MATLAB_RTW__Engine
- 格式:pdf
- 大小:1.60 MB
- 文档页数:40

RTW技术在轮机模拟器中的应用高德基;欧镇;卢森微【摘要】This paper introduce a method of using the code generation of MATLAB/Simulink to convert Matlab/Simulink to theC++ code in the process of constructing the mathematical model of the marine main engine in the turbine simulator. You can modify the module parameters in real time and put the data generated by the simulink into the SQL database through further development for the calling of other parts of the turbine simulator . And the virtual operating system of the marine main engine based on the virtools , for example, I introduce the concrete application of this technology.This can not only avoid the problem of writing the code ,but also meet the demand of real-time in the turbine simulator and provide the convenience for the development of the turbine simulator.%文中介绍了轮机模拟器中船舶主机数学模型的构建过程中,利用MATLAB/Simulink中代码转换工具,将Simulink中搭建的船舶主机模型转换为C++代码。
基于MATLAB/ RTW的实时控制系统开发2004-4-30 14:33:38 来源: 点击次数: 4次新疆大学电气工程学院张宏立摘要:本文简要介绍了MATLAB的RTW工具箱的功能和作用,并用一实例着重介绍了使用RTW中XPC 开发实时控制系统的方法和步骤,为快速,高效开发实时控制系统提供有效手段。
关键词:MATLAB RTW XPC 实时控制一引言MATLAB是Mathworks 公司80年代推出的优秀科学计算和系统仿真软件,它以丰富的函数、强大的工具箱和简便的编程环境而深受广大用户欢迎,尤其是它的Simulink工具箱更是为系统仿真和建模提供强有力的支持。
但是说到MATLAB在实时控制方面的应用,就很少有人了解,关于这方面的资料也很少。
而RTW(Real Time Workshop)正是Mathworks 公司为MATLAB在实时控制应用方面开发的专门工具箱[1]。
二 RTW功能介绍RTW是对MATLAB和Simulink功能的一个重要补充,以往我们在设计控制系统中,先在Simulink中建模和仿真,直至仿真结果满意为止。
但是真正要开发实际控制器时,我们需要重新使用C或者其它语言重新编程,而当设计好的控制器与实际被控系统相联后,可能控制效果就不如仿真效果那么理想了,因为在仿真时我们可能对模型作了一些假设和近似或忽略了实际系统可能受到的扰动和噪声,这样造成仿真与实际应用相脱节。
RTW的产生解决了这个问题,RTW支两种类型的实时目标设计[2]:一种是快速原型化目标设计,另一种是嵌入式目标设计。
所谓快速原型化目标设计又叫半实物仿真,就是指可以用Simulink设计出来的控制器直接去控制实际的被控对象,通过半实物仿真过程来观察控制效果,如果控制效果不理想,则可以直接在Simulink上调整控制器的结构或参数,直至获得满意控制结果。
这样调试好的控制器可以认为是实际控制器的原型(Prototype) ,显然此时的控制器显然要好于纯数字仿真下的控制器。

关于如何使用VC调用matlab engine编程刚开始学使用VC调用matlab engine编程的时候,遇到很多问题,就去百度找解决方法,但发现根本解决不了我的问题,因为网上大部分实例和步骤都是在matlab6.5和vc++6.0环境下完成的,但是现在我用的是matlab2010a,所以会出现很多环境配置的问题,写本文的目的是总结用我在用VC调用matlab engine编程过程中出现的问题和解决办法。
Matlab Engine 采用Client/Server的方式,通过ActivcX通道和Matlab接口来实现在VC编程环境中直接调用matlab中的指令。
调用使用的函数是:engEvalSting。
下面是自己的实践过程:如果是第一次使用,则要设置一下Visual C++6.0 编程环境中的include 和lib的路径指向。
我的matlab2010安装在D盘目录D:\MATLAB 2010一、设置VC相关属性。
(1)Visual C++6.0 编译环境的设置:通过菜单 Tools/ Options,打开Visual C++6.0设置属性页,进入 Directorie页面,在 Show Directories for 下拉列表中选择Include Files,添加路径:D:\MATLAB 2010\extern\include (这是我电脑中Matlab的安装路径);再选择下拉列表中的 Library Files,添加路径:D:\MATLAB 2010\extern\lib\win32\microsoft(我电脑中Matlab 的安装路径,但是在我查看资料的时候看到很多是D:\MATLAB2010\extern\lib\win32\microsoft\msvc60这个路径,但是我用的是MatlabR2010a,msvc60是matlab6.5老版本才有的,10.0版本没有这个文件,所以我们把路径设到D:\MATLAB 2010\extern\lib\win32\microsoft 就可以了)。

