CPA综合英语备考
- 格式:doc
- 大小:305.00 KB
- 文档页数:40

Accounting1.Accounting equation: Asset = Liability + Owner’s Equity2.Double entry accounting: debit (Dr) & credit (Cr)3.Historical cost, fair value, replacement cost, net realizable value, present value4.Financial statementBalance sheetAssets: cash, tradable financial assets, note receivable, accounts receivable (provision for bad/doubtful debts), prepaid accounts/prepayments/advances to suppliers, dividend receivable, interest receivable, other receivables, inventory;available-for-sale financial assets, hold-to-maturity investment, long-term accounts/note receivable, long-term equity investment, fixed assets (accumulated depreciation, impairment of fixed assets), disposal of fixed assets, construction-in-process (impairment of CIP), intangible assets (accumulated amortization, impairment), investment real estate, development expenditure, goodwill, deferred income tax assets, etc.Liabilities: short-term loan, tradable financial liability, employ compensation payable, taxes and dues payable, interest payable, dividend payable, non-current liabilities due within one year/current portion of non-current debt, accounts payable, note payable, unearned revenue/advances from customers, long-term loan, long-term payables, bonds payable, etc.Equity: paid-in capital/capital stock, capital reserves, treasury stock, surplus reserves, retained earningsIncome statementRevenue: sales (sales discount, allowance & returns, net sales), other operating incomeOperating costs: cost of goods sold/sales, other operating cost Sales tax and extra chargesOperating expenses: selling expenses, (general and) administrative expenses, interest expenses (financial expenses), impairment lossOperating incomeNon-operating income & expensesTotal profitIncome taxesNet income/profitStatement of cash flowscash flow from operating activities: direct method and indirect methodcash flow from investing activitiescash flow from financing activities5.CashCash in bankBank reconciliation6.ReceivablesAccounts receivables, notes receivables, other receivablesUncollectible receivables: factoringAllowance method: allowance for doubtful accountsEstimate based on a percentage of salesEstimate based on analysis of receivablesThe direct write-off method7.Inventory: period method vs. perpetual methodMaterials, WIP (work-in-process), finished goods, etc.FIFO (first-in first-out), the specific identification method, (moving) weighted average methodLower of cost or net realizable value method, provision for inventory impairment8.Fixed assets & intangible assetsFixed assetsDepreciation expenses, accumulated depreciation: original cost, residual value, useful/estimated lifeStraight-line method/average methodUnits-of-production methodDouble declining-balance methodSum-of-the-years-digits methodCapital expenditure vs. revenue expenditureFixed assets disposal: discarded, sold, traded/exchanged Gain/loss on disposal of fixed assetsIntangible assetsAmortizationR&D (research and development)9.Owner’s equityPaid-in capitalcommon stock, preferred stockcash dividend, stock dividend, stock split10.Foreign currency11.Business combination12.Lease: operating lease, financial lease13.Earnings per share会计1.会计恒等式:资产=负债+所有者权益2.复式记账法:借/贷3.历史成本,公允价值,重置成本,可变现净值,现值4.财务报表资产负债表资产:货币资金, 交易性金融资产,应收票据,应收账款(坏账准备),预付账款,应收股利,应收利息,其他应收款,存货,可供出售金融资产,持有至到期投资,长期应收账款/票据,长期权益投资,固定资产(累计折旧,固定资产减值),固定资产清理,在建工程(在建工程减值),无形资产(累计摊销,减值),投资性房地产,开发支出,商誉,递延所得税资产,等负债:短期贷款,交易性金融负债,应付职工薪酬,应付税费,应付利息,应付股利,一年内到期的非流动性负债,应付账款,应付票据,预收账款,长期贷款,长期应付款,应付债券,等权益:实收资本/股本,资本公积,库藏股,盈余公积,未分配利润/留存收益利润表/损益表营业收入:主营业务收入(销售折扣、折让和退回,销售收入净额),其他业务收入营业成本:主营业务成本,其他业务成本销售税金及附加营业费用:销售费用,管理费用,财务费用,减值损失营业利润营业外收支利润总额所得税净利润现金流量表经营活动所产生的现金流量:直接法和间接法投资活动所产生的现金流量筹资活动所产生的现金流量5.货币资金银行存款银行存款余额调节表6.应收款项应收账款,应收票据,其他应收款不可收回应收账款:应收账款让售备抵法:坏账准备销售收入占比法应收账款分析直接转销法7.存货:定期盘存制vs.永续盘存制原材料,在产品,产成品,等先进先出法,个别计价法,(移动)加权平均法成本与可变现净值孰低法,存货跌价准备8.固定资产和无形资产固定资产折旧费用,累计折旧:固定资产原值,残值,可使用年限直线折旧法/平均年限法工作量法双倍余额递减法年数总和法资本性支出 vs. 收益性支出固定资产处置:报废,出售,转让固定资产处理收益/损失无形资产摊销研发支出9.所有者权益实收资本普通股,优先股现金股利,股票股利,股票分割10.外币11.企业合并12.租赁:经营租赁,融资租赁13.每股收益。

2019年注册会计师考试辅导会计英语第五章股份支付随着各公司股权激励机制的推行,股份支付的会计处理成为近年考试的热点。
从历年专业阶段考试情况来看,主要会考查两种股份支付方式下对报表项目的影响,具有一定的综合性。
在复习时应重点把握权益结算的股份支付和现金结算的股份支付以及集团内股份支付的处理。
I. 权益结算的股份支付的确认和计量Recognition and Measurement of Equity-settled Share-based Payments以权益结算的股份支付换取职工提供服务的,应当以授予职工权益工具的公允价值计量。
The equity-settled share-based payment in return for employee services shall be measured at the fair value of the equity instruments granted to the employees.II. 现金结算的股份支付的确认和计量Recognition and Measurement of Cash-settled Share-based Payment以现金结算的股份支付,应当按照企业承担的以股份或其他权益工具为基础计算确定的负债的公允价值计量。
