综合英语语法总结
- 格式:doc
- 大小:369.50 KB
- 文档页数:60

课时一教学任务一、重点语法1.动词be(am,is,are)的用法:be动词包括“am”, “is”, “are”三种形式。
①第一人称单数(I)配合am来用。
句型解析析:I am+…②第二人称(You)配合are使用。
句型解析:You are+…③第三人称单数(He or She or It)配合is使用。
句型解析:She(He, It) is +……④人称复数 (we /you/they)配合are使用。
句型解析:We (You, They) are +……例句 We are in Class 5,Grade are my are good students.用法口诀:我(I)用am, 你(you)用are,is跟着他(he),她(she),它(it)。
单数名词用is,复数名词全用are。
变否定,更容易,be后not加上去。
变疑问,往前提,句末问号莫丢弃。
还有一条须注意,句首大写莫忘记。
1.用括号中适当的词填空。
1. I ________(am, are, is) from Australia.2. She _______ (am, are, is) a student.3. Jane and Tom _________(am, is, are) my friends.4. My parents _______ (am, is, are) very busy every day.5. _______ (Are, Is, Do, Does) there a Chinese school in New York6. _______ (Be, Are, Were, Was) they excited when he heard the news7. There _____ (be) some glasses on it.8. If he _____ (be) free tomorrow, he will go with us.2.用be 动词的适当形式填空1. I ______ a boy. ______ you a boy No, I _____ not.2. The girl______ Jack's sister.3. The dog _______ tall and fat.4. The man with big eyes _______ a teacher.5. ______ your brother in the classroom6. Where _____ your mother She ______ at home.7. How _______ your father8. Mike and Liu Tao ______ at school.9. Whose dress ______ this10. Whose socks ______ they11. That ______ my red skirt.12. Who ______ Ijeans ______ on the desk.______ a scarf for you.15. Here ______ some sweaters for you.16. The black gloves ______ for Su Yang.17. This pair of gloves ______ for Yang Ling.18. The two cups of milk _____ for me.19. Some tea ______ in the glass.20. Gao shan's shirt _______ over there.第二课时(1)英语人称代词和物主代词一、人称代词表示“我”、“你”、“他”、“她”、“它”、“我们”、“你们”、“他们”的词,叫做人称代词。

英语语法总结(优秀6篇)过去将来时篇一1、表示过去某一时刻或某一时间内正在进行的动作。
这一特定的过去时间通常有时间状语(从句)或由上下文来表示。
2、表示过去某一阶段一直在进行的动作。
但说话时不一定正在进行。
3、表示从过去某一时间的角度看将要发生的动作,用于某些动词。
(见现在进行时3)4、与always, frequently等副词连用,表示感情色彩。
英语语法16种英语时态总结篇二1. 一般现在时用法:A) 表示现在发生的动作、情况、状态和特征。
B) 习惯用语。
C) 经常性、习惯性动作。
例:He always helps others. (他总是帮助别人。
)D) 客观事实和普遍真理。
尤其要注意,如果前后文不是一般现在时,则无法保持主句、从句时态一致。
E) 表示一个按规定、计划或安排要发生的动作,(仅限于某些表示"来、去、动、停、开始、结束、继续'等的动词)可以与表示未来时间的状语搭配使用。
常见的用法是:飞机、火车、轮船、汽车等定期定点运行的交通方式。
例:The next train leaves at 3 oclock this afternoon.(下一趟火车今天下午3点开车。
)How often does this shuttle bus run? (这班车多久一趟?)F) 在时间和条件状语从句里经常用一般现在(有时也用现在完成时)表示将来事情。
例:When you have finished the report, I will have waited for about 3 hours.(等你完成这份报告的时候,我就已经等了将近3个小时了。
)2. 现在进行时(be doing)用法:现在正在进行的动作。
3. 现在完成时(have done)用法:A) 表示动作到现在为止已经完成或刚刚完成。
例:I bought a new house, but I _________ my old one yet, so at the moment I have two houses.A) didnt sell B) sold C) havent sold D) would sell答案是C) havent sold。

高中英语语法总结大全你应该明白一个事实,英语是单词和语法的综合,所以单词和语法都要拿下。
今天小编在这给大家整理了高中英语语法总结大全,接下来随着小编一起来看看吧!英语常用的句型结构1、S + vi2、S + link verb + predicative3、S + vt +o4、S + vt + o (间接) + o (直接)5、S +vt+ o + o c6、There be + s + …句子的成分1. 主语—主语是谓语讲述的对象,表示所说的“是什么”或“是谁”。
一般由名词、代词、不定式或相当于名词的词或短语来充当。
它在句首。
注意:不定式作主语时,常用形式主语it句型。
2. 谓语—说明主语“做什么”,“是什么”或“怎么样”。
谓语(谓语部分里主要的词)必须用动词。
谓语和主语在人称和数两方面必须一致。
它在主语后面。
3. 表语—表语说明主语“是什么”或者“怎么样”,由名词、形容词、副词、介词、不定式及相当于名词或形容词的词或短语来担任。
它的位置在系动词后面。
_注意区别:My job is teaching.(teaching 为表语) 与I am teaching now.(am teaching 为谓语)4. 宾语—宾语是动作、行为的对象,由名词、代词、不定式或相当于名词的词、短语来担任,它和及物动词一起说明主语做什么,在谓语之后。
5. 状语—状语用来修饰动词、形容词或副词。
一般表示行为发生的时间、地点、目的、方式、程度等意义,一般由副词、介词短语、不定式或相当于副词的词或短语来表示。
状语一般放在句末,但有的可以放在句首、句中。
6. 定语—定语是用来修饰名词或代词的。
形容词、代词、数词、名词、介词短语、不定式或相当于形容词的词或短语等都可以担任定语。
因为它是修饰名词或代词的,而名词和代词又可以作主语,还可以作表语和宾语,所以定语的位置很灵活,凡是有名词、代词的地方都可以有定语。
简单句、并列句、复合句句型:主语+谓语只包含一个主谓结构,而句子的各个结构都只由单词或短语表示。

七年级英语语法知识总结(10篇)七年级英语语法知识总结篇一一、七年级英语语法--词法(一)名词1.名词的数我们知道名词可以分为可数名词和不可数名词,而不可数名词它没有复数形式,但可数名词却有单数和复数之分,复数的构成如下:(1)在后面加s。
如:fathers, books, Americans, Germans, apples, bananas(2)x, sh, ch, s, tch后加es。
如:boxes, glasses, dresses, watches, wishes, faxes(3)①以辅音字母加y结尾的变y为i再加es 如:baby-babies, family-families, duty-duties, comedy-comedies, documentary-documentaries, story-stories②以元音字母加y结尾的直接加s。
如:day-days, boy-boys, toy-toys, key-keys, ways(4)以o结尾加s(外来词)。
如:radios, photos, 但如是辅音加o的加es:如: tomatoes西红柿, potatoes马铃薯(5)以f或fe结尾的变f为v再加es(s)。
