(管理学)management9
- 格式:ppt
- 大小:502.50 KB
- 文档页数:31

管理学第9版练习题附答案Chapter 6 Decision Making: The Essence of the Manager’s JobTRUE/FALSE QUESTIONSTHE DECISION-MAKING PROCESS1.Problem identification is purely objective.2.The second step in the decision-making process is identifying a problem.3. A decision criterion defines what is relevant in a decision.4.The fourth step of the decision-making process requires the decision maker tolist viable alternatives that could resolve the problem.5.Once the alternatives have been identified, a decision maker must analyze eachone.6.The step in the decision-making process that involves choosing a best alternativeis termed implementation.THE MANAGER AS DECISION MAKER7.Making decisions is with the essence of management.8.Managerial decision making is assumed to be rational.9.One assumption of rationality is that we cannot know all of the alternatives.10.Managers tend to operate under assumptions of bounded rationality.11.Studies of the events leading up to the Challenger space shuttle disaster pointto an escalation of commitment by decision makers.12. Managers regularly use their intuition in decision making.13.Rational analysis and intuitive decision making are complementary.14.Programmed decisions tend to be repetitive and routine.15.Rules and policies are basically the same.16.A policy is an explicit statement that tells a manager what he or she ought orought not to do.17.The solution to nonprogrammed decision making relies on procedures, rules, andpolicies.18.Most managerial decisions in the real world are fully nonprogrammed.19.The ideal situation for making decisions is low risk.20.Risk is the condition in which the decision maker is able to estimate thelikelihood of certain outcomes.21.Risk is a situation in which a decision maker has neither certainty norreasonable probability estimates.22.People who have a low tolerance for ambiguity and are rational in their way ofthinking are said to have a directive style.23.Decision makers with an analytic style have a much lower tolerance for ambiguitythan do directive types.24.Individuals with a conceptual style tend to be very broad in their outlook andwill look at many alternatives.25. Behavioral-style decision makers work well with others.26.Most managers have characteristics of analytic decisionmakers.27.According to the boxed feature, “Managing Workforce Diversity,” diverseemployees tend to make decisions faster than a homogeneous group of employees.28.The anchoring effect describes when decision makers fixate on initial informationas a starting point and then, once set, they fail to adequately adjust for subsequent information.29.The availability bias describes when decision makers try to create meaning out ofrandom events.30. The sunk cost error is when decision makers forget that current choices cannotcorrect the past.DECISION MAKING FOR T ODAY’S WORLD31.Today’s business world revolves around making decisions, usually with completeor adequate information, and under minimal time pressure.32.Managers need to understand cultural differences to make effective decisions intoday’s fast-moving world.33.According to the boxed feature, “Focus on Leadership,” when identifyingproblems, managers might be from a culture that is focused on problem solving, or their culture might be one of situation acceptance.34.According to the boxed feature, “Focus on Leadership,” findings from studies byGeert Hofstede and from GLOBE researchers show that inhigh uncertainty avoidance countries, decision making tends to be based more on intuition than on formal analysis.35.Highly reliable organizations (HROs) are easily tricked by their success.MULTIPLE-CHOICE QUESTIONSFor each of the following choose the answer that most completely answers the question.THE DECISION-MAKING PROCESS36.Decision making is typically described as ________________, which is a view thatis too simplistic.a.deciding what is correctb.putting preferences on paperc.choosing among alternativesd.processing information to completion37.A series of eight steps that begins with identifying a problem and concludes withevaluating the decision’s effectiveness i s the ________________.a.decision-making processb.managerial processc.maximin styled.bounded rationality approach38.________________ is the existence of a discrepancy between an existing and adesired state of affairs.a.An opportunityb. A solutionc. A weaknessd. A problem39.In identifying the problem, a manager _________________./doc/d417811801.html,pares the current state of affairs with where they would like to beb.expects problems to be defined by neon lightsc.looks for discrepancies that can be postponedd.will not act when there is pressure to make a decision40.Which of the following statements is true concerning problem identification?a.Problems are generally obvious.b. A symptom and a problem are basically the same.c.Well-trained managers generally agree on what is considered a problem.d.The problem must be such that it exerts some type of pressure on the managerto act.41. What is the second step in the decision-making process?a.identifying decision criteriab.allocating weights to the criteriac.analyzing alternativesd.identifying a problem42.To determine the _____________, a manager must determine what is relevant orimportant to resolving the problem.a.geocentric behavior neededb.number of allowable alternativesc.weighting of decision criteriad.decision criteria43.What is the third step in the decision-making process?a.allocating weights to the criteriab.analyzing the alternativesd.implementing the alternative44.If all criteria in the decision making are equal, weighting the criteria______________.a.improves decision making when large numbers of criteria are involvedb.is not neededc.produces excellent decisionsd.improves the criteria45.In allocating weights to the decision criteria, which of the following is helpfulto remember?a.All weights must be the same.b.The total of the weights should sum to .c.Every factor criterion considered, regardless of its importance, must receivesome weighting.d.Assign the most important criterion a score, and then assign weights againstthat standard.46.What is the step where a decision maker wants to be creative in coming up withpossible alternative?a.allocating weights to the criteriab.analyzing alternativesc.developing alternativesd.identifying decision criteria47. When analyzing alternatives, what becomes evident?a.the strengths and weaknesses of each alternativec.the list of alternativesd.the problem48.When developing alternatives in the decision-making process, what must a managerdo?a.list alternativesb.evaluate alternativesc.weight alternativesd.implement alternatives49.Selecting an alternative in the decision-making process is accomplished by__________________.a.choosing the alternative with the highest scoreb.choosing the one you like bestc.selecting the alternative that has the lowest priced.selecting the alternative that is the most reliable50.In Step 6 of the decision-making process, each alternative is evaluated byappraising it against the _____________.a.subjective goals of the decision makerb.criteriac.assessed valuesd.implementation strategy51.______________ includes conveying a decision to those affected and getting theircommitment to it.a.Selecting an alternativeb.Evaluating the decision effectivenessc.Implementing the alternativesd.Analyzing alternatives52.Which of the following is important in effectively implementing the chosenalternative in the decision-making process?a.getting upper-management supportb.double-checking your analysis for potential errorsc.allowing those impacted by the outcome to participate in the processd.ignoring criticism concerning your chosen alternative53. The final step in the decision-making process is to _______________.a.pick the criteria for the next decisionb.reevaluate the weightings of the criteria until they indicate the correctoutcomec.evaluate the outcome of the decisiond.reassign the ratings on the criteria to find different outcomes54.Which of the following is important to remember in evaluating the effectivenessof the decision-making process?a.You should ignore criticism concerning the decision-making process.b.You may have to start the whole decision process over.c.You will have to restart the decision-making process if the decision is lessthan 50 percent effective.d.Ninety percent of problems with decision making occur in the implementationstep.THE MANAGER AS DECISION MAKER55.Managers are assumed to be ______________; they make consistent, value-maximizingchoices within specified constraints.a.rationalb.leaders/doc/d417811801.html,anizedd.satisficers56.It is assumed that a perfectly rational decision maker ______________.a.does not follow rational assumptionsb.does not consider value maximizing as an objectivec.offers inconsistent decisionsd.would be objective and logical57.Managers can make rational decisions if _________________.a.the problem is ambiguousb.the goals are unclearc.the alternatives are limitedd.time constraints exist58. Which of the following is not a valid assumption about rationality?a.The problem is clear and unambiguous.b. A single, well-defined goal is to be achieved.c.Preferences are clear.d.Preferences are constantly changing.59.When managers circumvent the rational decision-making model and find ways tosatisfice, they are following the concept of _________________.a.jurisprudenceb.bounded rationalityc.least-squared exemptionsd.self-motivated decisions60.B ecause managers can’t possibly analyze all information on all alternatives,managers ______________, rather than ______________.a.maximize; satisficeb.maximize; minimizec.satisfice; minimized.satisfice; maximize61.The type of decision making in which the solution is considered “good enough”is known as _________________.a.intuitionb.satisfyingc.maximizingd.satisficing62.When a decision maker chooses an alternative under perfect rationality, she______________ her decision, whereas under bounded rationality she chooses a ______________ decision.a.minimizes; satisficingb.satisfices; maximizingc.maximizes; satisficingd.maximizes; minimizing63. An increased commitment to a previous decision despite evidence that it may havebeen wrong is referred to as _______________.a.economies of commitmentb.escalation of commitmentc.dimensional commitmentd.expansion of commitment64.Intuitive decision making is _______________.a.not utilized in organizationsb. a conscious process based on accumulated judgmentc.making decisions based on experience, feelings, and accumulated judgmentd.important in supporting escalation of commitment65.In studying intuitive decision making, researchers have found that__________________.a.managers do not make decisions based on feelings or emotionsb.managers use data from their subconscious mind to help make their decisionsc.rational thinking always works better than intuitived.accumulated experience does not support intuitive decisions66.All of the following are aspects of intuition except __________________.a.experienced-based decisionsb.affect-initiated decisionsc.cognitive-based decisionsd.programmed decisions67._____________ are straightforward, familiar, and easily defined.a.Unstructured problemsb.Structured problemsc.Unique problemsd.Nonprogrammed problems68.Structured problems align well with which type ofdecision making?a.programmedb.satisficingc.intuitiond.gut feeling69. ______________ decision making is relatively simple and tends to rely heavily onprevious solutions.a.Nonprogrammedb.Linearc.Satisficingd.Programmed70.A procedure _______________.a.is an explicit statement detailing exactly how to deal with a decisionb.is a series of interrelated sequential steps to respond to a structuredproblemc.is a set of guidelines that channel a manager’s thinking in dealing with aproblemd.allows a manager to use broad decision-making authority71.A ______________ is an explicit statement that tells a manager what he or she canor cannot do.a.procedureb.policyc.ruled.solution72.A policy ____________.a.typically contains an ambiguous termb.is used frequently when a manager faces a structured problemc.allows little discretion on the part of the managerd.offers strict rules as to how a problem should be solved73.What is a difference between a policy and a rule?a. A policy establishes parameters.b. A rule establishes parameters.c. A policy is more explicit.d. A rule is more ambiguous.74.A ______________ typically contains an ambiguous term that leaves interpretationup to the decision maker.a.systemb.rulec.solutiond.policy75.A business school’s statement that it “strives for productive relationshipswith local org anizations” is an example of a ________________.a.ruleb.policyc.procedure/doc/d417811801.html,mitment76.Unstructured problems _____________.a.are easily solvedb.present familiar circumstancesc.force managers to deal with incomplete or ambiguous informationd.are routine77.Nonprogrammed decisions are best described as ________________.a.recurring, but difficult to makeb.very similar to problems in other areas of the organizationc.requiring more aggressive action on the decision maker’s thought processesd.unique and nonrecurring78.When problems are ______________, managers must rely on ______________ in orderto develop unique solutions.a.structured; nonprogrammed decision makingb.structured; pure intuitionc.unstructured; nonprogrammed decision makingd.unstructured; programmed decision making79.Lower-level managers typically confront what type of decision making?a.uniqueb.nonroutinec.programmedd.nonprogrammed80.Which of the following is likely to make the most programmed decisions?a.the CEO of PepsiCo.b.the vice president of General Motors Cadillac Division.c.the head of the Minute Maid Division at Coca-Cola.d.the manager of the local McDonald’s.81.