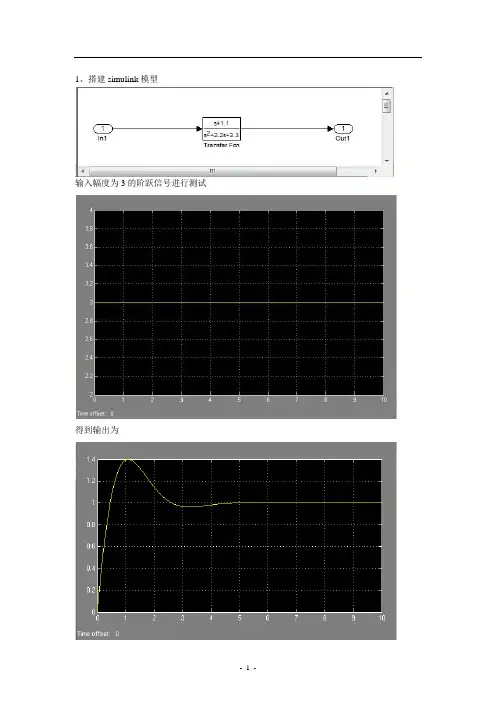
1、搭建simulink模型输入幅度为3的阶跃信号进行测试得到输出为2、设置matlab新安装的matlab及vc,需要进行配置,在matlab窗口中输入mex –setup按提示进行默认配置即可。
3、设置仿真参数4、生成c代码生成文件在matlab当前目录下model_grt_rtw文件夹下5、新建vc工程(windows窗体程序)添加模型源文件(由simulink模型自动生成的)6、设置vc环境添加matlab相关文件引用7、项目属性设置对新增加的c源文件,修改预编译头工程属性8、文件修改model.h中增加//added by clh/////////////////////////////// extern void MdlOutputs(int_T tid);extern void MdlUpdate(int_T tid);extern void MdlInitializeSizes(void);extern void MdlInitializeSampleTimes(void); extern void MdlInitialize(void);extern void MdlStart(void);extern void MdlTerminate(void);extern RT_MODEL_model *model(void);///////////////////////////////////////////使用函数的文件(form1.h)中增加引用extern"C"{#include"model.h"#include"model_private.h"//#include "model_types.h"//#include "rtwtypes.h"//#include "rtmodel.h"//#include "rt_nonfinite.h" }Button按钮处理中增加得到输出结果结果一致。
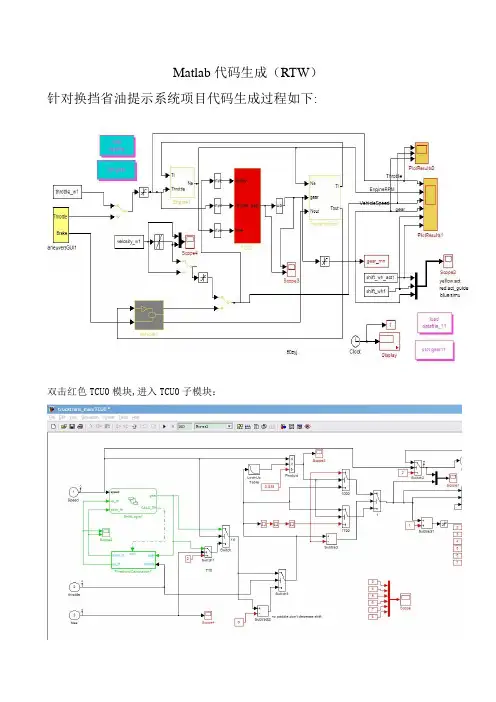
Matlab代码生成(RTW)针对换挡省油提示系统项目代码生成过程如下:双击红色TCU0模块,进入TCU0子模块:选择Simulation/Configuration Parameters,打开配置参数界面:配置Solver,选择Fixed—step,因为是离散变量操作;解码器Solver选择ode1(Euler),Fixed-step size选择0。
004(4ms),与单片机执行周期对应;Tasking mode for periodic sample times:选择SingleTasking配置Hardware Implementation:选择Infineon C16xReal—time Workshop配置:系统目标文件选择ert.tlc;Language:选择C;使能生成文件Generate makefile;Make command:make_rtw;Template makefile:ert_default_tmfReport:配置为全部使能参数配置完成后,然后,主要对TCU模块进行定点数转换,右键TCU模块,选择Fixed-Point/Fixed-Point Advisor选择Run/Run to failure,会自动进行定点数转换检测定点数检测完成后,右键TCU模块,选择Real-Time Workshop/Build Subsystem点击Build后,会自动生成代码,产生代码生成报告:代码会保存在相应的目录下:双击打开TUC0_ert_rtw,将代码生成的C文件,HEX文件添加到单片机Keil程序中:最后6个文件为matlab代码生成的头文件和C文件.然后在单片机头文件中,调用一下四个头文件:那么Keil编译是肯定能通过的。
生成代码在程序中调用:首先在初始化程序中,调用TCU0_initialize(0),来完成生成代码的初始化过程。
在主程序中,每次给TCU0_U.Speed(车速),TCU0_U.throttle(油门开度),TCU0_U.Nee(转速)重新赋值,车辆上这三个值可以周期性的通过CAN采集到,然后通过生成代码TCU0_step()计算,便可得出期望档位TCU0_Y。

使用MATLAB Engine实现与C混合编程(五)引擎应用程序1、简介引擎应用程序的实质是把MATLAB做为一个引擎,它允许从你自己的C++程序调用这个引擎。
在运行时,引擎作为一个进程单独运行,你的C++程序也作为一个进程单独运行,二者可以通过进程间的通信机制进行交互。
2、引擎库MATLAB引擎库包含了若干个控制MATLAB引擎的函数,如下所示:engOpen 启动MATLAB引擎engClose 关闭MATLAB引擎engGetArray 从MATLAB引擎中获取一个MATLAB矩阵engPutArray 向MATLAB引擎发送一个MA TLAB矩阵engEvalString 执行于一个MATLAB命令engOutputBuffer 创建一个存储MATLAB文本输出的缓冲区同时,引擎应用程序还可以使用前面提到的API函数。