如:knife-knives, wife-wives, half-halves, shelf-shelves, leaf-leaves, yourself-yourselves (6)单复数相同(不变的)有:fish, sheep, deer鹿子, Chinese, Japanese(7)一般只有复数,没有单数的有:people,pants, shorts, shoes, glasses, gloves, clothes, socks(8)单词形式不变,既可以是单数也可以是复数的有:police警察局,警察, class班,同学, family家,家庭成员(9)合成的复数一般只加主要名词,多数为后一个单词。

英语语法大全总结英语语法专题四:动词的时态和语态英语语法专题五:情态动词一、can和could1、can的用法(1)表示体力和脑力方面的力量。
(2)表示对如今的动作或状态进行主观的猜想,主要用在否认句和疑问句中。
(3)表示可能性,理论上的可能性,意为“有时候可能会”,可用于确定句。
(4)表示允许,意思与may接近。
(5)表示说话人的推想、怀疑、惊异、猜想或不愿定等,主要用于否认句、疑问句或感叹句中。
(6)can的特别句型cannot…too / enough表示“无论怎么。
也不过分”。
“越。
越好”。
cannot but+ do sth.表示“不得不,只好”。
2、could的用法(1)表示力量,指的是过去时间。
(2)表示允许,指的是过去时间。
(3)表示可能,可以指过去时间,也可以指如今时间,表示语气缓和。
(4)委婉客气地提出问题或陈述看法,指的是如今时间。
主要用于疑问句,回答时用can。
3、can与could的区分can表推想时只用于否认句和疑问句(could无此限制)。
couldn’t的可能性比can’t小。
4、can与be able to的区分(1)如今时:无区分,但后者不常用。
(2)完成时;can没有完成时,此时要用have(has,had)been able to。
(3)将来时:can没有将来时,要用will be able to。
(4)过去时:could表示一般力量,was/were able to 表示在详细场合通过努力胜利做成某事的力量。
二、may 和might1、may的用法(1)表示询问或说明一件事可不行以做。
(2)表示一件事或许会发生或某种状况可能会存在,通常用在确定句和否认句中。
留意:表示可能性时,can’t语气强,表示“不行能”,may not语气弱,表示“可能不”。
2、might的用法(1)表示询问或允许,指的是过去时间。
(2)表示可能发生的事,可以指过去时间,也可以指如今时间,语气更加不愿定,可能性比may小一些。

英语初中语法单词总结第1篇一、根据章节先把相同知识点归类。
事先要对教材知识点进行横向的把握,这样有利于明确复习方向,提高复习效率。
或许我们可以从这两个方面著手:1.词汇的归类总结。
语言学家Harmer认为“如果说结构是语言的骨骼,词汇就是最重的器官和血肉”词汇的积累和扩大始终是我们要关注的重点,这就决定了检测词汇很重要,关乎到学生对四会词语的基本使用。
我们一天复习三单元,这其中就包括三个单元的单词,课文、知识点。
我们是通过命题式的竞赛写相同种类的词或使用powerpoint做竞赛式的抢答来达到对单元词汇的初步巩固。
这两种方法都可以充分让学生使用脑子,动起手把知识有效地输出。
2.相似词句的归类,对比性地归纳,要着重与词类用法的检测。
通过最接近考试题型的笔头反复操练就能达到强化提高语法题目的解题技巧。
我个人觉得这个部分的检测不宜放太大的难度,毕竟考试是面对全体学生,测试的目的是要让他们学有所长学有所成。
培养学生创新的实践能力在此尤为值得我们关注了。
二、反复的练习是加以巩固学生对重点内容的最佳方法。
练习要注意多变性及灵活性。
我们的测试目的始终以检查学生对知识的掌握是否达到考纲要求为目的的,但是也不能忽视对不同学生优势培训。
我大致的分类——四个不同等级。
①选择题类型.难度低,适合检查全体学生对重点知识点的掌握情况,故可以放在第一次的复习课中;②句型转换.难道适中,此句型多会在同义句或画线提问的形式出现,可以考测学生对重点句型的认知深度;③翻译题,难度较大,这种题目既考学生对词组的熟练程度,也考学生对词组的应用能力,这是属于我们说的另一种拓展题目了。
④作文操练。
考学生的对词组的综合操控能了。
本人建议可以布置为1分钟的口语测试。
由于不仅提高学生的口语表达能力,还提高听力能力。
英语初中语法单词总结第2篇1.着重学习易混淆词之间的区别英语有很多单词声音或拼写相同,含义却很不相同。
这些同形异义词,同音异义词,同形异音词和同音异形词非常容易混淆,并导致常见的错误。
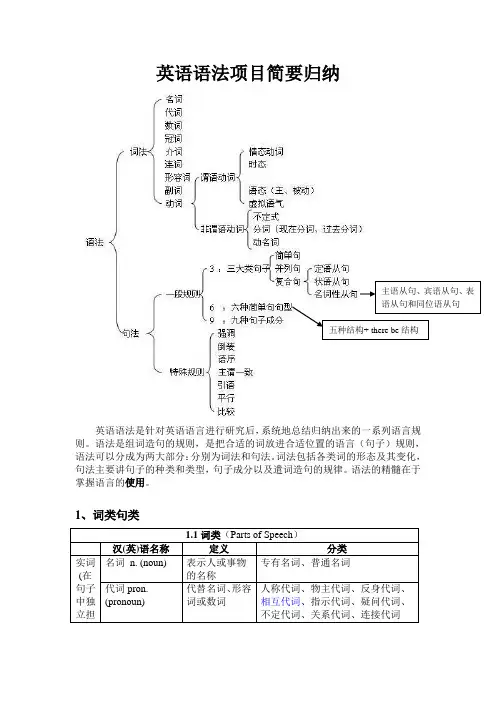
英语语法项目简要归纳英语语法是针对英语语言进行研究后,系统地总结归纳出来的一系列语言规则。
语法是组词造句的规则,是把合适的词放进合适位置的语言(句子)规则,语法可以分成为两大部分:分别为词法和句法。
词法包括各类词的形态及其变化,句法主要讲句子的种类和类型,句子成分以及遣词造句的规律。
语法的精髓在于掌握语言的使用。
1、词类句类2、词语介绍2.1、名词介绍名词(noun)是指人或事物的名称。
名词一般分为专有名词(proper noun)和普通名词(common noun)。
专有名词是个别的人、事物、地点、团体、机构等专有的名称,首字母通常大写。
名词按其所表示的事物的性质也可以分为可数名词(countable noun)和不可数名词(uncountable noun),可数名词有单数和复数形式。
2.2、代词介绍代词(pronoun)用于代替名词等。
代词分为人称代词、物主代词、指示代词、反身代词、相互代词、疑问代词、关系代词、连接代词和不定代词。
2.2.1.人称代词代替人或事物的名称,分为主格人称代词和宾格人称代词两种。
词两种。
形容词性物主代词相当于形容词,置于名词前做定语。
名词性物主代词2.3、数词介绍数词表示数量或顺序等。
分为基数词(cardinal number)和序数词(ordinal number)。
2.4、动词介绍但要与动词原形以及其被动语态一起使用,谓语动词增添情态色彩,表示说话人对有关行为或事物的态度和看法,认为其可能、应该或必要等。
情态动词后面加动词原形。
1.情态动词不能表示正在发生或已经发生的事情,只表示期待或估计某事的发生。
2.情态动词除ought 和have外,后面只能接不带to的不定式。
3.情态动词不随人称的变化而变化,即情态动词的第三人称单数不加-s。
情态动词不受任何时态影响即不加三单。
4.情态动词没有非谓语形式,即没有不定式、分词等形式。
2.5、感叹词感叹词是用来表示说话时表达的喜、怒、哀、乐等情感的词。

十大英语语法基础知识点归纳总结在学习英语的过程中,语法是一个非常重要的部分。
掌握好英语语法基础知识,不仅可以帮助我们正确地表达自己,还可以提高我们的英语水平。
下面,我将根据十大英语语法基础知识点,逐一进行总结和归纳,希望能够帮助大家更好地掌握这些知识。
1. 主谓一致主谓一致是指句子中的主语和谓语在人称和数上要保持一致。
在英语中,主谓一致是非常重要的语法规则,也是构成句子正确性的基础之一。
主语是第三人称单数时,谓语动词要加-s或-es。
2. 时态时态是表示动作或状态发生的时间的一种语法形式。
英语中有多种时态,包括一般现在时、一般过去时、一般将来时、现在进行时、过去进行时、将来进行时等。
掌握好各种时态的用法可以帮助我们准确地描述不同时间发生的动作或状态。
3. 名词复数名词复数是指表示两个或两个以上的个体、事物或概念的名词形式。
英语中名词复数的构成有规律可循,大多数名词在词尾加-s或-es就可以构成复数形式,但也有一些名词变化规律需要特别注意。
4. 冠词冠词是英语中用来限定名词的一种词类,包括定冠词“the”和不定冠词“a/an”。
冠词在句子中起着非常重要的限定作用,正确使用冠词可以让句子更加准确地表达出原意。
5. 代词代词是代替名词或名词词组的词语,用来避免重复或简化表达。
英语中的代词分为人称代词、物主代词、反身代词、指示代词、疑问代词、不定代词等多种类型,每种类型的代词都有着不同的用法和形式。
6. 动词时态和语态动词时态和语态是用来表示动作发生的时间和句子主语与谓语之间的关系。
英语中的动词时态包括一般现在时、一般过去时、一般将来时、现在进行时、过去进行时、将来进行时等,而语态则包括主动语态和被动语态。
7. 副词副词是用来修饰动词、形容词、副词或句子的成分,表示时间、地点、方式、原因、程度等。
在句子中,副词起着非常重要的修饰作用,可以让句子的表达更加生动和准确。
8. 介词介词是用来表示名词与其它词之间关系的一种虚词,包括表示时间、地点、方位、原因、目的等多种类型。