______________ is a situation in which a manager can make accurate decisionsbecause the outcome of every alternative is known.a.Certaintyb.Riskc.Uncertaintyd.Maximaxe.Maximin82.If an individual knows the price of three similar cars at different dealerships,he or she is operating under what type of decision-making condition?a.riskb.uncertaintyc.certaintyd.factual83.A retail clothing store manager who estimates how much to order for the currentspring season b ased on last spring’s outcomes is operating under what kind of decision-making condition?a.seasonalb.riskc.uncertaintyd.certainty84.______________ is a situation in which a decision maker has neither certainty norreasonable probability estimates available.a.Certaintyb.Riskc.Uncertaintyd.Maximax85.Nonprogrammed decisions are typically made under a condition of ________________.a.certaintyb.low levels of riskc.uncertaintyd.reliability86. A person at a horse racetrack who bets all of his or her money on the odds-basedlong shot to “win” (rather than “place” or “show”) is making what kind of choice?a.maximaxb.maximinc.minimaxd.minimin87.What best describes the psychological orientation of an individual making a“maximax” choice?a.optimistb.realistc.pessimistd.satisficer88.Optimistic managers could be expected to utilize their maximax orientation whenthey _______________.a.maximize the maximum payoffb.maximize the minimum payoffc.minimize the maximum regretd.minimize the minimum regret89.What is the psychological orientation of a decision maker who makes a “maximin”choice?a.optimistb.realistc.pessimistd.satisficer90.Which of the following best describes “maximizing the minimum possible payoff”?a.maximaxb.maximinc.minimaxd.minimin91.A manager who desires t o minimize his or her maximim “regret” will opt for a______________ choice.a.maximaxb.maximinc.minimaxd.minimin92. Decision makers using what decision-making style make fast decisions and focuson the short run?a.directiveb.behavioralc.analyticd.conceptual93.What types are characterized as careful decision makers with the ability to adaptor cope with unique situations?a.directive decision makersb.behavioral decision makersc.analytic decision makersd.conceptual decision makers94.Who are concerned about the achievements of thosearound them and are receptiveto suggestions from others?a.directive decision makersb.behavioral decision makersc.analytic decision makersd.conceptual decision makers95.Many managers use __________ or rules of thumb to simplify their decision making.a.heuristicsb.biasesc.errorsd.habits96.When decision makers tend to think they know more than they do or holdunrealistically positive views of themselves and their performance, they are exhibiting _______________.a.self-serving biasb.the anchoring effectc.immediate gratification biasd.overconfidence bias97.When decision makers seek out information that reaffirms their past choices anddiscount information that contradicts past judgments, they are exhibiting _______________.a.availability biasb.the anchoring effectc.self-serving biasd.confirmation bias98.When decision makers assess the likelihood of an event based on how closely itresembles other events or sets of events, they are using _______________.a.availability biasb.framing biasc.selective perception biasd.representation bias99.What is the tendency for decision makers to falsely believe that they would haveaccurately predicted the outcome of an event once that outcome is actually known?a.the hindsight biasb.the sunk costs errorc.the randomness biasd.the selective perception biasDECISION MAKING FOR TODAY’S WORLD100.According to the boxed feature, “Focus on Leadership,” when _______________, managers might come from a culture that gathers facts or from a culture that is more intuitive in gathering ideas and possibilities.a.developing alternativesb.implementing alternativesc.searching for informationd.identifying problems101.To make effective d ecisions in today’s fast-moving world, managers need to -_______________./doc/d417811801.html,e the five-stage decision-making processb.know when it is time to call it quitsc.ignore cultural differencesd.identify their style of decision making102.What is a characteristic that the experts say an effective decision-making process has?a.It is inconsistent.b.It acknowledges only objective thinking.c.It focuses on all factors—even those that do not seem important.d.It requires only as much information and analysis as is necessary.103. What term is used by Navy aviators to describe a gut feeling that something isn’t right?a.leemersb.the creepsc.uneasinessd.regret104.Managers of highly reliable organizations (HROs) get the input of _______________ and let them make decisions.a.CEOsb.frontline workersc.customersd.suppliers105.When highly reliable organizations (HROs) face complexity, they -_______________.a.try to simplify datab.aim for deeper understanding of the situationc.defer to the expertsd.act, then thinkSCENARIOS AND QUESTIONSFor each of the following choose the answer that most completely answers the question.THE DECISION-MAKING PROCESSDecisions, Decisions (Scenario)Sond ra needed help. Her insurance company’s rapid growth was necessitating making some changes, but what changes? Should they add to the existing information system or should they buy a new system? She was given the responsibility of analyzing the company’s pr esent information system and deciding what the company should do that would give them plenty of room. She was confused and needed help in making the correct decision.106.According to the decision-making process, the first step Sondra should take is to _____________.a.analyze alternative solutionsb.identify decision criteriac.evaluate her decision’s effectivenessd.identify the problem107. According to the decision-making process, the second step Sondra should take is to ____________.a.analyze alternative solutionsb.identify decision criteriac.evaluate her decision’s effectivenessd.allocate weights to the criteria108.Allocating weights to the criteria is the step in the decision-making process that occurs between identifying the decision criteria and ______________.a.developing the alternativesb.selecting alternativesc.implementing the alternatived.identifying the problem109.When Sondra is conveying her decision to those affected and getting their commitment to it, she is performing which stepin the decision-making process?a.analyzing alternative solutionsb.selecting alternativesc.implementing the alternatived.identifying the problem110.The very last step Sondra should take, according to the decision-making process, is to __________.a.analyze alternative solutionsb.select alternativesc.implement the alternatived.evaluate the decision’s effectivenessThe Car (Scenario)Colleen is a student, and her older brother has loaned her an old car. The car is in need of several repairs before she will feel comfortable driving it.111.Colleen needs a vehicle, but she has to decide if the vehicle is worth repairing. She is facing a(n) _____________, a discrepancy between an existing and a desired state of affairs.a.alternativeb.weighted problem setc.problemd.certainty avoidance situation112.In talking with an automotive repair person, Colleen needs to prioritize the repairs. Her first concern is safety of the vehicle. This step in the decision-making process is called __________________.a.weighting the decision criteriab.analyzing of alternativesc.identifying decision criteriad.selecting an alternativeTHE MANAGER AS DECISION MAKERThe Car (Scenario)Colleen is a student, and her older brother has loaned her an old car. The car is in need of several repairs before she will feel comfortable driving it.113.Colleen decides to have all of the problems fixed on the car. She assumes that the repair person has found all the problems and that there will be no problem correcting the imperfections within a specified budget. This is an example of a __________ decision.a.parochialb.irrationalc.ethicald.rational114.Colleen’s brother has a different view of the repairs. He assumes that the repair person is using the best information available, but there may be other unexpected repairs that might surface and that a higher budget might be more reasonable. He is using ______________.a.rational decision makingb.risk avoidancec.bounded rationalityd.Stage 4 decision making115.Colleen’s brother feels the car is worth repairing because he has owned several cars made by the same manufacturer as this car, and he has driven this car for several years. He is using _________ to determine that the car has value despite its need of repair.a.intuitive decision makingb.selective coordination of thought processesc.sunk costsd.return on investmentThe First Job (Scenario)Upon graduation, you search for a job with the university’s job placement center. Although you have studied and prepared to work in an advertising agency, the first job that you are offered is a supervisor in a manufacturing company working the afternoon shift from 3:00 . until 11:00 .116.If you had made a larger search using the Internet and other employment search processes, you might have been able to find more employment opportunities. This would have been a more _________ decision-making process.a.nonprogrammableb.uncertaind.perfectly rational117.Under bounded rationality, you would be expected to search for a job by ________________.a.looking at all the opportunities that can be analyzed in the time availableb.looking at all the opportunities availablec.looking “outside the box” in your searchd.analyzing all the opportunities until you find the perfect job118.If you use a shortened process of searching for a job, it is likely that you ___________ rather than maximized in your decision process.a.minimizedb.rationalizedc.satisficedd.agreed119.During your job search, you depend on __________ decision making by making your decision based on accumulated judgment and experience.a.experientialb.legalc.intuitived.formidableIs the Picture Clear? (Scenario)Sharon was the regional manager of a large cable television company. She faced many problems and decisions daily, such as how to price each market, who to hire, what kind of technology she should purchase, and how she should handle the increasing customer complaints. She needed some help sorting these issues out.120.When a customer calls and requests a refund for a partial month’s usage of cable, the fact that such situations are routine and most likely have a standard response would make the response a ______________ decision.a.standardb.routinec.policyd.programmed121.Sometimes Sharon follows a ______________, a series of interrelated sequential steps for responding to a structured problem.a.rulec.procedured.suggestion122.Sometimes Sharon instructs her local managers to follow ______________ when confronted with problem situations. Theseestablish parameters for the manager making the decision rather than specifically stating what should or should not be done.a.rulesb.proceduresc.policiesd.orders123.Unfortunately, Sharon also faces issues containing information that is ambiguous or incomplete, such as what kind of technology to purchase. These are known as ______________ problems.a.unstructuredb.variablec.randomd.hit-and-missManaging Your Career (Scenario)Michelle has a new job and is learning to perform the tasks assigned to her. Different situations demand different decision-making processes.124.Michelle finds a situation that instructs her in specific, interrelated, sequential steps to respond to a problem. This is referred to as a _____________.a.ruleb.policyc.broad guidelined.procedure125.Michelle finds a company directive that specifically restricts her from taking certain actions. This is a _____________.a.ruleb.policyc.broad guidelined.procedure。


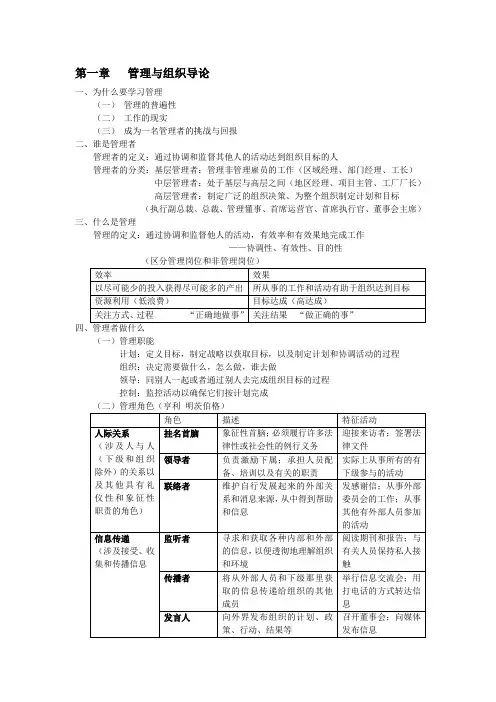
第一章管理与组织导论一、谁是管理者管理者是组织中这样的成员,他告诉别人该做什么以及怎么样去做。
管理者〔manager〕是这样的人,他们通过协调和监督其他人的活动到达组织目的。
管理者通常分为基层管理者、中层管理者和高层管理者。
二、什么是管理管理〔management〕通过协调和监督他人的活动,有效果和有效率地完成工作。
效率〔efficiency〕是指以尽可能少的投入获得尽可能多的产出。
效果通常指的是“正确地做事〞,即不浪费资源。
效果〔effectiveness〕通常指“做正确的事〞,即所从事的工作和活动有助于组织到达其目标。
在成功的组织中高效率和高效果是相辅相成的。
三、管理者做什么1、管理职能〔亨利.法尔约〕。
方案组织领导控制定义目标,制定战略,开发方案以协调活动决定需要做什么,怎么做,谁去做指导和鼓励所有群体和个人,解决冲突监控活动以确保它们按方案完成2、管理角色〔亨利.明茨伯格〕。
人际关系信息传递决策制定挂名首脑领导者联络者监听者传播者发言人企业家混乱驾驭者资源分配者谈判者3、管理技能〔罗伯特.卡茨〕。
技术技能:熟练完成特定工作所需要的特定领域的知识和技术。
人际技能:包括与单独的个人或群体中的其他成员和睦相处的能力。
概念技能:管理者对抽象、复杂情况进行思考和概念化的技能。
四、什么是组织组织〔organization〕是对人员的一种精心安排,以实现某些特定的目的。
组织的三个特征:明确的目的、人员、精细的结构。
现在的组织更倾向于依靠灵活的工作安排、雇员工作团队、开放的沟通系统和供给商联盟。
传统组织新型组织稳定的缺乏灵活性关注职位根据职位定义工作个人导向永久性职位命令导向由管理者作决策规那么导向相对均质的员工队伍工作日从上午8时到下午5时等级关系在上班时间利用组织设施从事工作动态的灵活的关注技能根据任务定义工作团队导向临时性职位参与导向雇员参与决策制定顾客导向多样化的员工队伍工作日长度没有限制横向的和网络化的关系在任何地点、任何时间工作第二章管理的昨天和今天一、管理的历史背景两个重大事件:776,亚当.斯密发表?国富论?主张组织和社会将从劳动分工或工作专业化中获得经济利益。

