四六级常考重点语法
- 格式:doc
- 大小:99.00 KB
- 文档页数:16

英语四六级常考语法精讲:时态四六级常考语法之时态1. 现在完成时、过去完成时以及将来完成时之间的区别1) 现在完成时:① 构成:have / has +过去分词② 语法意义及要点:A. 现在完成时表示一个过去开始的状态或动作持续到现在并可能继续持续下去,常同表示一段时间的状语连用。
如so far, up to now, since, for a long time等。
--He has worked as a teacher for many years.--Up till now, nothing has gone wrong.B. 现在完成时表示一个过去发生的对现在仍有影响的动作或事件。
常与不确定的过去时间状语连用,如yet, jus t, before, recently等;也同表示频度时间状语连用,如often, ever, never, sometimes, several times等;还可同包括现在时间在内的时间状语连用,如now, today, this morning等。
但不能同特定的过去时间状语连用(last yea r , in 1997等)。
--I have never learned Japanese before.--We have been quite busy lately (recently).C. 在时间或条件状语从句中,当表示将来完成时的意义时,要用现在完成时来代替将来完成时。
--We’ll start at 5 o’clock if it has stopped raining by then.--I shall go to see you when I have finished my homework.Note: 行为不能持续的瞬间动词(Instantaneous Verb), 如arrive, begin, come, go, start, leave, die, joi n等通常不能用于这一语法意义,即该类动词在现在完成时中不能与表示一段时间的状语连用。

(简明版)大学英语四级语法大全一、名词(Noun)名词是一个词汇类别,用于表示人、动物、事物、地点等。
在句子中,名词可以作为主语、宾语、定语、表语等。
例如:- 主语:Cats are cute animals.Cats are cute animals.- 宾语:I love dogs.dogs.- 定语:The green tree is beautiful.green tree is beautiful.- 表语:My brother is a doctor.doctor.二、代词(Pronoun)代词是一个词汇类别,用于替代名词。
它们可以替代特定的人或事物,以避免重复使用相同的名词。
例如:- 人称代词:I am going to the store.I am going to the store.- 物主代词:That book is mine.mine.- 指示代词:This is my car.This is my car.- 相互代词:They saw each other at the party.each other at the party.三、形容词(Adjective)形容词是用于描述名词或代词的词汇。
它们可以提供关于名词或代词的特征、性质、状态等信息。
例如:- 描述名词:She has a beautiful voice.beautiful voice.- 描述代词:I am so tired.so tired.- 修饰词组:He bought a red sports car.red sports car.四、副词(Adverb)副词是用于描述动词、形容词、其他副词或整个句子的词汇。
它们可以提供关于时间、地点、程度等信息。
例如:- 描述动词:She sings beautifully.beautifully.- 描述形容词:He is extremely tall.extremely tall.- 描述副词:She runs very fast.very fast.- 描述整个句子:Certainly, I can help you.Certainly, I can help you.五、动词(Verb)动词是用于表示动作、状态或发生事件的词汇。
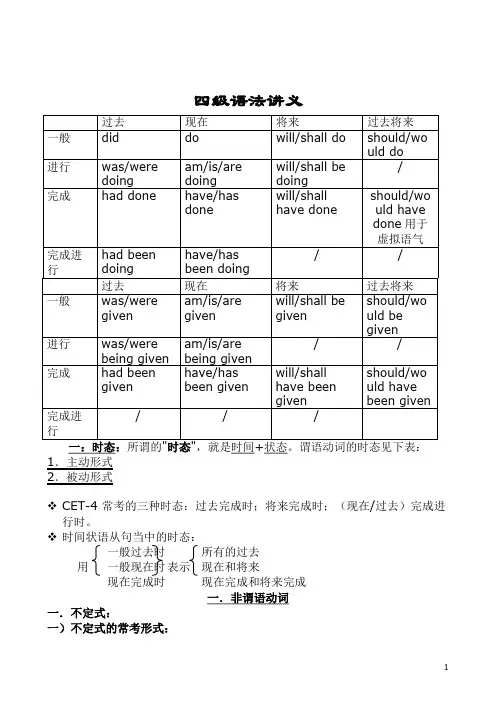
四级语法讲义一:时态:,就是时间+状态。
谓语动词的时态见下表:1.主动形式2.被动形式❖CET-4 常考的三种时态:过去完成时;将来完成时;(现在/过去)完成进行时。
❖时间状语从句当中的时态:一般过去时所有的过去用一般现在时表示现在和将来现在完成时现在完成和将来完成一.非谓语动词一.不定式:一)不定式的常考形式:1)一般形式:He decided to work harder in order to catch up withthe others.被动形式: He preferred to be assigned some heavier work to do.语法功能:表示与谓语动词同步发生2)完成形式:He pretended not to have seen me.被动形式:The book is said to have been translated into many languages.语法功能:表示发生在谓语动词之前二)不定式常考的考点:1)不定式做定语----将要发生2)不定式做状语----目的3)不定式充当名词功能---To see is to believe.三)不定式的省略1)感官动词 see, watch, observe, notice, look at, hear, listen to, smell, taste, feel+ do表示动作的完整性,真实性;+ doing表示动作的连续性,进行性I saw him work in the garden yesterday.昨天我看见他在花园里干活了。