英语语法知识总结定语从句限制性:先行词是物,which=that 先行词是人,who(m)=that非限制性,没有that和why一.关系代词(作宾语可省略)人:who(主) whom(宾)that(主,宾)whose(定)物: which(主,宾)that(主,宾)whose(定)inwhich in whose in whom关系副词when=on which in which at which period occasion场合,时刻stay停留先行词time day year week mouth 做状语where=at which in which position职位,位置activity point地点,位置先行词degree程度(to a degree在某种程度上)stage舞台condition situation情况,状况place city house school room statewhy: reason 原因状语for whicheg1. I live in Beijing ,which is the capital in China. (缺主语)I will go to Beijing , where my father works as a teacher.(缺地点状语)eg2. May 12th,2008 is the day when\on which an earthquake happened.(缺时间状语)May 12th ,2008 is the day which\that\~ I never forgot .(缺宾)eg3. I don’t want know the reason why you were late.The reason (which\that he told for his late )is true.(缺宾)二.介词+关系代词(看先行词搭配)只能用which指物,whom指人1, 介词+which物\whom人\whose物,人(V.)eg. Can you tell me the name of the man for whom you bought a book(buy sth for sb.)2,3,the only \very one of +n.复+关系代词+v.单eg. He is one of the student who have复made great progress.4,先行词是一句话、一件事v.单a Frenchman ,which was not true.1. I ,who am a Chinese ,will do my best for our country.2. Do you know the schools and students that are beingtalked about?3. He is one of the students who have made progress.4. He is the only\very one of the students who has madegreat progress.5. Great changes have taken place in china, which is knownto all.三. who 引导的定语从句1,先行词指人的不定代词one ones all anyone those no one none noboday anybody2, 先行词是I You he theyeg. Those ( who are late for school) will be punished.He (who laughs last) laughs the best.3, 在There be\live 结构中先行词指人。

英语语法总结全集(By Eleanor 灿灿)语法讲座一:名词和主谓一致语法讲座二:动词的时态与语态语法讲座三:情态动词语法讲座四:代词语法讲座五:形容词和副词语法讲座六:分词语法讲座七:动名词* 动名词与现在分词用法的区别语法讲座八:不定式语法讲座九:反意疑问句和倒装句语法讲座十:连词和状语从句语法讲座十一:名词性从句语法讲座十二:定语从句*关于非限定性定语从句*限制性和非限制性定语从句的区别语法讲座十三:虚拟语气语法讲座一:名词和主谓一致一、名词的分类英语中名词主要可以分为可数名词和不可数名词。
1 •可数名词可数名词一般都有单复数。
单数时,名词前可加不定冠词a/an ;复数时,前面可加数词,名词本身要改成复数形式。
可数名词的复数有规则和不规则两种变化。
规则的名词,只要在单数名词之后加“s”,“es或去“y” 加“ ies” 就行,如: an umbrella, twelve umbrellas; a factory, three factories 不规则的名词变化则要靠积累记忆,如: a mouse, ten mice; a policeman, six policemen 有少数可数名词,如sheep, works (工厂),Chinese等,它们的单复数同形:a sheep, four sheep; a chemical works, five chemical works此外,还有一些可数名词只有复数形式,女口clothes trousers, cattle, police, people(人,人民)等英语名词中还有一些合成词,它们的复数形式有三种可能:1)后面的部分变成复数形式:grown-ups, boy students grandchildren。
2)前面的部分变成复数形式:passers-bylookers-on, sons-in-law。
3)前、后都变成复数形式:men doctors, women drivers。

英语语法总结【通用5篇】1.英语语法总结一、关系代词引导的定语从句1、that 指人或物在从句中作主语,宾语或表语which 指物在从句中作主语,宾语或表语(作宾语时可以省略)who 指人在从句中作主语,宾语或表语whom 指人在从句中作宾语whose 指人或物在从句中作定语as 指人或物在从句中作主语,宾语或表语but 指人或物在从句中作主语,宾语或表语注意:指物时,whose+名词=the+名词+of which或 of which+the+名词2、as 的用法(1)常用于下列结构:such…as; so…as;the same…as; as…as注意:the same…as 表示同一类,不同一个the same…that 表示同一个(2)as与which的区别a、位置不同as可放在主句后,主句前或主句中间;which只能放在主句后。
b、as起连接作用,表达说话人的观点、看法,并指出主句内容的根据或出处,意为“正如,正像”。
Which相当于并列句,可以用and this来代替,意为“这一点,这件事’”。
注意:as常用于下列结构:as we know/ as is known to all, as we all can see, as has been said before/above,as might be excepted, as is often the case, 一般不能用which代替as。
c、在从句中作主语时,which既可作系动词be的主语也可作实义动词的主语,而as只可作系动词be的主语。
二、只用that不用which的情况1、.先行词为all , much, everything, nothing , something ,anything, nothing, none, the one等不定代词时2、先行词被only, any, few, little, no , all, just , very ,right等修饰时.3、当先行词是级或被形容词级修饰时。
英语语法术语总结(中英对照)1. 语法 grammar2. 句法 syntax3. 词法 morphology4. 结构 structure5. 层次 rank6. 句子 sentence7. 从句 clause8. 词组 phrase9. 词类 part of speech10. 单词 word11. 实词 notional word12. 虚词 structural word13. 名词 noun14. 专有名词 proper noun15. 普通名词 common noun16. 可数名词 countable noun17. 不可数名词 uncountable noun18. 抽象名词 abstract noun19. 具体名词 concret noun20. 物质名词 material noun21. 集体名词 collective noun22. 个体名词individual noun23. 介词 preposition24. 连词 conjunction25. 动词 verb26. 主动词 main verb27. 及物动词 transitive verb28. 不及物动词 intransitive verb29. 系动词 link verb30. 助动词 auxiliary verb31. 情态动词 modal verb32. 规则动词 regular verb33. 不规则动词 irregular verb34. 短语动词 phrasal verb35. 限定动词 finite verb36. 非限定动词 infinite verb37. 使役动词 causative verb38. 感官动词 verb of senses39. 动态动词 event verb40. 静态动词 state verb41. 感叹词 exclamation42. 形容词 adjective 43. 副词 adverb44. 方式副词 adverb of manner45. 程度副词 adverb of degree46. 时间副词 adverb of time47. 地点副词 adverb of place48. 修饰性副词 adjunct49. 连接性副词 conjunct50. 疑问副词 interrogative adverb51. 