罗宾斯《管理学》第九版试题罗宾斯《管理学》第九版试题Chapter 10 – Organizational Structure and DesignTrue/False QuestionsA MANAGER’S DILEMMA1. According to the boxed feature, ―A Manager’s Dilemma,‖ Nokia was once involved in industries rangingfrom paper to chemicals and rubber.True (moderate)2. According to the boxed feature, ―A Manager’s Dilemma,‖ Nokia has been competing in thetelecommunications industry since 1965.False (moderate)DEFINING ORGANIZATIONAL STRUCTURE3. Organizational design is the organization's formal framework by which job tasks are divided, grouped, and coordinated.False (difficult)4. The concept of work specialization can be traced back a couple of centuries to Adam Smith's discussion ofdivision of labor.True (moderate)5. The degree to which tasks in an organization are divided into separate jobs is division of labor.True (moderate)6. Historically, many organizations have grouped work actions by function departmentalization.True (moderate)7. Grouping jobs on the basis of product or customer flow istermed customer departmentalization.False (moderate)8. Geographic departmentalization has greatly increased in importance as a result of today’s competitivebusiness environmentFalse (moderate)9. A group of individuals who are experts in various specialties and who work together is a cross-functional team.True (moderate)10. Authority is the individual's capacity to influence decisions.False (difficult)11. Authority is synonymous with responsibility.False (easy)12. Responsibility is the rights inherent in a managerial position.False (easy)13. A manager's span of control refers to the number of subordinates who can be effectively and efficientlysupervised.True (moderate)14. The classical view of unity of command suggests that subordinates should have only one superior to whom they report.True (easy)15. The trend in recent years has been toward smaller spans of control.False (easy)16. When decisions tend to be made at lower levels in anorganization, the organization is said to bedecentralized.True (moderate)17. Decentralization describes the degree to which decision making is concentrated at a single point in theorganization.False (moderate)18. In the last 35 years, there has been a trend of organizations moving toward increased decentralization.True (easy)19. Appropriate organizational structure depends on four variables: the organization's strategy, size, technology, and degree of environmental uncertainty.True (difficult)20. Standardization refers to the degree to which jobs within the organization are standardized and the extent towhich employee behavior is guided by rules and procedures.False (moderate)ORGANIZATIONAL DESIGN DECISIONS21. An organic organization tends to be characterized by high specialization, extensive departmentalization,narrow spans of control, high formalization, a limited information network, and little participation indecision-making by low-level employees.False (moderate)22. An organic organization would likely be very flexible.True (moderate)23. Innovators need the efficiency, stability, and tight controls of the mechanistic structure.False (easy)24. The relationship between organizational size and structure tends to be linear.False (difficult)25. Joan Woodward attempted to view organizational structure from a technological perspective.True (moderate)26. Woodward demonstrated that organizational structures adapted to their technology.True (moderate)27. Woodward's findings support that there is "one best way" to organize a manufacturing firm.False (moderate)28. The strength of the functional structure is that it focuses on results.False (moderate) it is the strength of divisional structure.\\\\\\\29. According to the text, a functional structure creates strategic business units.False (moderate)COMMON ORGANIZATIONAL DESIGNS30. Project structures tend to be rigid and inflexible organizational designs.False (easy)Multiple ChoiceA MANAGER’S DILEMMA31. Accordi ng to t he company profile in ―A Manager’s Dilemma,‖ the organizational structure of Nokia is best described as ______________.a. mechanisticb. organic (moderate)c. centralizedd. formalized32. The factor contributing the most to Nokia’s success in the mobile phone industry according to the company profile in ―A Manager’s Dilemma‖ is ______________.a. new product development (moderate)b. government subsidiesc. national trade barriersd. weak competition33. ______________ is the process of creating an organization's structure.a. Human resource managementb. Leadingc. Organizing (moderate)d. Planninge. DepartmentalizationDEFINING ORGANIZATIONAL STRUCTURE34. According to the text, a(n) ______________ is the formal framework by which job tasks are divided,grouped, and coordinated.a. mission statementb. environmental scanc. internal resource analysisd. organizational structure (moderate)35. Which of the following is not one of the six key elements in organizational design?a. work specializationb. departmentalizationc. chain of commandd. bureaucratic design (difficult)e. span of control36. Work specialization is also known as ______________.a. departmentalization.b. centralization.c. span of control.d. formalization.e. division of labor. (easy)37. The term ______________ is used to describe the degree to which tasks in an organization are divided intoseparate jobs.a. work ethicsb. managerial capitalismc. social responsibilityd. work specialization (moderate)38. When did the idea of enlarging, rather than narrowing, job scope begin?a. 1950sb. 1960s (moderate)c. 1970sd. 1980se. 1990s39. Which of the following is not an example of the classical viewof division of labor?a. assembly-line productionb. Burger Kingc. Taco Belld. TQM (moderate)e. Kentucky Fried Chicken40. ______________ is the basis on which jobs are grouped inorderto accomplish organizational goals.a. Departmentalization (moderate)b. Centralizationc. Formalizationd. Coordinatione. Efficiency41. A local manufacturing organization has groups of employees whoare responsible for sales, marketing,accounting, human resources, etc. These are examples of what concept?a. authorityb. chain of commandc. empowermentd. departmentalization (moderate)e. social grouping42. Grouping sporting equipment in one area, men's clothing in another area, and cosmetics in a third area, is anexample of what kind departmentalization?a. customerb. product (easy)c. geographicd. processe. outcome43. Sales responsibilities divided into the southwest, midwest, southern, northern, and western regions would bean example of ______________ departmentalization.a. productb. geographic (easy)c. processd. outcomee. customer44. Grouping activities on the basis of customer flow is______________.a. functional departmentalization.b. product departmentalization.c. geographical departmentalization.d. process departmentalization. (moderate)e. technological departmentalization.45. What type of departmentalization expects that each department will specialize in one specific phase of the process or product production?a. productb. geographicc. process (easy)d. outcomee. customer46. What kind of departmentalization would be in place in a government organization where different publicservice responsibilities are divided into activities for employers, children, and the disabled?a. productb. geographicc. processd. outcomee. customer (moderate)47. Which of the following is not a form of departmentalization suggested by your text?a. functional departmentalizationb. product departmentalizationc. geographical departmentalizationd. process departmentalizatione. technological departmentalization (difficult)48. Today's competitive business environment has greatly increasedthe importance of what type ofdepartmentalization?a. geographicb. customer (difficult)c. productd. processe. outcome49. According to the text, managers are using ______________, which are groups of individuals who areexperts in various specialties and who work together.a. specialized teamsb. cross-demanded teamsc. cross-functional teams (moderate)d. simple structured teams50. Which of the following is a contemporary addition to thehistorical view of departmentalization?a. increased rigidityb. cross-functional teams (moderate)c. enhanced centralizationd. elimination of product departmentalizatione. addition of sales departmentalization51. Bringing together the company's legal counsel, research engineer, and marketing specialist for a project isan example of a(n) ______________.a. empowered team.b. process departmentalization.c. product departmentalization.d. cross-functional team. (moderate)e. continuous improvement team.52. The ______________ is the continuous line of authority that extends from upper organizational levels to thelowest levels and clarifies who reports to whom.a. chain of demandb. chain of command (easy)c. demand hierarchyd. continuous design structure53. To whom a worker reports concerns which aspect of organizational structure?a. chain of command (moderate)b. departmentalizationc. pay structured. line of commande. authority framework54. ______________ entitles a manager to direct the work of a subordinate.a. Responsibilityb. Legitimate powerc. Rankd. Operating responsibilitye. Authority (moderate)55. ______________ is the obligation to perform assigned activities.a. Authorityb. Responsibility (easy)c. Chain of commandd. Unity of commande. Formalization56. The ______________ principle (one of Fayol’s 14 principles of management) helps preserve the concept ofa continuous line of authority.a. unity of demandb. unity of command (moderate)c. demand structured. continuous demand57. Span of control refers to which of the following concepts?a. how much power a manager has in the organizationb. the geographic dispersion of a manager's subunits ofresponsibilityc. how many subordinates a manager can effectively and efficiently supervise (moderate)d. the number of subordinates affected by a single managerial ordere. the amount of time it takes to pass information down through a manager's line of command58. Other things being equal, the wider or larger the span of control, the more ______________ theorganizational design.a. bureaucraticb. democraticc. effectived. efficient (difficult)e. classical59. Wider spans of control may be viewed as more efficient, but eventually, wider spans tend to have whateffect on organizations?a. reduced effectiveness (difficult)b. increased turnoverc. loss of managerial powerd. customer dissatisfactione. rigid chains of command60. An organization that spends money on maintaining a well-trained work force can expect which of thefollowing span-of-control outcomes?a. increased contempt for managementb. increased voluntary turnoverc. centralized authorityd. less direct supervision (moderate)e. increased need for managerial-level employees61. A high-tech manager who supervises the development of a new computer chip needs ______________compared to a manager who supervises the mailing of unemployment insurance checks at the localgovernment office.a. about the same span of controlb. a narrower span of control (difficult)c. a wider span of controld. a more informal span of controle. elimination of the span of control62. In general, span of control is ______________ for managers.a. increasing (easy)b. decreasingc. staying the samed. significantly decreasinge. no longer important63. ______________ describes the degree to which decision making is concentrated at a single point in theorganization.a. Decentralizationb. Centralization (moderate)c. Transnationalismd. Cross sectional analysis64. If lower-level employees provide input or are actually given the discretion to make decisions, theorganization is ______________.a. formalized.b. centralized.c. decentralized. (easy)d. mechanistic.e. organic.65. Recently, there has been a distinct trend toward ______________.a. smaller spans of control.b. decentralized decision-making. (moderate)c. decreased flexibility.d. emphasis on chain of command.e. mechanistic organizations.66. Which of the following factors WOULD NOT influence an organization to have a higher degree ofcentralization?a. Environment is stable.b. Company is geographically dispersed. (difficult)c. Company is large.d. Decisions are significant.e. Organization is facing a crisis.67. ______________ refers to the degree to which jobs within the organization are standardized and the extentto which employee behavior is guided by rules and procedures.a. Standardizationb. Centralizationc. Chain of commandd. Strategye. Formalization (moderate)68. All of the following factors indicate that a decentralized organization would be most effective EXCEPTwhen ______________.a. the environment is complex.b. decisions are relatively minor.c. the organization is facing a crisis. (difficult)d. the company is geographically dispersed.e. effective implementation of strategies depends on managers having involvement and flexibilityto make decisions.69. Which of the following factors describes an environment in whicha high degree of decentralization isdesired?a. Environment is complex, uncertain. (moderate)b. Lower-level managers do not want to have a say in decisions.c. Decisions are significant.d. Company is large.e. Organization is facing a crisis or the risk of company failure.70. The ______________ organizational structure is characterized by high specialization, extensivedepartmentalization, narrow spans of control and high formalization.a. mechanistic (easy)b. organicc. contingencyd. adhocracye. functional71. Which of the following is NOT a characteristic of a mechanistic organization?a. high specializationb. wide spans of control (moderate)c. high formalizationd. limited information networke. extensive departmentalization72. What type of organizational form follows classical principles such as unity of command?a. organicb. linearc. decentralizedd. mechanistic (moderate)e. adhocracyORGANIZATIONAL DESIGN DECISIONS73. Which of the following would likely be found in mechanistic organizations?a. wide span of controlb. empowered employeesc. decentralized responsibilityd. few rules and/or regulationse. standardized job specialties (difficult)74. All of the following are characteristics of an organic organization EXCEPT:a. narrow spans of control. (moderate)b. cross-hierarchical teams.c. free flow of information.d. low formalization.e. cross-functional teams.75. In the early years of Apple Computers, its desire for highly proficient and creative employees who operatedwith few work rules was an example of what type of organization?a. bureaucraticb. mechanisticc. volatiled. nouvellee. organic (difficult)。
