初中英语语法 句子的种类
- 格式:doc
- 大小:24.36 KB
- 文档页数:12

五中基本句型一、主语+不及物动词(Subject+Intransitive Verb)例如:They are running.剖析:在此句中,谓语动词是不及物动词,不必加宾语就可表达一个完整的、明确无误的意思。
有时为了表示动作发生的频率、原因、结果、目的、场所、时间等,可以带状语修饰动词,但状语不算句子的主要成分。
The students are playing under the tree.常见的不及物动词有:come, go, listen, wait, climb, move, jump, laugh, sit, stay等。
二、主语+及物动词+宾语(Subject+Transitive Verb+Object)例如:We read English every morning.My sister likes bread.I finished reading the book.常见的及物动词有:like, finish, enjoy, want, play, make, help, take, read, tell, teach, do等。
三、主语+连系动词+表语(Subject+Link Verb+Predicative)例如:They are English teachers.The days get longer.剖析:此类句型的谓语动词是连系动词,它本身有一定的涵义,但不能独立作谓语,它必须和表语一起构成谓语。
表语通常由名词、形容词或相当于名词或形容词的词或短语充当,说明主语是什么或怎么样。
My book is on the desk.The trees turn green in spring.常见的连系动词有:be动词, 感官动词feel(感觉), look(看起来), 以及表示变化的动词get(变得), turn(变成), become(成为), go(变成)等。
四、主语+及物动词+间接宾语+直接宾语(Subject+Verb +Indirect Object +Direct Object)例如:He told me a story yesterday.Could you pass me the salt?间接宾语有时也可以改成一个由to或for引起的短语,放在直接宾语之后,即构成“主语+及物动词+直接宾语+介词+间接宾语”的句式。

初中英语语法——句子成分一、句子成分精讲句子成分:主语、谓语、宾语、表语、定语、状语、补语等。
主要成分:主语与谓语1、主语一个句子中需要加以说明或描述得对象。
主语得位置:一般位于句首,由名词、代词、数词或相当于名词得词、短语等充当。
The schoolis far from here、名词做主语She goesto schoolby bike、代词做主语Eightis alucky number。
数词做主语Theblindneedmore help。
名词化得形容词做主语There isapen on the desk、名词做主语Predicting the futureis interesting。
动名词做主语Tobe a doctor is my dream、不定式短语做主语2、谓语表示人或事物(主语)得动作与存在得状态.英语中由动词be、动词have与行为动词来充当谓语动词句子得时态与语态就是通过谓语表现出来。
谓语动词往往由一个或一个以上得助动词或情态动词加上主要动词构成。
分析句子得主语与谓语Mr。
Li teaches English、Hecan play the piano。
My parentsandIare having dinner.3、表语用来说明主语得身份、特征、性质、状态、表语得位置用在动词be与系动词得后面。
名词、代词、数词、介词短语、副词等都可以与连系动词一起构成复合谓语。
Your pen ison thedesk。
He gotvery angry.My dream istohave a robot、常见得系动词1。
be动词2、与感觉有关得动词look, sound, smell,taste, feel 等3。
表示状态变化得动词,意为“变得" “变成” 如get,grow, turn等上述两类词作连系动词时要用形容词作表语,千万不能用副词、4、宾语就是动作得对象或承受者、及物动词必须跟宾语。

初中英语语法基础句子结构与类型专题讲解一.句子的种类(一)根据结构划分:①简单句:(5种基本句型)S+Vi(主+谓)S+V系动词+ P (主+系+表)S+Vt+O(主+谓+宾)S+Vt+IO+DO(主+谓+间宾+直宾)S+Vt+O+OC(主+谓+宾+宾补)②并列句and, but, or, soThis is me and these are my friends.They must stay in water, or they will die.It’s not cheap, but it is very good.It was late, so I went to bed.③复合句:包含一个主句和一个或几个从句的句子叫复合句,从句由引导词或连词引导。
名词性从句(宾语,主语,表语,同位语)从句形容词性从句(定语从句)副词性从句(状语从句)(二)根据功能划分:陈述句, 祈使句, 感叹句,疑问句(一般疑问句,特殊疑问句,选择疑问句,反意疑问句等)1)陈述句:说明一个事实或陈述一种看法。
例如:Light travels faster than sound.光比声传播速度快。
(说明事实)The film is rather boring.这部电影很乏味。
(说明看法)2)疑问句:提出问题。
有以下四种:a. 一般疑问句:Can you finish the work in time?b. 特殊疑问句:Where do you live?c. 选择疑问句:Do you want tea or coffee?d. 反意疑问句:He doesn't know her, does he?3)祈使句:提出请求,建议或发出命令。
