机械专业考试试题
- 格式:doc
- 大小:116.50 KB
- 文档页数:6

机械专业综合试题考卷(带答案)一、选择题(每题1分,共5分)1. 下列哪种材料最适合用于制造齿轮?A. 塑料B. 铸铁C. 铝合金D. 钢答案:D2. 在四杆机构中,若最长杆与最短杆的长度之和小于其他两杆长度之和,则该机构为:A. 双曲柄机构B. 曲柄摇杆机构C. 双摇杆机构D. 摩擦机构答案:B3. 下列哪种液压元件用于控制液压系统的压力?A. 液压泵B. 液压缸C. 溢流阀D. 节流阀答案:C4. 下列哪种传动方式传动效率最高?A. 齿轮传动B. 带传动C. 链传动D. 摩擦传动答案:A5. 下列哪种加工方法适用于大批量生产?A. 车削B. 铣削C. 钻削D. 数控加工答案:D二、判断题(每题1分,共5分)1. 材料的硬度越高,其韧性越好。
(×)2. 在四杆机构中,曲柄摇杆机构可以实现转动转化为往复运动。
(√)3. 液压系统中的油箱主要用于储存液压油。
(√)4. 齿轮传动的噪声比带传动大。
(√)5. 数控机床加工精度不受操作者技能水平影响。
(√)三、填空题(每题1分,共5分)1. 材料的力学性能主要包括____、____、____等。
答案:强度、塑性、韧性2. 四杆机构的基本类型有____、____、____。
答案:曲柄摇杆机构、双曲柄机构、双摇杆机构3. 液压系统的三大元件是____、____、____。
答案:液压泵、液压缸、液压阀4. 齿轮传动的优点有____、____、____等。
答案:传动效率高、工作可靠、寿命长5. 数控加工的特点有____、____、____等。
答案:加工精度高、自动化程度高、生产效率高四、简答题(每题2分,共10分)1. 简述金属材料的热处理工艺及应用。
答案:热处理工艺包括退火、正火、淬火和回火等,主要用于改善材料的力学性能、降低硬度、提高切削性能等。
2. 什么是液压系统的压力损失?有哪些原因?答案:压力损失是指在液压系统中,液体流动过程中因摩擦、局部阻力等因素造成的压力下降。

机械专业基础试题及答案一、选择题1. 机械设计中,通常所说的“三视图”指的是:A. 正视图、侧视图、俯视图B. 正视图、侧视图、仰视图C. 正视图、侧视图、透视图D. 正视图、透视图、俯视图答案:A2. 在机械加工中,什么是“加工余量”?A. 材料的原始厚度B. 材料加工后剩余的厚度C. 材料加工前需要去除的部分D. 材料加工后增加的部分答案:C3. 机械传动中,齿轮传动的效率通常比带传动的效率:A. 高B. 低C. 相同D. 不确定答案:A4. 以下哪个不是机械工程材料的基本性能?A. 强度B. 硬度C. 韧性D. 颜色答案:D5. 机械零件的疲劳破坏通常发生在:A. 零件表面B. 零件内部C. 零件的焊接处D. 零件的接合处答案:A二、填空题6. 机械设计中,________是零件失效的主要原因之一。
答案:疲劳7. 材料的屈服强度是指材料在________条件下的最小屈服应力。
答案:塑性变形8. 在机械加工中,________是指加工后的零件尺寸与设计尺寸之间的差异。
答案:加工误差9. 机械传动中,________传动是依靠摩擦力来传递运动和动力的。
答案:带10. 机械零件的________是指在一定的温度和介质条件下,材料抵抗腐蚀的能力。
答案:耐腐蚀性三、简答题11. 简述机械设计中“强度”和“刚度”的区别。
答:强度是指材料在受到外力作用时,抵抗破坏的能力,通常用材料的屈服强度或抗拉强度来衡量。
刚度则是指材料或结构在受到外力作用时,抵抗变形的能力,通常用弹性模量来衡量。
12. 解释什么是“模数”和“齿数”在齿轮设计中的作用。
答:模数是齿轮设计中的一个基本参数,它定义了齿轮齿形的大小,通常用m表示,单位为毫米。
齿数是指齿轮上齿的数量,用z表示。
模数和齿数共同决定了齿轮的大小和传动比。
四、计算题13. 已知一个机械零件的直径为100mm,若要加工到直径为98mm,求加工余量。
解:加工余量 = 原始直径 - 加工后直径 = 100mm - 98mm = 2mm。

机械类专业基础知识试题机械类专业基础知识试题⼀、选择题(本⼤题 45 个⼩题,每⼩题 2 分,共90 分在每⼩题列出的四个选项中,只有⼀项符合题⽬要求,请将符合题⽬要求的选项字母代号选出,并填涂在答题卡上)1.如图所⽰,已知主、俯视图,正确的左视图是()2.如图所⽰,根据主、俯视图,判断 A、B 两点的相对位置,正确的是()A.点A 在点B 的右、前、上⽅B.点A 在点B 的右、后、上⽅C.点A 在点B 的右、前、下⽅D.点A在点B 的右、后、下⽅3.关于斜视图和局部视图的说法不正确的是()A.两者都是对物体的某⼀局部进⾏投影B.两者都是向基本投影⾯投影C.两者的标注内容相同 D.两者都可以不按投影关系配置4.选择图1-3 所⽰的正确的全剖视图()5.如图1-4 所⽰,已知主、俯视图,则与其对应的右视图是()6.在标注形位公差时,如果被测范围仅为被测要素的⼀部分时,应⽤()表⽰出该范围,并标出尺⼨。
A.粗点划线B.粗实线C.双点划线D.细实线7.⼀般配合尺⼨的公差等级范围⼤致是()A.IT1~IT7B.IT2~IT5C.IT5~IT3D.IT8~IT148.使⽤百分表测量轴类零件的圆柱度误差时,需注意()A.百分表指针⼀定要转动灵敏、稳定,允许有间隙误差A.⼯作台、V 型铁、百分表及轴不需要清洁C.不能使⽤车床代替⼯作台检测D.检测动作要轻、稳、准,记录要真实9.齿轮轮毂长度为35mm,安装齿轮的轴头部分B型普通平键键槽长度应加⼯为()。