第一章管理与组织导论一、为什么要学习管理(一)管理的普遍性(二)工作的现实(三)成为一名管理者的挑战与回报二、谁是管理者管理者的定义:通过协调和监督其他人的活动达到组织目标的人管理者的分类:基层管理者:管理非管理雇员的工作(区域经理、部门经理、工长)中层管理者:处于基层与高层之间(地区经理、项目主管、工厂厂长)高层管理者:制定广泛的组织决策、为整个组织制定计划和目标(执行副总裁、总裁、管理懂事、首席运营官、首席执行官、董事会主席)三、什么是管理管理的定义:通过协调和监督他人的活动,有效率和有效果地完成工作——协调性、有效性、目的性(一)管理职能计划:定义目标,制定战略以获取目标,以及制定计划和协调活动的过程组织:决定需要做什么,怎么做,谁去做领导:同别人一起或者通过别人去完成组织目标的过程控制:监控活动以确保它们按计划完成(二)管理角色(亨利明茨伯格)(三)管理技能(罗伯特卡茨)技术技能:熟练完成特定工作所需的特定领域的知识和技术人际技能:与单独的个人或群体中的其他成员和睦相处的能力概念技能:管理者对抽象、复杂情况进行思考和概念化的技能概念技能利用信息解决工作问题的能力识别创新的机会界定问题范围并实施解决方案从大量数据中筛选重要信息掌握技术上在商业的运用掌握组织运营模式沟通技能将构思表述为语言,转化为行动的能力同时、下属之间的信任倾听并提出问题表现技能:口头方式表现技能:书面或图示方式效果技能为企业使命或部门目标做出贡献关注顾客多任务:同时进行多项工作谈判技能项目管理检查工作并实施改进设定和维持内外的行为准则赋予受关注的事物和特殊活动优先权时间管理人际技能指导技能多样化技能:在不同的文化中与不同的人一起工作组织内部网络化组织外部网络化在团队中工作:合作与承诺(四)管理者工作是如何变化的(顾客、创新)(五)什么是组织组织:对人员的一种精心的安排,以实现某些特定的目的稳定的动态的第二章管理的昨天和今天一、管理的历史背景(一)亚当斯密《国富论》:主张组织和社会将从劳动分工或工作专业化中得到经济利益经济人观点(二)工业革命:机械力代替人力;大型组织需要正式化的管理——体现管理自然属性二、科学管理:应用科学方法确定从事工作的“最佳方式”→关注处于组织最低层次的管理(一)泰罗(科学管理之父)的四条管理原则1.对工人工作的每一个要素开发出一种科学方法,用以代替老的经验方法2.科学地挑选工人,并对他们进行培训、教育,使之成长3.与工人们衷心地合作,以保证一切工作都按已形成的科学原则去办4.管理当局与工人在工作和职责的划分上几乎是相等的,管理当局把自己比工人更胜任的各种工作都承揽下来缺陷:激励前提简单化,只考虑金钱是工作的唯一动机;将工人看作机器一部分;排除了高层管理者处理更广泛外部事务的机会(二)吉尔布雷斯夫妇的动作分类体系(使用照片来研究身体与四肢动作;显微定时器;归纳出17种手部基本动作的分类体系)(三)甘特与甘特图(奖励工资制、甘特图)三、一般行政管理理论:描述了管理者做什么以及什么构成了良好的管理实践→关注全部管理者的活动(一)法约尔的14条管理原则1 工作分工:专业化通过使雇员的工作更有效率,从而提高了工作的产出2 职权:管理者必须有命令下级的权力,职权赋予管理者的就是这种权力。

管理学第9版练习题附答案0001Chapter 3 Organizational Culture and Environment: The Constraints TRUE/FALSE QUESTIONSTHE MANAGER: OMNIPOTENT OR SYMBOLIC?1. In the symbolic view of management, managers are seen as directly responsible foran organization 's success or failure.2. The current dominant assumption in management theory suggests that managersare omnipotent.3. The view of managers as omnipotent is consistent with the stereotypical picture ofthe take-charge business executive who can overcome any obstacle in carrying out the org anization 's objectives.4. The symbolic view of management impact is useful in explaining the high turnoveramong college and professional sports coaches, who can be considered the“managers” of their teams.5. In the omnipotent view of management, much of an organization 's success orfailure is due to forces outside management 's control.6. In the symbolic view of management, it is unreasonable to expect managers to havea significant effect on the organization 's performance.7. In the omnipotent view of management, a manager's role is to createmeaning out of randomness, confusion, and ambiguity.THE ORGANIZATIO'NS CULTURE8. An organizational culture refers to a system of shared meaning.9. Organizational cultures influence how employees behave in an organization./doc/292092685.html,anizational culture isa perception, not reality.11.Presently, there is no method for analyzing or assessing organizational culture.12.Str ong cultures have more in flue nee on employees tha n docultures.weak13.An increasing body of evidenee suggests that strong cultures associated withhigh orga ni zati onal performa nee.are/doc/292092685.html,pensation structures are considered to be a primary dimension oforga ni zati onal culture.15.Most orga ni zatio ns have very weakcultures.16. An orga ni zatio n ' s foun der has little in flue neeonits culture.17.Rituals are repetitive sequences of activities rein forcethe key values of an orga ni zati on.that express and/doc/292092685.html,a ni zati onal stories typically containsig nifica nt eve nts or people. narrativeregarding19.Employee stock options are one example of mightreprese nt orga ni zati onal culture.material symbol that20.The link betwee n values and man agerialstraightforward.behavior is fairly CURRENT ORGANIZATIONAL CULTURE ISSUES FACING MANAGERS21.A strong ethical culture is likely to have a powerful positivein flue nee on employee behavior.22丄ow risk tolera nee gen erally leads to high ethical sta ndards within an orga ni zati on.23. C ompanies that allow their employees freedom tend to encourage inno vativecultures.24. To encourage a customer-responsiveculture, organizations should formalize and enforce strict customer service policies.25. C ustomer service employees tend to provide better customer service whe n they arevery clear about their employee roles.26. To in crease customer resp on sive ness, orga ni zati ons should hireemployees who are outgo ing and frie ndly.THE ENVIRONMENT27. The part of the environment directly related to achievement of an organization ' sgoals is the specific environment.28. The general environment refers to environmental factors operatingin side an orga ni zati on.29. E nvir onmen tal un certa inty can be divided into two dime nsions: degreeof trust and degree of in tegrati on.30. Because certainty is a threat to an organization ' s effectiveness,managers try to minimize it.31. The term suppliers in cludes providers of finan cial and labor in puts.32. Industry conditions are an example of an organization ' s generalen vir onment.33. Economic conditions are part of the organization ' s specificen vir onment.MULTIPLE-CHOICE QUESTIONSFor each of the followi ng choose the an swer that most completely an swers the questi on.THE MANAGER: OMNIPOTENT OR SYMBOLIC?34. Which of the followi ng represe nt the two views of man agerial impacton the success or failure of the orga ni zati on?a. omnipotent and symbolicb. omnipotent and reflectivec. symbolic and in teractived. reflective and in teractive35. The omn ipote nt view of man ageme nt states that____________ .a. the top manager is the only person in chargeb. managers are directly responsible for an organization ' s successor failurec. that there is only one boss in the organization, and she or he is resp on sible fordelegati ng ordersd. managers have little or no responsibility for an organization ' ssuccess or failure 36. ______________ The view of management is ________________ consistent with thestereotypical picture of the take-charge bus in ess executive who can overcome any obstacle in carrying out the organization ' s objectives. a. omnipotent b. symbolic c. functional d. systems most accurately reflects the symbolic responsible for an organization ' s success or no responsibility for an organization ' s directly responsible for an organization ' s d. Employees are directly responsible for an organizati or failure. 38. Internal constraints that restrict a manage r s decisionoptionsa. exist within every organizationb. do not exist, as all managers have decision-making discretionc. exist only to the extent that upper management imposes themd. exist only to the extent that followers won ' t do as they are told39. The current dominant assumption inmanagement theory suggestsa. a balaneed view of managers as symbolic and omnipotentb. an emphasis on the view that managers are symbolicc. an emphasis on the view that managers are omnipotentd.that both the symbolic and omnipotent views are obsolete 4O.According to the symbolic view, managers have a(n) ________________effect on substa ntive orga ni zati onal outcomes.37.Which of the followingview of man ageme nt?a. Managers are directlyor failure.b. Managers have littlesuccess or failure.c. External forces aresuccess or failure.on ' s successa. neutralb. controllingc. limitedd. unlimited41. Managers may be able to expand their areas of discretion bya. telling their employees what to dob. cha nging and in flue ncing their orga ni zati on ' s cultureand en vir onmentc. electing new government officials at the federal and state leveld. changing employers and working for a different boss42. The symbolic view of man ageme nt is based upon thebelief thatman agers symbolize ________ .a. con trol and in flue neeb. ambiguity and confusionc. stakeholders ' interestsd. decisions of top management43.ln reality, man agers are most accurately viewed as ________ .a. dominant over an organization ' s environmentb. neither helpless nor all powerfulc. powerless to in flue nee an orga ni zati on ' s performa need. ultimately responsible for organizational outcomesTHE ORGANIZATION S CULTURE44. ____________________________________________________ The culture of an orga ni zati on is an alogous to the ___________________________ of an in dividual.a. skillsb. personalityc. motivationd. ability45. AII orga ni zati onal cultures con sist of each of the followi ng excepta. shared valuesb. principlesc. innovationd. traditions46.0rganizational culture is concerned with how members perceivethe orga ni zati on, not whether they _________ .a. like the organizationb. like their peersc. like their bossesd. like their customers47.Stro ng cultures ____________ .a. are found in orga ni zatio ns with high employee tur no verb. have a mini mal in flue nee on employee decisi on makingc. can be found in all organizations that existd. have a greater in flue nee on employees tha n do weak cultures48. Employees in orga ni zati ons with strong cultures ____________ .a. are more committed to their organizationsb. are more likely to leave their organizationsc. are more willing to perform illegal activitiesd. are more likely to follow directives from peers49. Which of the following phrases is associated with the definition of orga ni zati onalculture?a. in dividual resp onseb. shared meaningc. diversity of thoughtd. explicit direct ions50. Which of the following is not considered to be a dimension oforga ni zati onal culture?a. attention to detailb. people orientationc. purchasing policiesd. aggressiveness51. Which of the follow ing dime nsions of orga ni zati onalculture isdefined as the degree to which an organization ' s actions and decisi ons emphasize maintaining the status quo?a. stabilityb. outcome orientationc. team orientationd. innovation and risk taking52. A company whose managers focus on results, rather than how results are achieved,most likely possesses a high degree of which of the follow ing?a. outcome orientationb. people orientationc. team orientationd. aggressiveness53. Sony Corporation ' s focus on product innovation is an example ofwhich of the follow ing dime nsions of orga ni zati onal culture?a. attention to detailb. people orientationc. outcome orientationd. aggressiveness54. Which of the followi ng most accurately reflects the differe nee betwee n strongcultures and weak cultures?a. Strong cultures tend to encourage employee innovation, while weak cultures donot.b. Weak cultures are found in most organizations, whereasstrongcultures are relatively rare.c. Strong cultures have less of an in flue nee on employee behaviortha n do weak cultures.d. Company values are more deeply held and widely shared in strong cultures than in weak cultures.55. Corporate ____________ are repetitive sequences of activitiesthat express and rein force the values of an orga ni zati on.a. Ianguagesb. ritualsc. symbolsd. ceremonies56. Which of the following represents the most significant waysthrough which corporate cultures are tran smitted to employees?a. rituals, myths, competitions, and Ianguageb. symbols, rituals, la nguage, and bus in ess systemsc. stories, rituals, symbols, and Ianguaged. Ianguage, stories, rituals, and rewards57. Whe n employees at Microsoft use terms such as work judo, eat ing your own dogfood, and flat food , they are using orga ni zati onala. Ianguagesb. ritualsc. symbolsd. ceremonies58. Most orga ni zatio ns have _________ cultures.a. very weakb. weak to moderatec. moderated. moderate to strong59. The original source of an organization ' s culture usuallya. is shared among the first workers hired into the organizationb. is formulated by the board of directors when the organization is formedc. identifies what the organization is successful doingd. reflects the vision or mission of the organization ' s founder/doc/292092685.html,anizational________________ typically contain narratives aboutsig nifica nt eve nts or people in the orga ni zati on.a. storiesb. ritualsc. chartsd. material symbols61. All of the following are mentioned in the textbook as examples of material symbolsexcept _________________________ .a. employee dress attireb. size of employee officesc. availability of stock optionsd. reserved parking spaces for certain employees62. The link betwee n orga ni zati onal values and man agerial behavior isa. usually uncertainb. fairly straightforwardc. often highly complexd. relatively dynamic63.ln learning an organization ' s specific Ianguage, members aredisplayi ng their ________________ .a. willi ngn ess to com muni cate with the orga ni zati on ' s stockholdersb. con fide nee that they will soon be promoted to greaterresp on sibilityc. willingness to help preserve the culture of the organizationd. consent to share material symbols with the other members of the orga ni zati on64. An organization ' s culture affects managers by ______________ .a. providing them with additional decision-making powerb. restricting them from disciplining certain employeesc. encouraging them to bend or even break company rulesd. establishing what is appropriate and expected behaviorCURRENT ORGANIZATIONAL CULTURE ISSUES FACING MANAGERS65. Which of the following is most likely to have a highly ethicalorga ni zati onal culture?a. a highly aggressive, competitive bus in essb. a company with high risk toleraneec. a bus in ess that focuses strictly on outcomesd. a bus in ess with outgo ing and frie ndly employees66. To en courage ethical cultures, man agers shoulda. enforce strict discipline policiesb. encourage employees to competec. act in their own self-interestd. serve as visible role models67. A company that primarily values