A cash-settled share-based payment shall be measured in accordance with the fair value of liability assumed by the enterprise which is calculated and recognized based on the shares or other equity instruments.III. 集团股份支付的处理Accounting Treatment of Group Share-based Payments企业集团(由母公司和其全部子公司构成)内发生的股份支付交易,应当按照以下规定进行会计处理:Share-based payment transactions which occur within the group (parent company and all its subsidiaries) should follow the accounting treatments below:(一)结算企业以其本身权益工具结算的,应当将该股份支付交易作为权益结算的股份支付处理;除此之外,应当作为现金结算的股份支付处理。

注册会计师英语复习笔记-词汇总论一、注会财经专业英语考试趋势及规律简要总结1.中国注册会计师考试加强对财经专业英语的考查力度已成为不可逆的大趋势。
2.相对“宽进严出”的“6+1”考试模式,作为收官之战的综合阶段考试对财经专业英语的考查力度不断加强,不但是100分以内的必答题,而且分值比重连年增加。
财经专业英语已成为广大注会学员能否最终修成“正果”,如愿拿到注会证书的一大挑战。
3.财经专业英语考查形式的层次感逐渐清晰,“两极分化”趋势明显,即:专业阶段对财经专业英语的考查形式为“中文读题英文答题”,综合阶段则为“英文读题英文答题”,对读、写、译的要求更为全面。
4.从2010年至今,综合阶段财经专业英语共计考查三年,加之样题,目前可以据此总结出一些基本规律,作为我们备考的参考。
这些规律主要涉及:考查形式、知识覆盖面、答题字数要求、表达方式要求、答题思路、文体要求等等。
所有上述这些内容,包括历年考题在内,在稍后的针对综合阶段的《财经英语》课程中会给大家进行深入的分析讲解。
总结:我们现在需要考虑的已经不是学不学财经专业英语的问题了,而是要研究如何把财经专业英语学好的问题!学好财经专业英语具有必要性(为了拿证书)、迫切性(时间不多矣)、挑战性(学起来不容易)、技巧性(要有正确的方法论)和实用性(不光为了应对考试,以后职场竞争、教育孩子也用得到)!二、学好注会财经专业英语,必须首先解决思想问题“软的往往是最硬的,虚的往往是最实的!”对于广大学员来讲,学好财经专业英语,不单单是技术问题,更是思想问题!就是愿不愿学、肯不肯学的问题!1.人在矮檐下,不得不低头!你想拿中国注会证书,就必须遵循中注协制定的游戏规则,他考什么,你就学什么!任何抱怨、指责、愤怒甚至谩骂都丝毫于事无补,只能更坏了你的心绪!清净心生智慧!满心都是“恼怒烦”,怎么能够静下心来学习好英语。
2.要不畏困难!要树立信心!(1)发昏当不了死!宁可战死,也不吓死!(2)英语说白了,也是一门技能,就跟会骑自行车一样!你十年不骑自行车,让你再骑,是不是稍微熟悉下还会骑?!英语也是如此,学过了,现在创造条件重温下,会很快重拾起来的!(3)要有“四心”必须下定战胜英语的决心、树立学好英语的信心、保持学习英语的耐心、拥有坚持学习的恒心!眼光要放长远,学好英语,不光为了应对考试,而是为了提升自身的核心竞争力,获得自身职业生涯的可持续发展。

注会综合阶段备考经验分享一、学习规划注会综合阶段备考是一个相对较长且内容较多的过程,因此需要有一个合理的学习规划。
首先,要明确每个科目的重点和难点,制定相应的备考计划。
其次,要根据自己的实际情况合理安排每天的学习时间,保证高效利用每一天。
最后,要根据自己的学习进度和调整计划,及时调整学习重点和时间安排。
二、科目选择在注会综合阶段备考中,要根据自己的实际情况和兴趣选择合适的科目。
一般来说,选择自己擅长的科目作为主攻科目,同时也要选择一到两个其他科目作为辅助科目。
这样可以提高备考效率,同时也能够减少压力。
三、知识点梳理在备考过程中,要对每个科目的重点和难点进行梳理。
可以通过整理笔记、制作思维导图或使用其他方式将知识点进行归纳总结。
这样可以帮助记忆和理解,同时也方便日后的复习。
四、题目练习做题是备考的重要环节,通过做题可以提高对知识点的理解和应用能力。
可以选择一些历年真题和模拟题进行练习,同时要注意做题的方法和技巧。
在做题过程中,要注意分析题目的要求,理清思路,避免盲目猜测答案。
五、真题模拟在备考过程中,要进行真题模拟练习。
可以选择一些历年真题进行模拟考试,以检验自己的备考水平和应试能力。
通过模拟考试,可以了解自己在时间分配、答题技巧等方面的不足,并及时调整备考策略。
六、答疑解惑在备考过程中,难免会遇到一些难以理解的知识点或题目。
这时可以通过参加培训班、加入学习小组或请教老师等方式来解决问题。
同时,也可以通过互联网搜索一些相关的解答和讨论,扩大自己的知识面。
七、复习总结备考过程中,要进行定期的复习和总结。
可以每周或每个月进行一次全面复习,巩固已学知识,查漏补缺。
同时,要及时总结备考经验和方法,找到适合自己的备考方式,提高备考效率。
八、心态调整备考是一个相对较长和辛苦的过程,所以要保持积极的心态。
适当的休息和放松,可以帮助恢复精力,保持专注度。
同时,要相信自己的能力,坚持到底,相信付出总会有回报。
以上就是我在注会综合阶段备考中的一些经验分享。

CPA会计英语讲义1. IntroductionThe Certified Public Accountant (CPA) examination is a professional accounting examination held worldwide to assess the knowledge and skills of individuals aspiring to become certified accountants. This exam covers various areas of accounting and requires a strong command of both accounting principles and the English language.In this CPA Accounting English Handbook, we will provide a comprehensive guide to help you improve your English language skills and prepare for the CPA exam. This handbook is divided into several sections, each focusing on a different aspect of accounting and corresponding English terminology.2. Accounting Principles and ConceptsTo understand accounting in English, it is important to first grasp the fundamental accounting principles and concepts. This section will cover topics such as:•The basic accounting equation•Accrual vs. cash basis accounting•Revenue recognition principles•Matching principles•Types of accounts (assets, liabilities, equity, revenue, and expenses)•Financial statements (balance sheet, income statement, and statement of cash flows)It is crucial to have a solid understanding of these concepts as they form the basis of all accounting practices.3. Financial Reporting and AnalysisFinancial reporting and analysis involve the preparation and interpretation of financial statements to assess the financial performance and position of an organization. This section will cover topics such as:•Financial statement analysis•Ratio analysis•Interpretation of financial ratios•Common financial reporting issues•Key financial metricsMastering the English terminology associated with financial reporting and analysis will enable you to effectively communicate and analyze financial information.4. Management AccountingManagement accounting focuses on the preparation, analysis, and interpretation of accounting information for internal decision-making purposes. This section will cover topics such as:•Cost accounting•Budgeting and forecasting•Variance analysis•Performance measurement•Product costingUnderstanding the English terminology related to management accounting is essential for analyzing business performance and making informed management decisions.5. Auditing and AssuranceAuditing and assurance involve the examination and verification of financial statements to ensure their accuracy and compliance with accounting standards. This section will cover topics such as:•Audit planning and risk assessment•Internal controls•Audit procedures•Ethical considerations in auditing•Audit reportMastering the English language