A.35mm B.30mm C.15mm D.40mm。
10.下列属于联接螺纹的是()A.普通螺纹 B.矩形螺纹C.梯形螺纹 D.锯齿形螺纹。
A.齿轮传动B.带传动C.蜗11.起重运输机械的传动系统要求具有⾃锁性能,应选择的传动类型是()杆传动D.链传动12.铸造铝合⾦箱体与箱盖⽤螺纹连接,箱体被连接处厚度较⼤,要求连接后,结构紧凑,且需经常拆卸箱盖,此时宜采⽤()。

机械工程专业试题及答案一、选择题(每题2分,共20分)1. 机械工程中,以下哪个不是常见的材料分类?A. 金属材料B. 非金属材料C. 复合材料D. 生物材料答案:D2. 机械设计中,以下哪个因素不是影响疲劳寿命的主要因素?A. 材料的疲劳强度B. 载荷的频率C. 温度D. 载荷的幅度答案:C3. 在机械制造中,以下哪个不是常用的加工方法?A. 车削B. 铣削C. 铸造D. 焊接答案:C4. 机械传动中,以下哪个不是常见的传动方式?A. 齿轮传动B. 皮带传动C. 链传动D. 电磁传动答案:D5. 机械工程中,以下哪个不是常见的热处理方法?A. 退火B. 正火C. 淬火D. 冷作硬化答案:D6. 在机械设计中,以下哪个不是常见的设计原则?A. 经济性原则B. 可靠性原则C. 艺术性原则D. 安全性原则答案:C7. 机械工程中,以下哪个不是常见的机械零件?A. 轴承B. 齿轮C. 弹簧D. 电阻答案:D8. 在机械制造中,以下哪个不是常见的测量工具?A. 卡尺B. 千分尺C. 量规D. 电阻表答案:D9. 机械工程中,以下哪个不是常见的润滑方式?A. 油润滑B. 脂润滑C. 干摩擦D. 水润滑答案:C10. 在机械设计中,以下哪个不是常见的失效模式?A. 磨损B. 疲劳C. 腐蚀D. 过载答案:D二、填空题(每空2分,共20分)1. 机械工程中的“三传一反”指的是______、______、______和______。
答案:传动、传递、转换、反应2. 机械设计中,为了提高零件的疲劳寿命,通常采用______、______等方法。
答案:表面硬化、应力集中消除3. 机械制造中,常用的金属加工方法包括______、______、______等。
答案:切削、铸造、锻造4. 机械传动中,常见的传动效率较高的传动方式有______、______等。
答案:齿轮传动、皮带传动5. 机械工程中的热处理方法主要包括______、______、______等。

机械制造类专业试题及答案一、单选题(每题2分,共20分)1. 机械制造中常用的材料分类不包括以下哪一项?A. 金属材料B. 非金属材料C. 复合材料D. 塑料材料答案:D2. 在机械加工中,下列哪个不是切削运动?A. 车削B. 铣削C. 磨削D. 焊接答案:D3. 以下哪个是机械制造中常用的测量工具?A. 卡尺B. 螺丝刀C. 扳手D. 电钻答案:A4. 机械加工中,下列哪个不是常见的加工误差来源?A. 刀具磨损B. 材料变形C. 设备老化D. 操作员疲劳答案:C5. 机械设计中,哪个参数不是影响零件强度的因素?A. 材料的强度B. 零件的尺寸C. 零件的表面光洁度D. 零件的形状答案:C6. 以下哪个不是机械制造中常用的热处理方法?A. 退火B. 正火C. 淬火D. 电镀答案:D7. 在机械制造中,以下哪个不是常见的传动方式?A. 齿轮传动B. 皮带传动C. 链传动D. 液压传动答案:D8. 机械制造中,以下哪个不是常见的加工工艺?A. 铸造B. 锻造C. 焊接D. 喷漆答案:D9. 机械设计中,以下哪个不是常见的设计原则?A. 经济性原则B. 可靠性原则C. 美观性原则D. 随意性原则答案:D10. 在机械制造中,以下哪个不是常见的机械故障类型?A. 磨损B. 断裂C. 腐蚀D. 过载答案:D二、多选题(每题3分,共15分)11. 机械制造中,以下哪些因素会影响加工精度?A. 机床的精度B. 操作员的技能C. 刀具的磨损D. 材料的硬度答案:ABCD12. 在机械设计中,以下哪些属于机械运动的基本形式?A. 平移B. 旋转C. 振动D. 摆动答案:ABD13. 机械制造中,以下哪些属于常见的机械加工方法?A. 车削B. 铣削C. 刨削D. 钻削答案:ABCD14. 在机械制造中,以下哪些属于机械材料的基本性能?A. 硬度B. 韧性C. 塑性D. 导电性答案:ABC15. 机械设计中,以下哪些属于机械零件的失效模式?A. 磨损B. 疲劳C. 腐蚀D. 断裂答案:ABCD三、判断题(每题1分,共10分)16. 机械制造中,所有的加工误差都是可以避免的。

机械考研专业试题及答案一、单项选择题(每题2分,共20分)1. 机械设计中,对轴承寿命影响最大的因素是()。
A. 轴承材料B. 轴承润滑C. 轴承安装精度D. 轴承工作温度答案:B2. 在机械加工中,切削速度对切削力的影响是()。
A. 正比B. 反比C. 无关D. 先增大后减小答案:A3. 下列哪种材料不属于金属材料()。
A. 钢B. 铜C. 陶瓷D. 铝答案:C4. 机械系统中,用于减少振动的元件是()。
A. 弹簧B. 阻尼器C. 齿轮D. 轴承答案:B5. 机械制图中,表示孔的直径为20mm的符号是()。