(强调"我看见了"这个事实)I saw him working in the garden yesterday.昨天我见他正在花园里干活。
(强调"我见他正干活"这个动作)❖感官动词后面接形容词而不是副词:The cake tastes good; It feels comfortable.2) 使役动词 have bid make let 等词后不定式要省略但同1)一样被动以后要还原toI ‘d like to have John do it.I have my package weighed.Paul doesn’t have to be ma de to learn.3) help help sb do help sb to do help do help to do四)有些动词后只跟不定式如:want,wish,hope,manage,promise,refuse,pretend,plan,offer,decide,agree,expect allow sb to do, cause sb to do , permit sb to do, enable sb to doforce sb to do. be more likely to do love to do warn sb to do be able to dobe ambitious to do. begin to do . start to do五) 有的时候to后面要接-ing形式accustom (oneself) to; be accustomed to; face up to; in addition to;look forward to; object to; be reduced to; resign oneself to; be resigned to; resort to; sink to; be used to; be alternative to; be close/closeness to; be dedication/dedicated to; beopposition/opposed to; be similarity/similar to.三、need/want 后的-ing形式具有被动的意思。

四六级必备:20个语法核心口诀1、英语的词类句子要由词组成,英语词类有十种:句中成分用实词,名、代、动、副、数、形容、冠、介、连词和感叹,虚词附加或沟通。
词类功能掌握了,造句之时好运用。
2、语序歌主、谓、宾、表同汉语,定语有同也有异。
状语位置更特殊,不能全和汉语比。
3、肯定句变一般疑问句have和be提句首,其它助词Do开头。
时间、人称由do变,动词只把原形留。
谓语助词有几个,第一助词提句首。
4、肯定句变否定句否定词语加not,放在be和have后。
其它要加动词do,do的后面加not,时间、人称由do变,动词原形总保留。
谓语若是助词多,not紧跟第一个。
5、名词的所有格名词只变数,不分主宾格。
人和动物类,可变所有格。
撇(’)后加s,相当汉语“的”。
时间、距离等,也变所有格。
6、名词变复数单数变为复数式,加上“s”统言之。
下列结尾名词后,要加“s”先加“e”:发音[∫][t∫][s]和[z],或是辅音加“o”时。
有些名词变复数,词尾变化要注意:“y”前字母是辅音,一律变“y”为“ie”;遇到“f/fe”,有时需要变“ve”少数名词不规则,特别情况靠硬记。
7、时间名词前所有介词的速记年月周前要用in,日子前面却不行。
遇到几号要用“on”,上午下午又是“in”。
要说某日上下午,用on换in才能行。
午夜黄昏用at,黎明用它也不错。
at也在时分前,说“差”用to,说“过”要用past。
8、介词用法歌介词加宾语,才能有实意。
表、定、状、宾、补,词组在句里。
9、介词顺口溜in在……里,out在……外,在旁边的是beside,靠近的为by。
on在……上,under在……下,above在上头,below在底下。
10、be的用法歌动词be,变化大,“I”用“am”“You”用“are”Is用于它(it)、他(he)、她(she)复数一定要用“are”,切莫用错闹笑话。
11、动词的时态四种时间各四式,联想对比便于记。

四六级语法知识点详解英语四六级考试是大学英语水平考试的一种,对于很多学生来说,语法是其中一个比较难以掌握的部分。
本文将详细解释四六级考试中常见的语法知识点,帮助学生更好地应对考试。
一、时态和语态1. Simple Present Tense(简单现在时)简单现在时表示经常或习惯性发生的动作、真理、客观存在的事实等。
结构:主语 + 动词原形(第三人称单数在动词后加s或es)例句:I eat breakfast every morning.(我每天早上吃早餐)2. Present Continuous Tense(现在进行时)现在进行时表示现在正在进行的动作。
结构:主语 + am/is/are + 动词ing形式例句:She is studying in the library now.(她正在图书馆学习)3. Simple Past Tense(简单过去时)简单过去时表示过去某个时间发生的动作或存在的状态。
结构:主语 + 动词过去式例句:They visited their grandparents last weekend.(他们上周末去看望了他们的祖父母)4. Past Continuous Tense(过去进行时)过去进行时表示过去某个时间正在进行的动作。