for auditing and assurance will enable you to effectively communicate audit findings and recommendations.6. TaxationTaxation is a crucial aspect of accounting, and understanding the English language associated with taxation is essential for tax planning and compliance. This section will cover topics such as:•Types of taxes•Tax planning strategies•Tax compliance•Tax deductions and credits•International taxationDeveloping proficiency in English terminology related to taxation will enhance your ability to navigate the complex world of tax regulations.7. Professional Ethics and ConductAs a professional accountant, it is important to adhere to ethical standards and mntn professional conduct. This section will cover topics such as:•Code of professional conduct•Ethical decision-making frameworks•Conflicts of interest•Confidentiality and professional secrecyMastering the English language associated with professional ethics will ensure you uphold the highest ethical standards in your accounting practice.ConclusionThis CPA Accounting English Handbook provides a comprehensive guide to improve your English language skills and prepare for the CPA exam. By mastering the English terminology associated with variousaccounting areas, you will enhance your ability to communicate effectively and succeed in your accounting career.Remember, practice is key. Continuously work on improving your English language skills through reading, listening, and speaking to confidently navigate the world of accounting in English.。

备考大学英语考试的十大技巧备考大学英语考试需要系统的学习和精心的准备。
作为考生,你可以像准备一场挑战性的旅行一样来对待这个过程。
以下是十大技巧,可以帮助你在备考过程中更加有效地提升英语水平和应对考试挑战。
首先,要像一位旅行家一样,制定一份详细的计划。
这个计划包括每天的学习时间、复习内容以及练习试题的安排。
通过规划,你可以确保每个阶段都有充足的准备时间,避免在最后关头仓促应付。
其次,建议你像一位专业运动员一样训练听力技能。
这意味着多听英语广播、影视节目和录音,提高理解能力和听取信息的速度。
通过不断练习,你可以更快速地适应考试中的听力部分。
第三,像一位探险家一样探索阅读材料。
扩展阅读能力是备考过程中不可或缺的一部分。
阅读各种英语文章和书籍,包括新闻报道、学术文章和小说,可以帮助你提升词汇量和理解能力。
第四,像一名艺术家一样练习写作技巧。
写作是考试中的一个重要部分,要能清晰地表达观点和想法。
练习写作不仅可以提高语法和拼写能力,还可以培养逻辑思维和组织文章的能力。
接下来,像一位学者一样深入研究语法知识。
英语语法虽然看似枯燥,但是它是语言的基础,对于正确表达意思至关重要。
理解基本的语法规则和常见的句型结构,可以帮助你在考试中避免常见的错误。
然后,像一名厨师一样精心准备词汇食谱。
积累和掌握大量的词汇是备考的关键之一。
通过背诵单词和短语,建立自己的词汇库,不仅可以提高听力和阅读理解能力,还能增加写作表达的丰富性。
此外,像一位演员一样练习口语表达。
口语部分要求流利和自信地表达观点,因此多与他人交流、参加英语角或进行口语模拟练习都是有效的方法。
这些练习可以帮助你在考试中更加从容地应对口语任务。
再者,像一位工匠一样打磨综合技能。
备考大学英语考试不仅要求单项技能的掌握,还需要综合能力的发挥。
因此,要定期进行模拟考试,全面评估自己的水平并找出不足之处,有针对性地进行强化训练。
最后,像一位运筹帷幄的将军一样制定应对策略。

Financial Management and Cost Management01. Financing Sources词汇:Finance lease:融资租赁Lessee:承租人Lessor:出租人Minimum lease payment:最低租赁付款额Operating lease:经营租赁Warrant:认股权证Convertible bond:可转换债券Redeemable:可赎回的Other long-term finance 其他长期筹资Finance Lease1.The lease transfers ownership of the asset to the lessee by the end of the lease term.2.The lessee has the option to buy the asset at a price expected to be lower than fair value at the time the option is exercised.3.The lease term is for the major part of the economic life of the asset.4.At the beginning of the lease, the present value of the minimum lease payments (MLPˊs)is approximately equal to the fair value of the asset.5.The leased assets are of a specialized nature so that only the lessee can use them without major modification.融资租赁:·在租赁期届满时,租赁资产的所有权转移给承租人·承租人有购买租赁资产的选择权,所订立的购买价格预计将远低于行使选择权时租赁资产的公允价值·租赁期占租赁资产可使用年限的大部分·租赁开始日最低租赁付款额的现值几乎相当于租赁开始日租赁资产的公允价值·租赁资产性质特殊,如果不做重新改制,只有承租人才能使用Warrants 认股权证Warrants is a type of certificate issued by entity to shareholders, which allows holders to purchase prescribed amount of shares at prescribed price in the given period.认股权证是公司向股东发放的一种凭证,授权其持有者在一个特定期间以特定价格购买特定数量的公司股票。
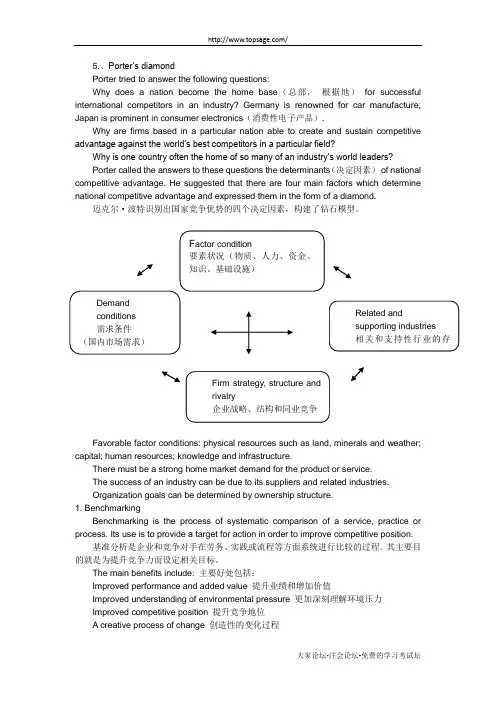
5.、Porter‟s diamondPorter tried to answer the following questions:Why does a nation become the home base (总部, 根据地) for successful international competitors in an industry? Germany is renowned for car manufacture; Japan is prominent in consumer electronics (消费性电子产品).Why are firms based in a particular nation able to create and sustain competitive advantage against the world‟s best competitors in a particular field?Why is one country often the home of so many of an industry‟s world leaders? Porter called the answers to these questions the determinants (决定因素) of national competitive advantage. He suggested that there are four main factors which determine national competitive advantage and expressed them in the form of a diamond.迈克尔·波特识别出国家竞争优势的四个决定因素,构建了钻石模型。
Favorable factor conditions: physical resources such as land, minerals and weather;capital; human resources; knowledge and infrastructure.There must be a strong home market demand for the product or service.The success of an industry can be due to its suppliers and related industries. Organization goals can be determined by ownership structure.1. BenchmarkingBenchmarking is the process of systematic comparison of a service, practice or process. Its use is to provide a target for action in order to improve competitive position. 基准分析是企业和竞争对手在劳务、实践或流程等方面系统进行比较的过程。