A. ⌀20B. Φ20C. 20D. 20mm答案:B6. 液压系统中,用于控制油液流动方向的元件是()。
A. 泵B. 阀C. 缸D. 油箱答案:B7. 机械传动中,能够实现远距离传动的装置是()。
A. 齿轮B. 链条C. 皮带D. 联轴器答案:C8. 机械加工中,用于提高加工精度的刀具是()。
A. 粗加工刀具B. 精加工刀具C. 标准刀具D. 非标刀具答案:B9. 机械设计中,用于计算零件强度的公式是()。
A. 材料力学公式B. 热力学公式C. 流体力学公式D. 动力学公式答案:A10. 机械系统中,用于储存能量的元件是()。
A. 弹簧B. 齿轮C. 轴承D. 联轴器答案:A二、多项选择题(每题3分,共15分)1. 机械设计中,影响齿轮寿命的因素包括()。
A. 齿轮材料B. 齿轮润滑C. 齿轮精度D. 齿轮安装精度E. 齿轮工作温度答案:A, B, C, D, E2. 机械加工中,常用的加工方法包括()。
A. 车削B. 铣削C. 钻孔D. 磨削E. 焊接答案:A, B, C, D3. 机械系统中,常见的传动方式有()。
A. 齿轮传动B. 链条传动C. 皮带传动D. 液压传动E. 气动传动答案:A, B, C, D, E4. 机械制图中,常用的尺寸标注方法包括()。
A. 水平标注B. 垂直标注C. 角度标注D. 直径标注E. 半径标注答案:A, B, C, D, E5. 机械设计中,常用的强度计算方法包括()。
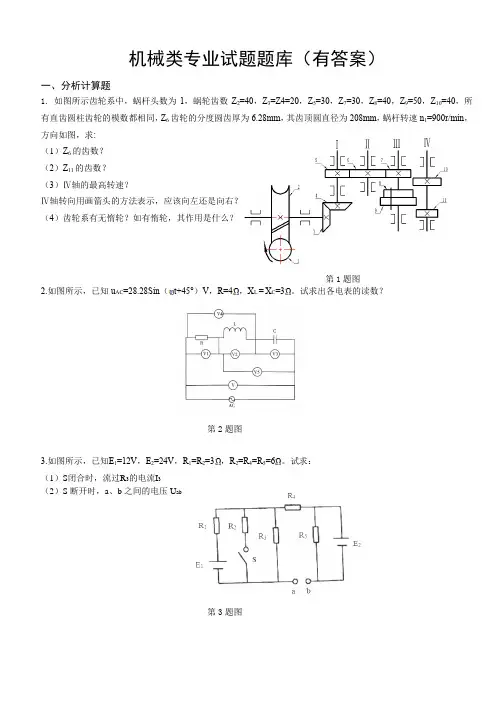
机械类专业试题题库(有答案)一、分析计算题1. 如图所示齿轮系中,蜗杆头数为1,蜗轮齿数Z2=40,Z3=Z4=20,Z5=30,Z7=30,Z8=40,Z9=50,Z10=40,所有直齿圆柱齿轮的模数都相同,Z6齿轮的分度圆齿厚为6.28mm,其齿顶圆直径为208mm,蜗杆转速n1=900r/min,方向如图,求:(1)Z6的齿数?(2)Z11的齿数?(3)Ⅳ轴的最高转速?Ⅳ轴转向用画箭头的方法表示,应该向左还是向右?(4)齿轮系有无惰轮?如有惰轮,其作用是什么?第1题图2.如图所示,已知u AC=28.28Sin(t+45°)V,R=4,X L =X C=3。
试求出各电表的读数?第2题图3.如图所示,已知E1=12V,E2=24V,R1=R2=3,R2=R4=R5=6。
试求:(1)S闭合时,流过R3的电流I3(2)S断开时,a、b之间的电压U ab第3题图二、综合应用题1.工业生产实践中,许多生产机械往往要求运动部件能正反两个方向运动,从而实现可逆运行。
在实际应用中,通过电动机的正反转控制就可以实现工作要求。
根据所学知识完成下列问题。
(1)将电动机正反转控制的原理图和控制电路接线图分别补画完整(要求具有过载保护、短路保护和接触器联锁)。
(2)电动机过载保护功能是通过哪个元件实现的?(3)在不通电状态下,万用表的红黑表笔接在控制电路电源线两端,按下SB1按钮,万用表读数约为1.8K ,万用表测出的阻值是哪个元件的阻值?若按下SB1按钮,万用表读数为0Ω,电路连接是否正常?(4)测量完毕,电路接线正常,合上电源开关QS ,按下SB1按钮,电动机正转运行,若要让电动机反转,此时应如何操作?M 3~FU1FU2FR SB3SB1SB2KM1KM2QSL1L2L3KM1KM2FRKM1KM2FU2FRSB1SB2SB32.用CA6140普通车床加工如图(a )所示的阶梯轴,毛坯采用Ф40×180的45棒料,粗、精加工分开,加工时采用一夹一顶装夹保证同轴度要求。

主管工程师理论考试试题—机械专业A一、选择题锅炉及压力容器类1.按《压力容器安全监察规程》的分类,高压容器属于第类压力容器A 一B 二C 三2.压力容器组焊不应采用焊接A 对接B 角接C 十字形3.《锅炉压力容器安全监察暂行条例》是为了保障锅炉压力容器的安全运行,保障人民生命和国家财产的安全,由颁布实施的A 国务院B 劳动部C 安全部4.锅炉按照用途分电站锅炉,锅炉,生活锅炉,船舶锅炉和机车锅炉A 热水B 固定式C 工业金属材料类1.根据经验,当碳当量的质量分数为时,钢的焊接性良好,不需要预热即可焊接A <0.4%B 0.4%-0.6%C 0.6%2.低碳钢的含碳量在范围内,因含碳量较低所以其焊接性能差。
A、0.04%~0.25%B、1.7%~4.5%C、0.25%~1.7%D、≤0.04%3.合金结构钢60Si2Mn的含碳量为()A.0.6%B. 6%C. 0.02%4.对于高负荷、重要的转轴,应选用()材料。
A. Q235;B.45钢;C. 20钢;D.40Cr。
5.随着钢中碳质量分数的增加,钢的塑性和韧性A 上升B 下降C 不变6.⒐下列材料中塑性最好的是 A ,具有较高的可锻造性能。
A、低碳钢B、中碳钢C、不锈钢D、铜合金7.淬火后再进行高温回火的热处理操作叫调质,广泛应用于()的热处理A.低碳钢B.中碳钢C.高碳钢8.()是指金属材料抵抗冲击载荷的能力。