a strong sense of purpose through meanin gfulwork has a(n) _________________________________________________ orga ni zati onal culture.a. spiritualb. customer-responsivec. ethicald. innovative68. Conscientious employees with good listening skills are highlyvaluable for building a(n) _________________________ organizationalculture.a. ethicalb. innovativec. customer-responsived. spiritual69. An innovative organizational culture is characterized by all ofthe followi ng characteristics except _________________.a. freedomb. conformityc. debatesd. risk taking70. Workplace spirituality has become importa nt in the con temporaryworkplace because it helps to _________________ .a. reduce unemployment ratesb. boost company profitsc. restore a sense of communityd. bring religio n into bus in ess71. Which of the followi ng is most characteristic of anorganization with a strong spiritual culture?a. Employees are encouraged to express themselves.b. Such companies experienee high employee turnover.c. Employees are rewarded for innovation and risk taking.d. Employees are required to join organized religions.72. Which of the followi ng best characterizes the relati on shipbetwee n spirituality and bus in ess profitability?a. Evide nee shows that spirituality and bus in ess profitability are in compatible.b. Limited evidenee suggests that spirituality may be compatible with profitability.c. Research shows that workplace spirituality constrains employeeperforma nee.d. High productivity has been extensively documented in spiritualworkplaces.THE ENVIRONMENT73.Exter nal en vir onment refers to _______________.a. forces outside the orga ni zati on that limit the orga ni zation sperforma neeb. factors and forces outside the organization that affect theorganization ' s performaneec. forces and in stituti ons in side the orga ni zati on that affect the organization ' s performaneed. forces in side the orga ni zati on that in crease the orga ni zati on ' s performa nee74. According to the textbook, the _______________ environment includesthose constituencies that have a direct and immediate impact onman agers' decisi ons and acti ons and are directly releva nt to theachievement of the organization ' s goals.a. generalb. specificc. sec on daryd. forward75. An organization ' s specific environment _________________ .a. is unique and changes with conditionsb. is the s ame regardless of the organization ' s agec. is determined by the top level of managementd. must be quantified to establish its existenee76. The main forces that make up an organization ' s specificen vir onment are ________ .a. suppliers, legislators, customers, and employeesb. customers, suppliers, competitors, and pressure groupsc. employees, competitors, pressure groups, and regulatorsd. suppliers, employees, competitors, and legislators/doc/292092685.html,anizations exist to meet the needs of which of the followingcon stitue ncies?a. customersb. legislatorsc. suppliersd. competitors78. When you think of an organization ' s suppliers, youa. know that they are the main customers of the organizationb. typically think of governments that pass the laws the organization must followc. know that they are located close to the organization itselfd. typically think in terms of organizations that provide materials and equipme nt79. Ma nagers seek to en sure a steady _______________ .a. cash flow from stockholders into the organizationb. flow of n eeded in puts at the lowest price availablec. flow of customers at the company ' s outlet storeat ad. flow of suppliers to keep the competition among supplierspeak80. Each of the follow ing is con sidered an orga ni zati onal supplierexcept providers of _________________ .a. finan cial in putsb. labor in putsc. materialsd. political pressure81. The In ternet is hav ing an impact on determ ining whom anorganization ' s competitors are because it has _______________ .a. defi ned the com mon markets for orga ni zati onsb. made certain products invaluable to customerc. virtually eliminated the need for shopping mallsd. virtually eliminated geographic boundaries82. For a company such as Walt Disney World in Florida, a bank would bean example of what kind of factor in their specific en vir onment?a. competitorb. supplierc. special-interest groupd. government agency83. Which of the follow ing is not an example of a specific en vir onmen tal factor?a. population demographicsb. political conditionsc. federal lawsd. all of the above84. For organizations such as hospitals, which hire nurses, the laborunion and the local labor market are examples of which of the followi ng specific en vir onmen tal factors?a. competitor and supplierb. customer and pressure groupc. both are examples of suppliersd. both are examples of pressure groups85. Typically, the specific organizational environment includes which of the follow ing?a. economic factorsb. political conditionsc. tech no logical factorsd. competitors86. United Parcel Service represents which of the following to the .Postal Service?a. competitorb. supplierc. customerd. government agency87. The gen eral en vir onment factor of econo mic con diti ons con sists of allof the followi ng except ______________ .a. legislation recently passed by Congressb. interest ratesc. cha nges in disposable in comed. stock market fluctuations88.Sociocultural con diti ons con sist of _____________ .a. demographic profiles of an organization ' s suppliersb. legal issues as determined by court decisionsc. the level of un employme nt and real econo mic in comes of workersd. changing expectations and values within society89. To a n ati onal broadcast n etwork such as NBC, your home DVD player is considered a _______________ .a. customerb. supplierc. special-interest groupd. competitor90. Groups such as Mothers Aga inst Drunk Drivi ng (MADD) are examples of whatfactor in the specific exter nal en vir onment?a. competitorsb. pressure groupsc. customersd. government agencies91. Typically, the general organizationalenvironment includes which of the follow ing?a. political conditionsb. bus in ess pla nsc. stakeholdersd. suppliers92. Compared to the specificenvironment, which of the following is an accurate stateme nt about the gen eral en vir onment of an orga ni zati on?a. It has less impact on the organization ' s operations.b. It has more impact on the organization ' s operations.c. It has about the same impact on an organization ' s operations.d. It is predominantly the concern of upper management.93. Which of the following genis not a component of an organization ' s eral en vir onment?a. economic conditionsb. political conditionsc. social conditionsd. industry conditions94.Interest rates, inflation rates, and stock market fluctuations areall examples of what factor in an organization ' s general environment?a. economicb. politicalc. sociald. tech no logical95. The America ns with Disabilities Act of 1990 is an example of aa. sociolegal conditionb. political/legal conditionc. political/sociological conditiond. sociocultural condition96. A decrease in contributions from the public to the United Way charityis most likely the result of which of the followi ng general en vir onmen tal factors?a. politicalb. socialc. tech no logicald. economic97. Which of the following groups includes individuals who were bornbetween the years 1946 - 1964?a. the Depression groupb. the World War II groupc. the baby boomersd. Generation X98. The members of which of the following groups are behaving infun dame ntally differe nt ways that are likely to greatly impactorga ni zati ons and man agers?a. the Depression groupb. the World War II groupc. the baby boomersd. Generation Y99. Automation represents an example of a(n) ________________ generalen vir onmen tal factor.a. tech no logicalb. demographicc. political/legald. economic100. Which of the follow ing has bee n the most rapidly cha nging component in an organization ' s general environment?a. globalb. economicc. sociald. tech no logical101. Which of the followi ng best represe nts a global general en vir onmen tal factor?a. in creased surveilla neeb. education levelsc. electronic meetingsd. international markets102. Which of the following are the two dimensions of environmental un certa in ty?a. degree of change and degree of complexityb. degree of change and degree of volumec. degree of complexity and degree of impactd. degree of impact and degree of timing103. If the components of an organization ' s environment changefrequently, the organization is operating in a _________________en vir onment.a. disruptiveb. diversec. dynamicd. difficult104. Managers try to minimize ______________ because it threatens orga ni zati onal effective ness.a. product developmentb. uncertaintyc. price chargesd. the number of suppliers105. _________ are any constituencies in an organization ' s external environment that are affected by the organization ' s decisi ons and actions.a. Stockholdersb. Pressure groupsc. Suppliersd. Stakeholders106. Degree of _______________ refers to the nu mber of comp onents in an organization ' s environment and the extent of the knowledge that the orga ni zati on has about those comp onen ts.a. stabilityb. opennessc. complexityd. tran siti on107. The first step of man agi ng exter nal stakeholder relati on ships is to ide ntify whom the stakeholders are. The second step is toa. determ ine what specific approach should be used to manage thestakeholder relatio nshipb. determine what the courts might do when stakeholder files a claimaga inst the orga ni zatio nc. determine what particular interests or concerns these stakeholdersmight haved. determine how many stakeholders there are in each stakeholder groupSCENARIOS AND QUESTIONSFor each of the following, choose the answer that most completely an swers the questi on.THE MANAGER: OMNIPOTENT OR SYMBOLIC?Apex Con structio n has hired Wen dell Phillips to provide man ageme ntcon sult ing for the orga ni zati on. Wen dell' s first assig nment involv es helping the company to improve productivity by recommending ways to strengthen managers ' supervisory skills.108. Wen dell no tices that the compa ny ' s top executives share a belief that managers are directly responsible for the organization ' s success or failure. This belief reflects a(n) _____________ view ofman ageme nt.a. traditionalb. omnipotentc. standardd. symbolic109. Wen dell in terviews many middle-level man agers and discovers that they share a differe nt view of man ageme nt.These in dividuals believethat exter nal factors con stra in man agers' in flue nee over outcomes.The mid-level man agers have a _____________ v iew of man ageme nt.a. traditionalb. omnipotentc. standardd. symbolicTHE ORGANIZATIONS CULTURECorporate Takeover (See nario)Todd works for SeaLa n Tech, an en vir onmen tal con suit ing firm that hasjust bee n purchased by Zerex, In c., a biomedical research orga ni zati on.Based on his early encoun ters with the new upper man ageme nt from Zerex, Todd feels that SeaLan is a “lower - key, friendlier ” organization. Heis concerned that the new company will eliminate SeaLan ' s old culture,and he does not like the prospects.110. If you were talk ing with Todd and asked him what the term culture meant, he would reply that, basically, it is _________________ .a. the formal rules of an organizationb. the nationality of the workers in the companyc. a system of shared meaningd. a system that reflects diversity and respect for differences111. Todd is concerned with the degree to which managers focus on results or outcomes rather tha n tech niq ues and theprocesses used toachieve those outcomes. He is concerned with ____________ .a. stabilityb. aggressivenessc. team orientationd. outcome orientation112. Todd no tices that man ageme nt is very concerned with the effects of outcomes on people within the organization. This is referred to asa. stabilityb. aggressivenessc. team orientationd. people orientation113. Todd is assessing the organization ' s_______________, the degree to which orga ni zatio nal activities emphasize maintaining the status quo in con trast to growth.a. stabilityb. aggressivenessc. team orientationd. outcome orientation114. Todd has been learning the seven dimensions of organizational culture. Which of the followi ng is not one of those seve n dime nsions?a. stabilityb. aggressivenessc. member orientationd. outcome orientationChanging Orga ni zati onal Culture (Seen ario)Mary has bee n asked by the compa ny preside nt to cha nge the organizational culture to reflect the company s neworganizationalgoals. As executive vice preside nt, she certa inly un dersta nds the goals, but is really not sure that she un dersta nds what to do about the culture.115. Mary asked employees if they knew what con stituted “ good employee behavior. ” She found that very few understood, and most had a variety of ideas.This is one in dicati on that her compa nya. has a strong cultureb. has a weak culturec. has no cultured. must have high tur no ver116. Mary also found out that in order to build a strong new culture,she should do all but which of the follow ing?a. hire employees who fit in with the company ' s cult ureb. develop socialization practices to build culturec. encourage a high turnover rate among employeesd. have management make organizational values clear117. Mary was surprised to find that most orga ni zati onal cultures area. weakb. weak to moderatec. moderate to strongd. strongTHE ENVIRONMENT。

![管理学_罗宾斯第九版_笔记1]](https://uimg.taocdn.com/4f25ad45a8956bec0975e3e1.webp)
《管理学》罗宾斯第九版核心内容笔记(林凯整理)整理者简介:林凯,拥有9年跨国公司工作经历,现为企业管理博士生,主要研究方向:商业模式创新;微博:/52linkai第Ⅰ篇绪论第1章管理与组织导论主要概念管理者(manager): 通过协调其他人的活动,从而达到与别人一起或者通过别人实现组织目标的人。