Don't be nervous!Let’s go fishing tomorrow.4)感叹句:表示说话人惊奇、喜悦、愤怒等情绪。
What good news it is ! How beautiful the girl is !二.简单句的基本句型介绍:1. 基本句型一:S+Vi (主+不及物动词)主语:可以作主语的成分有名词,主格代词,动词不定式,动名词等等。

初中英语语法句子的种类英语是国际通用语言,掌握良好的英语语法对于初中学生来说至关重要。
在学习英语语法时,了解并掌握不同种类的句子结构和用法是必不可少的。
本文将介绍初中英语语法中常见句子的种类,并对其结构和用法进行详细解析。
一、陈述句(Declarative Sentence)陈述句是最常见的句子类型,用于陈述事实、描述情况等。
陈述句一般由主语和谓语构成,常见的谓语动词有实义动词和系动词。
例如:1. My brother likes playing basketball.(我的弟弟喜欢打篮球。
)2. The cat is black.(这只猫是黑色的。
)二、疑问句(Interrogative Sentence)疑问句用于询问问题,一般以动词开头。
根据回答方式,疑问句可分为一般疑问句和特殊疑问句。
1. 一般疑问句(Yes/No Questions):一般疑问句的回答通常是“Yes”或“No”。
构成方式:助动词(或者是be动词)+主语+谓语动词(去掉助动词)+其他?例如: Are you happy?(你开心吗?)Does he like swimming?(他喜欢游泳吗?)2. 特殊疑问句(WH-Questions):特殊疑问句通常以疑问词(如what, where, when, why, how等)开头,回答需要提供具体信息。
例如:What is your name?(你叫什么名字?)Where does she live?(她住在哪儿?)三、祈使句(Imperative Sentence)祈使句用于表达请求、命令或建议等,一般省略主语。
常用动词原形构成祈使句,例如:1. Sit down, please.(请坐。
)2. Don't be late for class.(上课不要迟到。
)四、感叹句(Exclamatory Sentence)感叹句用于表达强烈的感情或情绪。
常常以感叹词(如how, what 等)开头。
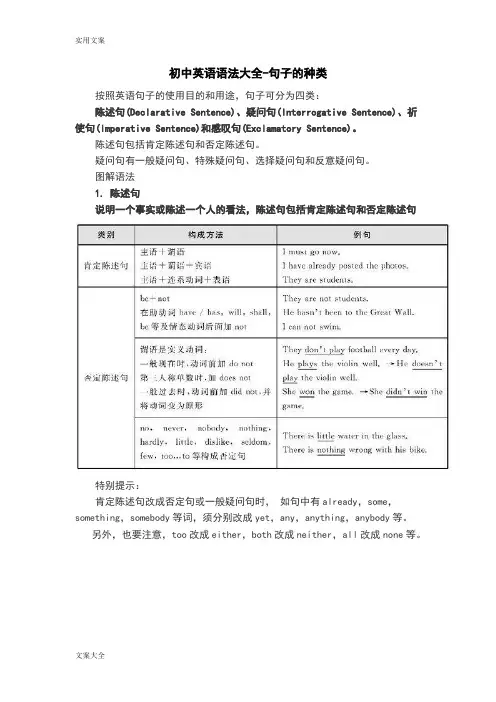
初中英语语法大全-句子的种类按照英语句子的使用目的和用途,句子可分为四类:陈述句(Declarative Sentence)、疑问句(Interrogative Sentence)、祈使句(Imperative Sentence)和感叹句(Exclamatory Sentence)。
陈述句包括肯定陈述句和否定陈述句。
疑问句有一般疑问句、特殊疑问句、选择疑问句和反意疑问句。
图解语法1. 陈述句说明一个事实或陈述一个人的看法,陈述句包括肯定陈述句和否定陈述句特别提示:肯定陈述句改成否定句或一般疑问句时,如句中有already,some,something,somebody等词,须分别改成yet,any,anything,anybody等。
另外,也要注意,too改成either,both改成neither,all改成none等。
2. 疑问句3. 常用的特殊疑问句4. 特殊的反意疑问句①主句是祈使句时,“will you?”意为“请求”,“won’t you?”表示提醒对方注意。
例句:Look at the blackboard, will you / won’t you?Don’t be late again, will you?②感叹句后的反意疑问,用一般现在时态的否定形式例句:What fine weather, isn’t it?How beautifully she sings, doesn’t she?③陈述部分是“I am …”时,用“aren’t I?”而不用“am not I?”例句:I'm working now, aren’t I?④陈述部分主语是everything,nothing,anything或something 时,疑问句主语用it例句:Something is wrong with my radio, isn’t it?Nothing is difficult, is it?⑤陈述部分的主语是somebody, nobody, everybody, anybody, no one,none, neither 时,疑问句的主语用they例句:Everyone is here, aren’t they?No one knows about it, do they?⑥陈述部分的主语是:1) this或that时,问句的主语用it2) these或those时,问句主语用they3) there be句时,反意疑问句中用there例句:This is a plane, isn’t it?These are grapes, aren’t they?There was a hospital here, wasn’t there?⑦陈述部分的主语是one时,问句的主语可用one,也可用you (美语用he)例句:One should be ready to help others, shouldn’t one?⑧陈述句中有few, seldom, never hardly,not,rarely,no,nobody,too…to等时,疑问句部分用肯定结构;如由前后缀构成否定词,疑问句部分仍用否定结构例句:He is never late for school, is he?You got nothing from him, did you?It is useless, isn’t it?⑨陈述部分主语是从句、不定式(短语)、动词-ing形式时,疑问句的主语用it例句:What you need is more important, isn’t it?