关系副词 relative adverb52. 代词 pronoun53. 人称代词 personal pronoun54. 物主代词 possessive pronoun55. 反身代词 reflexive pronoun56. 相互代词 reciprocal pronoun57. 指示代词 demonstrative pronoun58. 疑问代词 interrogative pronoun59. 关系代词 relative pronoun60. 不定代词 indefinite pronoun61. 物主代词 possessive pronoun62. 名词性物主代词nominal possessive pronoun63. 形容词性物主代词adjectival possessive pronoun64. 冠词 article65. 定冠词 definite article66. 不定冠词 indefinite article67. 数词 numeral68. 基数词 cardinal numeral69. 序数词 ordinal numeral70. 分数词 fractional numeral71. 形式 form72. 单数形式 singular form73. 复数形式 plural form74. 限定动词 finite verb form75. 非限定动词 non-finite verb form76. 原形 base form77. 从句 clause78. 从属句 subordinate clause79. 并列句 coordinate clause80. 名词从句 nominal clause81. 定语从句 attributive clause82. 状语从句 adverbial clause83. 宾语从句 object clause84. 主语从句 subject clause85. 同位语从句appositive clause86. 时间状语从句adverbial clause of time87. 地点状语从句adverbial clause of place88. 方式状语从句adverbial clause of manner89. 让步状语从句adverbial clause of concession90. 原因状语从句adverbial clause of cause91. 结果状语从句adverbial clause of result92. 目的状语从句adverbial clause of purpose93. 条件状语从句adverbial clause of condition94. 真实条件状语从句adverbial clause of real condition95. 非真实条件状语从句adverbial clause of unreal condition96. 含蓄条件句adverbial clause of implied condition97. 错综条件句adverbial clause of mixed condition98. 句子 sentence99. 简单句 simple sentence100. 并列句 compound sentence101. 复合句 complex sentence102. 并列复合句compound complex sentence 103. 陈述句 declarative sentence104. 疑问句 interrogative sentence105. 一般疑问句 general question106. 特殊疑问句 special question107. 选择疑问句 alternative question108. 附加疑问句 tag question109. 反义疑问句 disjunctive question110. 修辞疑问句 rhetorical question111. 感叹疑问句 exclamatory question112. 存在句 existential sentence113. 肯定句 positive sentence114. 否定句 negative sentence115. 祈使句 imperative sentence116. 省略句 elliptical sentence117. 感叹句 exclamatory sentence118. 基本句型 basic sentence pattern119. 句子成分 members of sentences120. 主语 subject121. 谓语 predicate122. 宾语 object123. 双宾语 dual object124. 直接宾语 direct object125. 间接宾语 indirect object126. 复合宾语 complex object127. 同源宾语 cognate object128. 补语 complement129. 主补 subject complement130. 宾补 object complement 131. 表语 predicative132. 定语 attribute133. 同位语 appositive134. 状语 adverbial135. 句法关系 syntatic relationship136. 并列coordinate137. 从属 subordination138. 修饰 modification139. 前置修饰 pre-modification140. 后置修饰 post-modification141. 限制 restriction142. 双重限制 double-restriction143. 非限制 non-restriction144. 数 number145. 单数形式 singular form146. 复数形式 plural form147. 规则形式 regular form148. 不规则形式 irregular form149. 格 case150. 普通格 common case151. 所有格 possessive case152. 主格 nominative case153. 宾格 objective case154. 性 gender155. 阳性 masculine156. 阴性 feminine157. 通性 common158. 中性 neuter159. 人称 person160. 第一人称 first person161. 第二人称 second person162. 第三人称 third person163. 时态 tense164. 过去将来时 past future tense165. 过去将来进行时past future continuous tense 166. 过去将来完成时past future perfect tense 167. 一般现在时 present simple tense168. 一般过去时 past simple tense169. 一般将来时 future simple tense170. 现在完成时 past perfect tense171. 过去完成时 present perfect tense172. 将来完成时 future perfect tense173. 现在进行时 present continuous tense174. 过去进行时 past continuous tense175. 将来进行时 future continuous tense176. 过去将来进行时 past future continuous tense 177. 现在完成进行时present perfect continuous tense178. 过去完成进行时past perfect continuous tense 179. 语态 voice180. 主动语态 active voice181. 被动语态 passive voice182. 语气 mood183. 陈述语气 indicative mood184. 祈使语气 imperative mood185. 虚拟语气 subjunctive mood186. 否定negation187. 否定范围 scope of negation188. 全部否定 full negation189. 局部否 partial negation190. 转移否定 shift of negation191. 语序 order192. 自然语序 natural order193. 倒装语序 inversion194. 全部倒装 full inversion195. 部分倒装 partial inversion196. 直接引语 direct speech197. 间接引语 indirect speech198. 自由直接引语 free direct speech199. 自由间接引语 free indirect speech200. 一致 agreement201. 主谓一致subject-predicate agreement202. 语法一致 grammatical agreement203. 概念一致 notional agreement204. 就近原则 principle of proximity205. 强调 emphasis206. 重复 repetition207. 语音 pronunciation208. 语调 tone209. 升调 rising tone210. 降调 falling tone211. 降升调 falling-rising tone212. 文体 style213. 正式文体 formal214. 非正式文体 informal215. 口语 spoken/oral English216. 套语 formulistic expression217. 英国英语 British English218. 美国英语 American English219. 用法 usage 220. 感情色彩 emotional coloring 221. 褒义 commendatory222. 贬义 derogatory223. 幽默 humorous224. 讽刺 sarcastic225. 挖苦 ironic226. 英语修辞手法:一、明喻(simile)二、隐喻(metaphor)三、提喻(synecdoche)四、拟人(personification)五、夸张(hyperbole)六、叠言(rhetorical repetition)七、借代(metonymy)八、双关语(pun)九、拟声(onomatcpocia)十、讽刺(irony)十一、通感(synesthesia)十二、头韵法(alliteration)。