基层管理者(first-line managers): 最底层的管理人员,管理着非管理雇员所从事的工作。
中层管理者(middle managers): 所有处于基层和高层之间的各个管理层次的管理者。
高层管理者(top managers): 承担着制定广泛的组织决策,为这个组织制定计划和目标的管理者。
管理(management): 通过协调和监督他人的活动,有效率和有效果地完成工作。
效率(efficiency): 是指以尽可能少的投入获得尽可能多的产出。
效果(effectiveness): 通常是指“做正确的事”,即所从事的工作和活动有助于组织达到其目标。
管理职能(亨利.法约尔,Henri Fayol)计划(planning)职能: 包括定义目标、制定战略以获取目标,以及制定计划和协调活动的过程。
组织(organizing)职能: 包括决定应该从事哪些任务,应该由谁来从事这些任务,这些任务怎么分类和归集,谁向谁报告,以及在哪一级作出决策的过程。
领导(leading)职能: 包括激励下属、帮助解决群体冲突、影响工作中的个体或团队、选择最有效的沟通渠道,或者以任何方式处理雇员的行为问题的过程。
控制(controlling)职能:评估和监控活动、比较与目标的偏差和纠正偏差的过程。
管理角色(management roles): 指特定的管理行为类型。
(亨利.明茨伯格,Henry Mintzberg)人际关系角色(interpersonal roles): 指涉及人与人(下级和组织外的人)的关系以及其他具有礼仪性和象征性职责的角色,包括挂名首脑、领导者和联络者。


管理学第9版练习题英文版附答案1Chapter 1 Introduction to Management and Organizations TRUE/FALSE QUESTIONSA MANAGER’S DILEMMA1.Today’s managers are just as likely to be women as they are men.2.Management affects employee morale but not a company’s financial performance.WHO ARE MANAGERS?3.In order to be considered a manager, an individual must coordinate the work of others.4.Supervisors and foremen may both be considered first-line managers.WHAT IS MANAGEMENT?5.Effectiveness refers to the relationship between inputs and outputs.6.Effectiveness is concerned with the means of getting things done, while efficiency is concerned withthe attainment of organizational goals.7. A goal of efficiency is to minimize resource costs.8.Efficiency is often referred to as “doing things right.”9.Managers who are effective at meeting organizational goals always act efficiently.WHAT DO MANAGERS DO?10.The four contemporary functions of management are planning, organizing, leading, and controlling.11.Determining who reports to whom is part of the controlling function of management.12.Directing and motivating are part of the controllingfunction of management.13.Fayol’s management functions are basically equivalent to Mintzberg’s management roles.14.The roles of figurehead, leader, and liaison are all interpersonal roles.15.Disturbance handler is one of Mintzberg’s interpersonal roles.16.Mintzberg’s informational management role involves receiving, collecting, and disseminatinginformation.17.Mintzberg’s resource allocation role is similar to Fayol’s planning function because it involves thecoordination of employee’s activities.18.Resource allocation and disturbance handling are both considered decisional roles.19.A finance manager who reads the Wall Street Journal ona regular basis would be performing thefigurehead role.20.Katz found that managers needed three essential skills: technical, human, and informational.21.Technical skills become less important as a manager moves into higher levels of management.22.Conceptual skills become less important as a manager moves into top management.23.Interpersonal skills involve a manager’s ability to think about abstract situations.24.Coaching and budgeting are skills closely related to the management function of leading.25.Budgeting is a skill that is related to both planning and controlling.26.In today’s world, organizational managers at all levels and in all areas need to encourage theiremployees to be on the look-out for new ideas and new approaches.27.Only first-line managers and employees need to be concerned with being customer-responsive.28.Innovation is only important in high-tech firms.WHAT IS AN ORGANIZATION?29.A distinct purpose is important in defining an organization.30.A nontaxable organization, such as the United Way, cannot be considered an organization. MULTIPLE-CHOICE QUESTIONSFor each of the following choose the answer that most completely answers the question.A MANAGER’S DILEMM A31.Which of the following statements regarding managers in today’s world is accurate?a.Their age range is limited to between 30 and 65.b.They are found only in large corporations.c.They can be found exclusively in for-profit organizations.d.The single most important variable in employee productivity and loyalty is the quality of therelationship between employees and their direct supervisors.32.According to data collected by Catalyst, a nonprofit research group, _________ percent of corporateofficers in Fortune 500 companies are women.a.55.3b.15.7c.39.7d.21.9WHO ARE MANAGERS?33.Someone who works with and through other people by coordinating their work activities in order toaccomplish organizational goals is ___________.a.an assembly line workerb. a laborerc. a managerd. a salesperson34.In the past, nonmanagerial employees were viewed as employees who ___________.a.reported to top executivesb.reported to middle managersc.supervised othersd.had no others reporting to them35.Which of the following types of managers is responsible for making organization-wide decisions andestablishing the plans and goals that affect the entire organization?a.first-line managersb.top managersc.production managersd.research managers36.All levels of management between the supervisory level and the top level of the organization aretermed _____________.a.middle managersb.first-line managersc.supervisorsd.foremen37.Which of the following levels of management is associated with positions such as executive vicepresident, chief operating officer, chief executive officer, and chairman of the board?a.team leadersb.middle managersc.first-line managersd.top managers38.Agency head or plant manager is most likely associated with which of the following?a.team leadersb.middle managersc.first-line managersd.top managers39.The lowest level of management is ______________.a. a nonmanagerial employeeb. a department of research managerc. a vice presidentd. a first-line manager40.Supervisor is another name for which of the following?a.team leaderb.middle managerc.first-line managerd.top manager41.Managers with titles such as regional manager, project leader, or plant manager are_______________.a.first-line managersb.top managersc.production managersd.middle managers42.Which of the following best reflects the management structure of a traditional organization?a.pyramidb.circlec.hub with spokesd.infinite line43.Division manager is associated with which of the following levels of management?a.team leadersb.middle managersc.first-line managersd.top managersWHAT IS MANAGEMENT?44._____________ is the process of getting activities completed efficiently and effectively with andthrough other people.a.Leadingb.Managementc.Supervisiond.Controlling45.The distinction between a managerial position and a nonmanagerial position is _______________.a.planning the work of othersb.coordinating the work of othersc.controlling the work of others/doc/b815723333.html,anizing the work of others46.Which of the following is an example of an efficient manufacturing technique?a.cutting inventory levelsb.increasing the amount of time to manufacture productsc.increasing product reject ratesd.decreasing product output47.Wasting resources is considered to be an example of managerial _____________.a.efficiencyb.effectivenessc.inefficiencyd.ineffectiveness48.An automobile manufacturer that increased the total number of cars produced at the same cost, butwith many defects, would be _____________.a.efficient and effectiveb.increasing efficiencyc.increasing effectivenessd.concerned with inputs49.Effectiveness is synonymous with _____________.a.cost minimizationb.resource controlc.goal attainmentd.efficiency50.Efficiency refers to _____________.a.the relationship between inputs and outputsb.the additive relationship between costs and benefitsc.the exponential nature of costs and outputsd.increasing outputs regardless of cost51.In successful organizations, ______________.a.low efficiency and high effectiveness go hand in handb.high efficiency and low effectiveness go hand in handc.high efficiency and high effectiveness go hand in handd.high efficiency and high equity go hand in hand52.Whereas _____________ is concerned with the means of getting things done, _____________ isconcerned with the ends, or attainment of organizational goals.a.effectiveness; efficiencyb.efficiency; effectivenessc.effectiveness; goal attainmentd.goal attainment; efficiencyWHAT DO MANAGERS DO?MANAGEMENT FUNCTIONS53.How many management functions were originally proposed in the early part of the twentieth century?a.threeb.fourc.fived.nine54._____________ was a French industrialist who first identified the basic management functions.a.Weberb.Taylorc.Herzbergd.Fayol55.Today, the basic management functions are considered to be ______________.a.planning, coordinating, staffing, and directingb.planning, organizing, leading, and directing/doc/b815723333.html,manding, organizing, leading, and staffingd.planning, organizing, leading, and controlling56.Which of the following management functions from the mid-1950s is no longer included in the basicfunctions of management?/doc/b815723333.html,mandingb.staffingc.leadingd.controlling57.Writing an organizational strategic plan is an example of the ______________ management function.a.leadingb.coordinatingc.planning/doc/b815723333.html,anizing/doc/b815723333.html,anizing includes _____________.a.defining organizational goalsb.hiring organizational membersc.motivating organizational membersd.determining who does what tasks59.A manager resolving conflict among organizational members is performing what function?a.controlling/doc/b815723333.html,mandingc.directingd.leading60.The process of monitoring, comparing, and correcting is called _____________.a.controllingb.coordinatingc.leading/doc/b815723333.html,anizingMANAGEMENT ROLES61.__________ developed a categorization scheme for defining what managers do, consisting of 10different but highly interrelated roles.a.Henri Fayolb.Henry Fordc.Henry Mintzbergd.Henry Morris62.According to Mintzberg’s management roles, the _____________ roles are those that involve peopleand other duties that are ceremonial and symbolic in nature./doc/b815723333.html,rmationalb.interpersonalc.technicald.decisional63.The roles of disseminator, figurehead, negotiator, liaison, and spokesperson are more important atthe __________ levels of the organization.a.lowerb.middlec.higherd.supervisory64.Which of the following is not an example of a decisional role according to Mintzberg?a.spokespersonb.entrepreneurc.disturbance handlerd.resource allocator65.A human resource manager attending a local Society for Human Resource Management meetingwould be functioning in which role?/doc/b815723333.html,rmationalb.leaderc.liaisond.disseminator66.A finance manager who reads the Wall Street Journal ona regular basis would be performing whichrole?a.figureheadb.monitorc.disseminatord.interpersonal67.The _____________ role is more important for lower-level managers than it is for either middle- ortop-level managers.a.leaderb.entrepreneurc.spokespersond.disseminator68.The emphasis that managers give to various roles seems to be based on their _____________./doc/b815723333.html,anizational levelb.tenure with the organizationc.experience in their fieldd.personality69.Which of the following is not an example of an interpersonal role according to Mintzberg?a.figureheadb.leaderc.liaisond.spokesperson70.According to Mintzberg’s management roles, the ______________ roles involve receiving,collecting, and disseminating information.a.interpersonal/doc/b815723333.html,rmationalc.technicald.decisional71.All of the following are examples of informational roles according to Mintzberg except____________.a.liaisonb.monitorc.disseminatord.spokesperson72.Which of the following is not an example of a decisional role according to Mintzberg?a.spokespersonb.entrepreneurc.disturbance handlerd.resource allocator73.All of the following are managerial roles that are more important at the higher levels of theorganization except ________________.a.leaderb.disseminatorc.figureheadd.negotiator74.Which of the fol lowing represents the most useful way of describing the manager’s job?a.rolesb.functionsc.skills/doc/b815723333.html,anizational level75.Many of Mintzberg’s roles align with the basic functions of management. For example, the_____________ role is a part of planning.a.figureheadb.leaderc.liaisond.resource allocation76.All three o f Mintzberg’s interpersonal roles are part of the _____________ function./doc/b815723333.html,anizingb.planningc.leadingd.controllingMANAGEMENT SKILLS77.Which of the following identified the three essential managerial skills?a.Katzb.Lewisbergc.Rainesd.Chambers78.The three essential managerial skills include _____________.a.technical, human, and empiricalb.human, empirical, and conceptualc.technical, interpersonal, and controllingd.technical, human, and conceptual79.Understanding building codes would be considered a _____________ skill for a building contractor.a.humanb.technicalc.conceptuald.empirical80.Which of the following is true concerning technical and managerial skills?a.Human skills and technical skills remain equally important as managers move to higher levels.b.Technical-skill needs remain necessary and human skills decrease as managers move to higherlevels.c.Human skills remain necessary and technical-skill needs decrease as managers move to higherlevels.d.Both human-skill and technical-skill needs decrease as managers move to higher levels.81.Managers with good __________ are able to get the best out of their people.a.human skillsb.conceptual skillsc.technical skillsd.visual skills82.Technical skills include _______________.a.leadership and efficiency in a certain specialized fieldb.knowledge of and proficiency in a certain specialized fieldc.familiarity with and interest in a general field of endeavord.skill and interest in a general field of endeavor83.The ability to work well with other