A.强度B.刚度C.韧性9.按GB/T2650-1989《焊接接头冲击试验方法》规定,采用缺口试样为标准A V型B U型C Y型10.低碳钢焊接消除应力的温度为°CA 500-600B 600-650C 650-700焊接类1.碳钢、低合金钢的焊条选择通根据等级,结构刚性,工作条件等选择相应等级的焊条A 强度B 厚度C 焊缝质量要求2.对焊缝冲击韧度、韧性要求较高的工作应采用焊条A 酸性B 不锈钢C 碱性3.碱性焊条比酸性焊条的焊缝抗裂性A 好B 差C 相同4.酸性焊条对铁锈、氧化皮和油脂的敏感性比碱性焊条A 大B 小C 相同轴承及密封类1.下列四种型号的滚动轴承中,必须成对使用的是A 深沟球轴承 B圆锥滚子轴承 C 推力球轴承2.下列三种类型的联轴器中,能够补偿两轴的相对位移以及可以缓和冲击,吸收共振的是A 齿式联轴器B 万向联轴器C 弹性套柱销联轴器3.下列轴承中,可同时承受以径向载荷为主的径向与轴向载荷的是?A .深沟球轴承B.角接触球轴承C.圆锥滚子轴承D.调心球轴承4.受中等冲击载荷、支承刚度较差、速度较高的两轴之间宜选用()。

机械专业教师考试试题一、选择题(每题2分,共20分)1. 机械设计中,以下哪个因素不是影响材料疲劳寿命的主要因素?A. 材料的表面粗糙度B. 材料的屈服强度C. 材料的硬度D. 材料的疲劳极限2. 在机械加工中,车削加工通常用于加工哪种类型的工件?A. 轴类零件B. 齿轮类零件C. 板类零件D. 壳体类零件3. 以下哪种材料不属于金属材料?A. 钢B. 铜C. 塑料D. 铝4. 机械系统中,以下哪个部件的主要功能是将旋转运动转换为直线运动?A. 齿轮B. 滑块C. 连杆D. 轴承5. 在机械制图中,以下哪个符号表示孔的尺寸?A. ∅B. ⊕C. □D. ○6. 以下哪个选项是机械加工中的切削液的主要作用?A. 润滑B. 冷却C. 清洗D. 所有以上选项7. 在机械设计中,以下哪种材料通常用于制造轴承?A. 木材B. 陶瓷C. 橡胶D. 塑料8. 以下哪个参数是衡量齿轮传动效率的重要指标?A. 齿轮比B. 齿数C. 模数D. 齿宽9. 在机械加工中,以下哪种加工方法可以实现高精度的表面加工?A. 车削B. 铣削C. 磨削D. 钻削10. 以下哪个选项是机械振动分析中常用的分析方法?A. 频谱分析B. 时域分析C. 统计分析D. 所有以上选项二、简答题(每题10分,共40分)1. 简述机械加工中的热处理工艺的目的和常见类型。
2. 描述机械系统中的静平衡和动平衡的区别。
3. 解释什么是机械传动中的传动比,并举例说明。
4. 阐述在机械设计中,为什么需要考虑材料的疲劳强度。
三、计算题(每题15分,共30分)1. 给定一个齿轮传动系统,主动齿轮的齿数为20,从动齿轮的齿数为40,试计算该系统的传动比。
2. 假设一个机械零件在循环载荷作用下,其材料的疲劳极限为500 MPa,安全系数为1.5,试计算该零件在设计时的最大允许应力。
结束语:以上是机械专业教师考试试题的全部内容,希望考生能够认真作答,展示出自己扎实的专业知识和技能。

机械设计专业试题及答案一、选择题1. 机械设计中,哪个因素是影响零件强度和刚度的主要因素?A. 材料选择B. 零件尺寸C. 表面处理D. 载荷大小答案:B2. 在机械设计中,疲劳强度计算通常采用哪种理论?A. 材料力学理论B. 弹性力学理论C. 塑性力学理论D. 断裂力学理论答案:D3. 以下哪个不是机械设计中常用的材料?A. 钢B. 铝C. 塑料D. 陶瓷答案:D4. 在机械设计中,以下哪种连接方式不属于固定连接?A. 螺纹连接B. 焊接C. 铆接D. 铰接答案:D5. 机械设计中,哪个参数是计算齿轮传动比的关键?A. 齿轮直径B. 齿轮模数C. 齿轮齿数D. 齿轮材料答案:C二、简答题1. 简述机械设计中材料选择的重要性。
答:材料选择在机械设计中至关重要,因为它直接影响到零件的性能、成本、加工工艺和使用寿命。
合适的材料可以提高机械的可靠性和安全性,减少维护成本,延长设备寿命。
2. 解释什么是应力集中,并举例说明其在机械设计中的影响。
答:应力集中是指在材料的某些局部区域,由于几何形状、材料不连续性或载荷方式的改变,导致应力值远高于平均应力的现象。
应力集中会增加零件的疲劳破坏风险,例如在轴的键槽处,由于应力集中,该部位的疲劳寿命会显著降低。
三、计算题1. 已知一个直径为50mm的圆杆,材料为45钢,其许用应力为200MPa。
若该圆杆承受最大拉力为10kN,请计算该圆杆是否安全。
解:首先计算圆杆的截面积A = π(D/2)^2 = π(0.05/2)^2≈0.00196m²,然后计算圆杆的应力σ = F/A = 10000/0.00196 ≈5102MPa。
由于σ > 200MPa,该圆杆不安全。
2. 一个齿轮的模数为5mm,齿数为20,求该齿轮的齿顶圆直径。
解:齿顶圆直径d = m(z+2),其中m为模数,z为齿数。
代入数值得d = 5(20+2) = 5 * 22 = 110mm。

机械专业类试题
一、选择题
1.下列元素单质与机械加工无关的是()。
a.铂
b. 镍
c. 铝
d. 钨
2.下列材料中,导热性能最好的是()。
a.铁
b. 铜
c. 铝
d. 铝合金
3.下列机械加工方法中,属于非传统加工方法的是()。
a.铣削
b. 钻削
c. 火花电切
d.插刀槽铣削
4.下列量规中,能够测量螺纹外径的是()。
a.卡尺
b. 千分尺
c. 环规
d. 测微计
5.下列防护装置中,用于防止工件离心力导致的伤害的是()。
a.护罩
b. 锁紧装置
c. 防护栏
d. 传感器
二、填空题
1.我国将机械工业划分为()个子行业。
2.机械零件的制造是机械加工与()两部分构成的。
3.铣刀是铣床上的主要切削工具,它主要有两种基本结构,即()型和()型。