3、一个例子从这个示例中,我们看出引擎应用程序是如何编制的:/** engdemo.c* This is a simple program that illustrates how to call the* MATLAB engine functions from a C program.*/#include#include#include#include "engine.h"#define BUFSIZE 256int main(){Engine *ep;mxArray *T = NULL, *result = NULL;char buffer[BUFSIZE];double time[10] = { 0.0, 1.0, 2.0, 3.0, 4.0, 5.0, 6.0, 7.0,8.0, 9.0 };8.0, 9.0 };6-6/** Start the MATLAB engine locally by executing the string* "matlab".* To start the session on a remote host, use the name of* the host as the string rather than \0* For more complicated cases, use any string with whitespace,* and that string will be executed literally to start MATLAB.*/if (!(ep = engOpen("\0"))) {fprintf(stderr, "\nCan't start MATLAB engine\n");return EXIT_FAILURE;} /*启动MATLAB引擎*//** PART I* For the first half of this demonstration, we will send data* to MATLAB, analyze the data, and plot the result.* Create a variable for our data.*/T = mxCreateDoubleMatrix(1, 10, mxREAL); /*创建一个矩阵*/mxSetName(T, "T"); /*设置矩阵的名字为“T”*/memcpy((void *)mxGetPr(T), (void *)time, sizeof(time)); /*向矩阵“T”赋值*//** 把矩阵“T”置入MATLAB引擎*/engPutArray(ep, T)/** Evaluate a function of time, distance = (1/2)g.*t.^2* (g is the acceleration due to gravity).*/engEvalString(ep, "D = .5.*(–9.8).*T.^2;");/*执行MATLAB 命令:D = .5.*(–9.8).*T.^2;*//** 绘制图象.*/engEvalString(ep, "plot(T,D);"); /*执行MA TLAB命令:绘图*/engEvalString(ep, "title('Position vs. Time for a fallingobject');"); /*执行MATLAB命令:给图象加标题*/engEvalString(ep, "xlabel('Time (seconds)');"); /*执行MATLAB命令:设置X轴坐标*/ engEvalString(ep, "xlabel('Time (seconds)');"); /*执行MATLAB命令:设置X轴坐标*/ engEvalString(ep, "ylabel('Position (meters)');"); /*执行MATLAB命令:设置Y轴坐标*//** Use fgetc() to make sure that we pause long enough to be* able to see the plot.*/printf("Hit return to continue\n\n");fgetc(stdin);/** We're done for Part I! Free memory, close MATLAB engine.*/printf("Done for Part I.\n");mxDestroyArray(T); /*从内存中撤销矩阵“T”*/engEvalString(ep, "close;"); /*关闭刚才显示图象的窗口*//** PART II* For the second half of this demonstration, we will request* a MATLAB string, which should define a variable X. MATLAB* will evaluate the string and create the variable. We* will then recover the variable, and determine its type.*//** Use engOutputBuffer to capture MATLAB output, so we can* echo it back.*/engOutputBuffer(ep, buffer, BUFSIZE); /*构建MATLAB文本输入缓冲区*/while (result == NULL) {char str[BUFSIZE];/** Get a string input from the user.