people, both individually and in a group, requires________________.a.technical skillsb.assessment skillsc.planning skillsd.human skills84.Which of the following types of skills are described with terms such as abstract situations andvisualization?a.interpersonalb.humanc.technicald.conceptual85.Which one of the following phrases is best associated with managerial conceptual skills?a.decision making/doc/b815723333.html,municating with customers/doc/b815723333.html,ing information to solve business problemsd.product knowledge86.Which of the following skills are more important at lower levels of management, as these managersare dealing directly with employees doing the organization’s work?a.humanb.technicalc.conceptuald.empirical87.Budgeting is associated with the management functions of planning and _____________.a.directing/doc/b815723333.html,anizingc.leadingd.controlling88.Mentoring is primarily associated with the management function of _____________.a.planning/doc/b815723333.html,anizingc.leadingd.controllingWHAT IS AN ORGANIZATION?89.An organization is ______________.a.the physical location where people workb. a collection of individuals working for the same companyc. a deliberate arrangement of people to accomplish some specific purposed. a group of individuals focused on profit making for their shareholders90.One of the common characteristics of all organizations is ____________, which is typicallyexpressed in terms of the organization’s goals.a.its peopleb.its goalsc.its systematic structured.its purpose91.One of the common characteristics of all organizations is _____________, which clarifies members’work relationships.a.its peopleb.its goalsc.its deliberate structured.its purpose92.A deliberate arrangement of people to accomplish some specific purpose is _____________.a. a structure.b. a process.c.an organization.d.an assembly operation93.A difference between traditional organizations and new organizations is that the new organizationstend to be more _____________.a.stable/doc/b815723333.html,mand orientedc.rule orientedd.dynamicWHY STUDY MANAGEMENT?94.Which of the following best describes the concept that management is needed in all types and sizesof organizations, no matter the country in which they’re located?a.the partiality of managementb.the segmentation of managementc.the universality of managementd.the cultures of management95.Universality of management means that _____________a.all managers in all organizations perform the four management functionsb.all managers in all organizations can perform their job thesame wayc.all organizations can hire any manager to perform the management jobsd.any manager can work in any organization and perform any management job96.As members of the general public, we have a vested interest in improving the way organizations aremanaged because _________________.a.we stand to benefit personally from an individual organization’s profitsb.we interact with organizations every single day of our livesc.if organizations don’t improve, we won’t have a place to work in the future/doc/b815723333.html,anizations supply inputs to other organizations/doc/b815723333.html,anizations that are well managed ____________.a.choose the best suppliers for their products/doc/b815723333.html,pete on an international basis because they have the best productsc.always have the lowest-cost productsd.develop a loyal customer base, grow, and prosper98.According to management expert Peter Drucker, management is about ______________.a.profitsb.peoplec.planningd.participation99.Which of the following types of managerial positions is most likely to involve clerical duties?a.shift supervisorb.regional department headc.project managerd.chief executive officer100. A manager’s success is typically _______________.a.dependent on how hard the manager worksb.how closely the manager supervises the employeesc.based on how skilled the manager is at the technical elements of the jobd.dependent on others’ work performance101. A primary responsibility of managers is creating a work environment that _______________.a.is safe and well litb.is clean and organizedc.allows employees to do their work to the best of their abilityd.provides excellent customer service102.Managers often ______________.a.are prevented from making business decisionsb.change their career paths during their work livesc.have opportunities to think creatively and use their imaginationsd.must depend on their employees for guidance in dealing with superiors103.Which of the following represents a challenge of management?a.enjoy relatively easy workb.work with a variety of peoplec.have little influence on organizational outcomesd.have to deal with a variety of personalities104.Each of the following represents a challenge of management except _______________.a.must operate with limited resourcesb.are highly valued by organizationsc.must motivate workers in uncertain situationsd.success depends on others’ performanceSCENARIOS AND QUESTIONSFor each of the following choose the answer that most completely answers the question.WHO ARE MANAGERS?Managerial Basic Training (Scenario)Imagine that your marketing company has just merged with a manufacturing organization. You have been asked to help provide some “basic” managerial training to the engineers in the research and development unit of the new sister company. To make sure you are covering the necessary issues, your boss has asked to see an overview of materials that you will be providing the engineers.105.Now that both companies are merged and are a systematic arrangement of people set to accomplish a specific purpose, they could be described as a(n) _____________.a.business unitb.multinational company/doc/b815723333.html,anizationd.holding company106.One of the first things the engineers need to learn is that _____________ are the people who direct the activities of others in an organization.a.directorsb.managersc.subordinatesd.line workers107.Another fact that engineers need to learn is that supervisors may frequently be referred to as _____________.a.middle managersb.top managersc.project leadersd.first-line managers108.Many of the engineers in the group are unclear about what managers actually do. Your training materials explain that a manager’s job focuses on _____________.a.the performance of clerical dutiesb.personal achievementc.helping others accomplish their work goalsd.supervising groups rather than individual employeesThe Customer Meeting (Scenario)Kelly, a production supervisor, is responsible for 10 employees who assemble components into a finished product that is sold to distributors. Kelly reports to Ben, a production manager, who in turn reports to Dan, a general manager, who reports to McKenna, a vice president of operations. Recently, McKenna asked Dan to have a meeting with Kelly and Ben regarding some customer concerns in the production area. The focus of the meeting was to judge the validity of the customer concerns, and to develop a specific plan to address these concerns.109.What is the commonality among Kelly, Ben, Dan, and McKenna?a.They all produce the same product.b.They all have the same job content.c.They all are managers.d.They all have the same vision.110.Kelly is considered to be what level of management?a.top managerb.superintendent of assemblyc.middle managerd.first-line manager111.Ben and Dan are considered to be what level of management?a.top managersb.middle managersc.superintendents of assemblyd.first-line managers112.McKenna is considered to be what level of management?a.top managerb.superintendent of assemblyc.middle managerd.first-line manager113.The structure of the managerial relationships among McKenna, Dan, Ben, and Kelly can best be described as a ____________.a.flexible work groupb.traditional pyramid structurec.innovative nuclear structure/doc/b815723333.html,munication hubWHAT IS MANAGEMENT?The Perfect Manager (Scenario)Brenda Kraft has proven herself to be an able manager. Her section has a high project completion rate with the highest-quality product and the lowest defects in her division. In addition,she accomplishes this with fewer full-time people than other managers. Some say that the secret of her success is in her ability to delegate responsibility and her understanding of the basic “management functions.”114.Brenda’s ability to complete activities efficiently and effectively with and through other people is known as _____________.a.managementb.leadershipc.coerciond.delegation115.Brenda’s ability to produce the same amount of product with fewer personnel is a reflection of her ___________.a.effectivenessb.process skillsc.leadershipd.efficiency116.The fact that Brenda completes her projects is an indication of her _____________ as a manager.a.leadershipb.effectivenessc.efficiencyd.attention to detail117.If Brenda accomplished her projects on time with high-quality results, but she took more time than other managers in the process, you could say that as a manager she was ____________.a.efficient, but not effectiveb. a leader, but not a top managerc.project oriented, but not effectived.effective, but not efficient118.The “management functions” exemplified by Brenda include all but which of the following?a.planningb.controlling/doc/b815723333.html,anizingd.calibratingWHAT DO MANAGERS DO?Joe the Manager (Scenario)As a production supervisor, Joe decides on Friday afternoon how many units of output his employees will be able to produce and on which days certain products will be run in his department. He also decides which of his employees are going to be responsible for operating which machines within the department next week, as his employees are multi-skilled assemblers. On Monday, he informs his employees of their assignments to specific machines by handing out assignment sheets. He tells the employees that the schedule is going to be difficult this week due to the increased number of units. He goes on to tell them that he is sure they can fulfill the schedule because they are such good and skilled employees. Each day during the week, Joe checks the amount of output that the employees have completed and the number of units that have been rejected.119.When Joe decides how many units of output his employees will be able to produce and on which days certain products will be run, he is performing which of the management functions?a.controllingb.leadingc.planning/doc/b815723333.html,anizing120.When Joe checks the amount of output that the employees have completed and the number of units that have been rejected, he is performing which of the management functions?a.controllingb.leadingc.planning/doc/b815723333.html,anizing121.When Joe tells the employees that he is sure they can fulfill the schedule because they are such good and skilled employees, he is performing which of the management functions?a.controllingb.leadingc.planning/doc/b815723333.html,anizingThe Busy Day (Scenario)Don Eskew, plant manager at Control Systems, Inc., sighed as he sipped his first cup of coffee at 5 A.M. and read his agenda for the day. He is giving two company tours in the morning: the first to a newspaper reporter who is writing a story on the new plant expansion, and the second to a group of Control Systems managers from the east coast. Don then has a meeting with the unit manager, Phil Johnson, to discuss Phil’s recent drop in performanc e (a task Don always hates). Next, Don is spending a couple of hours reviewing the trade journals he receives from his high-tech association and writing up a brief synopsis for his presentation next week to the division president. Finally, in the late afternoon, he will be reviewing the new equipment malfunction and deciding whether to bring in extra people to get the equipment running as soon as possible. Whew! Just anotherday in the glamorous life of a manager. 122.Together, all of the functions that Don performs during his busy day correspond to the management roles discovered in the late 1960s by which one of the following management researchers?a.Herzbergb.Skinnerc.Mintzbergd.Fayol123.When Don conducts the tour for the east coast managers, he will be operating in which of the management roles?a.leaderb.liaisonc.monitord.figurehead124.When Don meets with Phil to discuss Phil’s performance issues, Don will be operating in which management role?a.leaderb.figureheadc.monitord.disturbance handler125.What role will Don be performing when he gives the plant tour to the newspaper reporter?a.monitorb.figureheadc.disseminatord.spokesperson126.When Don reviews the new equipment malfunction, what management role will he play when deciding whether to bring in extra people?a.monitorb.disseminatorc.resource allocatord.disturbance handlerThe General Manager (Scenario)Michael is the general manager of a production facility. In a routine day, Michael might meet with city officials or civic leaders about environmental issues due to the plant’s presen ce in the community. After these meetings, he will then meet with the plant’s functional managers to discuss the concerns expressed by the city representatives. Other times, Michael might meet with the production manager, Betty, and the human resource manager, Joyce, to discuss a complaint filed by one of the employees in a production department. Michael might also spend time on the Internet looking for new technologies that can be used in the production processes of his plant.127.When Michael gains information from city officials or civic l eaders to learn how the plant’s operations may be affecting the environment, he is performing which management role?a.leaderb.resource allocatorc.entrepreneurd.monitor128.When Michael meets with Betty and Joyce to discuss a complaint filed by one of the employees in a production department, he is performing which management role?a.resource allocatorb.disturbance handlerc.liaison。