4.锥度是圆柱面与直线或圆柱面与平面之间的夹角,用。
机械员专业知识试题及答案一、单项选择题(每题2分,共20分)1. 机械传动中,齿轮传动的特点是什么?A. 效率高B. 结构简单C. 噪音大D. 体积小答案:A2. 以下哪个是机械设计中的基本原则?A. 经济性原则B. 舒适性原则C. 安全性原则D. 所有选项都是答案:D3. 机械加工中,车削加工主要适用于加工什么类型的零件?A. 内孔B. 外圆C. 齿轮D. 所有选项都是答案:B4. 液压系统中,液压泵的主要作用是什么?A. 提供动力B. 转换能量C. 控制压力D. 储存能量答案:B5. 机械制图中,第三角投影法与第一角投影法的主要区别是什么?A. 视图数量不同B. 视图方向不同C. 投影方式不同D. 标注方式不同答案:C二、多项选择题(每题3分,共15分)6. 机械制造中,常见的热处理工艺包括哪些?A. 退火B. 正火C. 淬火D. 回火E. 所有选项都是答案:E7. 机械设计中,需要考虑的力学性能包括哪些?A. 强度B. 硬度C. 韧性D. 塑性E. 所有选项都是答案:E8. 机械加工中,常用的量具包括哪些?A. 卡尺B. 千分尺C. 游标卡尺D. 百分表E. 所有选项都是答案:E三、判断题(每题1分,共10分)9. 所有的机械零件都需要进行热处理。
()答案:×(错误)10. 机械设计时,应优先考虑零件的强度和刚度。
()答案:√(正确)四、简答题(每题5分,共20分)11. 简述机械传动的分类及其特点。
答案:机械传动主要包括齿轮传动、皮带传动、链传动、蜗轮蜗杆传动等。
齿轮传动效率高,结构紧凑;皮带传动适用于远距离传动,但效率较低;链传动适用于高速传动,但噪音较大;蜗轮蜗杆传动适用于垂直传动,但效率较低。
12. 简述机械加工中常见的加工误差来源。
答案:机械加工中的误差来源包括机床误差、刀具误差、夹具误差、工件材料误差以及操作者技能误差等。
五、计算题(每题10分,共15分)13. 已知一个齿轮的模数为3mm,齿数为20,求该齿轮的齿顶圆直径。
机械专业试题库及答案一、选择题1. 机械设计中,为了提高零件的疲劳强度,通常采用哪种方法?A. 增加材料的硬度B. 增加零件的尺寸C. 表面硬化处理D. 增加零件的重量答案:C2. 在机械加工中,什么是“三面一刀”原则?A. 刀具的三个面和一个刃口B. 工件的三个面和一个切削刃C. 工件的三个面和一个基准面D. 刀具的三个面和一个基准面答案:D3. 以下哪个不是机械传动的类型?A. 齿轮传动B. 皮带传动C. 液压传动D. 磁力传动答案:D4. 在材料力学中,哪个参数用来描述材料的弹性?A. 屈服强度B. 抗拉强度C. 弹性模量D. 硬度答案:C5. 机械加工中,什么是“五轴加工”?A. 五个方向的加工B. 五个轴同时加工C. 五个轴的数控加工D. 五个轴的独立加工答案:C二、填空题6. 机械零件的失效形式主要有________、________和腐蚀。
答案:断裂、磨损7. 热处理工艺中的“退火”是指将金属材料加热到一定温度,保温一段时间后,以________的速度冷却。
答案:缓慢8. 机械设计中的“静平衡”是指转子在________状态下的平衡。
答案:静止9. 在机械制造中,精度等级通常用________来表示。
答案:IT(International Tolerance)10. 金属材料的“塑性”是指材料在________时不发生断裂的性质。
答案:拉伸三、简答题11. 简述机械零件的疲劳失效机理。
答案:机械零件的疲劳失效是指在反复加载和卸载的过程中,即使应力水平低于材料的屈服强度,零件也会发生逐渐的损伤累积,最终导致断裂。
疲劳失效通常发生在零件的应力集中区域,如孔、缺口或表面缺陷处。
12. 描述机械加工中的“数控加工”特点。
答案:数控加工是一种利用数字程序控制机床进行加工的方法。
它具有加工精度高、加工效率高、加工复杂形状能力强等特点。
数控加工可以自动完成零件的加工过程,减少了人为操作的误差。
四、计算题13. 已知一圆柱形轴的直径为50mm,材料的许用应力为120MPa,若要求轴能承受的最大弯矩为1000Nm,请计算该轴的最小长度。
机械专业考试试题及答案一、选择题(每题2分,共20分)1. 机械设计中,通常所说的“三要素”是指:A. 材料、工艺、成本B. 材料、工艺、性能C. 材料、结构、性能D. 结构、工艺、性能答案:C2. 在机械传动中,齿轮传动的特点是:A. 传动比稳定,效率高B. 结构简单,成本低廉C. 承载能力大,寿命长D. 传动平稳,噪音小答案:A3. 以下哪个不是机械加工的方法?A. 车削B. 铣削C. 焊接D. 磨削答案:C4. 机械零件的失效形式主要包括:A. 磨损、腐蚀、断裂B. 变形、腐蚀、磨损C. 断裂、变形、腐蚀D. 磨损、断裂、变形答案:D5. 机械制造中,常用的热处理方法不包括:A. 淬火B. 正火C. 退火D. 焊接答案:D...二、填空题(每空1分,共10分)1. 机械设计中,通常需要考虑零件的________、________和________。
答案:强度、刚度、稳定性2. 机械加工中,刀具材料的选择应考虑刀具的________、________和________。
答案:硬度、韧性、耐热性3. 在机械传动中,________传动具有传动比稳定、效率高的特点。