结构:主语 + was/were + 动词ing形式例句:I was watching TV when she called me.(她打电话给我时,我正在看电视)5. Simple Future Tense(简单将来时)简单将来时表示将来要发生的动作或存在的状态。
结构:主语 + will + 动词原形例句:We will have a party next week.(我们下周要开个派对)6. Future Continuous Tense(将来进行时)将来进行时表示将来某个时间正在进行的动作。
结构:主语 + will be + 动词ing形式例句:I will be sleeping when you arrive.(当你到达时,我将正在睡觉)7. Passive Voice(被动语态)被动语态用于强调动作的承受者而不是施动者。


英语四级必考知识点英语四级对于应届⽣求职招聘⾄关重要,是考银⾏和公务员的硬性条件。
分数越⾼,意味着⾃⾝的英语能⼒,学习能⼒越强,接下来⼩编给⼤家分享关于英语四级必考知识,希望对⼤家有所帮助!英语四级必考知识1语法部分考查重点1、虚拟语⽓的考点为:would rather+that从句+⼀般过去时;It is vital/ necessary/ important/ urgent/ imperative/ desirable/ advisable/ natural/ essential+that+(should)动词原形;proposal/suggestion+that+动词原形;It is time/about time/high time+that+⼀般过去时;lest+that+should+动词原形;if only+that+would+动词原形。
2、状语从句的考点为:⾮if引导的条件状语从句,此类句⼦多⽤at times,provided,so long as,in case,once等来替代if;由even if/so,now that,for all等引导的让步状语从句;just/hardly...when引导的时间状语从句;more than,as...as,not so much as,the same as,as much as等引导的⽐较状语从句。
3、独⽴主格结构多以逻辑主语+分词的形式出现。
4、情态动词多与完成时形式连⽤。
5、定语从句重点考查介词+关系代词(which)和as作为关系代词。
英语四级必考知识2词汇部分考查重点1、动词、名词与介词的搭配如:popular/patient+with;yield/solution/adapt/transfer/access+to;accuse/require+of;charge+for;under+discussion等等。
2、习惯⽤法如:confess to/set about/be used to+doing;be supposed to/have/make sb.+do等。

英语四六级语法题考点经典总结一、非谓语动词近几年的语法测试中非谓语动词约占31.1%,平均每年近5道题,可谓是语法项目考查的重点,那么非谓语动词的考查都有哪些特点,解答时又应注意些什么呢?下面我和大家就一起来分析一下:1、非谓语动词考查特点1) 谓语动词与非谓语动词的判断对谓语动词与非谓语动词区别的考查主要集中在独立主格结构,如:All things ___ because of the snowstorm, many passengers could do nothing but take the train.(1999.1)A. had been canceledB. have been canceledC. were canceledD. having been canceled四个选项中有三个是谓语动词,只有D是非谓语动词,只要同学们能判断出这里是非谓语动词做状语,则不用考虑时态的问题,答案自明。
2) 谓语动词后不定式与动名词的选择谓语动词后接不定式还是接动名词也是四级语法测试中的一个题眼。
如:①I don't mind ____ the decision as long as it is not too late.(2000.1)A. you to delay makingB. your delaying makingC. your delaying to makeD. you delay to make②Had I remembered ____ the windows, the thief would not havegot in.(1996.1)A. to closeB. closingC. to have closedD. having closed③Your hair wants ______ . You'd better have it done tomorrow.A. cutB. to cutC. cuttingD. being cut(1997.6)这类题涉及三个方面:谓语动词后应该接不定式还是动名词?即可接不定式又可接动名词时,结构和意思上有何差别?不定式与动名词用主动形式还是用被动形式?3) 做定语的非谓语动词的选择从近几年的考查情况来看,对做定语的非谓语动词的考查有两种情况:(1)对一般概念的考查,而不是固定结构中的非谓语动词做定语。

英语四级考试语法结构与词汇一、语法结构部分。
1. 时态。
- 一般现在时。
- 用法:表示经常发生的动作、存在的状态或客观事实。
- 结构:主语 + 动词原形(第三人称单数主语时动词加 -s或 -es)。
例如:I play football every Sunday.(play,动词原形,[pleɪ])He plays football every Sunday.(plays,动词第三人称单数形式,[pleɪz])- 一般过去时。
- 用法:表示过去某个时间发生的动作或存在的状态。