⑩陈述部分由think, believe, suppose, imagine等引导的宾语从句:1) 主语是第一人称时,问句与从句的主谓语一致2) 主语是其他人称,问句与主句的主谓语一致例句:I think he will come, won’t he?I don’t think he can pass the exam, can he?He believed you had seen her before, didn’t he?? have是实义动词时,疑问句用助动词do,does,did;have 是助动词,则不然例如:They had a meeting just now, didn’t they?She’s been to many places of interest, hasn’t she?? 陈述部分有have /has /had to 时,疑问句要用助动词的否定形式例句:You have to water the vegetables now, don’t you?? 陈述部分有had better时,疑问句中用hadn’t刘局:We had better go to school at once, hadn’t we?? 陈述部分有must:1) 作“一定;必须”解释时,疑问句用mustn’t或needn’t;2) 表示推测,作“一定是;必定”解释时,疑问句需根据其后的动词原形选用相应的形式;3) 对过去动作推测时,问句的助动词用did或have;4) 对过去的状态推测时,问句的be用was例句:He must work hard at physics, mustn’t he?You must go to Guangzhou, needn’t you?You mustn’t smoke here, must you?Tom must be at home, isn’t he?She must have finished her work, hasn’t/didn’t she?He must have been a policeman, wasn’t he?? 陈述部分有ought to,used to,疑问句要用 shouldn’t,usedn’t / didn’t例句:Jill used to be a teacher, usedn’t / didn’t she?? 陈述句部分是复合句时,疑问句的主语和助动词要与主句一致例句:He was reading when the teacher came in, wasn’t he?特别提示:反意疑问句是“否定陈述句+肯定问句”时,如回答内容是肯定的,用“Yes+肯定结构”,反之,用“No+否定结构”。
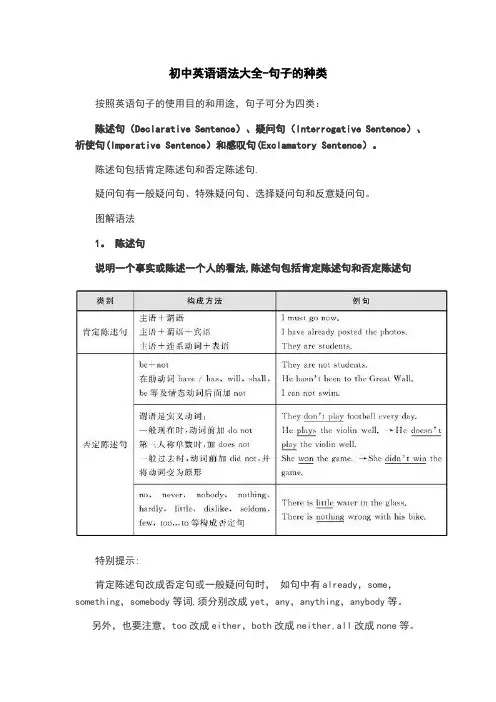
初中英语语法大全-句子的种类按照英语句子的使用目的和用途,句子可分为四类:陈述句(Declarative Sentence)、疑问句(Interrogative Sentence)、祈使句(Imperative Sentence)和感叹句(Exclamatory Sentence)。
陈述句包括肯定陈述句和否定陈述句.疑问句有一般疑问句、特殊疑问句、选择疑问句和反意疑问句。
图解语法1。
陈述句说明一个事实或陈述一个人的看法,陈述句包括肯定陈述句和否定陈述句特别提示:肯定陈述句改成否定句或一般疑问句时,如句中有already,some,something,somebody等词,须分别改成yet,any,anything,anybody等。
另外,也要注意,too改成either,both改成neither,all改成none等。
2. 疑问句3. 常用的特殊疑问句4. 特殊的反意疑问句①主句是祈使句时,“will you?"意为“请求",“won't you?”表示提醒对方注意。
例句:Look at the blackboard, will you / won’t you?Don’t be late again, will you?②感叹句后的反意疑问,用一般现在时态的否定形式例句:What fine weather, isn’t it?How beautifully she sings, doesn’t she?③陈述部分是“I am …”时,用“aren’t I?"而不用“am not I?”例句:I'm working now, aren’t I?④陈述部分主语是everything,nothing,anything或something 时,疑问句主语用it例句:Something is wrong with my radio, isn’t it?Nothing is difficult, is it?⑤陈述部分的主语是somebody, nobody, everybody, anybody, no one, none, neither 时,疑问句的主语用they例句:Everyone is here, aren't they?No one knows about it, do they?⑥陈述部分的主语是:1) this或that时,问句的主语用it2) these或those时,问句主语用they3) there be句时,反意疑问句中用there例句:This is a plane, isn’t it?These are grapes, aren’t they?There was a hospital here, wasn’t there?⑦陈述部分的主语是one时,问句的主语可用one,也可用you (美语用he)例句:One should be ready to help others, shouldn't one?⑧陈述句中有few, seldom, never hardly,not,rarely,no,nobody,too…to等时,疑问句部分用肯定结构;如由前后缀构成否定词,疑问句部分仍用否定结构例句:He is never late for school, is he?You got nothing from him, did you?It is useless, isn’t it?