如何准备英语考试?备战英语考试:从策略到技巧,百炼多角度复习体系英语考试是衡量标准语言能力的重要指标,也是通往更广阔机会的桥梁。
作为教育专家,我将从多个角度,帮助大家形成一个科学、高效的英语考试备考复习体系。
一、知己知彼,百战不殆:1. 深度剖析考试大纲:弄懂吃透考试大纲,明确考试目标、题型、考察重点和评分标准。
2. 模拟试题,了解题型:做历年真题或模拟试题,了解考试难度、节奏和答题技巧。
3. 分析自身优势与劣势:自我评估,找到自身薄弱环节,制定并执行针对性备考策略。
二、夯实基础,打好学习根基:1. 词汇积累,厚积薄发:掌握核心词汇和常用短语,并进行反复练习和运用。
2. 语法精进,灵活运用:从基础语法规则开始学习,逐步理解并掌握语法应用场景。
3. 阅读理解,提升逻辑:培养和训练逻辑思维能力,善于分析文章结构、提取关键信息和推测文章主旨。
4. 听力训练,增强敏感度:多听英语材料,训练听力理解能力,增强对英语语音和语调的敏感度。
5. 口语表达,多说多练:多练习口语表达,提升流利度和准确性。
三、掌握方法,高效复习准备:1. 合理安排时间,制定科学计划:将备考目标细化分解,制定合理的学习计划,避免学习无序。
2. 精炼笔记,高效系统复习:课堂笔记简洁明了,便于后期复习,重点内容可整理和综合归纳。
3. 错题集锦,查缺补漏:记录错题,分析错误原因,并进行针对性练习,避免重复错误。
4. 寻求帮助,突破瓶颈:面临学习难题,主动寻求教师、同学或专业辅导机构的帮助。
5. 保持积极心态,战胜考前焦虑:保持自信,合理调节情绪,避免过度紧张或焦虑,以最佳状态迎接考试。
四、考试技巧,提升应试能力:1. 合理分配时间,掌控答题节奏:提前规划好答题时间,避免时间分配不均,影响答题效率。
2. 由易到难,稳步前进:遇到难题不要慌乱,先做基础题,建立自信,再攻克难点。
3. 审题细致,避免误解:认真阅读试题,理解题意,尽量减少因理解偏差而导致答题错误。

cpa综合阶段英语作答英文回答:The CPA exam is a standardized test administered by the American Institute of Certified Public Accountants (AICPA) to individuals who wish to become certified public accountants (CPAs). The exam is divided into four sections: Auditing and Attestation (AUD), Business Environment and Concepts (BEC), Financial Accounting and Reporting (FAR), and Regulation (REG). Candidates can choose to take the exam in either English or Spanish.There are several advantages to taking the CPA exam in English. First, English is the language of business in the United States and most other countries around the world. This means that CPAs who are proficient in English will have a wider range of job opportunities available to them. Second, the CPA exam is written in English, so candidates who take the exam in English will not have to worry about translating the exam questions. Third, there are moreresources available to candidates who are studying for the CPA exam in English.However, there are also some disadvantages to taking the CPA exam in English. First, candidates who are not native English speakers may find it difficult to understand the exam questions and materials. Second, candidates who are not fluent in English may make mistakes on the examthat they would not make if they were taking the exam in their native language.Ultimately, the decision of whether to take the CPA exam in English or Spanish is a personal one. Candidates should consider their own language skills and circumstances when making this decision.中文回答:注册会计师考试(CPA)是由美国注册会计师协会(AICPA)管理的一项标准化考试,面向希望成为注册会计师(CPA)的个人。

非专业牛人考CPA一次性过六门的经验分享题记:很多人都有梦想,有的是做律师,有的是做会计师、注册会计师,或者其他什么职业的“师”等。
但是无论选择在什么行业里出类拔萃,都是要下血本,都是要刻苦努力的。
就比如说考注册会计师需要考注册会计师考试一样……“有梦想谁都了不起,有勇气就会有奇迹。
”下面,我为大家分享一下我的注册会计师考试经验,希望对各位考注会的朋友都会有一些启发。
12月24日凌晨查成绩那一刻,自己的确是万分惊讶了一下。
然后惊喜了良久。
本来在考完后,就已经不抱有任何幻想能一次性通过了。
但,有勇气真的就会有奇迹,梦想真的很了不起。
这个结果对我来说,确实来之不易,其中蕴含的辛酸也许只有亲身经历过才能体会。
自今年九月份考完试后,就不断被要求分享经验。
其实,我没有什么经验秘诀可谈,有的只是辛酸血泪史。
但,还是想写点东西,希望能帮助和鼓舞更多的人“梦想成真”。
众多师兄弟妹同学在面临抉择考CPA的时候,也许可以想想:“那个平时好像很傻的周启光,不是都一次通过了CPA六门吗?像我这样优秀的人肯定也没问题。
”我之所以,选择一次性考六门CPA也是直接受到了中国政法大学方科师兄的鼓舞。
【当然,方科师兄绝对是牛人,法大传奇人物,我和师兄不是一个级数的。
但非常感激师兄无私的帮助和教导,从没嫌弃我这样一个智力低下的人。
】CPA只是一纸证书,一个人最重要的还是能力的培养。
期间重要的是CPA的学习过程,以及一个人的学习能力,结果只是某种程度对努力的肯定。
本文主要目的的想为了给各位想考CPA的一些粗浅的过来人之谈,给出一个“弱智”人士也可以一次通过CPA六门的成功事例,说明CPA并不是你们想象中的神话,给一些想而又不敢尝试的人一些鼓舞。
如果不是受到多个(真的N个那么多)同学师弟师妹的要求,介绍一些CPA的备考“经验”。
我真的不会这么自告奋勇去写一篇这么长的东西!这篇东西,是平安夜通宵写出来的,算是给大家的一个“圣诞礼物”。
所以,请一些素质低下的人,换位思考一下,也理性思考一些。
cpa一年六科备考详细计划在准备CPA考试时,制定一个详细的备考计划非常重要。
下面是一份CPA一年六科备考详细计划,帮助同学们更好地备考。
第一部分:阶段一1月份- 确定备考时间表和学习计划。
- 完成注册和缴费。
- 准备CPA考试大纲和考试指南。
- 复习高级会计学和财务管理的基本概念。
2月份- 复习财务成本管理和绩效管理的基本概念。
- 开始解题和做模拟题。
- 加强语文和英语水平。
3月份- 复习审计和税法的基本概念。
- 完成官方模拟考试。
- 评估自己的备考情况并制定下一步计划。
第二部分:阶段二4月份- 重点复习高级会计学和财务管理。
- 开始深入学习审计和税法。
- 加强阅读和听力能力。
- 复习财务成本管理和绩效管理。
- 完成一些模拟考试和练习题。
- 提高写作和口语能力。
6月份- 深入学习审计和税法。
- 完成官方模拟考试。
- 评估备考情况并制定下一步计划。
第三部分:阶段三7月份- 加强模拟考试和练习题的做题量。
- 复习高级会计学和财务管理的重点。
- 提高阅读和听力能力。
8月份- 深入学习财务成本管理和绩效管理。
- 复习审计和税法的重点。
- 提高写作和口语能力。
9月份- 完成官方模拟考试。
- 进行模拟考试的复习和总结。
- 评估备考情况并制定下一步计划。
第四部分:阶段四- 复习高级会计学和财务管理的难点。
- 加强财务成本管理和绩效管理的复习。
- 提高阅读和听力能力。
11月份- 深入学习审计和税法的难点。
- 完成官方模拟考试。
- 提高写作和口语能力。
12月份- 完成最后一次官方模拟考试。
- 进行综合测试和复习。
- 调整备考计划并做好心理准备。
以上是一份CPA一年六科备考详细计划,同学们可以根据自己的实际情况进行适当的调整。
希望同学们能够成功通过CPA考试。
cpa英语应试指导范文模板及概述说明1. 引言1.1 概述CPA英语考试是中国注册会计师(Certified Public Accountant)资格考试中的一项重要内容,对于想要在会计领域取得专业认证的考生来说,具有关键性的意义。
英语作为全球通用的商务交流语言,在会计职业中也扮演着重要角色。
因此,掌握并提高CPA英语成绩至关重要。
1.2 文章结构本文旨在为考生提供CPA英语应试指导以及范文模板,从而帮助他们更好地准备和应对考试。
文章分为四个部分:引言、CPA英语应试指导、范文模板及概述说明和结论。
1.3 目的本文的目的是通过详细解读CPA英语考试并提供相关指导,帮助考生充分了解该科目的要求和注意事项,并提供范文模板供参考。
通过理论和实践相结合的方式,希望能够使考生在备战CPA英语考试时更加有信心,并获得更好的成绩。
通过深入介绍CPA英语应试指导的核心要点,本文旨在帮助读者系统化地学习和掌握相关知识。
另外,为了给读者更直观的参考和指导,提供了范文模板,并对其进行详细概述说明。
最后,结论部分对全文进行总结回顾,并提供一些关于CPA英语应试的建议,以及展望未来该领域的发展方向。
通过本文的阅读和理解,读者将会对CPA英语考试有更深入的认识和理解,并能够通过所学知识和技巧在实战中取得优异成绩。
同时,也希望本文可以为CPA 考生提供一些建议和思路,使他们能够更好地规划备考策略,并在职业发展中获得成功。
2. CPA英语应试指导:2.1 第一要点:在CPA考试的英语应试中,我们要注意以下几点:首先,对于阅读理解部分,我们应该先通读全文,了解大意。