- 结构:主语+动词的过去式。
例如:I saw a movie yesterday.(saw,see的过去式,[sɔː],动词)- 现在进行时。
- 用法:表示现在正在进行的动作。
- 结构:主语+be动词(am/is/are)+动词的 -ing形式。
例如:She is reading a book.(is,be动词第三人称单数形式,[ɪz];reading,动词的 -ing形式,['ri ːdɪŋ])- 过去进行时。
- 用法:表示过去某个时刻正在进行的动作。
- 结构:主语+be动词(was/were)+动词的 -ing形式。
例如:He was watching TV at 8 o'clock last night.(was,be动词第一、三人称单数过去式,[wɒz];watching,动词的 -ing形式,['wɒtʃɪŋ])2. 从句。
- 定语从句。
- 概念:在句中作定语,修饰名词或代词。
- 关系代词:who(指人,主格,[huː]),whom(指人,宾格,[huːm]),which(指物,[wɪtʃ]),that(指人或物,[ðæt])。
例如:The boy who/that is standing there is my brother.(这里who/that引导定语从句修饰the boy)- 名词性从句。

大学英语四级必考语法汇总大学英语四级考试是学生们普遍参加的考试,语法是其中必考的部分,以下是四级必考语法汇总:1. 时态英语时态有12种,四级考试中要掌握以下几种:- 一般现在时:表示经常性或惯性的动作,或现在的状况。
- 现在进行时:表示现在正在进行的动作。
- 一般过去时:表示过去某个时间发生的动作或情况。
- 过去进行时:表示过去某个时间正在进行的动作。
- 现在完成时:表示过去的动作对现在造成的影响或结果。
- 过去完成时:表示过去某个时间之前曾经发生的动作或状态。
- 将来时:表示将来某个时间发生的动作。
2. 从句从句是指一个完整的句子,它在句子中充当某个成分,四级考试中要掌握以下几种:- 定语从句:修饰某个名词或代词。
- 主语从句:作为主语的从句。
- 宾语从句:作为宾语的从句。
- 同位语从句:阐述前面名词或代词的内容。
- 状语从句:修饰或补充主句的内容。
- 结果状语从句:表示结果的从句。
- 让步状语从句:表示让步的从句。
- 条件状语从句:表示条件的从句。
3. 词性和词组四级考试中需要掌握名词、代词、动词、形容词和副词的用法,以及一些固定用法的词组,例如:- be based on:基于。
- be fond of:喜欢。
- as soon as possible:尽快。
- break the ice:打破僵局。
4. 语态英语语态有两种,四级考试中需要了解和区分主动语态和被动语态,以及两种语态在句子中的变化。
5. 语气英语语气有三种,四级考试中需要了解和区分陈述语气、祈使语气和虚拟语气。
以上就是大学英语四级必考语法的汇总,希望对大家备考有所帮助。

洛基英语,中国在线英语教育领导品牌双重所有格物主代词不可与a, an, this, that, these, those, some, any, several, no, each, every, such, another, which等词一起前置,修饰一个名词,而必须用双重所有格。
公式为:a, an, this, that +名词+of +名词性物主代词。
如:a friend of mine.each brother of his.1)物主代词既有表示所属的作用又有指代作用,例如:John had cut his finger; apparently there was a broken glass on his desk.约翰割破了手指,显而易见,他桌子上有个破玻璃杯。
物主代词有形容词性(my, your等)和名词性(mine, yours等)两种,形容词性的物主代词属于限定词。
名词性的物主代词在用法上相当于省略了中心名词的--'s属格结构,例如:Jack's cap意为The cap is Jack's.His cap意为The cap is his.2) 名词性物主代词的句法功能a. 作主语,例如:May I use your pen? Yours works better.我可以用一用你的钢笔吗? 你的比我的好用。
b. 作宾语,例如:I love my motherland as much as you love yours.我爱我的祖国就像你爱你的祖国一样深。
c. 作介词宾语,例如:Your should interpret what I said in my sense of the word, not in yours.你应当按我所用的词义去解释我说的话,而不能按你自己的意义去解释。
d. 作主语补语,例如:The life I have is yours. It's yours. It's yours.我的生命属于你,属于你,属于你。
英语四六级重点语法英语四六级重点语法汇总动名词1. 某些动词后要接动名词某些及物动词后能用动名词而不能用不定式作宾语,其中最常用动词的有admit, avoid, appreciate, complete, consider, delay, deny, dislike, enjoy, escape, excuse, fancy, finish, forgive, involve, imagine, can’t help, mind, miss, postpone, practise, prevent, quit, resent, risk, resist, suggest等。
