.These two new instruments can be designed to recapitalize a financial institution before a destructive run is likely to commence,and to reduce a financial institution’s incentives for socially excessive risk taking."⏹Early Warning Indicators10.Answer:BForward-looking and not coarse(i.e.,granular)measures.In regard to(A),(C)and(D), each is FALSE.Instead,true statements include the following:●Both internal and external measures are necessary:Says Choy,"It is importantto recognize that liquidity events can start either within the bank or may beinfluenced by external elements resulting from the environment within which thebank operates.For example,an idiosyncratic deposit run may result from eitherthe disclosure of poor performance or due to a systemic failure.EWIs should bepositioned to capture emerging internally-driven stress events before theybecome public knowledge,for example,through monitoring of loan performance,planned significant accounting adjustments,and operational losses.Alternatively,a systemic crisis such as a sovereign default or banking system crisis maytrigger liquidity dislocations in parts of the financial market system,disrupting thefunding of any institutions that are exposed to those markets."●Measures are only academic unless they are lined to an escalation process●Measures must track business-as-usual(BAU)environments AND stressedenvironments:Says Choy,"institutions should include stressed measures and limits into their EWI lists in order to gauge the adequacy of the firm’s liquidity buffer for a stressed environment.Additionally,stress testing results may also expose previouslyunidentified or emerging concentrations and risks that could threaten the viability of the institution."⏹Intraday Liquidity Risk Management11.Answer:ATotal payments is a measure for understanding intraday flowsIn regard to (B),(C)and (D),each is a measure for quantifying and/or monitoring risk levels⏹Repurchase Agreements and Financing12.Answer:CGiven that Pasquini is a borrower in the repo market,the transaction is a repo from the perspective of the firm (but a reverse repo from the perspective of the lender).The contract price is calculated as follows:0.5%30$25,000,0001$25,010,417360⨯⎛⎫⨯+= ⎪⎝⎭13.Answer:DCollateral is an important counterparty credit risk mitigant.Repo loans are secured by collateral,which makes the lender much less vulnerable to a decline in the creditworthiness of the borrower.Collateral haircuts are important in mitigating liquidity risk in repo transactions.The lender is exposed to the risk of the value of the collateral declining during the repo term,which can be mitigated by requiring (higher)haircut values,that is,discounts to the value of the posted collateral.14.Answer:CThe trader’s first statement is incorrect.The difference between the federal funds rate and the general collateral (GC)rate is known as the fed funds-GC spread.The special spread is the difference between the GC rate and the special rate for a particular security.The trader’s second comment is correct.During times of financial crises,the spread betweenthe federal funds rate and the general collateral rate widens as the willingness to lend Treasury securities declines,lowering the GC rate(thereby increasing the spread).15.Answer:C"While repo investors care about the quality of the collateral they accept,they do not usually care about which particular bond they accept.Hence,while repo investors can be very particular about which classes of securities they will take as collateral, e.g., Euro-area government bonds with less than five years to maturity,they will not insist on receiving any particular security within that delineated class.For this reason these investors are said to accept general collateral,which trades at general collateral repo rates.The types and determination of repo rates are discussed later in this chapter."16.Answer:DAll are accurate17.Answer:DShort sellers are not cited;further,equity capital is the most stable source of funds because"equity holders do not have to be paid according to any particular schedule and because they cannot compel a redemption of their shares."18.Answer:ASpecial rates are typically less than general collateral rates19.Answer:CThe reverse:On-the-run special spreads are smallest immediately after an auction,and tend to increase over the cycle,reaching their peak immediately before the next auction.Monitoring Liquidity20.Answer:C21.Answer:DThe term structure of expected liquidity,TSL(e),is a combination of the term structures of cumulative expected cash flows(TSECCF)and liquidity generation capacity(TSCLGC)22.Answer:CCash risk at Risk(CFaR)is inaccurate but the other three are correct.The definition given for(C)is a second definition for liquidity risk:The amount of economic losses due to the fact that on a given date the algebraic sum of positive and negative cash flows and of existing cash available at that date,is different from some(desired)expected level.Illiquid Asset23.Answer:A.24.Answer:C.Turnover bias is made-up.。
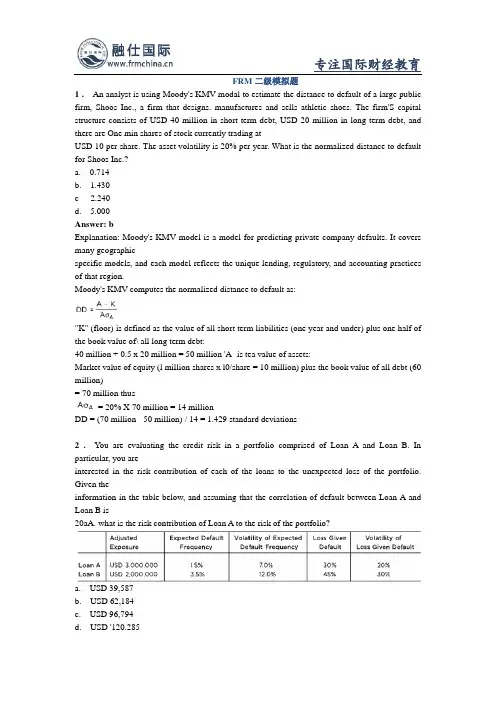
FRM二级模拟题1 . An analyst is using Moody's KMV modal to estimate the distance to default of a large public firm, Shoos Inc., a firm that designs. manufactures and sells athletic shoes. The firm'S capital structure consists of USD 40 million in short-term debt, USD 20 million in long-term debt, and there are One min shares of stock currently trading atUSD 10 per share. The asset volatility is 20% per year. What is the normalized distance to default for Shoos Inc.?a. 0.714b. 1.430c- 2.240d. 5.000Answer: bExplanation: Moody's KMV model is a model for predicting private company defaults. It covers many geographicspecific models, and each model reflects the unique lending, regulatory, and accounting practices of that region.Moody's KMV computes the normalized distance to default as:"K" (floor) is defined as the value of all short term liabilities (one year and under) plus one half of the book value of\ all long term debt:40 million + 0.5 x 20 million = 50 million 'A- is tea value of assets:Market value of equity (l million shares x l0/share = 10 million) plus the book value of all debt (60 million)= 70 million thus= 20% X 70 million = 14 millionDD = (70 million - 50 million) / 14 = 1.429 standard deviations2 . You are evaluating the credit risk in a portfolio comprised of Loan A and Loan B. In particular, you areinterested in the risk contribution of each of the loans to the unexpected loss of the portfolio. Given theinformation in the table below, and assuming that