⑨陈述部分主语是从句、不定式(短语)、动词-ing形式时,疑问句的主语用it例句:What you need is more important, isn’t it?⑩陈述部分由think, believe, suppose, imagine等引导的宾语从句:1) 主语是第一人称时,问句与从句的主谓语一致2) 主语是其他人称,问句与主句的主谓语一致例句:I think he will come, won’t he?I don’t think he can pass the exam, can he?He believed you had seen her before, didn’t he?? have是实义动词时,疑问句用助动词do,does,did;have 是助动词,则不然例如:They had a meeting just now, didn’t they?She’s been to many places of interest, hasn't she??陈述部分有have /has /had to 时,疑问句要用助动词的否定形式例句:You have to water the vegetables now, don’t you?? 陈述部分有had better时,疑问句中用hadn’t刘局:We had better go to school at once, hadn’t we?? 陈述部分有must:1) 作“一定;必须”解释时,疑问句用mustn’t或needn’t;2) 表示推测,作“一定是;必定"解释时,疑问句需根据其后的动词原形选用相应的形式;3) 对过去动作推测时,问句的助动词用did或have;4) 对过去的状态推测时,问句的be用was例句:He must work hard at physics, mustn’t he?You must go to Guangzhou, needn’t you?You mustn’t smoke here, must you?Tom must be at home, isn’t he?She must have finished her work, hasn’t/didn’t she?He must have been a policeman, wasn’t he??陈述部分有ought to,used to,疑问句要用 shouldn’t,usedn’t / didn’t例句:Jill used to be a teacher, usedn’t / didn’t she??陈述句部分是复合句时,疑问句的主语和助动词要与主句一致例句:He was reading when the teacher came in, wasn't he?特别提示:反意疑问句是“否定陈述句+肯定问句”时,如回答内容是肯定的,用“Yes+肯定结构”,反之,用“No+否定结构”。

初中英语语法大全——句子成分、句子种类和结构一.句子成分1. 句子成分概述组成句子的各个部分即句子成分。
句子成分包括:主语、谓语、表语、宾语、定语、状语和补足语等。
主语和谓语是句子的必需部分。
宾语、表语和补足语是句子的必要部分。
其他成分,如定语和状语,是句子的辅助部分。
(1) 必需部分→主语和谓语句子必须有主语和谓语。
有些句子只含有主语和谓语。
eg: Birds sing. Birds+sing. 鸟儿在歌唱。
eg:The sun was shining=The sun + was shining. 太阳照耀着。
(2) 必要部分→宾语、表语和补足语有些谓语后面必须接宾语或者补足语才能构成完整的句子。
eg: I like(什么?)= I like music. 我喜欢音乐。
eg:The boy hit (什么?)=The boy hit the cat. 那个男孩打了那只猫。
(3) 辅助部分→修饰语句子不只是由主语、谓语、宾语、补足语等成分构成,还包括各种修饰语,来构成各种长句或意思丰富的句子。
eg: He became a writer(什么时候?) → He became a writer last year. 他去年成为了一位作家。
eg: There is a swimming pool(哪里?) →There is a swimming pool in the small town. 小镇上有个游泳池。
2. 主语主语是句中动作、行为、性质或状态的主体,是一个句子谈论的主题。
主语可以由名词、代词数词、不定式动名词(短语)、从句等来担任。
eg: A horse runs much faster than a cow.马比牛跑得快很多。
eg: We wish him success.我们祝愿他成功。
(3)谓语谓语用来说明主语的行为动作或所处的状态态。
谓语由动词充当,一般放在主语的后面。
谓语的中心词有人称、数和时态的变化。

【初中英语】初中英语语法关于句子种类的总结
【—语法关于句子种类的总结】下文是老师为大家带来的对句子种类的总结,涉及到各个句子的学习,供同学们参考。
(一)根据使用目的,它可以分为陈述句、疑问句、祈使句和感叹句。
1)陈述句(declarativesentences):说明一个事实或陈述一种看法。
光速比音速慢。
光比声音传播得快。
(陈述事实)
thefilmisratherboring. 这部电影很乏味。
(说明看法)
2)疑问句:提问。
有四种类型:
a. 一般疑问句(general
初中地理
questions):
你能按时完成工作吗?
你能按时完成工作吗?
b、特殊问题(WQ问题;HQ问题):
wheredoyoulive? 你住那儿?
你怎么知道的?你怎么知道的?
c. 选择疑问句(alternativequestions):
你想买咖啡吗?
你是要茶还是要咖啡?
d、附加问题:
hedoesn'tknowher,doeshe?
他不认识她,是吗?
3)祈使句(imperativesentences):提出请求,建议或发出命令,例如:请坐。
请坐。
don'tbenervous! 别紧张!
4)感叹句:表达说话者的惊讶、喜悦、愤怒和其他情绪,例如:
whatgoodnewsitis! 多好的消息啊!