She suggested spending another day in the mountain area.There’s no way to escape doing the work.She is considering asking her employer for a rise.Note:①在need、want、require、deserve等动词后的动名词相当于不定式的被动式The clock needs/wants repairing. (=The clock needs/wants to be repaired)The disabled deserve respecting. (=The disabled deserve to be respected.)②在like、hate、prefer等动词后,如果表示一般倾向,则用动名词作宾语;如果指具体的某次发生在将来的行动,则要用不定式。
I like reading books of this kind, but I don’t like to read that book.She prefers walking to cycling.I prefer to stay at home today.③在remember、forget、regret等动词后,如果用动名词作宾语,则表示该宾语的动作发生在动词谓语的动作之前;如果用不定式作宾语,则表示宾语的动作发生在动词谓语的动作之后I remembered locking the door. (=I remembered that I hadlocked the door.)I remembered to lock the door (=I remembered that I was to lock the door.)I regret telling you about it. (=I regret that I told you about it.)I regret to tell you he has fallen ill. (=I regret that I am to tell you he has fallen ill.)2. 动名词作介词的宾语动名词可作介词的宾语,与介词一起构成介词短语,在句中作定语、状语或表语。
大学英语四六级语法讲义一、识别句子成分必须记住的原理1.衡量是否是一个句子的标准:是否有动词,有动词就是句子,反之不是句子。
2.英语构句原则规定:一个简单句中只能有一个谓语动词。
3.长难句的构成:主句、从句、介词短语、非谓语动词。
(1)主句的辨识:谓语动词(2)从句的辨识:连词+与之匹配的谓语动词A.从介词开始到其后跟的名词结束(3)介词短语:B.从介词开始到动名词结束C.从介词开始到动名词的宾语结束)动名词(doing)to do动词不定式(非谓语动词:(4))ing现在分词(do e)过去分词(don4.衡量长难句划分是否正确的标准:整个句子中谓语动词的个数比连词多一个5.长难句划分方法:连动切割法·连动切割法:将句子中的所有连词和动词(连词、动词的排列不分先后)作为切割长难句的基础,断开主句和从句。
·长难句划分的具体步骤:【第一步】断开主句和从句通读整个句子找出所有的连词或动词,并将连词和动词匹配起来(主要是针对从句而言,主句不存在连词,从句连词和动词的匹配遵守就近原则),然后再给动词匹配主语(主句的主语在谓语之前找;从句的主语在连词和与之匹配的谓语动词中间找,如果它们中间没有任何词语,那么连词本身就是这个从句的主语。
)在进行第一步的时候注意以下5 种情况:如果动词前没有任何(落单的)连词,那么该动词应该是主句的谓语。
1如果动词前有两个或两个以上的连词,那么动词和连词的匹配遵守就近原则。
2如果动词比连词多两个或两个以上,说明有连词省略了或者把过去分词错当3成谓语动词。
切割嵌套的从句:从句往往从连词开始到从句中的第二个谓语动词出现之前4结束。
有些词既可以是连词,也可以具有别的词性5例如:that:既可以是连词,也可以是代词或者限定词;than、before、after、until 等既可以是连词也可以是介词【第二步】断开介词短语和非谓语动词二、总结复习句子的主要成分1、主语(1)定义:主语是动作的发出者。
四六级语法题常考重点语法在英语学习中占据重要的地位,而在四六级考试中,语法题是非常常见且重要的部分。
掌握语法的常考重点,可以帮助我们提高答题准确性和效率。
本文将介绍四六级语法题的常考重点,希望对大家备考有所帮助。
一、时态1. 一般现在时:表达习惯性、经常性动作,真理、法则等。
例:He often goes to the gym.2. 现在进行时:表示正在进行的动作。
例:They are studying in the library.3. 一般过去时:表示过去的动作或状态。
例:She visited her grandparents last weekend.4. 过去进行时:表示过去某个时间点正在进行的动作。
例:I was watching TV when you called.5. 现在完成时:表示过去发生的动作对现在造成的影响或仍然持续的动作。
例:We have lived here for five years.6. 过去完成时:表示在过去某一时间点或动作之前完成的动作。
例:By the time I arrived, they had already left.二、语态1. 被动语态:主语是动作的承受者,谓语动词用过去分词形式。
例:The book was written by him.2. 完成被动语态:表示动作的完成和被动。
例:The work will have been finished by tomorrow.三、虚拟语气1. 虚拟条件句:- 对现在情况的虚拟:If + 动词过去式,主语 + would/could/might + 动词原形。