答案:齿轮4. 机械零件的失效分析中,________是常见的失效形式之一。
答案:断裂5. 机械制造中,________是一种常用的提高材料硬度和耐磨性的热处理方法。
答案:淬火...三、简答题(每题10分,共30分)1. 简述机械设计的基本要求。
答案:机械设计的基本要求包括满足使用功能、可靠性、经济性、安全性、环保性等。
设计时需要综合考虑零件的材料选择、结构设计、工艺流程、成本控制等多方面因素。
2. 描述机械加工中的切削过程及其重要性。
答案:机械加工中的切削过程是指利用切削工具对工件进行去除材料,形成所需形状和尺寸的过程。
切削过程的重要性在于它直接决定了零件的加工精度和表面质量,是实现机械产品制造的关键步骤。
3. 解释什么是机械零件的疲劳失效,并简述其产生的原因。
机械专业单招试题及答案一、选择题(每题2分,共20分)1. 机械设计中,材料的屈服强度是指材料在()条件下的应力。
A. 弹性变形B. 塑性变形C. 断裂D. 疲劳破坏答案:B2. 以下哪个不是机械加工的常见方法?A. 车削B. 铣削C. 焊接D. 磨削答案:C3. 机械零件的疲劳寿命主要受以下哪个因素影响?A. 材料的硬度B. 零件的尺寸C. 工作载荷的循环次数D. 零件的形状答案:C4. 在机械设计中,为了提高零件的疲劳寿命,常采用以下哪种方法?A. 增加零件的尺寸B. 增加零件的硬度C. 增加零件的表面粗糙度D. 减少零件的应力集中答案:D5. 机械传动中,齿轮传动的主要优点是()。
A. 结构简单B. 传动效率高C. 噪音大D. 维护方便答案:B6. 轴承的类型中,滚动轴承与滑动轴承相比,其主要优点是()。
A. 摩擦系数小B. 承载能力大C. 制造成本高D. 结构复杂答案:A7. 机械零件的热处理工艺中,淬火的主要目的是()。
A. 提高硬度B. 提高韧性C. 减小变形D. 减小应力答案:A8. 机械工程中,静力学的基本任务是研究物体的()。
A. 运动状态B. 平衡状态C. 受力分析D. 动力学特性答案:B9. 机械零件的疲劳破坏通常发生在()。
A. 表面B. 内部C. 接触面D. 应力集中处答案:D10. 在机械设计中,为了减少零件的磨损,常采用以下哪种方法?A. 增加零件的硬度B. 增加零件的尺寸C. 增加零件的表面粗糙度D. 采用润滑剂答案:D二、填空题(每空2分,共20分)1. 机械设计中,材料的弹性模量是指材料在______条件下的应力与应变的比值。
答案:弹性变形2. 机械加工中,车削是利用______对工件进行旋转切削。
答案:车床3. 机械零件的疲劳寿命与其承受的______成正比。
答案:循环载荷次数4. 机械传动中,齿轮传动的效率较高,但噪音和______较大。
答案:振动5. 轴承的类型中,滚动轴承与滑动轴承相比,滚动轴承的摩擦系数______。
机械专业技术人员试题库(附答案)一、填空题1、离心压缩机按气体运动方式可分为:离心式、轴流式、(离心轴流组合式)。
2、机械密封按运动方式分为旋转式和(静止式)。
3、压力容器的设计压力不得低于最高工作压力,装有安全泄放装置的压力容器,其设计压力不得低于安全阀的(开起)压力或爆破片的爆破压力。
4、压力容器上安全阀应垂直安装,并应装设在压力容器液面以上(气相)空间部分,或装设在与压力容器气相空间相连的管道上。
5、压力容器是指盛装(气体)、液化气体或最高工作温度高于等于标准的液体,承载一定压力,其范围规定为最高工作压力大于或等于(0∙1)Mpa,内直径大于等于(0.15)m,容积大于等于(0.025)m3的密闭设备。
6、汽轮机按作用原理分类,分为(冲动式)汽轮机和(反动式)汽轮机两种。
7、滚动轴承基本结构包括内圈、外圈、滚动体、保持架四个部分。
8、常用的三种管壳式换热器有固定管板式换热器、U型管式换热器、浮头式换热器。
9、压力容器的定期检验分为外部检查、内外部检查和耐压试验。
10、离心泵串联可以提高(扬程),并联可以提高流量。
11、设备润滑管理要求作到“三滤五定"。
三滤是指:从领料大桶到岗位储油桶、从岗位储油桶到油壶、(从油壶到加油点);五定是指:定人、定点、(定质)、定量、(定时)。
12、压力管道的定义为:利用一定的压力,用于输送气体或液体的管状设备,其范围规定为最高工作压力大于或等于S1Mpa的气体、液化气体、蒸汽介质或可燃、易爆、有毒、有腐蚀性、最高工作温度高于或等于标准沸点的介质,且工程直径大于(25mm)的管道。
13、液化气及瓦斯设施与管线在安装或检修完成后,必须按规定做(水压试验)和(气密试验),并要有一定的(保压时间),达到无渗漏,无显著变形与有均匀膨胀。
14、滚动轴承失效的基本形式有:(磨损失效)、疲劳失效、腐蚀失效等。
15、特种设备的使用单位,在特种设备投入使用前或投用后30日内必须到技术监督部门进行注册登记办理(使用证)。