然后,针对每个段落或者问题作出归纳总结。
同时,注意识别关键词,以帮助我们定位答案。
最后,在回答问题时要依据文章提供的具体细节进行分析。
其次,在写作部分,重点是组织思路和表达清晰。
在写作过程中可以采用逻辑顺序或者时间顺序来展开论述。
同时,在选取论据时要充分运用自身知识和实际生活经验,并通过举例、引用权威数据等方式来加强说服力。
cpa一年6门计划表
注册会计师考试(CPA)一年六门是一项具有挑战性的任务,需要精心规划和充足的时间准备。
以下是一个大致的计划表,供您参考:
备考阶段
1.第一阶段(1-2个月):主要是熟悉六门科目的内容,了解每门科目的考试大纲和题型,同时建立起各科目的基础概念和知识框架。
这个阶段需要对各科目有一个整体的认识,以便于后续的深入学习。
2.第二阶段(3-5个月):在这个阶段,需要开始深入学习各科目的具体内容,并进行有针对性的练习。
这个阶段需要注重理解和掌握各科目的知识点,同时开始进行题目的练习,以巩固所学知识。
3.第三阶段(6-7个月):在这个阶段,需要开始进行模拟考试和真题练习。
模拟考试可以帮助你熟悉考试的流程和时间管理,真题练习则可以让你了解考试的难度和出题方式。
这个阶段还需要对前期学习的知识点进行查漏补缺,强化对薄弱环节的理解和掌握。
4.第四阶段(8-9个月):在这个阶段,需要对各科目进行全面的复习,强化对知识点的记忆和理解。
同时,需要注重做题的速度和准确性,提高应试能力。
5.第五阶段(10个月):这是最后的冲刺阶段,主要是进行模拟考试和真题练习,以及复习各科目的知识点。
这个阶段需要注重调整心态,保持积极乐观的态度,同时保证充足的休息和饮食,以便在考试中发挥出最佳水平。
以上是一个大致的计划表,具体的时间安排还需要根据个人的实际情况进行调整。
在备考过程中,需要保持耐心和毅力,不断鼓励自己,相信自己能够完成这个挑战。
如何准备英语考试,掌握答题技巧?英语考试备考策略:从理解到技巧,制胜考场作为一名教育专家,我自然知道英语学习的重要性,而高效备考复习则是取得成功的关键。
打算参加英语考试,不光是死记硬背单词和语法,更必须掌握科学的答题技巧,才能在考场上游刃有余,实现理想和目标成绩。
一、夯实基础,打牢根基1. 词汇积累:英语考试的核心基础是词汇量。
我建议考生制定合理的词汇学习计划,借用不同类型的词汇书、单词卡片、手机APP等多种工具,并增强例句、词根词缀等方法,将词汇融入到真实的语境中,更深刻地记忆。
2. 语法精练:语法是英语学习的基石。
考生必须深入理解语法规则,尤其是比较常见的语法现象,并通过练习巩固。
建议从基础语法入手,循序渐进,并在考试类型和特别要求上重点学习相关语法知识。
3. 阅读训练:泛读能力是英语考试中不可或缺的一部分。
考生应选择与考试难度和题材相符的阅读材料,并注重培养阅读理解能力,比如阅读理解、精读、略读等。
4. 写作训练:写作能力是英语考试的重点考察内容。
考生可以练习写作模板、学习积累常用词汇和句型,并注重实际逻辑结构和语言表达,增强写作水平。
建议多通过模拟考试,并及时反思和改进。
二、掌握技巧,应试挥洒自如1. 读题技巧:认真审题是答题的第一步,也是极为关键的一步。
考生应认真阅读题目要求,明确考查点和答题方向,避免含糊其词。
2. 时间管理:考试时间有限,合理分配时间极为关键。
建议考生提前规划好时间,并根据不同题型分配时间,避免出现时间不足或浪费的情况。
3. 答题策略:不同题型有不同的答题策略。
例如,阅读理解题要学会收集关键词、预测答案,并通过原文推理和判断;写作题要特别注重逻辑结构、语言表达和字数要求,并注意避免语法错误。
4. 心理调节:考前一个月保持良好的心态,尽量减少焦虑和兴奋,才能发挥出最佳水平。
建议考生进行适度的放松训练,例如做深呼吸、冥想等,并相信自己的实力。
三、勤于练习,积累知识经验1. 模拟考试:模拟考试是测定备考复习成果的重要途径。
如何准备英语考试?英语考试备考策略:从基础进一步夯实到技巧精进作为教育专家,我自然明白英语考试的难度和重要性。
为了帮助学生取得美好的理想成绩,我将从以下几个方面详细阐释备考策略:一、基础夯实,百炼成钢1.词汇:词汇是英语学习的基础,也是考试中的重中之重。
建议学生可以使用词汇书、词根词缀等工具,并加强例句记忆,特别注重理解词义和用法。
此外,还可以实际泛读英文文章、看英文电影等,在语境中不知不觉地学习积累词汇。
2.语法:语法是语言的骨架,理解语法规则有助于更好地理解句子结构和如何表达意思。
建议学生系统学习英语语法,完全掌握基础语法知识,并每天练习巩固。
3.泛读:阅读是提高英语水平的重要途径,也是考试中不可或缺的一部分。
建议学生广泛阅读不同类型的英文文章,注意培养阅读理解能力,并注重词汇积累和语法分析。
4.听力:听力能力的提升需要大量的练习,建议学生听英文广播、看英文电影、听英文歌曲等,并特别注意培养和训练听力技巧,例如听音识词、抓住关键词、预测内容等。
5.口语:口语训练需要从模仿开始,建议学生模仿英语母语人士的语音语调,并通过练习对话、朗读等,增加口语表达能力。
二、技巧提升,事半功倍1.时间管理:英语考试时间紧迫,合理分配时间十分有利。
建议学生提前制定考试计划,合理安排学习内容,并注重练习时间管理技巧,例如计时练习、模拟考试等。
2.应试技巧:考试技巧是获得好成绩的关键。
建议学生了解考试题型、考试规则,并掌握一些应试技巧,比如快速阅读、排除干扰项、合理猜测等。
3.心理调整:良好的心理状态是考试成功的保障。
建议学生保持积极的心态,不要过分紧张,并进行一些心理调节,例如做深呼吸、放松练习等。
4.模拟考试:模拟考试是检验学习成果的重要手段。
建议学生定期进行模拟考试,熟悉考试环境和题型,并根据模拟考试结果调整学习策略。
三、针对性学习,有的放矢1.了解考试大纲:不同考试的侧重不同,建议学生认真阅读考试大纲,明确考试内容、考查重点和题型分布,并根据大纲制定学习计划。
注会考试英语讲义一、相关背景1、2007年注册会计师考试在英语测试选考的同时,将在会计和审计两门课程中直接增加10分的英语附加题。
这一变化主要是为了满足中国经济和行业发展对国际人才的需要。
财政部CPA考试委员会将根据今年的考试情况进一步研究如何将英文附加题逐步推广到其他考试科目中。
据此看来,在CPA各科考试中加重英语的分量将是一个趋势。
2、增加英语附加题后,会计、审计总分为110分,及格分仍为60分,总体考试时间不变。
英语附加题要求用英语回答,所以考生朋友们一定要根据本人英语水平选择作答。
有一定英语基础(大学英语四、六级水平,掌握一定的财经英语词汇),打算选答英语附加题的考生朋友更应该合理规划和安排时间,在考试时认真阅读试卷首页的特别提示和答题导语,争取尽可能多的在英语附加题上拿分。
英语基础较差的考生朋友不要慌乱,心态要放平和,力争前面的100分,如果时间允许可尝试做英语附加题。
二、可能的题型因为只有10分的英语题,所以估计出客观题的可能性不大,很有可能是主观题,并且是专业题。
题型可能包括:名词解释,英汉互译,问答(理论性的或业务性的)。
三、会计英语讲解会计报表中英文对照Accounting1. Financial reporting(财务报告)includes not only financial statements but also other means of communicating information that relates, directly or indirectly, to the information provided by a business enterprise’s accounting system----that is, information abo ut an enterprise’s resources, obligations, earnings, etc.2. Objectives of financial reporting: 财务报告的目标Financial reporting should:(1) Provide information that helps in making investment and credit decisions.(2) Provide information that enables assessing future cash flows.(3) Provide information that enables users to learn about economic resources, claims against those resources, and changes in them.3. Basic accounting assumptions 基本会计假设(1) Economic entity assumption 会计主体假设This assumption simply says that the business and the owner of the business are two separate legal and economic entities. Each entity should account and report its own financial activities.(2) Going concern assumption 持续经营假设This assumption states that the enterprise will continue in operation long enough to carry out its existing objectives.This assumption enables accountants to make estimates about asset lives and how transactions might be amortized over time.This assumption enables an accountant to use accrual accounting which records accrual and deferral entries as of each balance sheet date.