(二)句子按结构可分为以下三类:
1)简单句(simplesentences):只包含一个主谓结构句子叫简单句,例如:她收集邮票。
她喜欢集邮。
(主) (谓)。

句子的基本结构句子的基本成分句子的基本成分有以下几种:主语、谓语、宾语、表语、定语、状语、补语、同位语。
1、主语:句子的主体,全句述说的对象。
一般由名词、代词、不定式、动名词或从句担当,位于句首。
The boy needs a pen. Smoking is bad for you = To smoke is bad for you2、谓语:说明主语的动作或状态。
由动词或系动词加表语担任,常置于主语后。
The train leaves at 6 o’clock.She is reading.3、宾语:表示动作的对象。
一般由名词或代词担当,常置于谓语后。
He won the game. He likes playing computer.4、表语:用以表述主语的特征、状态、身份等。
一般由名词或形容词担任,置于系动词或be动词之后。
He is a student. We are tired.注意:除了be 系动词外,还有一些动词也可以用作系动词,1)表感官的动词: feel, smell, taste, sound, look, appear, seem 等。
2)表转变变化的动词: become, get, grow, turn, go等。
3)表延续的动词: remain, keep, hold, stay, rest等。
5、定语:对名词或代词起修饰、限定作用的词、短语或句子。
The black bike is mine.(形容词)The boy in blue is Jim.(介词短语)I have nothing to do today.(动词不定式)注意:1) 当定语修饰不定代词如:nothing , anything , everything , something等时,定语要放在其后作后置定语。
例如:I tell him something interesting.2) 不定式、短语或从句作定语时,也放在被修饰的名词之后。


初中英语五种基本句型一.句子是由主语、谓语动词、表语、宾语、宾语补足语等组成的,依其组合方式可分为五种基本句型,句子成分的表示法S:Subject(主语)V:Verb(动词)O:Object(宾语)P:Predicative(表语)OC:Object Complement(宾语补足语)二.五种基本句型种类句型主语谓语部分第1种S+V We work.(不及物)第2种S+V+O He plays(及物) the piano第3种S+V+P We are(系动词) students第4种S+V+ ino (间接宾语) +DO(直接宾语) She gave(及物) me a pen第5种S+V+O+OC He made(及物) the boy laugh第1种句型:主语+不及物动词:S+V Birds fly.鸟飞.主语谓语(不及物动词) 地点状语He runs in the park.他在公园里跑.此句型是“主语+不及物动词”构成句子的主体部分。
因为是不及物动词,后面当然不能带宾语了,但是可以有状语来修饰。
例如上面例句中的in the park,是地点状语。
Class begins.(begin在句中是不及物动词)开始上课。
比较we begin Our class at eight. 我们八点钟开始上课。
该句属于第2种句型,begin在句中是及物动词,由此可见有些动词既可作及物动词也可以作不及物动词。
只能当不及物动词的词sleep 睡觉walk 步行swim 游泳happen(take place)发生go去come来work 工作laugh 笑stay呆在…… arrive 到达第2种句型:主语+及物动词+宾语:S+V+OMy father read the book.我父亲读过那本书.主语谓语 (及物动词) 宾语有些不及物动词后面加上介词就可把它看成一个及物动词,后面就可以加宾语了。
You must listen to me. 你必须听我的。
初中英语语法--句子的种类英语中的句子可以按其作用或者按其语法结构(即句子的形式)两种标准分类。
下面是具体的分类依据和结果。
1)按其作用或使用目的,句子可分为:陈述句:This is a truck. 这是一辆卡车。
疑问句:Is this a truck? 这是卡车吗?祈使句:Drive the truck away. 把卡车开走。
感叹句:What a big truck it is! 多么大的卡车!2)按语法结构,句子可分为:简单句:I am busy. 我很忙。
并列句:I am busy washing, but he is playing Majiang with them.我在忙着洗衣服,但他却在跟他们打麻将牌。
复合句:Although I am busy washing, he is playing Majiang with them.尽管我在忙着洗衣服,他却在与他们一块打麻将牌。
一、陈述句:用于说明一件事,表示一种看法或表达某种心情的句子,都是陈述句。
陈述句分为肯定陈述句和否定陈述句。
1肯定句He is a middle school teacher. 他是一位中学老师。
(一般现在时)She is cleaning the room. 她正在收拾屋子。
(现在进行时)They have visited the museum. 他们已经参观过这所博物馆了。
(现在完成时)He did a lot of washing yesterday. 他昨天洗了好多衣服。
(一般过去时)They had already finished quarrelling when I came. 我来时他们已经争吵完了。
(过去完成时) The meeting will begin at once. 会议马上就要开始了。
(一般将来时)2否定句(1)使用not否定:He isn't a worker. 他不是个工人。
初中英语语法句子的种类英语是一门广泛使用的语言,在初中阶段,学生学习英语语法是非常重要的。
了解不同种类的句子结构和语法规则,可以帮助学生更好地理解和运用英语。
本文将介绍初中英语中常见的句子种类。
1. 简单句简单句是由一个主语和一个谓语构成的句子。
主语通常是一个名词或代词,而谓语则是一个动词或者动词短语。
例如:- I study English every day.- He is a good student.2. 并列句并列句由两个或多个简单句组成,它们通过连词(如and、but、or)相连。
两个并列句的结构和语法相似。
例如:- I like playing basketball, and my sister likes playing tennis.- He is not only smart but also hardworking.3. 复合句复合句由一个主句和一个或多个从句组成。
从句可以作为主句的一部分,承担名词、形容词或副词的功能。
从句通常由连词(如because、when、although)引导。
例如:- I like the movie, which was released last week.- He went to bed early because he was tired.4. 条件句条件句是由一个条件从句和一个主句构成的句子。
条件从句通常由if引导,表示某种条件或假设。
例如:- If it rains, we will stay at home.- She will be late unless she hurries up.5. 疑问句疑问句是用来提问的句子。