the correlation of default between Loan A and Loan B is20aA. what is the risk contribution of Loan A to the risk of the portfolio?a. USD 39,587b. USD 62,184c. USD 96,794d. USD '120.285Answer: bExplanation: Risk contribution is a critical risk measure for assessing credit risk. Tha risk contribution of a riskyassets 'RC" to the portfolio unexpected loss, is defined as the incremental risk that the exposure of a single assetcontributes to the portfolio's total risk. Mathematically:UL A = 3,OOOJOOO x sqrt(l.5% x 20LY02十30%2 X 7%2) = 96.793 .59UL B= 2,000.000 x sqrt(3.5% x 30%2 + 459102 x 120/b2) = 155.769.06UL P = sqrt(96793.592 + 155,769.062+ 2 x 20% X 96,793.59 x 155,769.06) = 199,158.17RCA = (96.793.592 + 20% X 96,793.59 x 155,769.06) / 199,158.17 = 62,184.193 . A hedge fund is considering taking positions in various tranches of a collateralized debt obligation (CDO).The fund's chief economist predicts that the default probability will decrease significantly and that the defaultcorrelation will increase. Based on this prediction, which of the following is a good strategy to pursue?a.Buy the senior tranche and buy the equity trancheb.Buy the senior tranche and sell the equity tranche.c.Sell the senior tranche and sell the equity tranche.d.Sell the senior tranche and buy the equity trancheAnswer :dExplanation: The decrease in probability of default would increase the value of the equity tranche Also, a default of the equity tranche would increase the probability of default of the senior tranche, due to increased correlation, reducing its value. Thus, it is better to go long the equity tranche and short the senior tranche.4 . Sacks Bank has many open derivative positions with Lake Investments. A description and current marketvalues are displayed in the table below:In the event that Lake defaults, what would be the loss to Sacks if netting is used?a. USD 5 millionb. USD 10 millionc. USD 25 milliond. USD 35 millionAnswer: bExplanation: Netting means that the payments between the two counterparties are netted out. so that only a netpayment has to be made. With netting. Sacks is not required to make the payout of 25 million. Hence the loss willbe reduced to:35 million - 25 million = 10 million5 . Mike Merton is the head of credit derivatives trading at an investment bank. He is monitoringa new creditdefault swap basket that is made up of 20 bonds, each with a l% annual probability of default. Assuming theprobability of any one bond defaulting is completely independent of what happens to other bonds in thebasket, what is the probability that exactly one bond defaults in the first year.a. 2.06%b. 3.OIYoc- 16.S%d. 30.1%Answer: CExplanation: C2lOpl 0 _ p)19 = 20 x 0.01 x (1 - 0.01)19 = 0.1652。
frm 二级百题期货风险管理二级考题 - 风险管理策略期货市场作为金融市场的重要组成部分,具有较高的风险性。
有效的风险管理策略对于投资者来说至关重要。
下面将介绍几种常见的期货风险管理策略。
首先是止损单策略。
止损单是一种设置在期货合约价格下方的委托单,用于控制投资者的损失。
当价格跌破止损价位时,止损单自动触发,触发时以市价进行交易。
通过设定适当的止损价位,投资者可以限制损失的额度,并及时止损,避免继续亏损。
其次是套利策略。
套利是通过同时购买和出售不同市场上密切相关但价格存在差异的期货合约,以获取无风险利润的交易策略。
通过套利,投资者可以利用市场上的价格差异来获得风险较低的收益。
常见的套利策略包括跨市场套利、时间套利和跨品种套利等。
第三是多空对冲策略。
多空对冲是指投资者同时开设多头和空头两个相对的头寸,以抵消市场风险。
在市场中,多头头寸代表看涨期货合约的持仓,而空头头寸代表看跌期货合约的持仓。
通过多空对冲,投资者可以有效地规避市场波动带来的风险,实现风险的最小化。
最后是动态资金管理策略。
这种策略基于投资者对市场行情的判断,调整投资组合的资金配置,以应对市场变化。
动态资金管理包括增减仓位、调整止损价位和利润目标等。
投资者可以根据市场风险程度和预期回报来灵活调整仓位和风险控制参数,从而实现风险的有效管理。
总的来说,期货风险管理策略是投资者在期货市场中进行风险控制的重要手段。
止损单策略、套利策略、多空对冲策略和动态资金管理策略是投资者常用的风险管理策略。
投资者可以根据自身的投资目标和风险承受能力,选择合适的策略来实现风险的有效管理。
理财规划师(二级)实操知识投资规划章节练习试卷6(题后含答案及解析)题型有:1.2,红利分配率为40%,所宣布的最近一次的收益是每股10元。
预计泛亚公司每年都会分红,泛亚公司所有再投资的股权收益率都是20%,红利刚刚发放。
根据案例,回答下列题目:17.投资者对泛亚公司股票的预期收益率为()。
A.12.80%B.16.20%C.22.30%D.27.30%正确答案:B解析:根据资本资产定价模型,可得:预期收益率k=E(rp)=rf+β[E(rf)==9%+1.2×(15%-9%)=16.2%。
知识模块:投资规划18.预期股利增长率为()。
A.8.30%B.10%C.12%D.13.40%正确答案:C解析:预期股利增长率:g=(1-b)×ROE=(1-40%)×20%=12%。
知识模块:投资规划19.当前股票的内在价值为()元。
A.82.36B.94.21C.104.27D.106.67正确答案:D解析:V0=D1/(k-g)=10×40%×(1+12%)/(16.2%-12%)=106.67(元)。
知识模块:投资规划20.持有泛亚公司股票一年后的收益率为()。
A.19.51%B.21.52%C.22.45%D.23.95%正确答案:D解析:一年后股票的价格:P1=V1=V0(1+g)=106.67×1.12=119.47(元);则一年后的收益率为:E(r)=(D1+P1-P0)/P0=(4.48+119.47-100)/100×100%=23.95%。
知识模块:投资规划案例5:汤小姐持有华夏公司股票100股,预期该公司未来3年股利为零增长,每期股利30元。
预计从第4年起转为正常增长,增长率为5%。
目前无风险收益率7%,市场平均股票要求的收益率为11.09%,华夏公司股票的标准差为2.8358,市场组合的标准差为2.1389,两者的相关系数为0.8928。
frm二级考试答案1. 以下哪个选项是FRM(金融风险管理师)考试的主办机构?A. CFA InstituteB. GARP (Global Association of Risk Professionals)C. ACCA (Association of Chartered Certified Accountants)D. CFP Board答案:B2. FRM二级考试通常包含多少个科目?A. 4个B. 5个C. 6个D. 7个答案:C3. FRM二级考试中,以下哪个科目不属于考试内容?A. 市场风险管理与测量B. 信用风险管理与测量C. 操作风险与弹性D. 投资组合管理答案:D4. FRM二级考试通常在每年的哪两个月份举行?A. 五月和十一月B. 六月和十二月C. 一月和七月D. 二月和八月答案:A5. 根据GARP的规定,FRM二级考试通过后,考生需要在多少年内积累两年的相关工作经验以获得FRM认证?A. 3年B. 4年C. 5年D. 6年答案:C6. FRM二级考试的通过标准是什么?A. 必须在所有科目中都获得60%以上的分数B. 总分数达到70%以上C. 至少有60%的科目达到70%以上的分数D. 总分数达到60%以上答案:D7. FRM二级考试的题型是什么?A. 多项选择题B. 简答题C. 案例分析题D. 计算题答案:A8. FRM二级考试的考试时长是多少?A. 4小时B. 5小时C. 6小时D. 7小时答案:C9. FRM二级考试中,以下哪个风险类型不属于市场风险的范畴?A. 利率风险B. 汇率风险C. 商品价格风险D. 法律风险答案:D10. FRM二级考试中,以下哪个风险类型不属于信用风险的范畴?A. 违约风险B. 信用迁移风险C. 流动性风险D. 交易对手风险答案:C。
frm 二级practice 53题作为一名职业写手,我们的任务是根据所提供文本完成以下任务:第一步,了解文本背景和目的;第二步,分析文本关键信息;第三步,制定实践策略;第四步,总结实践成果。
在本篇文章中,我们将以frm二级practice 53题为例,详细阐述如何高效地完成这项任务。
首先,我们需要了解文本背景和目的。
frm(Financial Risk Manager)是全球金融风险管理领域权威的认证,被誉为“风险管理领域的MBA”。
二级practice 53题则是针对frm二级考试的一道典型题目,旨在考察考生对金融市场和金融工具的理解以及风险管理策略的应用。
接下来,我们分析文本关键信息。
题目描述了一个投资者在金融市场中的投资决策过程,包括资产配置、风险管理等方面的内容。
为了顺利完成这道题目,我们需要掌握以下几个关键点:1.投资者的风险偏好和投资目标2.各种金融工具的特点和风险收益特性3.资产配置的原则和方法4.风险管理策略的运用在掌握关键信息的基础上,我们制定实践策略。
针对这道题目,我们可以采取以下步骤:1.确定投资者的风险偏好和投资目标。
根据题目描述,投资者希望在风险可控的前提下实现资产增值。
2.分析金融工具。
题目提到了股票、债券和期货等金融工具。
我们需要了解这些工具的特点、风险收益特性,以便为投资者选择合适的投资品种。
3.进行资产配置。
根据投资者的风险偏好和投资目标,以及各种金融工具的风险收益特性,我们可以制定资产配置方案。
资产配置的原则包括分散投资、长期投资、动态调整等。
4.应用风险管理策略。
针对投资过程中的潜在风险,我们可以采用以下策略:一是投资组合保险策略,通过动态调整资产比例,实现风险和收益的平衡;二是采用止损指令,设定投资限制,降低损失风险。
最后,我们总结实践成果。
通过以上步骤,投资者在控制风险的同时实现了资产增值。
实践证明,了解文本背景、分析关键信息、制定实践策略是解决这类问题的关键。