英语语法总结优秀9篇英语语法总结篇一名词的形式变化主要有单数、复数、所有格的变化。
例:There are many students living at school,the(child) houses are all far from schoo1.由students一词可以判断出横线处应填复数,且作为houses的定语,所以应用其所有格形式,故答案为child的复合变化形式—— 复数的所有格children’s。
技巧二:动词形式变化动词的形式变化比较多,有谓语的变化(时态、语态、语气),有非谓语的变化(不定式、动名词、现在分词、过去分词)。
例:A talk(give) tomorrow is written by Professor Zhang.句中的is written是整句的谓语,所以横线所在的动词应当用作非谓语。
从tomorrow可以看出,报告是“将来”作的,故用不定式;且报告是give动作的承受者,故可以判断出横线所在处用give的不定式被动式——to be given。
英语语法大全篇二一、名词复数规则1.一般情况下,直接加-s,如:book-books, bag-bags, cat-cats, bed-beds2.以s. x. sh. ch结尾,加-es,如:bus-buses, box-boxes, brush-brushes, watch-watches3. 以辅音字母+y结尾,变y为i, 再加-es,如:family-families, strawberry-strawberries4、以f或fe结尾,变f或fe为v, 再加-es,(但有一个特例:roofrarr;roofs)。
如:knife-knives leaf-leaves wife-wives thief-thieves wolf-wolves5.以o结尾的单词,如果有生命,加-es;如果没有生命,加-s。
如:①有生命:potato-potatoes tomato-tomatoes mango-mangoeshero-heroes Negro- Negroes②没生命:radio-radios piano-pianos photo-photos zoo-zoos6.不规则名词的复数变化:(一)完全不规则:woman-women policeman-policemen policewoman-policewomenmouse-mice child-children foot-feet tooth-teeth man-men(二)单数复数词形相同:fish-fish sheep-sheep deer-deer people-peopleChinese-Chinese Japanese-Japanese二、一般现在时【No. 1】一般现在时的功能1.表示事物或人物的特征、状态。
第一章句子成份概述:学好句子成份是学好其他任何语法项目的前提,是重点中的重点。
英语的句子成份无外乎包括:主语、谓语(动词)、宾语、表语、状语、补语、同位语、定语,其中主语和谓语(动词)为句子的主干,换言之,一个句子中可以没有其他任何成份,但不可没有主语和谓语,只有出现一个主语和一个谓语那么这就是一个完整的句子。
如:Birds fly 鸟会飞虽然只有两个单词,但却是一个完整的句子。
又如:the book that I bought in the book store near the post office.我在邮局附近的一个书店里买的那本书。
没有谓语,因此这并不是一个句子,只是一个短语,(that 从句只是修饰the book 的一个定语)以下我们就对所有句子成份逐个学习。
一.主语(主语分为句子主语,形式主语和逻辑主语)(一)句子主语:句子主语一般位于句首(倒装除外),是一句话主要陈述的对象。
在一个句子中若无句子主语,那么其他任何成份就都失去意义了。
例:I can speak English.试想如果没有“I”的话,那么can speak English 还有何意义呢?又如:My watch was broken.试想如果没有“My watch”的话,那么还谈的上“Was broken”吗?但如果是这样的话,那么祈使句怎么解释呢?是不是所有的祈使句都没有意义呢?如:Shut up!闭嘴!其实在问以上问题的时候我们都忽略了一个问题,那就是祈使句并不是没有句子主语,只不过当祈使句的主语是“You”的时候,我们把它省掉了而已,因此上句的原形是“You shut up!”这样一来问题就不攻自破了。
(二)形式主语:英语代词中只有it可以做形式主语和形式宾语,且多用于口语中。
英语的语言结构特点是句子成份由短到长像火车一样。
如:I can see a bird flying in the sky.主谓语从句宾语后置定语或宾语补足语但有时候句子的主语过长,这就不符合英语国家人民的说话习惯了,而显得句子头重脚轻,过于笨重。
【#英语资源# 导语】英语是全球使用范围最广的一门语言,也是国际上通用的语言,在当今英语是一门不错的一门学科,如果你想学好英语,会读英语会写英语那是远远不够的,就像你会读中文写中文一样,不会用它来组成一句完整的话,英语的音标就像中文的拼音一样,那自然英语的语法就像中文的语法一样,我们都是中国人都会说中文,那自然中文的语法就不用说了,那今天我们就谈谈英语的语法吧!下面是?无忧考网整理的内容,希望对你们有帮助!1.英语语法归纳总结一、关系代词引导的定语从句1、that 指人或物在从句中作主语,宾语或表语which 指物在从句中作主语,宾语或表语(作宾语时可以省略)who 指人在从句中作主语,宾语或表语whom 指人在从句中作宾语whose 指人或物在从句中作定语as 指人或物在从句中作主语,宾语或表语but 指人或物在从句中作主语,宾语或表语注意:指物时,whose+名词=the+名词+of which或 of which+the+名词2、as 的用法(1)常用于下列结构:such…as; so…as;the same…as; as…as注意:the same…as 表示同一类,不同一个the same…that 表示同一个(2)as与which的区别a、位置不同as可放在主句后,主句前或主句中间;which只能放在主句后。
b、as起连接作用,表达说话人的观点、看法,并指出主句内容的根据或出处,意为“正如,正像”。
Which相当于并列句,可以用and this来代替,意为“这一点,这件事’”。
注意:as常用于下列结构:as we know/ as is known to all, as we all can see, as has been said before/above,as might be excepted, as is often the case, 一般不能用which代替as。
c、在从句中作主语时,which既可作系动词be的主语也可作实义动词的主语,而as只可作系动词be的主语。
英语语法大全知识点总结
英语语法大全知识点总结
一、句型
1、简单句
简单句是由一个主语和一个谓语构成的句子,如:
He is a student.
2、疑问句
疑问句是由一个助动词或系动词等开头的句子,一般有问句、特殊疑问句和选择疑问句。
如:
Are you a student?
3、否定句
否定句是由一个否定词(not, never, no, nobody等)开头的句子,如:
He is not a student.
4、感叹句
感叹句是表达为感情的句子,如:
What a beautiful day!
5、复合句
复合句是由一个主句和一个从句构成的句子,如:
He said he wanted to go to the cinema.
二、时态
1、一般现在时
一般现在时是指表示一般性,经常性动作或事物的存在状态,如: He goes to school every day.
2、现在进行时
现在进行时是指表示正在进行或发生的动作,如:
He is playing football now.
3、一般过去时
一般过去时是指表示过去某个时间发生的动作或情况,如:
He went to school yesterday.