(3) Time period assumption 会计分期假设This assumption assumes that the economic life of a business can be divided into artificial time periods.The most typical time segment = Calendar YearNext most typical time segment = Fiscal Year(4) Monetary unit assumption 货币计量假设This assumption states that only transaction data that can be expressed in terms of money be included in the accounting records, and the unit of measure remains relatively constant over time in terms of purchasing power.In essence, this assumption disregards the effects of inflation or deflation in the economy in which the entity operates.This assumption provides support for the "Historical Cost" principle.4. Accrual-basis accounting 权责发生制会计5. Qualitative characteristics 会计信息质量特征(1) Reliability 可靠性For accounting information to be reliable, it must be dependable and trustworthy.Accounting information is reliable to the extend that it is:Verifiable: means that information has been objectively determined, arrived at, or created. More than one person could consider the facts of a situation and reach a similar conclusion. Representationally faithful: that something is what it is represented to be. For example, if a machine is listed as a fixed asset on the balance sheet, then the company can prove that the machine exists, is owned by the company, is in working condition, and is currently being used to support the revenue generating activities of the company.Neutral: means that information is presented in accordance with generally accepted accounting principles and practices, and without bias.(2) Relevance 相关性Relevant information is capable of making a difference in the decisions of users by helping them to evaluate the potential effects of past, present, or future transactions or other events on future cash flows (predictive value) or to confirm or correct their previous evaluations (confirmatory value).(3) Understandability 可理解性Understandability is the quality of information that enables users who have a reasonable knowledge of business and economic activities and financial reporting, and who study the information with reasonable diligence, to comprehend its meaning.(4) Comparability 可比性Comparability: suggests that accounting information that has been measured and reported in a similar manner by different enterprises should be capable of being compared because each of the enterprises is applying the same generally accepted accounting principles and practices. Consistency: suggests that an entity has used the same accounting principle or practice from oneperiod to another, therefore, if the dollar amount reported for a category is different from one period to the next, then chances are that the difference is due to a change like an increase or decrease in sales volume rather than being due to a change in the method of calculating the dollar amount.(5) Substance over form 实质重于形式Substance over form emphasizes the economic substance of an event even though its legal form may provide a different result.It requires that business enterprise should perform accounting recognition, measurement and reporting in accordance with the economic substance rather than the legal form of an event or transaction.(6) Materiality 重要性Information is material if its omission or misstatement could influence the resource allocation decisions that users make on the basis of an entity’s financial report. Materiality depends on the nature and amount of the item judged in the particular circumstances of its omission or misstatement. Deciding when an amount is material in relation to other amounts is a matter of judgment and professional expertise.(7) Conservatism 谨慎性Conservatism dictates that when in doubt, choose the method that will be least likely to overstate assets and income, and understate liabilities and expenses.(8) Timeliness 及时性Timeliness means having information available to decision makers before it loses its capacity to influence decisions. If information becomes available only after the time that a decision must be made, it has no capacity to influence that decision and thus lacks relevance.6. Basic accounting elements 基本会计要素(1) Asset 资产An asset is a resource that is owned or controlled by an enterprise as a result of past transactions or events and is expected to generate economic benefits to the enterprise.(2) Liability 负债A liability is a present obligation arising from past transactions or events which are expected to give rise to an outflow of economic benefits from the enterprise.A present obligation is a duty committed by the enterprise under current circumstances. Obligations that will result from the occurrence of future transactions or events are not present obligations and shall not be recognized as liabilities.(3) owners’equity 所有者权益Owners’ equity is the residual interest in the assets of an enterprise after deducting all its liabilities.Owners’ equity of a company is also known as shareholders’ equity.(4) Revenue 收入Revenue is the gross inflow of economic benefits derived from the course of ordinary activities that result in increases in equity, other than those relating to contributions from owners.