试卷答案:FRM 诺曼底PART 2-201905操作风险测量与管理(40道题)01.正确答案:B解析Board of directors and senior executives acquiesce wrongdoing shows bad risk culture and weak risk willingness, and risks in major deals show the deficits in bank’s major products.02.正确答案:D解析Enterprise risk management (ERM) is basic requirement, so 5 independent risk offices are not enough. Internal control requires mandatory vacation system, and public disclosure needs unbiased information.03.正确答案:D解析The boards of directors for banks have responsibility for: (1) approval of risk management policies and procedures, (2) ensuring that operating managers have the requited technical capabilities, (3) evaluating performance of risk management activities, and (4) maintaining oversight of risk management activities.04.正确答案:C解析With the business impact view, the scorecard provides a high-level understanding of the risks embedded in data quality problems (i.e., a combined and summarized view). It considers various data quality problems that occur in various business processes.05.正确答案:C解析Record level consistency is consistency between one set of data values and another set within the same record. Cross-record level consistency is consistency between one set of data values and another set in different records.06.正确答案:A解析There are 4 steps in RCSA. First step is that risks associated with each business unit’s and line’s activities should be identified and assessed thoroughly. Second step is that control effect are considered and added to RCSA, then risk self-assessment (RSA) could consider risk mitigation. Third step is that risk metrics and other OpRisk initiatives should be prepared and linked to the RCSA program. The forth step should be that control tests should be assessed that how well the controls in place mitigate potential risks.07.正确答案:C解析Huddle bias suggests that groups of individuals tend to avoid conflicts that can result from different viewpoints or opinions. Availability bias is related to the expert’s experience in dealing with a specific event or loss risk. Anchoring bias occurs when an expert limits the range of a loss estimate based on personal knowledge. Context bias occurs when questions are framed in a way that influences the responses of those being questioned.08.正确答案:B解析In FIRST database, most risk events belong to CPBP, because the most remarkable events are for this kind. However, in ORX database, most risk events are for EDPM, which is in line with the reality.09.正确答案:C解析Operation risk capital requirement = (5.4 + 0 + 30)/3= 11.810.正确答案:D解析In AMA, a model must include the four data elements: internal loss data, external loss data, scenario analysis, and business environment internal control factors.11.正确答案:A解析Business Lines Beta Factors:18%: IB: (corporate finance, trading and sales), payment and settlement1 5%: Commercial banking, agency services12%: Retail banking, retail brokerage, asset management12.正确答案:B解析POT GP requires two parameters (i.e., scale and tail/shape) but we must also specify a threshold (u).13.正确答案:C解析Dowd: “We have assumed so far that the stochastic process driving our data is i.i.d., but most financial returns exhibit some form of time dependency (or pattern over time). This time dependency usually takes the form of clustering, where high/low observations are clustered together. Clustering matters for a nkllumber of reasons, including: It violates animportant premise on which the earlier results depend, and the statistical implications of clustering are not well understood. There are two simple methods of dealing with time dependency in our data. Perhaps the most common (and certainly the easiest) is just to apply GEV distributions to block maxima. This is the simplest and most widely used approach. It exploits the point that maxima are usually less clustered than the underlying data from which they are drawn, and become even less clustered as the periods of time from which they are drawn get longer.”14.正确答案:A解析A Poisson distribution is frequently assumed for the distribution of operational risk event frequency (i.e., number of losses per year). In contrast, a Weibull distribution is used when modeling the severity of operational risk losses. Therefore, the Poisson distribution is the more appropriate one to use to model the distribution of frequency. A Frechet distribution has “heavy” tails, which suggests that there is a greater likelihood of an extreme event occurring. In contrast, a Gumbel distribution has “light” tails, which suggests that compared to the Frechet distribution, there is a lesser likelihood of an extreme event occurring. Gumbel distributions are similar to normal and lognormal distributions where there is a lesser likelihood of an extreme event occurring. Therefore, the Frechet distribution is the more appropriate one to use to model the distribution of severity.15.正确答案:A解析The adjusted or second generation RAROC is the RAROC minus the risk-free rate divided by the beta: (15% - 3%)/1.50 = 8.0%. The project should be rejected because the ARAROC is less than the excess market return of 16% - 3% = 13%.16.正确答案:B解析The market’s excess return = 8% - 2% = 6%; ARAROC = (11% - 2%)/1.6 = 5.625%, which is lower than 6% so the project is not accepted.17.正确答案:D解析All of the statements are correct. BHCs should have risk identification processes effectively identifying all risk exposures for assessing capital needs. Reputational risk, like strategic risk and compliance risk, falls under the category of “other risks” and ar e more difficult to quantify. Nevertheless, there are a wide range of methods BHCs employ to evaluate other risks.18.正确答案:A解析A liquidity crisis could materialize if repo creditors become nervous about a bank’s solvency and choose not to renew their positions. If enough creditors choose not to renew, the bank could likely be unable to raise sufficient cash by other means on such short notice, thereby precipitating a crisis. However, this vulnerability is directly related to the proportion of assets a bank has pledged as collateral. Bank A is least vulnerable since it has the least dependence on short-term repo financing (i.e., the lowest percentage of its assets out of the four banks is pledged as collateral: 272/823 = 33%).19.正确答案:C解析Only the last statement is wrong. Spreads tend to be small immediately after auctions and to peak before auctions. Immediately after an auction of a new OTR security, shorts can stay in the previous OTR security or shift to the new OTR. This substitutability tends to depress special spreads. Extra supply of the OTR security immediately following a re-opening auction tends to depress special spreads.20.正确答案:C解析LVaR = $1,000 + 0.5(10,000)(0.02) = $1,100.21.正确答案:C解析UL = VaR – EL (VaR与WCL worst-case loss同义)The risk-weight function does indeed include an effective maturity adjustment .22.正确答案:C解析Basel II total risk charge = CRC + MRC + ORCCRC = 650 × 75% × 8% = $ 39 millionORC = 15% × 80 = 12 millionTotal = 39 + 40 + 12 = $91 million23.正确答案:C解析The longer-term funding ratio is equal to the available amount of stable funding divided by the required amount of stable funding. Under Basel III, this ratio must equal or exceed 100%. Small Bank’s net stable funding ratio = $255/$250 = 102%.24.