机械专业理论试题及答案一、选择题(每题2分,共20分)1. 机械设计中,通常采用哪种方法来减小零件的应力集中?A. 增加零件的厚度B. 减小零件的尺寸C. 采用圆滑过渡D. 增加零件的硬度答案:C2. 下列哪个不是机械传动的基本类型?A. 齿轮传动B. 带传动C. 液力传动D. 磁力传动答案:D3. 机械加工中,通常采用哪种方式来提高加工精度?A. 增加加工速度B. 采用高精度机床C. 增加加工次数D. 减少加工材料的硬度答案:B4. 在机械设计中,材料的屈服强度是指:A. 材料开始发生永久变形的应力B. 材料开始发生弹性变形的应力C. 材料发生断裂的应力D. 材料发生疲劳破坏的应力答案:A5. 轴承的寿命是指:A. 轴承从安装到失效的时间B. 轴承从制造到安装的时间C. 轴承从安装到需要维护的时间D. 轴承从制造到失效的时间答案:A6. 机械系统中,静平衡是指:A. 系统在运动状态下的平衡B. 系统在静止状态下的平衡C. 系统在任何状态下的平衡D. 系统在受力状态下的平衡答案:B7. 机械零件的疲劳破坏通常发生在:A. 零件的表面B. 零件的内部C. 零件的连接处D. 零件的任何部位答案:A8. 机械加工中,为了减少切削力,通常采用:A. 增加切削速度B. 减小切削速度C. 增加切削深度D. 减小切削深度答案:B9. 机械零件的热处理通常用于:A. 提高零件的硬度B. 降低零件的强度C. 增加零件的韧性D. 减小零件的重量答案:A10. 机械设计中,动平衡试验的目的是:A. 确定零件的质量B. 确定零件的尺寸C. 确定零件的平衡状态D. 确定零件的疲劳寿命答案:C二、简答题(每题10分,共30分)1. 请简述机械传动系统的基本组成。
答案:机械传动系统通常由动力源、传动元件和执行机构组成。
动力源提供能量,传动元件负责传递和转换能量,执行机构则将能量转换为机械运动。
2. 什么是机械加工的“三要素”?答案:机械加工的“三要素”包括切削速度、进给速度和切削深度。
一判断题目(10分)
1.钢比铸铁铸造性能好,所以常用来铸造形状复杂工件。
X
2.加工硬化是工件表面硬度和塑性提高的一种现象。
X
3.铝合金淬火后硬度提高。
4.CA6140床最大切削直径是140mm。
X
C表示车床,A表示第一次重大改进,6表示落地及普通车床,1表示普通车床,
40是机床主参数,回转直径为400毫米。
5.增加加工设备是提高生产率的一种方法。
6.箱体零件工艺一般采用统一基准原则
二单项选择题目(15分)
1.普通平键主要用途是()
平键根据用途不同,平键可分为普通平键、导向平键和滑键三种。
其中普通平键用于静联接,导向平键和滑键用于动联接。
2.凸缘式联轴节是(刚性联轴节)
3.正常条件下,滚动轴承的主要失效形式是(滚动体与滚道表
产生疲劳点蚀)
4.四爪卡盘找正用(百分表)
5.属于形状公差的是()
6.哪种定位方法不能采用?(欠定位)
7.装卡工件和改变切削用量属于(B)
A正常时间B辅助时间C休息时间 D
8.一般形状简单的工件毛坯采用:
A铸造B锻造C型采D去1元店买个现成的
三双选题(10分) 其中两个都选对,给2分,选对一个给1分,无顺序要求。
1.渐开线圆柱齿轮可见的两条线是(齿顶圆)(分度圆)
2.下列属于非接触式密封的是:(迷宫式)(间隙式).
3.机械传动的优点是:(传动比准确)(故障易发现,易维修)4.ISO9000系列包括(全面质量管理)(全面质量保证)
5.磨削时如何降低表面粗糙度(一些关于速度的选项)
6.下列哪两种材料不能气割:
A45 B铝合金C20 D不锈钢
简答题(5X4=25分)
1. 简述数控机床的特点.
1·加工精度高,具有稳定的加工质量;
2·可进行多坐标的联动,能加工形状复杂的零件;
3·加工零件改变时,一般只需要更改数控程序,可节省生产准备时间;
4·机床本身的精度高、刚性大,可选择有利的加工用量,生产率高(一般为普通机床的3~5倍);
5·机床自动化程度高,可以减轻劳动强度;
6·对操作人员的素质要求较高,对维修人员的技术要求更高。
2. 简述切削液的作用。
1.润滑作用
2.冷却作用
3.清洗作用
4.防锈作用
5.其它作用
除了以上4种作用外,所使用的切削液应具备良好的稳定性,在贮存和使用中不产生沉淀或分层、析油、析皂和老化等现象。
对细菌和霉菌有一定抵抗能力,不易长霉及生物降解而导致发臭、变质。
不损坏涂漆零件,对人体无危害,无刺激性气味。
在使用过程中无烟、雾或少烟雾。
便于回收,低污染,排放的废液处理简便,经处理后能达到国家规定的工业污水排放标准等。
3. 用40Cr刚制造模数为3的齿轮,其加工工艺路线为:下料――锻造――
正火――粗加工――调质――精加工――表面淬火――回火――磨削,请说明各热处理工艺的目的。
4. 什么是过定位,欠定位,完全定位,不完全定位?
夹具上工件定位件所能限制的工件自由度小于按照相关工艺规程要求所必须限制的自由度,称为欠定位。
夹具上几个定位件都可能限制工件的同一个或若干个自由度,造成工件定位不稳定或破坏正确定位,称为过定位。
5. 加工时选择粗基准面的原则有哪些?
①. 为保证加工表面与不加工表面之间的位置精度,则应以不加工表面作为粗基准;
②. 为保证零件上的重要表面加工侠量小而均匀,则要以该表面作为粗基准;
③. 为使毛坯上多个表面的加工余量较为均匀,应选择能使其余毛坯面到所选粗基准的位置误差得到均匀的毛坯面为粗基准。
如阶梯轴的置身辅助副本基准应该选中间阶梯的端面;
④. 在没有设计要求保证表面余量均匀的情况下,若零件每个表面都需加工,则应选择加工小的表面为粗基准;
⑤. 粗基准应便于定位、装夹和加工;
⑥. 粗基准应尽可能平整、光整:有飞边、浇口、冒口的表面以及分型面、分模面不应作为粗基准;
⑦. 同一定位自由度方向的粗基准一般只允许使用一次。
五问答计算题(4X10=40分)
1. 下表列出了几种牌号的钢,选择相应的热处理方法与该牌号刚应用
场合.