(5) Expense 费用Expenses are the gross outflow of economic benefits resulted from the course of ordinary activities that result in decreases in owners’ equity, other than those relating to appropriations of profits to owners.(6) Profit 利润Profit is the operating result of an enterprise over a specific accounting period. Profit includes the net amount of revenue after deducting expenses, gains and losses directly recognized in profit of the current period, etc.7. Five measurement attributes 会计计量属性(1) Historical cost 历史成本Assets are recorded at the amount of cash or cash equivalents paid or the fair value of the consideration given to acquire them at the time of their acquisition. Liabilities are recorded at the amount of proceeds or assets received in exchange for the present obligation, or the amount payable under contract for assuming the present obligation, or at the amount of cash or cash equivalents expected to be paid to satisfy the liability in the normal course of business.(2) Current replacement cost 现时重置成本Assets are carried at the amount of cash or cash equivalents that would have to be paid if a same or similar asset was acquired currently. Liabilities are carried at the amount of cash or cash equivalents that would be currently required to settle the obligation.(3) Net realizable value 可实现净值Assets are carried at the amount of cash or cash equivalents that could be obtained by selling the asset in the ordinary course of business, less the estimated costs of completion, the estimated selling costs and related tax payments.(4) Present value 现值Assets are carried at the present discounted value of the future net cash inflows that the item is expected to generate from its continuing use and ultimate disposal. Liabilities are carried at the present discounted value of the future net cash outflows that are expected to be required to settle the liabilities within the expected settlement period.(5) Fair value 公允价值Assets and liabilities are carried at the amount for which an asset could be exchanged, or a liability settled, between knowledgeable, willing parties in an arm’s length transaction.8. Financial statements 财务报表(1) Balance sheet 资产负债表A balance sheet is an accounting statement that reflects the financial position of an enterprise at a specific date.(2) Income statement 损益表An income statement is an accounting statement that reflects the operating results of an enterprise for a certain accounting period.(3) Statement of cash flows 现金流量表A cash flow statement is an accounting statement that reflects the inflows and outflows of cash and cash equivalents of an enterprise for a certain accounting period.(4) Statement of changes in owners’equity 所有者权益变动表A statement of changes in owners’ equity reports the changes in owners’ equity for a specific period of time.(5) Notes to financial statements 财务报表附注Notes to the accounting statements are further explanations of items presented in the accounting statements, and explanations of items not presented in the accounting statements, etc.9. Accounting entry 会计分录Debit: CashCredit: Common Stock10. Basic accounting equation 基本会计等式Assets = Liabilities + owners’ equity11. List of present and potential users of financial information 财务信息的使用者investors, creditors, employees, suppliers, customers, and governmental agencies.四、审计英语讲解Auditing1. Assurance engagements and external audit◇Materiality, true and fair presentation, reasonable assuranceMateriality is the magnitude of an omission or misstatement of accounting information that, in the light of surrounding circumstances, makes it probable that the judgment of a reasonable person relying on the information would have been changed or influenced by the omission or misstatement. An auditor must consider materiality both in (1) planning the audit and designing audit procedures and (2) evaluating audit results.◇Appointment, removal and resignation of auditors◇Types of opinion: standard unqualified opinion, Unqualified with additional explanatory language, qualified opinion, adverse opinion, disclaimer of opinion◇Professional ethics: independence, objectivity, integrity, professional competence, due care, confidentiality, professional behavior◇Engagement letter2. Planning and risk assessment◇General principles○Plan and perform audits with an attitude of professional skepticism○Audit risks = inherent risk ×control risk ×detection risk(1) Inherent risk refers to the likelihood of material misstatement of an assertion, assuming no related internal control. This risk differs by account and assertion.(2) Control risk is the likelihood that a material misstatement will not be prevented or detected ona timely basis by internal control. This risk is assessed using the results of tests of control.(3) Detection risk is the likelihood that an auditor’s procedures lead to an improper conclusion that no material misstatement exists in an assertion when in fact such a misstatement does exist. The auditor’s substantive tests are primarily relied upon to restrict detection risk.