*/printf("Enter a MATLAB command to evaluate. Thiscommand should\n");printf("create a variable X. This program will thendetermine\n");printf("what kind of variable you created.\n");printf("For example: X = 1:5\n");printf(">> "); /*要求用户输入一个MATLAB命令*/fgets(str, BUFSIZE–1, stdin); /*获得用户输入*//** Evaluate input with engEvalString.*/engEvalString(ep, str); /*执行用户输入的MATLAB命令*/engEvalString(ep, str); /*执行用户输入的MATLAB命令*//** Echo the output from the command. First two characters* are always the double prompt (>>).*/printf("%s", buffer+2); /*显示该MATLAB命令的执行情况*//** Get result of computation.*/printf("\nRetrieving X...\n");if ((result = engGetArray(ep,"X")) == NULL)/*判断是否可以从MATLAB 引擎中获得矩阵“X”*/printf("Oops! You didn't create a variable X.\n\n");elseprintf("X is class %s\t\n", mxGetClassName(result));/*显示矩阵“X”的类型*/} /* while(result==NULL)*//** We're done! Free memory, close MATLAB engine and exit.*/printf("Done!\n");mxDestroyArray(result); /*从内存中撤销矩阵“T”*/engClose(ep); /*关闭MATLAB引擎*/return EXIT_SUCCESS; /*返回*/}4、引擎应用程序的编译对于象上例中的控制台程序,可以在MATLAB命令行中直接使用带-f参数的mex命令编译。


文章编号:1003-1251(2005)04-0043-03基于M AT LAB /RT W 的车载无刷直流电机调速系统代码自动生成吴志红,孙 萌,毛明平(同济大学,英飞凌2同济微控制器与嵌入式系统实验室,上海200092)摘 要:介绍了一种根据系统仿真模型自动生成嵌入式C 代码的嵌入式系统设计方法.结合基于英飞凌C164C I 微控制器的车载无刷直流电机调速系统的开发,详细说明了使用MAT LAB /RT W (实时代码工作空间)工具集将系统仿真模型自动转换为嵌入式系统C 代码并编译下载到微控制器中运行的方法.还对仿真和实验数据进行了比较分析.结果表明,系统实际运行结果与仿真结果之间具有很高的相似性,从而验证了自动生成代码的正确性和可靠性.关键词:MAT LAB /RT W 实时代码工作空间;C164C I ;代码自动生成;车载无刷直流电机调速系统中图分类号:T M38314 文献标识码:A收稿日期:2005-04-26作者简介:吴志红(1961—),男,浙江宁波人,教授,博士生导师1 传统的嵌入式系统开发方法将系统设计与代码实现分开,开发周期长,已经不能满足市场的要求.本文结合基于英飞凌C164C I 微控制器的车载无刷直流电机调速系统的开发,利用MAT LAB /RT W 工具集将SI M UL I N K 仿真模型自动转换为嵌入式C 代码并自动编译下载到微控制器中,从而实现系统设计和代码实现的统一,可缩短开发周期,降低开发成本,可以快速地适应市场对新型车辆电气传动设备的需求[1].1 微控制器代码自动生成与下载流程 基于MAT LAB /RT W 工具集的微控制器代码开发流程如图1所示. 首先在MAT LAB /SI M UL I N K 可视化平台下搭建系统模型,然后通过MAT LAB /RT W 工具集生成面向微控制器编译器(这里为TaskingC166)的C 代码,并进一步编译,链接和下载,在微控制器上测试运行,完成系统实现.从整个过程来看,设计人员在只需要在图形化建模和仿真环境中,搭建系统SI M UL I N K 模型,图1 基于MAT LAB /RT W 工具集的微控制器代码开发流程图完成系统的设计.使用微控制器代码的全自动化生成技术,开发者不需要书写任何代码,即可获得准确并高度优化的微控制器代码.2 无刷直流电机调速系统双闭环控制策略的代码自动生成 现代汽车,尤其是高档轿车对电传动系统快速响应能力要求极高,因此车载无刷直流电机调速系统通常采用双闭环控制,内环是调节电流的第4期 吴志红等:基于MAT LAB /RT W 的车载无刷直流电机调速系统代码自动生成电流环,外环是调节转速的转速环.车辆中工作环境恶劣,用于位置检测的霍尔传感器的信号经常会受到干扰,因此位置检测采用无传感器方案,通过检测电机定子反电动势过零点获得转子位置信息,从而同步导通逆变器开关管[2].系统框图如图2所示.图2 车载无刷直流电机无位置传感器双闭环调速系统框图 在系统设计和仿真结束后,用户只需要完成2步操作就可实现双闭环控制器的代码自动生成:设置SI M UL I N K 仿真变量属性和设置RT W 选项.图3给出双闭环控制策略的SI M UL I N K 仿真框图.图3 无刷直流电机双闭环数字P I 控制器仿真框图2.1 设置S I M U L I NK 仿真变量属性用户根据实际需要和微控制器的数据处理能力,在SI M UL I N K 仿真界面中设定仿真变量的输入输出属性和数据字长.