一般疑问句以助动词或be动词开头,也可以以疑问词开头。
例如:- Do you like pizza?- Where is the library?6. 感叹句感叹句用于表示惊讶、赞美、喜悦等情感。
感叹句通常以“What”或“How”开头。
初中英语语法大全-句子的种类按照英语句子的使用目的和用途,句子可分为四类:陈述句(Declarative Sentence)、疑问句(Interrogative Sentence)、祈使句(Imperative Sentence)和感叹句(Exclamatory Sentence)。
陈述句包括肯定陈述句和否定陈述句。
疑问句有一般疑问句、特殊疑问句、选择疑问句和反意疑问句。
图解语法1. 陈述句说明一个事实或陈述一个人的看法,陈述句包括肯定陈述句和否定陈述句特别提示:肯定陈述句改成否定句或一般疑问句时,如句中有already,some,something,somebody等词,须分别改成yet,any,anything,anybody 等。
另外,也要注意,too改成either,both改成neither,all改成none等。
2. 疑问句3. 常用的特殊疑问句4. 特殊的反意疑问句①主句是祈使句时,“will you?”意为“请求”,“won’t you?”表示提醒对方注意。
例句:Look at the blackboard, will you / won’t you?Don’t be late again, will you?②感叹句后的反意疑问,用一般现在时态的否定形式例句:What fine weather, isn’t it?How beautifully she sings, doesn’t she?③陈述部分是“I am …”时,用“aren’t I?”而不用“am not I?”例句:I'm working now, aren’t I?④陈述部分主语是everything,nothing,anything或something 时,疑问句主语用it例句:Something is wrong with my radio, isn’t it?Nothing is difficult, is it?⑤陈述部分的主语是somebody,nobody,everybody,anybody,no one,none,neither 时,疑问句的主语用they例句:Everyone is here,aren’t they?No one knows about it,do they?⑥陈述部分的主语是:1) this或that时,问句的主语用it2) these或those时,问句主语用they3) there be句时,反意疑问句中用there例句:This is a plane, isn’t it?These are grapes, aren’t they?There was a hospital here, wasn’t there?⑦陈述部分的主语是one时,问句的主语可用one,也可用you (美语用he)例句:One should be ready to help others, shouldn’t one?⑧陈述句中有few,seldom,never hardly,not,rarely,no,nobody,too…to等时,疑问句部分用肯定结构;如由前后缀构成否定词,疑问句部分仍用否定结构例句:He is never late for school, is he?You got nothing from him, did you?It is useless, isn’t it?⑨陈述部分主语是从句、不定式(短语)、动词-ing形式时,疑问句的主语用it例句:What you need is more important,isn’t it?⑩陈述部分由think,believe,suppose,imagine等引导的宾语从句:1) 主语是第一人称时,问句与从句的主谓语一致2) 主语是其他人称,问句与主句的主谓语一致例句:I think he will come, won’t he?I don’t think he can pass the exam, can he?He believed you had seen her before, didn’t he?? have是实义动词时,疑问句用助动词do,does,did;have 是助动词,则不然例如:They had a meeting just now, didn’t they?She’s been to many places of interest, hasn’t she?? 陈述部分有have /has /had to 时,疑问句要用助动词的否定形式例句:You have to water the vegetables now, don’t you?? 陈述部分有had better时,疑问句中用hadn’t刘局:We had better go to school at once, hadn’t we?? 陈述部分有must:1) 作“一定;必须”解释时,疑问句用mustn’t或needn’t;2) 表示推测,作“一定是;必定”解释时,疑问句需根据其后的动词原形选用相应的形式;3) 对过去动作推测时,问句的助动词用did或have;4) 对过去的状态推测时,问句的be用was例句:He must work hard at physics, mustn’t he?You must go to Guangzhou, needn’t you?You mustn’t smoke here, must you?Tom must be at home, isn’t he?She must have finished her work, hasn’t/didn’t she?He must have been a policeman, wasn’t he?? 陈述部分有ought to,used to,疑问句要用shouldn’t,usedn’t / didn’t例句:Jill used to be a teacher, usedn’t / didn’t she?? 陈述句部分是复合句时,疑问句的主语和助动词要与主句一致例句:He was reading when the teacher came in, wasn’t he?特别提示:反意疑问句是“否定陈述句+肯定问句”时,如回答内容是肯定的,用“Yes+肯定结构”,反之,用“No+否定结构”。
初中英语语法大全句子种类集团标准化工作小组 [Q8QX9QT-X8QQB8Q8-NQ8QJ8-M8QMN]初中英语语法大全-句子的种类按照英语句子的使用目的和用途,句子可分为四类:陈述句(Declarative Sentence)、疑问句(Interrogative Sentence)、祈使句(Imperative Sentence)和感叹句(Exclamatory Sentence)。
陈述句包括肯定陈述句和否定陈述句。
疑问句有一般疑问句、特殊疑问句、选择疑问句和反意疑问句。
图解语法1. 陈述句说明一个事实或陈述一个人的看法,陈述句包括肯定陈述句和否定陈述句特别提示:肯定陈述句改成否定句或一般疑问句时,如句中有already,some,something,somebody等词,须分别改成yet,any,anything,anybody等。
另外,也要注意,too改成either,both改成neither,all改成none 等。
2. 疑问句3. 常用的特殊疑问句4. 特殊的反意疑问句①主句是祈使句时,“will you”意为“请求”,“won’t you”表示提醒对方注意。