4、过去进行时
过去进行时是指表示过去某个时间正在发生的动作。
新题型:- Which of the following sentences is INCORRECT?- Which of the following determiners (限定词) can be placed before both singular count nouns and plural count nouns?- Which of the following refelxive pronouns (反身代词) is used as an appositive (同位语)?- Which of the following sentences expresses WILLINGNESS?- Which of the italicized parts functions as a subject?- Which of the italicized parts functions as an object?- All the following sentences have an appositive EXCEPT .- Which of the following best explains the meaning of “Shall we buy the tickets first”?- Which of the following contains an adverbial clause of cause?- Which of the following prepositional phrases can function as an adverbial?- Which of the following prepositional phrases is an adverbial of concession?- "..." The sentence means that .《综合教程》(修订版)第一册1)simple past, past progressive, past perfect; 一般过去时,过去进行时,过去完成时Use of simple past tense:1) The simple past tense is used to talk about completed actions and habits in the past.e.g. Shakespeare died in 1616.We used to walk a mile in the morning when we were in London.2) Past tense of verbs such as want, wonder, hope is used for polite inquiries.e.g. I wondered how you liked the film.Use of past progressive:1) The past progressive indicates a limited duration of time and is thus a convenient way toindicate that something took place (in the simple past) while something else was happening.e.g. Carlos lost his watch while he was running.2) The past progressive can express incomplete action.e.g. I was sleeping on the couch when Bertie smashed through the door.※as opposed to the simple past, which suggests a completed actione.g. I slept on the couch last night.3) The past progressive is also used to poke fun at or criticize an action that is sporadic buthabitual in nature.e.g. Tashonda was always handing in late papers.4) We use the past progressive of verbs such as wonder to show politeness.e.g.I was wondering if you could give me a lift.※This use is even more polite and tentative than the simple past.Use of past perfect tense:1) The past perfect tense expresses the idea that something occurred before another action in thepast. It can also show that something happened before a specific time in the past.e.g. I had never seen such a beautiful beach before I went to Kauai.2) If the past perfect tense is not referring to an action at a specific time, it is not optional. Compare the examples below. Here the past perfect tense is referring to a lack of experience rather than an action at a specific time. For this reason, the past perfect tense cannot be used.e.g. She never saw a bear before she moved to Alaska. Not CorrectShe had never seen a bear before she moved to Alaska. Correct2)verbs of perception + ing form/ -ed form/ infinitive form;感官动词的-ing/-ed/不定式形式Verbs of perception are a set of verbs denoting the use of one of the physical senses. Some verbs of perception see, look at, hear,listen, and feel, along with watch and sense can be used with objects followed by verbs in -ing form, -ed form and infinitive form.e.g. We heard you leave. (Emphasis on our hearing.)We heard you leaving. (Emphasis on your leaving.)John has never heard the piece played before. (Emphasis on the passive voice of play.)3)special word order with as and though as/though 引导的让步状语从句In a concessive clause introduced by though or although, the complement or the adverbial can be placed at the beginning of the sentence. The formula for the inversion is:e.g. Old as / though he is, he works hard as a young man.Hard as / though he studied, he did not pass the examination.Unit 21)generic reference and specific reference of a/an and the 不定冠词和定冠词的形式、语法意义及用法We usually use “the” when we talk about things that are unique: the sun, the sky, etc, and about things that are context specific and are known by both the speaker and the listener. If we want to describe a particular instance of these we can use “a/an”.e.g. I could see the plane (context specific, both the speaker and the listener know about theplane that is mentioned) high up in the sky (unique).When I woke up there was a bright blue sky (an instance).2)go to school or go to the school 用法区别A/an, the and zero articles can all be used in set collocations or fixed collocations and idioms. Caution that collocations with different choices of articles can mean differently.e.g. A man is standing in the front of the house. (The man is in the house.)A tree is standing i n front of the house. (The tree is outside the house.)I go to school every day. (=I go to the school to study every day.)I went to the school today. (=Today I went to some place and that place was a school.)Unit 31)more…than construction; 了解和掌握比较级最高级的结构、用法和所表达的意义※You can use “a little”, “ a lot”, “a bit”, “a great deal”, “any”, “far”, “ even”“still”, and “much” in front of more than construction.e.g. Tom is a little younger than Tim.You get far more than you pay for it.2)as…as construction;The basic pattern is as +adjective / adverb + as.e.g. John is as bright as Bob.The swimming pool isn't as wide as that one.※You can use “just”, “almost”, “nearly” , “quite” in front of "as… as"construction,e.g. Listening skills are just as important as speaking.Maybe I didn't love you quite as often as I should have.3)the mostThe superlative construction is used when three or more than three people or things are compared. In this construction there is usually a scope of comparison which may be expressed by a prepositional phrase, a relative clause, or a non-finite clause. Sometimes the scope of comparison is understood in the context and need not be expressed. In some set expressions, a scope of comparison is unnecessary at all. The negative form of the superlative construction is "the least", which, in practical usage, is usually replaced by the superlative degree of antonymous adjectives or adverbs.e.g. This is the least difficult book I have ever read.The idea of highest degree can also be expressed by other constructions. In some contexts the positive or comparative degree expresses the same meaning as is usually conveyed by the superlative.e.g. George did more work than anyone else.Nothing in my life shook me so deeply as my first visit to China.Unit 41)any, each, all, every and their compounds; any, each,all,every以及它们的复合词2)countable and uncountable nouns; 可数名词和不可数名词Common nouns can be classified into 1) countable nouns and uncountable nouns, or 2)individual nouns, collective nouns, material nouns and abstract nouns. Usually individual nouns and collective nouns are countable while material nouns and abstract nouns areuncountable. But sometimes abstract nouns and material nouns can be countable if they are used in specific sense, for example with an attribute.e.g. My children are a great joy (an attribute) to me.His room, at sixteen dollars a day, was a disappointment (something specific, and something that disappoints people).Sri Lanka produces many teas (many kinds of tea).3)prepositions 介词的用法和特点及其语法意义Unit 51)imperative sentences; 祈使句Imperative sentences, also known as “commands” begin with a verb in the imperative mood and express a command, an instruction, an order, a warning, a request, a suggestion, a wish, an invitation, etc.There are three kinds of imperatives: the second person imperatives, the first person imperative, and the third person imperatives.For the second person imperatives, if we want to enhance the force of the imperative, we can add an emphatic DO or YOU at the beginning of the sentence.e.g. Mr. Smith, you sit over there.Do come in.Let me have a look.Let’s stop and finish it later.Don’t let anyone shirk his responsibility.2)question tags added to imperative clauses; 祈使句的反意问句的构成和作用Sometimes we add question tags to the imperative sentences to soften the imperative tone.For the second person imperatives, after a positive imperative, the question tag can be “will/would/can/can’t/won’t you/?” “Won’t” is used to invite. “Will you” is often used as request. “Won’t you” is used to show less forceful orders. “Would” is less forceful than “will”and much less common. “Can’t you” can show the speaker’s annoyance. After a negative imperative, the question tag is “will you?”If t he part addressed includes only the speaker the question tag usually is “will/won’t you?” If the part addressed includes both the speaker and the listener, the tag should be “shall we?”e.g.Don’t be so noisy, will you?Stop talking, will/won’t/would/can/can’t you?Let me drive you home, will you?Let’s take a taxi, shall we?3)anther, other(s), the other(s) 用法特点及表达的意义*“Another” means 1) additional, one more (sometimes two more, three more ...) person or thing of the same type; 2) a different one, not the same person or thing.e.g. I need another week / two weeks to finish this investigation.We finally moved to another apartment.*“Other” is always followed by plural nouns. It means 1) additional; 2) else, different. “Others” means more people or things.e.g. Danny is playing with two other children.Saudi Arabia produces more oil than any other country (Singular noun must be used after “any other”.)I only know about this book, but there might be others (= other books).