例如,图3中s peed_com 2mand 变量代表调速系统的转速给定,在实际系统中由C164C I 内的10位A /D 转换器通过读取电位计的电位信号获得,因此设置为16位整型(int16_T );s peed_feedback 变量表示转速传感器(这里是光电编码器)传回的转速反馈值,根据调速系统的额定转速和光电编码器的参数将其设置为无符号16位整型(uint16_T );代表逆变器直流母线电流的current_feedback 变量,根据A /D 转换器的精度将其设置为无符号16位整型(uint16_T );输出变量u_this 表示脉宽调制信号(P WM )的占空比,根据微控制器P WM 信号发生器的特性将其设置为16位无符号整型(uint16_T ).2.2 设置RT W 选项用户需要完成以下设定:选择目标语言编译器(T LC ):目标语言编译器将SI M UL I N K 仿真框图转换为面向特定编译器的嵌入式C 代码.车载无刷直流电机调速系统采用C164C I 微控制器,相应的目标语言编译器是c166.tlc .指定编译引导文件:编译引导文件是一个用M 语言编写的函数,作用是指明底层驱动函数库所在的路径,并将其以参数的形式传递给RT W.代码优化:用户通过这个选项选择是否在代码自动生成的过程中对代码进行优化,如对定点运算进行自动标定.开发实践表明:在需要进行大量运算的场合,如电气传动系统开发中,经过优化的代码的运行效率完全可以和手工编写的代码相媲美.关联底层驱动函数:用户通过"include input/out put driver functi on hooks"选项将C164C I 微控制器底层驱动函数库中的输入输出设备驱动代码自动添加到生成的代码中.指定RT W 操作(Build Acti on ):用户指定用何种方式运行自动生成的16进制代码.共有两种方式:下载到目标硬件中运行(Downl oad and Run )和在离线仿真器中运行(Run in Si m ulat or ).3 自动生成代码的仿真与实际运行测试结果 用户完成相应配置后,点击"Build"按钮,自动生成代码完成后,可以在MAT LAB 命令窗口看到如下信息:###Created executable:Double Loop.hex ###Successful comp leti on of C166Real 2Ti m e・44・沈阳理工大学学报 2005年Target build p r ocedure f or model:Double Loop 为了验证自动生成的代码,实验中将微控制器的实际运行结果保存下来,通过串行口读取到PC机中绘出曲线并同仿真结果进行比较,图4和图5分别是给定转速800r/m in条件下的转速阶跃相应仿真曲线和实际运行曲线:图5 转速阶跃响应实际运行曲线图4 转速阶跃响应仿真曲线 比较结果显示:系统仿真结果和根据仿真模型生成的控制器代码的执行结果在动态响应和稳态响应指标上非常接近;实验同时表明:可以在Si m ulink仿真平台上方便地调整参数、修改算法并可立即在实验平台上运行验证,从而高效快捷地贯彻设计人员的意图.自动生成的代码在无刷直流电机双闭环P I控制器中的实际运行结果表明:微控制器各项控制功能均能够正常实现,系统运行结果和仿真结果接近,多次实验表明,自动生成的代码运行可靠,效率很高.4 结束语 实践表明,采用RT W代码自动生成技术极大的加快了车载无刷直流电机调速系统的开发进程.运行测试证实:调速系统性能达标,自动生成代码的可靠性和效率完全可以得到保证.代码自动生成技术在车载无刷直流电机调速系统开发项目中的成功应用为实现嵌入式系统的自动化开发提供了一条新思路.参考文献:[1]杨涤.系统实时仿真开发环境与应用[M].北京:清华大学出版社,2002.[2]Robert Bosch G mbH.Aut oelektrik,Aut oelektr onik[M].B raun2schweig:V ieweg Verlag,2002.[3]陈伯时.电力拖动自动控制系统[M].北京:机械工业出版社,2000.[4] B.K.Bose.Modern Power Electr onics and AC D rives[M].En2gle wood:Prentice Hall,2002.Auto ma ti c Code2Genera ti on of Veh i cle2ba sed BrushlessDC M otor Speed Regul a ti on System Usi n g M ATLAB/RT W ToolsWU Zhi2hong,S UN Meng,MAO M ing2p ing(I nfineon2Tongji Aut omotive Electr onics Lab,Tongji University,Shanghai200092,China)Abstract:Trying t o m ini m ize the ti m e consu mp ti on and cost of the whole p r oduct,this paper intr oduces a ne w devl opment p r ocedure,based on the MAT LAB/RT W which aut omatically converts the contr oller si m ulati on model int o e mbedded C codes and aut omatically comp iles and downl oaded int o the target contr oller,using the