例:If I were you, I would buy that car.- 对过去情况的虚拟:If + 过去完成时,主语 + would/could/might + have + 过去分词。
例:If he had studied harder, he would have passed the exam.2. 虚拟语气的动词:- 建议:suggest, propose, recommend- 要求:insist, demand, require- 命令:order, command, instruct- 希望:hope, wish, prefer例:I suggest that he buy a new phone.四、介词用法1. 表示时间:at, in, on- at:具体时间点- in:一段时间、月份、季节、年代- on:具体日期、星期几例:I will meet you at 7 o'clock tomorrow morning.2. 表示地点:at, in, on- at:小范围地点- in:大范围地点、城市、国家- on:街道、门牌号、具体位置例:She lives at/in/on 123 Main Street.五、连接词1. 并列连词:and, but, or, so, for, nor, yet例:I like apples and oranges.2. 从属连词:although, because, when, while, since, if, unless例:I will come tomorrow if I have time.六、关系代词1. who:指人,充当主语或宾语例:The girl who is sitting there is my friend.2. whom:指人,充当宾语例:I met a girl whom I used to know.3. which:指物,充当主语或宾语例:The book which is on the table belongs to me.七、比较级和最高级1. 比较级:形容词比较、副词比较、as...as例:She is taller than her sister.2. 最高级:形容词最高级、副词最高级、the + 序数词例:She is the tallest girl in the class.八、数量词1. much/many:修饰不可数名词/可数名词复数例:There is much water in the bottle.2. little/few:修饰不可数名词/可数名词复数例:He has little money left.九、倒装句1. 完全倒装:表示地点或方向的副词置于句首,谓语动词置于主语之前。
英语四六级语法:非谓语动词攻克秘笈非谓语动词是四六级英语的重点,真题试卷中随处可见。
非限定动词是谓语的非谓语形式,不受人称和数的限制,在句中可以作除谓语以外的其他任何成分。
非限定动词有三种,即不定式,动名词和分词(过去分词和现在分词)。
下面带大家一起系统学习一下这三种非谓语动词的基本知识。
一、动词不定式不定式具有动词的性质,在句中可有自己的宾语,并可被状语修饰。
同时还具有名词、形容词和副词的性质,在句中可作主语、宾语、表语、宾语补语、定语、状语等成分。
例如:1.To become a good teacher was my hope 。
(不定式做主语)2.Our purpose is to finish the job in three weeks。
(不定式作表语)3.She hopes to get something from the sales。
(不定式作宾语)4.My parents won’t allow me to stay out late。
(不定式作宾补)5.He was the first to arrive。
(不定式作定语)6.He was an idiot not to have realized it。
(不定式作状语)注意:动词不定式的否定形式为:“not+ to do”。
如 They decided not to call off the plan。
二、动名词1.动名词作主语,如:Learning a foreign language is not easy。
2.动名词作表语,用来表示主语的内容。
如:My hobby is collecting stamps。
3.动名词作宾语,一般放在动词或动词词组后。
如:The shirt can ‘t stand washing。
4.注意事项(1)动名词的被动式其形式为“being+过去分词”,如 He narrowly escaped being run over。
洛基英语,中国在线英语教育领导品牌不定冠词的用法冠词是虚词,本身不能单独使用,也没有词义,它用在名词的前面,帮助指明名词的含义。
英语中的冠词有三种,一种是定冠词(the Definite Article),另一种是不定冠词(the Indefinite Article),还有一种是零冠词(Zero Article)。
不定冠词a (an)与数词one 同源,是"一个"的意思。
a用于辅音音素前,一般读作[e],而an则用于元音音素前,一般读做[en]。
1) 表示"一个",意为one;指某人或某物,意为a certain。
A Mr. Ling is waiting for you.2) 代表一类人或物。
A knife is a tool for cutting with.Mr. Smith is an engineer.3) 词组或成语。