牌号热处理方法应用
40Cr 轴类调质
GCr15 淬火+低温回火轴承
20Cr 渗碳+淬火+回火齿轮类材料
16Mn 热轧(或正火) 桥梁结构
65Mn 淬火+中温回火弹簧
热处理方法: 热轧(或正火),淬火+低温回火,淬火+中温回火,渗碳+淬火+回火,调质。
应用:桥梁结构,轴承,齿轮类材料,弹簧,轴类。
40cr特性及用途
中碳调制钢,冷镦模具钢。
该钢价格适中,加工容易,经适当的热处理以后可获得一定的韧性、塑性和耐磨性。
正火可促进组织球化,改进硬度小于160HBS毛坯的切削性能。
在温度550~570℃进行回火,该钢具有最佳的综合力学性能。
该钢的淬透性高于45钢,适合于高频淬火,火焰淬火等表面硬化处理等。
用途
这种钢经调质后用于制造承受中等负荷及中等速度工作的机械零件,如汽车的转向节、后半轴以及机床上的齿轮、轴、蜗杆、花键轴、顶尖套等;经淬火及中温回火后用于制造承受高负荷、冲击及中等速度工作的零件,如齿轮、主轴、油泵转子、滑块、套环等;经淬火及低温回火后用于制造承受重负荷、低冲击及具有耐磨性、截面上实体厚度在25mm以下的零件,如蜗杆、主轴、轴、套环等;经调质并高频表面淬火后用于制造具有高的表面硬度及耐磨性而无很大冲击的零件,如齿轮、套筒、轴、主轴、曲轴、心轴、销子、连杆、螺钉、螺帽、进气阀等。
此外,这种钢又适于制造进行碳氮共渗处理的各种传动零件,
如直径较大和低温韧性好的齿轮和轴[7]。
GCr15钢
是一种合金含量较少、具有良好性能、应用最广泛的高碳铬轴承钢。
经过淬火加回火后具有较高的硬度、均匀的组织、良好的耐磨性、高的接触疲劳性能。
该钢冷加工塑性中等,切削性能一般,焊接性能差,对形成白点敏感性能大,有回火脆性。
实际就是Cr15。
GCr15是一种最常用的高铬轴承钢,具有高的淬透性,热处理后可获得高而均匀的硬度。
耐磨性优于GCr9,接触疲劳强度高,有良好的尺寸稳定性和抗蚀性,冷变形塑性中等,切削性一般,焊接性差,对白点形成敏感,有第一类回火脆性。
在滚珠轴承制造中,用以杂质壁厚12mm.外径<250mm的H级至C级的轴承套,直径25.4-50.8mm的钢球;直径<22mm的滚子,此外也可用作承受大负荷.要求高耐磨性.高弹性极限.高接触疲劳强度的其他机械零件及各种精密量具冷冲模等。
如机床的滚珠丝杆,涡轮喷气发动机喷嘴的喷口.柱塞.活门.衬套等。
20Cr
与15Cr钢相比,有较高的强度及淬透性,在油中临界淬透直径达4 ~22mm,在水中临界淬透直径达11~40mm,但韧性较差,此钢渗碳时仍有晶粒长大倾向,降温直接淬火对冲击韧性影响较大,所以渗碳后需二次淬火以提高零件心部韧性,无回火脆性;钢的冷应变塑性高,可在冷状态下拉丝;可切削性在高温正火或调质状态下良好,但退火后较差;焊接性较好,焊后一般不需热处理,但厚度大于15mm的零件在焊前需预热到100~150℃。
应用举例
这种钢大多用于制造心部强度要求较高,表面承受磨损、截面在30mm以下的或形状复杂而负荷不大的渗碳零件(油淬),如:机床变速箱齿轮、齿轮轴、凸轮、蜗杆、活塞销、爪形离合器等;对热处理变形小和高耐磨性的零件,渗碳后应进行高频表面淬火,如模数小于3的齿轮、轴、花键轴等。
此钢也可在调质状态下使用,用于制造工作速度较大并承受中等冲击负荷的零件,这种钢还可用作低碳马氏体淬火用钢,更进一步增加钢的屈服强度和抗拉强度(约增加1.5~1.7倍)。
16Mn是什么材料
16Mn为钢材中的一种材质。
过去钢材的一种叫法。
16Mn钢属于碳锰钢,碳的含量在0.16%左右,屈服点等于343MPa(强度级别属于343MPa级)。
16Mn钢的合金含量较少,焊接性良好,焊前一般不必预热。
但由于16Mn钢的淬硬倾向比低碳钢稍大,所以在低温下(如冬季露天作业)或在大刚性、大厚度结构上焊接时,为防止出现冷裂纹,需采取预热措施。
65Mn
锰提高淬透性,φ12mm的钢材油中可以淬透,表面脱碳倾向比硅钢小,经热处理后的综合力学性能优于碳钢,但有过热敏感性和回火脆性。
用作小尺寸各种扁、圆弹簧、座垫弹簧、弹簧发条,也可制作弹簧环、气门簧、离合器簧片、刹车弹簧及冷拔钢丝冷卷螺旋弹簧。
65Mn 钢板强度.硬度.弹性和淬透性均比65号钢高,具有过热敏感性和回火脆性倾向,水淬有形成裂纹倾向。
退火态可切削性尚可,冷变形塑性低,焊接性差。
受中等载荷的板弹簧,直径达7-20mm的螺旋弹簧及弹簧垫圈.弹簧环。
高耐磨性零件,如磨床主轴.弹簧卡头.精密机床丝杆.切刀.螺旋辊子轴承上的套环.铁道钢轨等
2. 一幅轴装配设计图,需要指出设计图中6个错误中的5个,并如何改
正.
(和这图类似,但不完全是这图)
3. 使用车床加工一外圆柱表面,加工前工件直径为62mm,加工后工件
直径为54mm,主轴转速为240r/min,刀具进给速度为96mm/mim,求切削速度、进给量、切削深度。
4. 分别说明下图1和图2中的a和b,哪个更符合加工工艺?请说明原因。
(与下两图几乎完全相同)。