C164C Im icr ocontr oller,t o drive a brushless DC mot or used in the vehicle electrical drive syste m.Experi m ent indicates a satisfact ory coincidence bet w een si m ulati on and experi m ental results,which verifies the validity and reliability of the p r oposed p r ocedure.Key words:MAT LAB/RT W;C164C I;aut omatic code generati on;vehicle2based brushless DC mot or s peed regulati on syste m・54・第4期 吴志红等:基于MAT LAB/RT W的车载无刷直流电机调速系统代码自动生成。
2017-2018学年第一学期研究生课程拟聘助教名单公示根据《北京航空航天大学研究生“三助”聘用工作暂行规定》(北航人字[2005]44号)的相关要求,本学期拟聘用以下人员为助教,名单如下:学院代码课程代码课程名称审批数拟聘助教姓名拟聘助教培养学号1 011705 先进结构材料特色实验 1 尚勇BY1401118 011302 材料近代测试方法 1蒋亚绿SY1601132董莹BY1601128张潇BY1401134 011309 材料科学与工程学科综合课(博)0.5 赵芊SY17013301 王景景SY1701235 011709材料腐蚀失效与表面防护技术特色试验1刘腾义BY1401115冯晨旭ZY1601117 011305 材料热力学与动力学 1 秦芳彧BY1501150 011703先进树脂基复合材料制造和模拟特色试验0.5孙林凤ZY1601220于冰ZY16012352 001703 通信与信息技术综合实验 3王娜SY1602111林志兴SY1602307王红林SY1602123 021538 卫星导航0.25 张航SY1602504 021302 线性系统理论0.25 岳振宇ZY1602305 021308 检测、估计与调制理论 1.25周锐BY1502123张旭旺BY1402151 001213 矩阵理论 2赵飞ZY1502321莫德森ZY1502212 021312 数字图像处理与识别0.5 李家钰ZY1602108 021560 智能优化方法0.5 席星BY1602107 021399 科学写作与报告 1 杨朋BY1402136 021311 现代空中交通管理 1 刘钊瑄BY1602108 021550 密码学与网络安全 1 张妍婷BY1702134021301 随机过程理论 2 孙利伟BY1502164 021555 信息系统安全概率0.25 陈星月SY16024163 031201 矩阵理论1 邵鹏飞SY16031171 薛蔚敏SY16091461 叶倩文SY15091451 徐加欢SY1603209 031553 虚拟现实技术及应用0.50 王佳楠SY1603518 031519 计算智能0.50 乔美娜ZY1603202 031710基于matlab RTW/ENGINE的建模仿真实验0.50 闫培SY1603707 031301 线性系统0.50 于灏BY1503154 001714 ARM9嵌入式系统实验0.50 赵树磊SY16036104 041301 粘性流体力学 1 候杰萱BY1704146 041538 现代测试技术与数据处理 1 赵连鹏BY1604159 041713 小型航空发动机整机试验 1 刘臣BY1704139 041701 现代流体测试技术综合实验 1 张秉龙BY1404131 041399 科学写作与报告 1 唐幸炎SY16043095 051311 现代控制理论及应用B 1.5 黄园园ZY1605126 051709 飞行力学实验Ⅰ(飞行原理)0.5 陈石SY1605302 051301 现代力学基础0.5 康清亮ZY1505132 051702 固体力学实验Ⅱ0.5 王博BY15051430.5 池宇希BY1705144 051501 疲劳强度0.5 隗依岸SY1705411 051313 飞行器气动设计理论与方法0.5 王泽溪BY1505177 051506 隐身原理0.5 姜家新ZY1605128 051312 飞行力学理论及应用0.5 张程ZY1605408 051526 直升机空气动力学0.5 聂文松BY17051116 061315 计算机科学与技术学科综合课 1 王嘉豪BY1706129 061507 信息系统集成技术 1 谢志普BY1506143 061308 程序设计语言原理 1 王晴SY1606103 061302 算法设计与分析 3 王吉平ZY1606304郭炜锋SY1606324 061305 新型计算机网络 1王迪ZY1606506周红刚ZY1606519061701/ 067701 计算机网络与通信实验 4刘竟爽SY1606404李若巍ZY1506307任洪森ZY1606509韩京飞SY16064057 001732 三维CAD软件建模试验 3王添BY1507149闫守鑫ZY1607316陈洋ZY1607324 071318 热制造学基础 1 王月BY1707148 071509 智能控制及其应用 1 梁凯ZY1607504 071536 海洋工程概论 1 谢东健SY1607103 071304 计算机软件技术基础 1 刘磊SY1607424 071510 现代无损检测技术 1 李文涛BY1507107 071701 单片机系统实验 1 