a little / a few / a lot / a type of / a pile / a great many / many a / as a rule / in a hurry / in a minute / in a word / in a short while / after a while / have a cold / have a try / keep an eye on / all of a sudden名词名词可以分为专有名词(Proper Nouns)和普通名词(Common Nouns),专有名词是某个(些)人,地方,机构等专有的名称,如Beijing,China等。
普通名词是一类人或东西或是一个抽象概念的名词,如:book,sadness等。
普通名词又可分为下面四类:1)个体名词(Individual Nouns):表示某类人或东西中的个体,如:gun。
2)集体名词(Collective Nouns):表示若干个个体组成的集合体,如:family。
状语从句(Adverbial Clause)一、时间状语从句1. when, as, while 和wheneverwhen 表示某个具体的时间,可指一段时间和一点时间,可表示短暂动作,又可表示持续动作。
As所表示的动作与主句动作同时发生,具有延续的含义,一般与延续性动词连用。
While 只表示持续性的动作或状态,强调主句的动作在从句动作发生的过程中。
Whenever指的是“任何时间”。
例如:When you arrive in London, please give us a call.When I was watching TV, my mother suddenly came in.3) He entered the room when (while, as) the meeting was going on.4) While she was reading a novel, her mother was cooking the dinner.It rains whenever he has the class.Whenever that man says “To tell you the truth”, I suspect that he‟s about to tell a lie.NT: 当as意为“当…时候”时,主要与表示动作或发展过程的动词连用,用于连接两个逐渐发展或演变的动作或状态。
通常情况下不与表示感觉的动词,表示感情的动词,表示精神活动的动词和表示拥有的动词连用。
As the day goes on, the weather gets worse.2.before 和afterbefore 引导的从句的动作通常发生在主句动作之后,如果从句是过去时,主句一般要用过去完成时。
After引导的从句动作通常发生在主句动作之前,如果主句要用过去时,从句则要用过去完成时。
例如:1) The plane had taken off before he arrived at the airport.2) After he had lived in the south for 20 years, he decided to go to seek his fortune in the north.3) He was still tired even after he had had eight hours of sleeping.但是如果不强调先后,或是因为从句中使用的是某个状态动词,after和before句子结构中的谓语动词也可以都用一般过去时。
例如:They arrived at the cinema after the film began.3. till 和until这两个词的用法十分近似,都表示“直到…“,但在句首只能用until 。
在肯定句中,主句要用延续性动词;在否定句中,until 或till可以和非延续性动词连用,这时until和before 同义。
例如:Not until they had finished the work did they go home.I did not lose my confidence until I failed seven times.I did not go to bed until my mother came back.We ran and ran, till I thought my heart would burst.4.as long as, every time, each time, next timeas long as表示“只要”;every time 表示“每次”;each time表示“每逢”;next time 表示“下次”,它们可以直接引导句子。
1)I am happy as long as my children are.2) He will continue working as long as he has the strength.She will not sit so long as she can lie on the bed.She smiles every time she sees me.I am going to see him next time he comes to Shanghai.5. once, as soon as, the instant (that), the moment(that),, the minute(that), directly 和immediately 这几个连词引导的从句都表示从句动作一发生,主句动作随即发生, 意为“一…就”。
例如:1) She came to the scene immediately she heard of the bad news.2) They told me the news the moment they got the message.3) Once you understand this rule, you will have no further difficulty.4) She wept aloud as soon as she heard the news.6. No sooner …than 和hardly (scarcely) …when这两个连词词组都是表示主句与从句动作随即发生,意为“一…就“。