例句:Look at the blackboard, will you / won’t youDon’t be late again, will you②感叹句后的反意疑问,用一般现在时态的否定形式例句:What fine weather, isn’t itHow beautifully she sings, doesn’t she③陈述部分是“I am …”时,用“aren’t I”而不用“am not I”例句:I'm working now, aren’t I④陈述部分主语是everything,nothing,anything或something 时,疑问句主语用it例句:Something is wrong with my radio, isn’t itNothing is difficult, is it⑤陈述部分的主语是somebody, nobody, everybody, anybody, no one, none, neither 时,疑问句的主语用they例句:Everyone is here, aren’t theyNo one knows about it, do they⑥陈述部分的主语是:1) this或that时,问句的主语用it2) these或those时,问句主语用they3) there be句时,反意疑问句中用there例句:This is a plane, isn’t itThese are grapes, aren’t theyThere was a hospital here, wasn’t there⑦陈述部分的主语是one时,问句的主语可用one,也可用you (美语用he)例句:One should be ready to help others, shouldn’t one⑧陈述句中有few, seldom, never hardly,not,rarely,no,nobody,too…to等时,疑问句部分用肯定结构;如由前后缀构成否定词,疑问句部分仍用否定结构例句:He is never late for school, is heYou got nothing from him, did youIt is useless, isn’t it⑨陈述部分主语是从句、不定式(短语)、动词-ing形式时,疑问句的主语用it例句:What you need is more important, isn’t it⑩陈述部分由think, believe, suppose, imagine等引导的宾语从句:1) 主语是第一人称时,问句与从句的主谓语一致2) 主语是其他人称,问句与主句的主谓语一致例句:I think he will come, won’t heI don’t think he can pass the exam, can heHe believed you had seen her before, didn’t hehave是实义动词时,疑问句用助动词do,does,did;have 是助动词,则不然例如:They had a meeting just now, didn’t theyShe’s been to many places of interest, hasn’t she陈述部分有have /has /had to 时,疑问句要用助动词的否定形式例句:You have to water the vegetables now, don’t you陈述部分有had better时,疑问句中用hadn’t刘局:We had better go to school at once, hadn’t we陈述部分有must:1) 作“一定;必须”解释时,疑问句用mustn’t或needn’t;2) 表示推测,作“一定是;必定”解释时,疑问句需根据其后的动词原形选用相应的形式;3) 对过去动作推测时,问句的助动词用did或have;4) 对过去的状态推测时,问句的be用was例句:He must work hard at physics, mustn’t heYou must go to Guangzhou, needn’t youYou mustn’t smoke here, must youTom must be at home, isn’t heShe must have finished her work, hasn’t/didn’t sheHe must have been a policeman, wasn’t he陈述部分有ought to,used to,疑问句要用 shouldn’t,usedn’t / didn’t例句:Jill used to be a teacher, usedn’t / didn’t she陈述句部分是复合句时,疑问句的主语和助动词要与主句一致例句:He was reading when the teacher came in, wasn’t he特别提示:反意疑问句是“否定陈述句+肯定问句”时,如回答内容是肯定的,用“Yes+肯定结构”,反之,用“No+否定结构”。
初中英语语法------句子的种类A英语中的句子按其使用目的,句子可分为:陈述句、疑问句、祈使句、和感叹句。
Eg:陈述句:This is a dog.疑问句:Is this a dog?祈使句:Open your eyes!感叹句:What a beautiful building it is!简单句:I am studying.并列句:I was born in a small village and I lived there for nearly ten years.复合句:As soon as I get there, I'll call you.1 陈述句凡是说明一件事情,提出一个看法,或者是表达一种心情的句子都是陈述句。
大多数的句子都是陈述句,陈述句可以用肯定式和否定式。
陈述句句末用句号“.”,通常用降调。
Eg:We live in Beijing.We don't live in Beijing.(1) be 动词、一般动词(实义动词)、情态动词的否定句I am not a student. I don't know him.He can't speak English.be 动词的否定句句型:主语+ be动词+ not + …I wasn't good at English.They weren't at home yesterday.He isn't my cousin.进行时和被动语态都有be 动词,它们的否定句与be动词的否定句同形。
Eg:They aren't cleaning the room.The child was not looked after by anybody.将来时(will,shall)、完成时及情态动词的被动语态不能用be动词否定句型。