王琛ZY16075128 001902 经济学思想0.5 金佳宇BY1708114 081303 高等数学规划0.5 王蒙BY1708137 081301 高级微观经济学 1 唐启鑫SY1608202 081305 应用计量经济学 1 秦鹏BY16081219091304 抽象代数Ⅱ0.5 栾伟BY1709103 091308 微分流形0.5 孟梦SY1509126 091307 微分方程数值解1 王坤BY1109112 091399 科学写作与报告091301 实分析0.5 聂媱BY1609116001201/001202数值分析A/数值分析B 8李源SY1709117李浩楠SY1609114赵小明SY1609115徐涛BY1609107陈莉BY1709119 甄玉青SY1709154 李清意SY1709116001203/ 001204 矩阵理论A/矩阵理论B 5黄子晏SY1509116李灵SY1509119彭真SY1709129王龙飞BY1509101李将SY1609116001205/ 001206 数理统计A/数理统计B 11张璐SY1509159谢文俊SY1309144吴静SY1609165杨玉鑫SY1709158曹雅茹SY1609104牛璐BY1609114刘学SY1709123姜艳梅SY1609113刘宗南SY1609126石颖SY1709131冯昊翔SY1609109001209 应用泛函分析 4 丁思静SY1609106 吴祖平SY1609143 聂媱BY1609116 赵梦婷SY160915810 101501 人体功效学0.4 路艳艳SY1710141 101505 植介入医疗器械与人工器官101301 生物医学工程前沿0.5 廖婕SY16101110.4 崔洋洋ZY1710104 101705 生物技术实验0.5 赵莹彤SY16102320.4 李钱SY1710132103307 高级生物力学0.5 张亚星SY16102250.4 田原SY1710209 101514 医学新进展及专题讲座 1 姜桂爽SY1710237 104306 高级解剖生理学0.45 刘美君SY1710136 101310 空天生理学及医学工程(引智)0.45 代晓景ZY171010511 111535 航空航天发展研究0.5 李桓峰SY1611202 111324 定量研究方法与建模0.5 王雪晴SY1611122 111320 组织管理学0.5 韩亦姣SY1511105 111525 治理理论专题0.5 候静文SY1611107 001903 人文专题课:高技术战略与管理0.5 宋承霖ZY1711207 001904人文专题课:宏观经济政策与中国工业发展0.5 吴玥乐SY161121412 001132/001121英语一外(硕/博)14何丹丹ZY1712409葛宇ZY1712404马玥SY1712105程酩纳SY1612104王敏洁SY1712313王婷婷SY1712314白静SY1712301吴舒晴SY1712315马思清ZY1712416张丽红SY1712318赵露璐SY1712322徐甜甜SY1712317候丽娜SY1712102张睿琳SY171231914 141516 可靠性工程导论0.5 李昂SY1614125 141302 可靠性数学基础0.5 史晓SY1614201 141706 环境实测数据与实验剖面设计0.5 袁铭ZY1614219 141702 电源系统热设计实验0.5 陈亚增ZY161410415 151301 现代控制理论(Ⅱ) 1 石本可BY1715108151318 数字图像处理0.5 张蕊SY1615219 151534 模糊数学0.5 赵鹏飞SY151533017 171308 现代控制理论及方法 1 廖世刚SY1617202 171702 光电子技术实验0.5 贾永泽SY1617103 171310 新型传感技术及应用0.5 李昊予SY1617343 171516 微光机电系统0.5 刘迪ZY1617106 171707 光电仪器与测量专业实验0.5 姜梦茹ZY161712820201510 法理学 1 蒋宇凡SY1720109 001901 人文专题课:法学专题系列讲座0.5 王晋彦SY162012426 001907人文专题课:现代设计与图形创意0.5 鲁琛SY1426110 001906 人文专题课:中国绘画艺术欣赏0.5 陈子蕴SY162610328 001111 中国特色社会主义理论与实践研究6杨波SY1628106李东坤SY1728109尹笑颜SY1628105杨乔松SY1628112蔡梦迪SY1728106郑钊SY1628112青岛研究院001204 矩阵理论B 1郑坚ZY1717420米致远ZY1717417 001112 自然辩证法概论0.5 黄乐政ZY1713409 001111中国特色社会主义理论与实践研究0.5 张学东ZY1707616 公示时间为:2017年10月25日—2017年10月31日,单位和个人可以通过电话反映问题。
利用MATLAB-RTW移植发动机控制系统的方法与实践岳龙;赵民德;吴朝晖
【期刊名称】《系统仿真学报》
【年(卷),期】2005()z2
【摘要】介绍使用MATLAB中的Real-Time Workshop解决汽车电子问题的成功经验.以前的发动机控制程序只能运行于单一的ECU平台,而且没有实时操作系统的支持.首先利用Simulink成功的继承了以前的发动机控制算法代码,然后通过自动代码生成过程,为不同平台(包括一款符合OSEK标准的操作系统)生成了C代码,最终利用第三方编译工具生成了可执行代码,成功完成了对发动机喷油和点火的控制过程.由于得到RTW的帮助,整个移植过程只用了一个月的时间,而且生成的可执行程序运行稳定.