正确答案:C解析At its meeting in March 2008, the Basel Committee reviewed comments received and decided to expand the scope of the capital charge (i.e., expand the incremental default risk charge , IDRC, to the incremental risk charge, IRC). The decision was taken in light of the recent credit market turmoil where a number of major ranking organizations haveexperienced large losses, most of which were sustained in banks’ trading books. Most of those losses were not captured in the 99%/10-day VaR. Since the losses have not arisen from actual defaults but rather from credit migrations combined with widening of credit spreads and the loss of liquidity, applying an incremental risk charge covering default risk only would not appear adequate. For example, a number of global financial institutions commented that singling out (挑出) just default risk was inconsistent with their internal practices and could be potentially burdensome.25.正确答案:C解析Basel II relies heavily on external credit ratings and the Committee has a focus to reduce reliance on external ratings. Regarding A, Basel III will add the liquidity coverage ratio and the net stable funding ratio. Regarding B, Basel III will phase-in the countercyclical buffer requirement. Regarding D, this is true. The new leverage ratio (Tier 1/Total Exposure) began in 2013 as an additional measure.26.正确答案:A解析The capital conservation buffer is intended to provide an extra cushion against loss in times of stress. It is 2.5% Common Equity Tier 1 capital to risk-weighted assets, which in effect increases the total Common Equity Tier 1 capital ratio to 7%.27.正确答案:A解析Due to the nature of the banking industry, Basel II/III is more focused on systemic risk as opposed to trying to achieve a safety level for the whole company. However, it does focus on three risk classes, which are all asset-specific (market risk, credit risk, and operational risk). The goal of Basel II/III is to operate above capital requirements under Pillar 1.28.正确答案:C解析Too-big-to-fall risk suits both banks and CCPs.29.正确答案:B解析Bot h residential real estate exposure and commercial real estate exposure could be analyzed in new standardized approach.30.正确答案:C解析Because banks were able to use a wide range of models for calculating the AMA, there was more flexibility to these approaches than under the new SMA. TSA and ASA wereolder approaches rather than variations of the SMA. AMA did account for internal losses. The SMA is non-model-based, whereas the AMA did incorporate bank-specific models.31.正确答案:D解析Its primary advantage is that it is simple-to-implement: the basic LVaR simply adds one-half the spread to adjust for liquidity risk.32.正确答案:B解析What is needed is a liquidity adjustment that reflects the response of the market to a possible trade. The formula to use is the ratio of LVaR to VaR:33.正确答案:C我的答案:未作答解析34.正确答案:A解析Funding liquidity risk or balance sheet risk results when a borr ower’s credit position is either deteriorating or is perceived by market participants to be deteriorating. It also occurs when the market deteriorates. Under these conditions, creditors may withdraw credit or change the terms of credit. In this case, the lender is increasing the haircut and is thus changing the terms of credit. Glenn Fund’s creditworthiness does not actually have to decline for a lender to withdraw credit or change the terms of credit.35.正确答案:D解析D is False, the opposite is the case. In general, the liquidity risks are related in potentially causal chains.36.正确答案:A解析Some argue that information technology, marketing, and financial innovation result in economies of scope for large bank holding companies. Conversely, the recent financial crisis raised the concern that the size of bank holding companies creates diseconomies of scope with respect to risk management.37.正确答案:C解析The 2011 CCAR required banks to provide results from their own stress scenarios but the EBA Irish did not. After the 2011 EBA Irish tests, €24 billion was required to increase the capital of several banks. The 2011 CCAR, unlike the SCAP and the 2012 CCAR, only required the disclosure of macro-level scenario results. The EBA Irish did not change the stress horizon from two years to one year.38.正确答案:B解析Country risk refers to using a service provider based in a foreign country and subjecting the financial institution to potential economic and political risks in that country. Clearly, it is not a relevant risk arising from the breach of confidential customer data.39.正确答案:C解析Interest rate risk is the broad market variable captured by VaR while credit risk is the specific variable captured by the specific risk charge (SRC).40.正确答案:B解析The three common “lines of defense” suggested by the Basel Committee on Banking Supervision and employed by firms to control operational risks are: (1) business line management, (2) an independent operational risk management function, and (3) independent reviews of operational risks and risk management.。
2010 FRM Level II百题巅峰班讲义(下册)讲师:吴轶 CFA FRM PRM CQF CISI2011年05月Part 3 Credit Risk ManagementKey Point: Joint Default Probability1.Consider an A-rated bond and a BBB-rated bond. Assume that the one-year probabilities ofdefault for the A- and BBB-rated bonds are 2% and 4%, respectively, and that the joint probability of default of the two bonds is 0.15%. What is the default correlation between the two bonds?A.0.07%B. 2.6%C.93.0%D.The default correlation cannot be calculated with the information provided.Answer: BKey Point: Credit EventsDowngrade from a rating agency isn’t defined as credit event.Key Point: Default Probability Calculation2. A portfolio consists of 17 uncorrelated bonds, each rated B. The 1-year marginal defaultprobability of each bond is 5.93%. Assuming an even spread of default probability over theyear for each of the bonds, what is the probability of exactly 2 bonds defaulting in the first month?A.0.0325%B.0.325%C.0.024%D.0.24%Answer: BGiven a 1-year marginal default rate of 5.93%, the 1-month marginal default rate is = 0.00508. The number of combinations of 2 bonds from 17 bonds is 17.16/2, and so the probability of exactly 2 bonds defaulting in the first month is: (17*162) + 0.005082 + (1 – 0.00508)15 = 0.325%3. A corporate bond will mature in three years. The marginal probability of default in year oneis 3%. The marginal probability of default in year two is 4%. The marginal probability of default in year three is 6%. What is the cumulative probability that default will occur during the three-year period?A.12.47%B.12.76%C.13%D.13.55%Answer: AThis is one minus the survival rate over three years: S3(R) = (1 −d1)(1 −d2)(1 −d3) = (1 −0.03)(1 −0.04)(1 −0.06) = 0.8753. Hence, the cumulative default rate is 0.1247.Key Point: Recovery Rate4.Which of the following statement is incorrect?A.Recovery rates are negatively related to default rates.B.The distribution of recovery rates is often modeled with a gamma distribution.C.The legal environment is also a main driver of recovery rates.D.From Moody’s, the average recovery rate for senior unsecured debt is around f = 37%.Answer: BThe distribution of recovery rates is often modeled with a beta distribution.Key Point: Using Spread to price Default Risk¾Risk-neutral PD5.The risk-free rate is 5% per year and a corporate bond yields 6% per year. Assuming arecovery rate of 75% on the corporate bond, what is the approximate market implied one-year probability of default of the corporate bond?A. 1.33%B. 4.00%C.8.00%D. 1.60%Answer: B6. A loan of $10 million is made to a counterparty whose expected default rate is 2% per annumand whose expected recovery rate is 40%. Assuming an all-in cost of funds of LIBOR for the lender, what would be the fair price for the loan?A.LIBOR + 120bpB.LIBOR + 240bpC.LIBOR − 120bpD.LIBOR + 160bpAnswer: A7.The zero coupon bond of an A-rated company maturing in five years is trading at a spread of1% over the zero-coupon bond of a AAA-rated company maturing at the same time. The spread can be explained by:I.Credit riskII.Liquidity riskIII.Tax differentialsA.I onlyB.I and II onlyC.I and III onlyD.I, II, and IIIAnswer: BTax differentials cannot explain the difference because both bonds are corporate bonds and subjectto taxes. By contrast, the A-rated bond has higher credit risk and possibly lower liquidity,implying a higher yield.8.Suppose XYZ Corp. has two bonds paying semiannually according to the following table.The recovery rate for each in the event of default is 50%. For simplicity, assume that eachbond will default only at the end of a coupon period. The market-implied risk-neutralprobability of default for XYZ Corp. isRemaining Maturity Coupon(30/360) Price T-bill rate6 months8% 99 5.5%1 year9% 100 6%A.Greater in the first six-month period than in the secondB.Equal between the two coupon periodsC.Greater in the second six-month period than in the firstD.Cannot be determined from the information providedAnswer: AFirst, we compute the current yield on the six-month bond, which is selling at a discount. Wesolve for y∗ such that 99 = 104/(1 + y∗/200) and find y∗ = 10.10%. Thus, the yield spread for thefirst bond is 10.1 − 5.5 = 4.6%. The second bond is at par, so the yield is y∗= 9%. The spread forthe second bond is 9 − 6 = 3%. The default rate for the first period must be greater. The recoveryrate is the same for the two periods, so it does not matter for this problem.9.You are analyzing two comparable (same credit rating, maturity, liquidity, rate ) US callablecorporate bonds. The following data is available for the nominal spread over the US Treasuryyield curve and Z spread and option-adjusted spread (OAS ) relative to the US Treasury spotcurve:X YNominal spread 145 130Z spread 120 115OAS 100 105The nominal spread on the comparable option-free bonds in the market is 100 basis points.Assuming that there is no model risk with your OAS model, which of the followingstatements is correct?A.X only is undervalued.B.Y only is undervalued.C.X and Y both are undervalued.D.Neither X nor Y is undervalued.Answer: BKey Point: Merton Model10.According to the Merton model, if the firm’s debt has a face value of $60 and the value of thefirm is $50 when the debt matures, what is the payoff to the debt holders and to the shareholders?Payoff to Debt Holders Payoff to Share HoldersA.$50 $10B.$10 $0C.$10 $10D.$50 $0Answer: DThe payment to debt holders = Dm - max (Dm - Vm, 0) = 60 - max (60 - 50, 0) = $50The payment to the firm’s stock holders = max (Vm - Dm, 0) = max (50-60, 0) = $0At maturity of the debt, if the value of the firm’s assets is less than the value of the firm’s debt, then the firm goes into default.Key Point: KMV Model11.You are given the following information about firm A:·Market value of asset at time 0 = 1000·Market value of asset at time 1 = 1200·Short-term debt = 500·Long-term debt = 300·Annualized asset volatility = 10%According to the KMV model, what are the default point and the distance to default at time 1?Default Point Distance to DefaultA.800 3.33B.650 7.50C.650 4.58D.500 5.83Answer: CDefault Point=1 5003006502+×=(), Distant to Default=1 12005003002 4.58120010%−+×=×()Key Point: Credit Exposure12.If a counterparty defaults before maturity, which of the following situations will cause acredit loss?A.You are short Euros in a one-year euro/USD forward FX contract, and the euro hasappreciated.B.You are short Euros in a one-year euro/USD forward FX contract, and the euro hasdepreciated.C.You sold a one-year OTC euro call option, and the euro has appreciated.D.You sold a one-year OTC euro call option, and the euro has depreciated.Answer: B13.Consider a long position of the up-out call option with the cap price 120 and strike price 100.When the stock price increases from 80 to 130 and decreases back to 110, which of the following positions have the credit exposure?A.Long positions of the up-out call option when the stock price increases from 85 to 99.B.Long positions of the up-out call option when the stock price increases from 103 to 119.C.Long positions of the up-out call option when the stock price increases from 122 to 129.D.Long positions of the up-out call option when the stock price decreases from 127 to 115.Answer: BKey Point: Credit Exposure of the Interest Rate Swap14.Assume that swap rates are identical for all swap tenors. A swap dealer entered into aplain-vanilla swap one year ago as the receive-fixed party, when the price of the swap was 7%. Today, this swap dealer will face credit risk exposure from this swap only if the value of the swap for the dealer isA.Negative, which will occur if new swaps are being priced at 6%B.Negative, which will occur if new swaps are being priced at 8%C.Positive, which will occur if new swaps are being priced at 6%D.Positive, which will occur if new swaps are being priced at 8%Answer: C15.Assume that the DV01 of an interest rate swap is proportional to its time to maturity (whichat the initiation is equal to T). Assume that interest rate curve moves are parallel, stochastic with constant volatility, normally distributed, and independent. At what time will the maximum potential exposure be reached?A.T/4B.T/3C.T/2D.3T/4Answer: B16.Determine at what point in the future