主句动词用过去完成时。
如果No sooner, hardly 或scarcely位于句首,主句要倒装。
例如:1) He had no sooner entered the house then it began to rain.2) No sooner had he entered the house, than it began to rain.3) He had hardly gone to bed when the telephone rang.4) Hardly had he gone to bed when the telephone rang.二、地点状语从句地点状语从句表示在主句中某一动作或状态发生的地点或进行的方向,这类从句通常由Where, wherever或everywhere引导,可以放在主句前,也可以放在主句后。
Where指“在某个地方”,wherever指“在任何一个地方”,everywhere指“每一…地方”, 意思与wherever 相近。
例如:1) Bamboo grows well where it has plenty of rain.2) Wherever you go, whatever you do, I will be here waiting for you..3) Everywhere you go, I will follow you.三、条件状语从句1. if 和unlessif 表示正面的条件,意为“如果”,unless表示反而的条件,意为“除非,如果不”例如:1) If you‟ve got exams tomorrow, why aren‟t you studying?2) The sports meeting will begin tomorrow unless it rains.NT:在条件状语从句中常用一般时表示将要发生的动作。
2. providing, provided (that), supposing, suppose (that), on condition that 和in case这些连词(词组)意思相近,有“如果,只要,假如,假使,在…条件下”等意思。
例如:1) Y ou can arrive in Beijing earlier for the meeting provided yo u don‟t mind taking the night train.2) On condition that the liquid is cooled still further, it will turn to a solid.3. only if和if onlyOnly if 引导的从句用陈述语气,意为“只要”; if only引导从句要用虚拟语气,意为“要是…就好了”。
1) Only if you have persistence, you can achieve great success.2) If only I had wings, I would be able to travel around the world easily.4. where有时也可以表示条件(常用于谚语和习语)1) Where there is a will, there is a way.(有志者事竟成)。
2) There is never peace where men are greedy.(人类贪欲不止,世界和平无望)。
3) Birth is nothing where virtue is not.(如果没有品德,出身再好也等于零)。
四、原因状语从句1.because, since, as 和forbecause 表示原因语气最强,常用于回答以疑问词“why”引导的疑问句。
because 从句一般位于主句后面。
for引导的从句并不说明主句行为发生的直接原因,只是提供一些有助于说明情况的补充说明,且不可位于主句前。
since 表示一种附带的原因,或者表示已知的显然理由,意为“既然”,引导的从句常放在句首。
As所表示的理由最弱,只是对主句的附带说明,重点在主句, as通常放在主句前。
例如:1) The teacher is strict with us because he wants us to make rapid progress.2) Since you are free today, you had better help me with my mathematics.3) As the day was fine, they decided to go on a trip.4) It rained last night, for the ground is wet this morning.2.seeing (that), considering (that), now (that) , in that, given (that)这几个连词同since意思相近,都有“鉴于某个事实”的意思。
例如:1) Now that you are a big boy, you must behave better.2) Men differ form brutes in that they can think and speak.3) Given it is going to rain tomorrow, the sports meet will be put off to next month.3. not…because本结构中not否定的是because引导的整个从句。