【总页数】4页(P27-30)
【关键词】自动代码生成;OSEK标准;ECU;移植
【作者】岳龙;赵民德;吴朝晖
【作者单位】浙江大学,杭州,310027 浙江大学,杭州,310027 浙江大学,杭
州,310027
【正文语种】中文
【中图分类】TP391.9
【相关文献】
1.利用数据流分析发动机控制系统软故障 [J], 陈强
2.利用故障诊断仪对发动机电子控制系统进行故障诊断 [J], 王金金
3.利用旁通空气的摩托车发动机怠速控制系统研究 [J], 吴锋;杨志家;潘胜军
4.利用发动机速度变化进行工作的A/F稀限控制系统 [J], 为名.,T;李亚兴
5.利用故障码及数据排除发动机控制系统故障 [J], 曹守军
因版权原因,仅展示原文概要,查看原文内容请购买。
RTWT操作步骤准备工作:确认已经安装好了C编译器,以及kernel。
C编译器的安装:在matlab命令栏中输入:mex -setup,根据步骤提示进行安装。
Kernel的安装:在matlab命令栏中输入:rtwintgt -install,根据步骤提示进行安装。
可以选择测试例子。
rtvdpRTWT操作步骤:一、建立Simulink模型1.创建simulink模型(1)从MATLAB命令行下输入如下命令,生成一个路径:!mkdir f:\rtwin_model_example(2)将路径ext_mode_example设为当前工作路径:cd f:/rtwin_model_example(3)建立Simulink模型rtwin_mode_exampl e如下,并将其存储为rtwin_model.mdl.信号发生器与传递函数的设置如下:2.仿真参数的设置打开Simulation| Configuration Parameters对话框,设置仿真参数如下:Solver选项卡:设置Type为Fixed_step,并选择ode5(Dormand-Prince)算Fixed step size:0.001 , Mode设置为:Single Tasking。
3.示波器参数的设置在模型rtwin_model中,双击打开Scope模块窗口,单击Parameters按钮,Scope的属性设置及图形窗口的坐标设置如下:最后存盘。
4.运行一个非实时的Simulink仿真,观察输出。
二、实时应用1. 设置实时的仿真参数打开Simulation | Configuration Parameters对话框。
单击Real-Time Workshop选项卡。
对Real– Time Workshop列表分别进行如下设置:①选定Target selection选项,单击Browse按钮打开系统目标文件浏览器,选定Real-timewindows target选项,并单击OK按钮。
如何在C/C++语言里调用Matlab引擎(engine)——(上篇)windows下的Visual C++平台Windows下调用Matlab引擎要做好以下三点设置(1)设置头文件目录(2)设置库文件目录,并添加链接库输入项libeng.lib和libmx.lib(3)设置环境变量以下以Visual Studio 2008为例来说明如何设置这三点:1、添加头文件目录依次选择:“工具”->“选项”,调出对话框后再在对话框左边“选择项目和解决方案”->“VC++目录”然后在右边选择“显示以下内容的目录”下的选框选择“包含文件”,再在目录列表的最下边空行处选中添加:matlab安装目录下的\extern\include路径比如我的是:C:\Program Files\MATLAB\R2011a\extern\include如果现在生成项目,链接将不会通过,比如可能会出现:1>engwindemo.obj : error LNK2019: 无法解析的外部符号_mxDestroyArray,该符号在函数_WinMain@16 中被引用1>engwindemo.obj : error LNK2019: 无法解析的外部符号_mxGetPi,该符号在函数_WinMain@16 中被引用1>engwindemo.obj : error LNK2019: 无法解析的外部符号_engClose,该符号在函数_WinMain@16 中被引用1>engwindemo.obj : error LNK2019: 无法解析的外部符号_engGetVariable,该符号在函数_WinMain@16 中被引用1>engwindemo.obj : error LNK2019: 无法解析的外部符号_engOutputBuffer,该符号在函数_WinMain@16 中被引用1>engwindemo.obj : error LNK2019: 无法解析的外部符号_engEvalString,该符号在函数_WinMain@16 中被引用1>engwindemo.obj : error LNK2019: 无法解析的外部符号_engPutVariable,该符号在函数_WinMain@16 中被引用等链接错误;这就需要设置下面的库文件目录2、添加库文件目录在刚才调出来的对话框中,设置库目录:选择“显示以下内容的目录”下的选框选择“库文件”添加matlab目录下的C:\Program Files\MATLAB\R2011a\extern\lib\win32\microsoft注意:如果是项目要生成的是64位程序那么应该选择的是C:\Program Files\MATLAB\R2011a\extern\lib\win64\microsoft点击确定退出对话框,然后给项目添加链接库输入项:在解决方案资源管理器里选择对应的项目单机右键选择最下面的“属性”弹出属性对话框,在右边依次选择“配置属性”->“链接器”->“输入”,然后在右边“附加依赖项”那一项加上libeng.lib libmx.lib单击确定退出注意:(1)不要删除原有的依赖项(2)依赖项之间用空格隔开做到这一步时生成时就没问题出现了,但是运行程序时会出现“因为计算机中丢失libeng.dll”等类似问题第(3)步就解决这个问题的。