a derivatives portfolio will reach its maximum potentialexposure. All the derivatives are on one underlying, which is assumed to move in a stochastic fashion (variance in the underlying’s value increases linearly with time passage). The derivatives portfolio’s sensitivity to the underlying is expected to drop off as (T − t)2, where T is the time from today until the last contract in the portfolio rolls off, and t is the time from today.A.T/5B.T/3C.T/2D.None of the aboveAnswer: ATaking now the variance instead of the volatility, we haveσ2 = k(T −t)4 ×t,where k is a constant. Differentiating with respect to t, setting the derivative to zero, we have t = T/5.17.Assume that you have entered into a fixed-for-floating interest rate swap that starts today andends in six years. Assume that the duration of your position is proportional to the time to maturity. Also assume that all changes in the yield curve are parallel shifts, and that the volatility of interest rates is proportional to the square root of time. When would the maximum potential exposure be reached?A.In two monthsB.In two yearsC.In six yearsD.In four years and five monthsAnswer: BExposure is a function of duration, which decreases with time, and interest rate volatility, which increases with the square root of time. Define T as the original maturity and k as a constant. This give σ(Vt) = k(T − t)√t. Taking the derivative with respect to t gives a maximum at t = (T/3). This gives t = (6/3) = 2 years.Key Point: Credit Exposure of the Currency Swap¾With a positively sloped term structure, the receiver of the floating rate (payer of the fixed rate) has a greater credit exposure than the counterparty.¾The receiver of a low-coupon currency has greater credit exposure than the counterparty.18.Which one of the following deals would have the greatest credit exposure for a $1,000,000deal size (assume the counterparty in each deal is an AAA-rated bank and has no settlement risk)?A.Pay fixed in an Australian dollar (AUD) interest rate swap for one year.B.Sell USD against AUD in a one-year forward foreign exchange contract.C.Sell a one-year AUD cap.D.Purchase a one-year certificate of deposit.Answer: DThe CD has the whole notional at risk. Otherwise, the next greatest exposure is for the forward currency contract and the interest rate swap. The short cap position has no exposure if the premium has been collected. Note that the question eliminates settlement risk for the forward contract.19.Which of the following 10-year swaps has the highest potential credit exposure?A. A cross-currency swap after 2 yearsB. A cross-currency swap after 9 yearsC.An interest rate swap after 2 yearsD.An interest rate swap after 9 yearsAnswer: A20. BNP Paribas has just entered into a plain-vanilla interest-rate swap as a pay-fixedcounterparty. Credit Agricole is the receive-fixed counterparty in the same swap. The forward spot curve is upward-sloping. If LIBOR starts trending down and the forward spot curve flattens, the credit risk from the swap will:A. Increase only for BNP ParibasB. Increase only for Credit AgricoleC. Decrease for both BNP Paribas and Credit AgricoleD. Increase for both BNP Paribas and Credit AgricoleAnswer: BWith an upward-sloping term structure, the fixed payer has greater credit exposure. He receives less initially, but receives more lately. This back-loading of payments increases credit exposure. Conversely, if the forward curve flattens, the fixed payer (i.e., BNP Paribas) has less credit exposure. Credit Agricole must have greater credit exposure. Alternatively, if LIBOR drifts down, BNP will have to pay more, and its counterparty will have greater credit exposure.Key Point: Hair Cut, Exposure Limits, and Netting Agreement¾ Hair Cut: 1 (T-bill), 3 (T-note), 8 (T-bond) ¾1max(,0)max(,0)Ni i Net Exposure V V ===∑ 1max(,0)max(,0)Ni i Exposure V V ===∑Gross21. A diversified portfolio of OTC derivatives with a single counterparty currently has a netmark-to-market value of USD 20,000,000 and a gross absolute mark-to-market value (the sum of the value of all positive-value positions minus the value of all negative-value positions) of USD 80,000,000. Assuming there are no netting agreements in place with the counterparty, determine the current credit exposure to the counterparty.A. Less than or equal to USD 19,000,000B. Greater than USD 19,000,000 but less than or equal to USD 40,000,000C. Greater than USD 40,000,000 but less than USD 60,000,000D. Greater than USD 60,000,000Answer: CDefine X and Y as the absolute values of the positive and negative positions. The net value is X − Y= 20 million. The absolute gross value is X + Y = 80. Solving, we get X = 50 million. This is the positive part of the positions, or exposure.22.What are the benefits of novation?A.Both parties are allowed to walk away from the contract in the event of default.B.In a bilateral contract, it is specified that on default, the non-defaulting party nets gainsand losses with the defaulting counterparty to a single payment for all coveredtransactions.C.Financial market contracts can be terminated upon an event of default prior to thebankruptcy process.D.Obligations are amalgamated with others.Answer: DKey Point: Credit Triggers & Time Puts¾Credit triggers specify that if either counterparty’s credit rating falls below a specified level, the other party has the right to have the swap cash settled. These triggers are useful when the credit rating of a firm deteriorates slowly, because few firms directly jump from investment-grade into bankruptcy.¾Time puts, or mutual termination options, permit either counterparty to terminate unconditionally the transaction on one or more dates in the contract. This feature decreases both the default risk and the exposure. It allows one counterparty to terminate the contract if the exposure is large and the other party’s rating starts to slip.Key Point: Credit Derivatives 1 - CDS23. A portfolio consists of one (long) $100 million asset and a default protection contract on thisasset. The probability of default over the next year is 10% for the asset and 20% for the counterparty that wrote the default protection. The joint probability of default for the asset and the contract counterparty is 3%. Estimate the expected loss on this portfolio due to credit defaults over the next year with a 40% recovery rate on the asset and 0% recovery rate for the counterparty.A.$3.0 millionB.$2.2 millionC.