They will not be sent to the front.They will be not sent to the front.×情态动词的否定句句型:主语+情态动词+ not + 动词原形Eg:I can't do it myself.You mustn't take the books out.You must not go there alone.一般动词的否定句.句型:主语+ do/does/did + not + 动词原形Eg:They didn't live in Shanghai.He doesn't do his homework every day.They didn't have the class-meeting yesterday afternoon.现在完成时的否定句句型:主语+ have/has+ not + 动词的过去分词+……I haven't finished reading the book yet.He hasn't had his breakfast yet.过去完成时的否定句句型:主语+ had+ not + 动词的过去分词+……He hadn't finished reading the book by the end of last month.(2).否定结构应注意事项使用not 的部分否定含有not的句子,如果使用了very, always以及不定代词all, both, every 及every的复合词,则表示部分否定。
Eg:I don't play football very well. It isn't always hot here in summer.not的其他否定表示1. not…at all 一点也不…I'm not tired at all. I don't like it at all.2. not…any more, not…any longer 再也不…I don't live here any longer. = I no long live here.I can not eat any more. = I can eat no more.使用not 以外的否定词表示否定1.用no表示:no+名词= not any…一点也不…There is no wind. = There is not any wind. 2. never 绝不I will never forget you. He has never been abroad.3. few / little 几乎没有He has few friends.Few people understand the difference. I have little money.There is little water in the glass. 4. no one = nobody 无人No one knows the answer.= Nobody knows the answer. 什么也没有5.nothing = not anythingI have nothing to do today.没有任何人;什么也没有6. none of …None of them can answer it.I eat none of the food.的句子含有否定副词seldom /hardly7.He can hardly write his name. . We seldom watch TV .) 的句型表示否定太…以至于不…( too…to…He is too old to work.不定代词的肯定和否定形式否定否定肯定肯定not any, no none, no some allnot anything, nothing no one something everyone, eachfew nothing a few everythinglittle a little Each, both, either neither, not either2 祈使句表示请求、命令。
建议等。
句子没有时态变化,谓语动词一律用原形。
句子中通常不用主语,句末用感叹号或者句号,用降调。
1.含有第二人称主语的祈使句Be careful!Don't make such a noise.肯定的祈使句型动词原形+ …+(省略主语)Stand up.Be quiet, please.1.有时,为了加强语气,可以在动词之前加do. Do sit down.Do study hard.2.用客气的语气表示祈使句时,可在句首或句尾加上please,但如果在句尾加please时,那在please之前一定要加一个逗号“,”。
Go this way, please.3.祈使句中如果有唤语,一定要用逗号“,”隔开,放在句首或句尾。
Li Ming, come here.Come here, Li Ming.否定的祈使句句型Don't +动词原形+…Don't swim in the river. Don't be late.Please don't be noisy.句型转换之祈使句和陈述句的改写…= You must祈使句.Come here. = You must come here.t do that again. 'Don't do that again. = You mustn? …Please + 祈使句= Will you (please)Please help me. = Will you (please) me ? 2 含有第一、第三人称主语的祈使句s say goodbye here. Let't let him do that again.Don' 肯定的祈使句…(me, us)+动词原形+ 句型let+第一人称动词原形+…)或名词let+第三人称代词(him/her/it/them+let me try again. s go at once.Let'Let Tom go there himself.否定的祈使句+…'Lets + not + 动词原形+…'t let + 第三人称代词的宾格或名词+动词原形Dons not say anything about it. Let't let them play with fire. 'Don 句型转换Use your head and you will find a way. If you use your head, you will find a way.感叹句3引导,一表示喜怒哀乐等强烈感情时用感叹句。
感叹句分为两种:一种以what 引导。
句尾用感叹号,通常用降调。
种以howWhat a clever boy he is.How clever the boy is. 引导的感叹句1 what陈述句(主语+谓语)+名词(或形容词+名词)what + 句型What a beautiful city it is!What a fine day!What an honest man he is!What big apples these are! What a tall boy Tom is!What fools they are! 2 how 引导的感叹句句型How+形容词或副词+陈述句(主语+谓语)!How hot it is today!How high the kite is flying! How beautiful the girl is!How fast he runs!How I want to be a teacher!How well she can skate! How busy you are!感叹句:How busy are you? 疑问句:引导的感叹句3 if only 引导的感叹句通常表示一种强烈的愿望,特别是表示对一些不能实现only 用if的或没有实现的愿望的遗憾感。
/were 一般过去时主语+ 句型if only +If only I knew her telephone number! If only he were here!句型if only +主语+ could / would + have +过去分词If only we could have gone to the party!4 其他形式的感叹句感叹句除用what和how引导外,还有许多其他形式,如可用陈述句,疑问句,祈使句等,有时甚至一个单词或一个短语也可构成感叹句。