*“The other (one)” me ans t he second of the two people or things. “The others” (= the other ones) means the rest of the people or things. Note that here there must be a specific context.e.g. You can park on the other side of the street.She’s much brighter than all the other children in her class (“In her class” serves as a specific context.).Unit 61)simple prepositions and complex prepositions; 介词和复合介词①The prepositions, such as in, of, at, and to, are all single words. We call them SIMPLEPREPOSITIONS.②COMPLEX PREPOSITIONS consist of two- or three-word combinations acting as asingle unit. Here are some examples: according to, but for, except for, in terms of, in point of, with regard to, in the case of, etc.e.g. regardless of but for in terms of except for according to in case of2) conjunctions 连词Conjunctions are used to express a connection between words. There are two types of conjunctions. COORDINATING CONJUNCTIONS(or simply COORDINATORS) connect elements of equal syntactic status.e. g. Paul and DavidI play tennis but I don't play well.meat or fishOn the other hand, SUBORDINATING CONJUNCTIONS (or SUBORDINATORS) connect elements of unequal syntactic status.e.g. I left early because I had an interview the next day.I'll be home at nine if I can get a taxi.Unit 71)modal auxiliary + infinitive; 情态动词+不定式的构成方式及表达的不同语法意义Modal auxiliaries are a special type of verb in English language.Syntactically, modal auxiliaries (or “modals” for short) can only be the initial element of a finite verb phrase and are invariably followed by a bare infinitive.e.g.*Notice that: when a modal auxiliary takes the predictive meaning, the infinitive after it may appear in the perfect form to denote past timeShe must have seen how scared I was and reached over.and in the progressive form to denote future time.I sh ouldn’t be eating them anyhow.When the modal auxiliary takes the non-predictive meaning, the infinitive after it usually appears in its base form as in the first example.I could hear small pockets of soothing conversation everywhere.2) be going to and will; be going to和will的用法区别to” for decisions about the future that have already been made.e.g.“Shall I ask Sandra?” “No, she won’t want to be disturbed.”The sky has gone really dark. There’s going to be a storm.I’ll pick him u p at 8. (an offer; making an arrangement now)I’m going to collect the children at 8. (this was previously arranged)3) hypothetical past 假设性过去时的用法及语法意义(虚拟)We use hypothetical past to talk about unreal condition in the present, future and past. And in this case, we use simple past to replace the original simple present or simple future, and past perfect to replace the original past tense.e.g. I am so nervous → If only I weren’t so nervous.You are not telling the truth → I wish you were telling the truth.You didn’t listen to me and you are in great trouble now. If you had listened to me, you wouldn’t be in such trouble now.Unit 81)real and unreal conditionals; 真实条件句和非真实条件句2)it + be + … + that 强调句的用法及表达的不同语法意义Sentences introduced by "It is"or "It was"are often used to emphasize a specific subject or object. The introductory clause is then followed by a relative pronoun. “It + be + … + that” can be used to highlight the subject, object, adverbial of time, place, manner, cause.e.g.It is Jenny who spends all her money on shoes. (subject)It is shoes that Jenny spends all her money on. (object)It was in London that he met his first wife. (place)It was only when he phoned that I realized what had happened. (time)It is learning English that I find most enjoyable nowadays. (gerund action)Unit 91)simple present tense; 一般现在时①The simple present is used in the expression of eternal truths and proverbs, scientific andother statements made for all time.e.g. A rolling stone gathers no moss.London stands on the River Thames.②The simple present can express habitual or recurrent actions.e.g. Percy often goes to his office by underground.He always sleeps with his windows open.③The simple present can be used to denote a momentary phenomenon that exists at the time of speaking.e.g.What’s the matter with you? You look pale.④The simple present can be used to denote future time.e.g. I hope she likes the flowers.If it doesn’t rain tomorrow, we will go to the countryside.⑤The simple present can occasionally be used to denote past time. This use of the simplepresent is usually found with such verbs as tell, say, hear, write, learn.e.g.Mary tells me you’re entering college next year.I hear poor old Mrs. Smith has lost her son.2)present progressive; 现在进行时①The present progressive is used to denote an action in progress at the moment of speaking.e.g.Hurry up! We’re all waiting for you.②The present progressive can express an action in progress at a period of time including thepresent.e.g. Jane is studying law while her sister is doing physics.③The present progressive is used to denote a future happening according to a definite plan or arrangement.e.g.I’m going to Shanghai for the summer holiday.When you are talking with him, take care not to mention this.④The present progressive can be used to denote an action in the immediate past and to make even politer requests with such verbs as hope, wonder.e.g.You don’t believe it? You know I’m telling the truth.I’m wondering if I may have a word with you.3)progressive verb vs. non-progressive verbs 延续性动词和非延续性动词的用法和语法意义The present progressive is commonly associated with durative dynamic verbs such as work, play, study, live, write, etc. which are progressive verbs. Those momentary verbs, denoting very short duration, such as shoot, jump, nod, put, etc. and stative verbs such as think, know, belong, believe, like, etc., are non-progressive verbs.e.g.Peter shoots and —yes, it’s a goal. The crowd are cheering and the other players arerunning up to congratulate him.Unit 101)The passive voice; 被动语态If the agent is important (the person, company or thing that does the action) , use “by”. If it is not definite and does not carry any essential information, it can be omitted.※Only verbs that take an object can be used in the passive voice.e. g. Houses are built.My bike was stolen.2)subordination 引导状语从句的连词的用法和语法意义Subordination (abbreviated variously SUBORD, SBRD, SUBR or SR) is a complex syntactic construction in which one or more clauses are dependent on the main clause. Dependent clauses are also called “subordinate clauses”.Subordinate clauses are introduced by a subordinating conjunction, such as, after, although, as much as, as long as, as soon as, because, before, if, in order that, lest, since, so that, than, that, though, unless, until, when, whenever, where, wherever, whether, and while, etc.e.g. I don't know if George is awake yet.George overslept because his alarm clock was broken.Unit 111)reported speech; 间接引语的表述方法Note:● Backshift of Simple Present is optional if the situation is still unchanged or if you agree with the original speaker.● Advisory expressions with must, should and ought are usually reported using advise / urge.● The expression let’s is usually reported using suggest. In this case, there are variouspossibilities for reported speech: gerund or statement with should.2)subject-verb agreement 主谓一致的用法Most likely, your verb will agree with the first noun to the left of the verb.e.g. The Supreme Court judge decides the appropriate penalty.Occasionally, a sentence has the subject after the verb instead of before it. This strategy is often used for poetic effect.e. g. Over the ripples glides a small canoe.If subjects are joined by or or nor, the verb should agree with the closer subject.e. g. Either the actors or the director is at fault.The relative pronouns (who, whom, which, and that) are either singular or plural, depending on the words they refer to.e. g. The sales manager is a good researcher who spends a great amount of time surfingthe Web for information.Indefinite pronouns(someone, somebody, each, either one, everyone, or anyone) are considered singular and need singular verbs although they may convey plural meaning.e. g. Anyone who wants to pursue higher education has to pass entrance exams.A few nouns can be either plural or singular, depending on whether they mean a group or separate individuals. These words are rarely used as plurals in modern writing.e. g. The jury is sequestered.A few subjects look plural but are really singular or vice versa.e. g. The news of the discovery is spreading.The mass media have publicized the facts.Unit 121)the relative clause; 关系从句的形式及语法意义A relative clause is a clause that is introduced by a relative word—either by a relative pronoun or by a relative determiner, or by a relative adverb. Relative clauses may be restrictive or non-restrictive. antecedenta) The relative that is normally used as subject complement in an SVC construction or there beconstruction. In this use, "that" is usually omitted.e.g. When Mary was born, Dorothy decided her daughter would be the singer (that) shealways wanted to be.The 9.15 is the fastest train (that) there has ever been.b) When the antecedent is an indefinite pronoun such as all, anything, something, or nothing,the following relative clause usually requires a relative that as subject, and that/zero asobject.e.g. All that live must die.All (that) I want is peace and quiet.c) When the antecedent is composed of a personal head with determiners as only, all, any, andwhen the antecedent takes a premodifier