$1.8 millionD.None of the aboveAnswer: CThe only state of the world with a loss is a default on the asset jointly with a default of theguarantor. This has probability of 3%. The expected loss is $100,000,000 × 0.03 × (1 − 40%) = $1.8 million.24.When an institution has sold exposure to another institution (i.e., purchased protection) in aCDS, it has exchanged the risk of default on the underlying asset for which of the following?A.Default risk of the counterpartyB.Default risk of a credit exposure identified by the counterpartyC.Joint risk of default by the counterparty and of the credit exposure identified by thecounterpartyD.Joint risk of default by the counterparty and the underlying assetAnswer: DThe protection buyer is exposed to the joint risk of default by the counterparty and underlying credit. If only one defaults, there is no credit risk.25.We are asked to value a credit default swap on a $10 million, two-year agreement, whereby A(the protection buyer) agrees to pay B (the guarantor, or protection seller) a fixed annual fee in exchange for protection against default of two-year bonds XYZ. The payout will be the notional times (100 − PB), where PB is the price of the bond at expiration, if the credit event occurs. Currently, XYZ bonds are rated A and trade at 6.60%. The two-year T-note trades at6.00%.Ending StateStartingState A B C DA 0.90 0.07 0.02 0.01B 0.05 0.90 0.03 0.02C 0 0.01 0.85 0.05D 0 00 0 1A.43800B.42800C.44800D.45800Answer: B26.Wallace, an emerging market bond trader, is holding a 5-year USD Malaysian corporate bondin his book. He is concerned about the risk of his position. Which of the following statements concerning the risk of his position is incorrect?A.The corporate bond could be upgraded so that it would have a higher rating thanMalaysian sovereign debt, but it is highly unlikely.B. Buying protection with a CDS would hedge the corporate bond position against somerisks but it would do a poor job of hedging the position if there is a drop in liquidity for emerging market sovereign bonds.C. A short position in Ringgits sovereign bond from Malaysia would always help hedge thecorporate bond against currency risk if the corporation is an exporter.D. A short position in a 5-year U.S. treasury and buying protection on the corporate bondusing a CDS would be a better hedge than just buying protection on the corporate bond.Answer: CKey Point: Credit Derivatives 2 - TRS27. A bank holds USD 60 million worth of 10-year 6.5% coupon bonds that are trading at a cleanprice of USD 101.82. The bank is worried by the exposure due to these bonds but cannot unwind the position for fear of upsetting the client. Therefore, it purchases a total return swap (TRS) in which it receives annual LIBOR + 100 bps in return for the mark-to market return on the bond. For the first year, the LIBOR sets at 6.25%, and by the end of the year the clean price of the bonds is at USD 99.35. The net receipt/ payment for the bank in the total return swap will be to:A. Receive USD 1.97 millionB. Receive USD 2.23 millionC. Pay USD 2.23 millionD. Pay USD 1.97 millionAnswer: A101.8299.35607.15*60*60 6.5* 1.97101.82101.82mm m m −+−=28. Risk Averse Bank (RAB) has made a loan of USD 100 million at 8% per annum. RAB wantsto enter into a total return swap under which it will pay the interest on the loan plus the change in the mark-to-market value of the loan, and in exchange, RAB will get LIBOR + 30 basis points. Settlement payments are made annually. What is the cash flow for RAB on the first settlement date if the mark-to-market value of the loan falls by 2% and LIBOR is 6%?A. Net inflow of USD 0.3 millionB. Net outflow of USD 0.3 millionC. Net inflow of USD1.7 millionD.Net outflow of USD 1.7 millionAnswer: A29. Gamma industries inc issues an inverse floater with a face value of USD 50.000.000 thatpays a semiannual coupon of 1150% minus LIBRO gamma industries intends to execute an arbitrage strategy and earn a profit by selling the notes. Using the proceeds to purchase a bond with a fixed semiannual coupon rate of 6.75% a year, and then hedge the risk by entering into an appropriate swap. Gamma industries receive a quote from a swap dealer witha fixed rate of 5.75% and a floating rate of LIBOR. What would be the most appropriate typeof swap of Gamma industries, Inc., to enter into to hedge its risk?A.Pay-fixed, receive-fixed swapB.Pay-floating, receive-fixed swapC.Pay-fixed, receive-floating swapD.The risk cannot be hedged with a swapAnswer: BShort inverse floater: -11.5% +LIBORLong a bond: +6.75%Net profit: -4.75% +LIBORThe swap in the market: 5.75% ~ LIBOR, so the LIBOR in the market is overpriced.Key Point: Credit Derivatives 3 – Structured Products & CDO30.King Motors Acceptance Corporation (KMAC), the finance arm of King Motors, issues anauto-loan asset-backed security that consists of a senior tranche, denoted Tranche A in the amount of $50 million and an interest payment of 5 percent, and two subordinated tranches, denoted Tranches X and Z respectively, each with a face amount of $35 million. Tranche X pays investors annual interest at a rate of 6.5 percent while Tranche Z pays investors annual interest at a rate of 7.5 percent. Which of the following methods of credit support would NOT affect the credit quality of subordinated Tranche X?A.The total amount of the auto loans that make up the asset-backed issue is $125 million.B.The weighted average interest rate on the auto loans making up the pool is 6.4 percent.C.Any defaults on the part of King Motor’s customers will be first absorbed by Tranche Z.D.KMAC has a reserve in the amount of $10 million that will remain on KMAC’s balancesheet.Answer: DAn investor’s claim when purchasing an ABS is solely with the ABS and no longer with the originator. The fact that KMAC has $10 million set aside means nothing for the ABS issue if it remains on KMAC’s balance sheet and is not part of the ABS issue. The other answer choices all describe forms of credit support that will support at least Tranches X and A, if not all 3 tranches. By having Tranche Z be subordinate to Tranche X, Tranche X has additional support. Also, loans of $125 million are used to back asset-backed securities worth ($50 + $35 + $35) = $120 million, which means the issue, is over-collateralized. The weighted average interest rate paid on the securities is approximately 6.2%. If the weighted average interest rate on the loans that make upthe pool is 6.4% that means there is an excess spread between the loans and securities that also provides support for the entire issue.31.The maximum benefits to the buyer of a credit-linked note (CLN) accrue when:A.there is a small credit