第一章管理与组织导论一、管理1.管理是在特定的组织内外环境下,通过协调和监督他人的活动,能够有效率和有效果地与别人一起或者通过别人实现组织目标的过程。
2.管理的定义包含三层含义:(1)过程代表了一系列进行中的有管理者参与的职能或目标。
这些职能划分为计划、组织、领导和控制;(2)协调他人的工作区分了管理岗位和非管理岗位。
(3)管理活动强调效率和效果。
效率是指正确地做事,不浪费资源,以最小投入获取最大产出;效果是指做正确的事,通过完成任务而使组织达到目标。
效率注重过程,效果注重结果。
因此,管理当局既要关注达到和实现组织目标,还要尽可能有效率地完成工作。
在成功的组织中高效率与高效果是相辅相成的,而不良的管理通常既是低效率的也是低效果的,或者虽然有效果但却是低效率的。
二、管理的职能1)计划是设立和明确组织目标,制定实现组织目标的途径和方案。
计划是管理的起点,确定目标和途径是计划职能的两大任务。
它包括定义目标,制定战略以获取目标,以及制定计划和协调活动的过程。
2)组织是为了实现计划活动所规定的目标,实施计划活动所制定的行动方案,管理者必须进行的工作安排。
它包括决定应该从事哪些任务,应该由谁来从事这些任务,这些任务怎么分类和归集,谁向谁报告,以及在哪一级作出决策的过程。
3)领导是指和别人一起或通过别人去完成组织目标,这是因为每个组织都是由人组成的。
它包括激励下属,影响工作中的个体或团队,选择有效的沟通方式,或者处理雇员的行为问题等。
4)控制是指监控,比较,纠正的过程。
监控是指关注事情是否在按计划进行;比较包括衡量和评估工作绩效,并与预定的目标相比较;纠正是指如果比较中发现显著的偏差,管理者要使工作绩效回到正常轨道。
在实际管理工作中,管理者并不总是按照先计划、组织、领导,然后控制这个顺序工作。
但这并不否认这些职能的重要性。
不论工作次序如何,管理。
者在管理时确实进行着计划、组织、领导和控制。
三、管理角色(一)管理角色是指特定的管理行为类型。
Chapter 7 – Foundations of PlanningTrue/False Questions4. Research indicates that managers who plan always outperform managers who do not plan.False (moderate)9. Plans that specify the details of achievement of the overall objectives are calledoperational plans.True (difficult)10. Directional plans have clearly defined objectives.False (moderate)12. Standing plans are created in response to programmed decisions that managers make andinclude policies, rules, and procedures.True (moderate)13. The greater the environmental certainty, the more plans need to be directional andemphasis placed on the short term.False (moderate)22. An organization's real goals are what they actually plan on accomplishing, rather thanwhat they hope to accomplish.False (moderate)24. Real goals are official statements of what an organization says its goals are.False (easy)Multiple Choice36. One purpose of planning is that it minimizes ______________ and ______________.a. cost; timeb. time; personnel needsc. waste; redundancy (difficult)d. time; wastee. mistakes; cost38. What does the evidence suggest about organizations that plan compared to organizationsthat do not plan?a. Planning organizations always outperform nonplanning organizations.b. Nonplanning organizations always outperform planning organizations.c. Planning organizations generally outperform nonplanning organizations (easy)d. Nonplanning organizations generally outperform planning organizations.e. They generally perform at about the same level.45. Which of the following is the foundation of planning?a. employeesb. goals (easy)c. outcomesd. computerse. the planning department46. According to the text, _____________ are documents that outline how goals are going tobe met and which typically describe resource allocations, schedules, and other necessary actions to accomplish the goals.a.strategiesb.goalsc.plans (moderate)d.policiese.procedures50. Which of the following is true concerning an organization's stated objectives?a. They issue identical objectives to all constituents.b. Organizations typically have internal and external sets of objectives.c.They may issue different objectives to stockholders, customers, employees, and thepublic.(moderate)d. It is illegal to issue conflicting stated objectives.e. Stated objectives are usually in line with short-term actions.54. What should a person do to understand what are the real objectives of the organization?a. observe organizational member actions (moderate)b. attend a stockholders annual meetingc. read their statement of purposed. read their annual reporte. watch television news reports59. When we categorize plans as being single-use versus standing, we categorize them by______________.a. breadth.b. specificity.c. frequency of use. (easy)d. depth.e. time frame.61. Based on the information presented in the text, ______________ are short term,specific, and standing.a. operational (moderate)b. long-termc. strategicd. specifice. directional67. An organizational plan that has a 6-year time frame would be considered what type ofplan?a. operationalb. short-termc. strategicd. intermediatee. long-term (moderate)68. Strategic plans tend to include a time period of usually ______________.a. 1 year.b. 1-3 years.c. 3 years or more. (moderate)d. 5 years or more.e. at least 10 years.71. Compared to directional plans, what type of plan has clearly defined objectives?a. strategicb. single-usec. short-termd. specific (moderate)e. standing76.Planning accuracy with a high degree of environmental change tends to produce which ofthe following results?a. Planning accuracy is likely.b. Planning accuracy becomes much more important.c. Planning accuracy becomes less important.d. Planning accuracy is less likely. (moderate)e. Planning accuracy occurs in the long-run.78. A ______________ plan is a one-time plan designed to meet the needs of a uniquesituation and created in response to nonprogrammed decisions that managers make.a. single-use (easy)b. short-termc. directionald. standinge. strategic79. A small town's preparation for a visit by the President of the United States would beconsidered what type of plan?a. strategicb. directionalc. standingd. long-terme. single-use (moderate)81. A city's policy concerning skateboarding on downtown sidewalks providing guidance forpolice action would be considered what type of plan?a. standing (difficult)b. contingencyc. directionald. single-usee. strategic84. Where in the organizational hierarchy are traditional goals determined?a. front-line employeesb. team leadersc. lower-level managersd. middle managerse. top managers (moderate)89. A management system in which specific performance goals are jointly determined byemployees and their managers is known as ______________.a.management by objectives. (moderate)b.means-ends chain.c.traditional goal setting.d.management by opinions.91. Which of the following is not one of the four common elements of Management ByObjectives (MBO)?a. goal specificityb. participative decision-makingc. an explicit time periodd. a systems loop (difficult)e. performance feedback93. Management By Objectives (MBO) can be described by which of the following statements?a. an autocratic systemb. a "bottom up" systemc. a "top down" systemd. both a "top down" and a "bottom up" system (difficult)e. a static system105. According to the boxed feature, “Managing in an E-Business World,” probably the biggest change for planning in e-business is that ______________.a.the environment is more stable.b.customers are calling the shots. (moderate)c.employees are making the demands.d.only a few competitors exist.Essay Questions122. In a short essay, list and discuss the four reasons for planning.Answera.Planning establishes coordinated effort. It gives direction to managers andnonmanagers alike. When employees know where the organization or work unit aregoing and what they must contribute to reach goals, they can coordinate theiractivities, cooperate with each other, and do what it takes to accomplish thosegoals. Without planning, departments and individuals might be working at cross-purposes, preventing the organization from moving efficiently toward its goals.b.Planning reduces uncertainty by forcing managers to look ahead, anticipate change,consider the impact of change, and develop appropriate responses. It alsoclarifies the consequences of actions managers might take in response to change.Even though planning can’t eliminate change, managers plan in order to anticipatechanges and develop the most effective response to them.c.Planning reduces overlapping and wasteful activities.When work activities arecoordinated around established plans, wasted time and resources and redundancy canbe minimized. Furthermore, when means and ends are made clear through planning,inefficiencies become obvious and can be corrected or eliminated.d.Planning establishes goals or standards that are used in controlling. If managersare unsure of what they are trying to accomplish, they will be unable to determinewhether or not the goal has actually been achieved. In planning, goals and plansare developed. Then, through controlling, actual performance is compared againstthe goals, significant deviations are identified, and necessary corrective actionis taken. Without planning, there would be no way to control.(moderate)127. In a short essay, list and discuss five characteristics of well-defined goals.Answer(1) A well-designed goal should be written in terms of outcomes rather than actions.The desired end result is the most important element of any goal and, therefore, thegoal should be written to reflect this. (2) Next, a goal should be measurable and quantifiable. It’s much easier to determine if a goal has been met if it’s measurable. In line with specifying a quantifiable measure of accomplishment, (3) a well-designed goal should also be clear as to a time frame. Although open-ended goals may seem preferable because of their supposed flexibility, in fact, goals without a time frame make an organization less flexible because a manager is never sure when the goal has been met or when he or she should call it quits because the goal will never be met regardless of how long he or she works at it. (4) Next a well-designed goal should be challenging but attainable. Goals that are too easy to accomplish are not motivating and neither are goals that are not attainable even with exceptional effort.(5) Next, well-designed goals should be written down. Although actually writing downgoals may seem too time consuming, the process of writing the goals forces people to think them through. In addition, the written goals become visible and tangible evidence of the importance of working toward something. (6) Finally, well-designed goals are communicated to all organizational members who need to know the goals.Making people aware of the goals ensures that they’re “on the same page” and working in ways to ensure the accomplishment of the organizational goals.(moderate)128. In a short essay, list and discuss the five steps in the goal-setting process.Answera.Step 1: Review the organization’s mission, the purpose of the organization.These broad statements of what the organization’s purpose is and what it hopes toaccomplish provide an overall guide to what organizational members think isimportant. It’s important to review these statements before writing goals becausethe goals should reflect what the mission statement says.b.Step 2: Evaluate available resources. A manager doesn’t want to set goals thatare impossible to achieve given the available resources. Even though goals shouldbe challenging, they should be realistic. If the resources a manager has to workwith doesn’t allow for the achievement of that goal no matter how had the managertries of how much effort is exerted, that goal shouldn’t be set.c.Step 3: Determine individually, or with input from others, the goals. These goalsreflect desired outcomes and should be congruent with the organizational missionand goals in other organizational areas. These goals should be measurable,specific, and include a time frame for accomplishment.d.Step 4: Write down the goals and communicate them to all who need to know.Writing goals down forces people to think them through and also makes those goalsvisible and tangible evidence of the importance of working toward something.e.Step 5: Review results and whether goals are being met. Make changes, as needed.Once the goals have been established, written down, and communicated, a manager isready to develop plans for pursuing the goals.(difficult)129. In a short essay, list and discuss the three contingency factors that affect planning.Answera.Level in the organization–for the most part, operational planning dominatesmanagers’ planning efforts at lower levels. At higher organizational levels, theplanning becomes more strategy oriented.b.Degree of environmental uncertainty–when environmental uncertainty is high,plans should be specific, but flexible. Managers must be prepared to reword andamend plans as they’re implemented. At times, managers may even have to abandon their plans.c.Length of future commitments –the more that current plans affect futurecommitments, the longer the time frame for which managers should plan. This commitment concept means that plans should extend far enough to meet those commitments made when the plans were developed. Planning for too long or for too short a time period is inefficient and ineffective.(moderate)。
方案1:《管理学》 management管理是什么,主要讲了概论、管理者角色、计划、决策和目标管理第一部分基本概念管理是一个协调工作的活动过程,以便能有效率和效果地同别人一起,或通过别人一起实现组织目标的过程。
Management in all business and organizational activities is the act of getting people together to accomplish desired goals and objectives using available resources efficiently and effectively.1、管理的目的----实现组织目标。
goal--accomplish desired goals and objectives2、管理的核心----协调。
Core---Coordination3、管理的基础----组织。
Basis---organizing现代管理理论一般将管理职能分为4个:(1)计划 planning 计划包含的风险度;计划的主体是个人还是团队;管理者参与环境扫描程度。
(2)组织 organizing 员工拥有的自主权大小organizations have the autonomy of the size of the staff;;依个人还是团队完成任务;部门间的相互联系程度 The degree of interdepartmental linkages (3)领导leading 管理者对员工的关心程度 care staff ;管理者与员工的沟通程度the degree of communication between managers and employees;领导方式与风格选择leadership style(4)控制 controlling 员工自律与外控方式的选择control, staff discipline and external control mode choice;绩效评估标准的选择;Performance evaluation criteria selection 预防控制的使用prevention and control of the use.Management comprises planning, organizing, leading or directing, and controlling an organization (a group of one or more people or entities) or effort for the purpose of accomplishing a goal管理学---指研究管理活动的客观规律与方法的科学。