in the superlative degree,the following relative clause is normally introduced by that rather than who or which.e.g. Any man that wants to succeed must work hard.Newton was one of the greatest men that ever lived.d) A non-restrictive relative clause is usually introduced by who, whom, whose, which. Theantecedent of which may be a clause or part of a cause.e.g. This book, which only appeared a year ago, has already gone through several editions.He tried to stand on his hands for five minutes, which — as you know — is rather a difficult thing to do.2)the present and the future 现在时和将来时的不同形式即语法意义Future time is expressed by means of model auxiliaries, by semi-auxiliaries, or by the simple present and present progressive forms.1) will/shall +verbe.g. The next train to Shanghai will leave at 8 a.m.We shall know the result next week.2) be going to +verbe.g.He’s going to be a doctor, when he grows up.3) be +-ing (present participle): Verbs of movement from one place to another such as go, come, leave, start, arrive, etc. can be used in this structure.e.g. The plane is taking off at 6.30.4) be to +(infinitive)e.g.I’m to have tea with Betty this afternoon.5) simple presente.g. I’ll give it to you after I return..Unit 131)the infinitive and the –ing participle as object; 现在分词和不定式作为宾语的用法a)Verbs that are followed by –ing participle include: admit, fancy, delay, miss, involve, postpone,finish, imagine, avoid, deny, risk, practise, consider, enjoy, etc.b)Verbs that are followed by the infinitive include: decide, hope, pretend, deserve, promise,attempt, offer, agree, plan, aim, afford, manage, threaten, refuse, learn, fail, etc.c)Either infinitive or –ing participle without change of meaningVerbs that can take either an infinitive or an –ing participle as object include attempt, begin, can’t bear, continue, deserve, dread, hate, intend, like, loathe, love, need, neglect, omit, plan, prefer, require, start, etc. Following these words, an infinitive or an –ing participle can alternate without change in basic meaning.There are cases, however, where the transforms are not in free variation.i) After process verbs such as begin, cease, continue, start and emotive verbs such as can’tbear, deserve, dread, hate, intend, like, loathe, love, need, neglect, omit, plan, prefer, require, the infinitive is commonly used to refer to a specific act while the –ing participle is used to refer to a general act.e.g. I can’t bear living alone.I can’t bear to see the child so badly treated.Phil prefers doing it that way.He prefers to go by train this evening.ii) After need, want, require, deserve, an active -ing participle can be used to denote a passive meaning which can also be expressed by a passive infinitive.e.g. This letter needs signing by the manager.= This letter needs to be signed by the manager.The house wants rewiring.= The house wants to be rewired.iii) After begin and start, either infinitive or –ing form is possible, but when the infinitive is a stative verb, or when begin/start is in the progressive, we use the infinitive form.e.g. We began to see what he meant.It’s beginning to rain.d) Either infinitive or –ing participle with different meaningsThe verbs such as forget, go on, leave off, mean, regret, remember, stop, etc. that can take an infinitive or an –ing participle with different meanings fall into five sub-classes:i) After remember, forget and regret, the infinitive refers to the next action that follows the first, and the –ing participle to a previous event.e.g. Can’t you remember telling me the story last night?= You told me the story last night. Can’t you remember it?You must remember to tell him all that.= You must tell him all that. Don’t forget it.ii) After s top, leave off, go on, the –ing participle functions as object, while the infinitive as adverbial of purpose.e.g. They stopped watching TV at 9:30.= At 9:30 they did not watch TV any more.He left off writing the book.= He stopped writing the book.He left off to write the book.He left some place in order to write the book.iii) After try, mean, can’t help, the choice between an infinitive and an–ing participle depends on the meaning of the preceding verb itself.e.g. Your plan would mean spending hours.I didn’t mean to make you angry.iv) After agree, decide,there is a choice between the infinitive and “preposition + -ing”.e.g. They agreed to share the remuneration.They agreed on sharing the remuneration.v) After encourage, permit, allow, recommend, advise, authorise, either the –ing participle or the infinitive with an expressed logical subject can be used. Allow doing/allow sb to doe.g.She doesn’t allow smoking here.She doesn’t allow us to smoke here.2)the non-finite forms as adverbial and noun phrase modifier; 非限定性形式做名词短语、副词短语修饰语The non-finite forms include the –ing clause and the infinitive clause. An –ing participle clause usually refers to an active and/or progressive event, an –ed participle clause refers to an passive and/or experienced event while an infinitive clause suggests an event to be experienced. They can be used as adverbial or as noun phrase modifier.e.g. She looked at us with a smiling face.To determine the number of cells, a sample is put under a microscope.Unit 141)need; need的用法Need can be a lexical verb as well as a modal auxiliary. As a lexical verb, it is followed by a to-infinitive. As a modal auxiliary, it is non-assertive, which means it is usually used in negative sentences or questions. Note that in answer to a question introduced by need, we should use must in a positive response and needn’t in a negative response.e.g. Do we need to stay this evening?Need we work late today?No, we needn’t, but we must tomorrow.When inquiring about the necessity of doing something, either must or need can be used. If the answer is negative, we can only use needn’t or don’t have to rather than mustn’t.e.g. Need/must I see a doctor at once?No, you needn’t / don’t have to for the time being.“Needn’t have +-ed” implies that somet hing was done but was unnecessary.e.g.I needn’t have gone to the station.2)the non-finite form as noun phrase modifiers 名词性短语修饰语的用法及其语法意义The –ing form of most intransitive verbs of English can be used attributively as adjectives to indicate what someone or something is doing. –ed adjectives may refer to a person’s mental or emotional reaction to something or describe the expression or manner of the person affected. Most –ed adjectives are related to transitive verbs and have a passive meaning. A few –ed adjectives are related to the intransitive verbs and have an active meaning.e.g. Most people like fresh food and don’t like frozen food.Some people say it is an interesting book while others say that it is a boring one.《综合教程》(修订版)第二册would v.s. used to; used to v.s. be used to“Would do” refers to past actions and habits as well. Remember that “would” is also used in a conditional sense. It’s a good idea not to use “would” in questions and negative sentences, as its meaning can easily be misunderstood in a conditional sense.e. g. We’d spend a lot of money on projects that didn’t help the company.They would ask a lot of crazy questions that didn’t seem to make any sense.“Used to do” expresses something that we often did in the past, but don’t do anymore. It isoften used in the positive form to speak about repeated actions. Generally, we use the form to contrast past habits with present situations.e. g. I used to go jogging three times a week when I lived in Italy. Now, I’m too busy and canonly jog once a week.Janice used to live in New York, but moved to Seattle last year.“Be used to (doing) sth.” means someone has experienced something so that it no longer seems surprising, difficult or strange. It is always followed by a noun or gerund.e. g.Sally is used to spending hours in front of the computer every day.They’ve always lived in hot countries so they aren’t used to the cold weather here.would, should, might, couldWould can be used in some forms that are viewed as more formal or polite. It can also be used to express willingness.e. g.Would you get me a glass of water?I told him not to go, but he would not listen.Should is used to indicate that an action is considered by the speaker to be obligatory. It is used to form the future tense of the subjunctive mood, usually in the first person.e. g.You should brush your teeth every day.If I should be late, go without me.Might can be used to express a present time possibility or uncertainty. It can be used in the first person to express that future actions are being considered. It can be used in a question to ask for permission.e. g.John is not in the office today, and he might be sick.I might go to the mall later.Might your phone?Like could and would, might can also be used in polite requests and suggestions.The auxiliaries could, would and might can be used to express differing degrees of politeness.Thus, might expresses the highest degree of politeness.Could is used to express ability. It is also used to express beliefs about situations.Could can be used to make requests.e. g. I could speak English.He couldn’t have left already; why would he want to get there so early?Could you pass me the cheese?didn’t need to do / needn’t have doneBoth these patterns are used to talk about past events.“Needn’t have done something”。