downgradeB.there is no credit downgradeC.there is a large credit downgradeD.there is a defaultAnswer: BThe benefit to the CLN buyer is that the buyer earns a high return if there is no downgrade or default. The buyer’s primary risk is that there is a downgrade or default and the buyer earns a lower return.32.Which of the following statements about a cash collateralized debt obligation’s (CDO)special-purpose vehicle (SPV) is TRUE?A.In cash CDO, the SPV invests in the actual securities that are used to generate paymentto the tranches.B.In a synthetic CDO, the SPV invests in the actual securities that are used to generatepayment to the tranches.C.In a synthetic CDO, the SPV does not invest in the actual securities that are used togenerate payment to the tranches. Instead they invest only in a risk-free bond.D.In cash CDO, the SPV does not invest in the actual securities that are used to generatepayment to the tranches. Instead they invest in a default swap and a risk-free bond.Answer: AA cash collateralized debt obligation’s (CDO) special-purpose vehicle (SPV) invests in the actual securities that are used to generate payment to the tranches. A synthetic CDO's SPV does not invest in the actual securities that are used to generate payment to the tranches. Instead they invest in a default swap and a risk-free bond, and a cash CDO's SPV invests in the actual securities that are used to generate payment to the tranches.33.In a typical collateralized bond obligation (CBO), a pool of high-yield bonds is posted ascollateral and the cash flows from the collateral are structured as several classes of securities (the offered securities) with different credit ratings and a residual piece (the equity), which absorbs most of the default risk. When comparing the market value weighted average rating of the collateral and that of the offered securities, which of the following is true?A.The market value-weighted average rating of the collateral is about the same as theoffered securities.B.The market value-weighted average rating of the collateral is higher than the offeredsecurities.C.The market value-weighted average rating of the collateral is lower than the offeredsecurities.D.The market value-weighted average rating of the collateral may be lower or higher thanthe offered securities.Answer: CThe rating of the collateral must be between that of the offered securities and the residual. Say that the collateral is rated B, with 5% probability of default (PD); the offered securities represent 80% of the total market value. These are more highly rated than the collateral because the equity absorbs the default risk. If the offered securities are rated BB (with 1% PD), the equity must be such that 80% × 0.01 + 20% × x = 0.05, which yields an PD of 21% for the equity, close to a CCC rating.34. A standard synthetic CDO references a portfolio of 10 corporate names. Assume thefollowing. The total reference notional is X, and the term is Y years. The reference notional per individual reference credit name is X/10. The default correlations between the individual credit names are all equal to one. The single-name CDS spread for each individual name is 100 bp, for a term of Y years. The assumed recovery rate on default for all individual reference credits is zero in all cases. The synthetic CDO comprises two tranches, a 50% junior tranche priced at a spread J, and a 50% senior tranche priced at spread S. All else constant, if the default correlations between the individual reference credit names are reduced from 1.0 to 0.7, what is the effect on the relationship between the junior tranche spread J and the senior tranche spread S?A.The relationship remains the sameB.S increases relative to JC.J increases relative to SD.The effect cannot be determined given the data suppliedAnswer: CIf the correlation is one, all names will default at the same time, and the junior and senior tranche will be equally affected. Hence, their spread should be 100bp, which is the same as for the collateral. With lower correlations, the losses will be absorbed first by the junior tranche. Therefore, the spread on the junior tranche should be higher, which is offset by a lower spread for the senior tranches.35.Which of the following statements about collateralized debt obligations squared (CDO2) isFALSE?A.CDO2 are CDOs that invest in other CDOs.B.Yields on CDO2 are typically lower than yields on CDOs.C.CDO2 can be very complicated.D.There is often an overlap of assets held with CDO2.Answer: BCDO2 are CDOs that invest in other CDOs. They are complicated and often there is an overlap of assets held with CDO2. They typically offer higher yields than regular CDOs.Key Point: Portfolio Credit Risk ModelCreditMetrics CreditRisk+KMV CreditPf.View Originator J.P. Morgan Credit Suisse KMV McKinseyModeltype Bottom-up Bottom-up Bottom-up Top-down Risk definition Market value Default losses Default losses Market valueRisk drivers Asset values Default rates Asset values Macro factorsCredit events Rating change/DefaultDefaultContinuousdefault prob.Rating change/DefaultProbability UnconditionalUnconditionalConditional Conditional Volatility Constant Variable Variable VariableCorrelation From equities(structural)Default process(reduced-form)From equities(structural)From macrofactorsRecovery rates Random Constant withinbandRandom RandomSolution Simulation/AnalyticAnalytic Analytic Simulation36.Which of the following statements about credit risk models is correct?A.KMV models offer a structural approach to measuring credit risk that is based on creditmigration.B.CreditRisk+ models offer an actuarial approach to measuring credit risk that treats thebankruptcy and recovery processes as endogenous.C.KMV models are an extension of Merton’s option pricing model employing equity pricevolatility as a proxy for asset price volatility.D.CreditRisk+ models, like the reduced-form models, use a chi-squared distribution todescribe default.Answer: CA Incorrect. KMV models are NOT based on credit migration.B Incorrect. In CreditRisk+ models, the bankruptcy/recovery processes are exogenous.C Correct. KMV models employ equity price volatility as a proxy for asset price volatility.D Incorrect. CreditRisk+ models use a Poisson or Poisson-like distribution to describe default.37.The RiskMetrics model generates VaR directly from the mean and variance parameters of theportfolio, which does not provide an estimate of the worst-case scenario loss. Note that the RiskMetrics method does account for correlation between asset classes. Which of the。