○Risk-based approach◇Understanding the entity and knowledge of the businessThe CPA should obtain a level of knowledge of the client’s business that will enable effective planning and performance of the audit in accordance with generally accepted auditing standards. This knowledge helps the auditor in(1) Identifying areas that may need special consideration(2) Assessing conditions under which accounting data are produced, processed, reviewed and accumulated(3) Evaluating accounting estimates for reasonableness (e.g., valuation of inventories, depreciation, allowance for doubtful accounts, percentage of completion of long-term contracts)(4) Evaluating the reasonableness of management representations(5) Making judgments about the appropriateness of the accounting principles applied and theadequacy of disclosures◇Assessing the risks of material misstatement and fraud○Materiality (level), tolerable error◇Analytical proceduresAnalytical procedures are normally used at three stages of the audit: (1) planning, (2) substantive testing, and (3) overall review at the conclusion of an audit. They are required during the planning and overall review stages.Analytical procedures used for 3 purposes:(1) Planning nature, timing, and extent of other auditing procedures(2) Substantive tests about particular assertions(3) Overall review in the final stage of audit◇Planning an audit◇Audit documentation: working papers◇The work of others○Rely on the work of experts○Rely on the work of internal audit3. Internal controlInternal control is a process effected by an entity’s board of directors, management, and other personnel—designed to provide reasonable assurance regarding the achievement of objectives in the following categories: (1) reliability of financial reporting, (2) effectiveness and efficiency of operations, and (3) compliance with applicable laws and regulations.Five components of internal control(1) control environment(2) risk assessment(3) control activities(4) information and communication(5) monitoring◇The evaluation of internal control systems○Tests of control○Substantive procedures (time, nature, extent)◇Transaction cycles: revenue, purchases, inventory, etc.4. Audit evidence◇Obtain sufficient, appropriate audit evidence◇Assertions contained in the financial statements: completeness, occurrence, existence, measurement, presentation and disclosure, rights and obligations, valuation◇The audit of specific items○Receivables: confirmation○Inventory: counting, cut-off, confirmation of inventory held by third parties○Payables: supplier statement reconciliation, confirmation○Bank and cash: bank confirmation◇Auditing sampling5. Review◇Subsequent events◇Going concern◇Management representations◇Audit finalization and the final review: unadjusted differences6. Reporting审计1.鉴证业务和外部审计◇重要性,真实、公允反映,合理保证◇注册会计师的聘用,解聘和辞职◇审计意见类型:标准无保留意见,带解释段的无保留意见,保留意见,否定意见,无法表示意见◇职业道德:独立、客观和公正,专业胜任能力,应有的关注,保密性,职业行为◇审计业务约定书2.审计计划和风险评估◇一般原则○计划和执行审计业务应保持应有的职业怀疑态度○审计风险=固有风险×控制风险×检查风险○风险导向型审计◇了解被审单位◇估计重大错报或舞弊的风险○重要性水平,可容忍误差◇分析性复核程序◇制定审计计划◇审计记录:工作底稿◇利用其他人的工作○利用专家工作○利用内部审计人员的工作3.内部控制◇内部控制系统评价○控制测试○实质性程序(时间,性质,范围)◇交易循环:收入循环、采购循环、存货循环,等等。
CPA综合英语备考复习重要性建议顺序:(1)职业道德+审计+公司战略(2)财管+经济法(3)会计+税法Unit 1 职业道德准则China Code of Ethics for Certified Public Accountants3.因经济利益对独立性产生的不利影响7.兼任审计客户的董事或高级管理人员Concurrently employed by the accounting firm andUnit 2 审计Auditing1.审计计划Audit Planning实际执行的重要性The materiality of actual execution确定实际执行的重要性需要注册会计师运用职业判断,并考虑下列因素的影响:CPA should use professional judgment when determining the materiality of actual execution and consider the effects of following factors:a.对被审计单位的了解;Understanding the auditee;b.前期审计工作中识别出的错报的性质和范围;The nature and scope of misstatements identified in preliminary audit work;c.根据前期识别出的错报对本期错报作出的预期。
Prediction of current period misstatements according to previous period misstatements identified.通常而言,实际执行的重要性通常为财务报表整体重要性的50%-75%。
Generally, performance materiality will be at 50% to 75% of the materiality for the financial statements as a whole.实际执行的重要性接近整体重要性50%的情况:a.非连续审计;b.以前年度审计调整较多;c.项目总体风险较高。
Under the following circumstances, the performance materiality will be close to 50% of the overall materiality for the financial statements: a.It is a non-recurring audit; b.There were many audit adjustments in previous years; c.The overall risk of the project is high.接近75%的具体情况:a.连续审计,以前年度审计调整较少;b.项目总体风险较低。
The performance materiality will be close to 75% of the overall materiality for the financial statements under the following circumstances: a.It is a recurring audit and there were few audit adjustments in previous years; b.The overall risk of the project is low.2.风险评估和风险应对Risk Assessment and Responding to the Risk Assessment(1)风险评估注册会计师应当实施下列风险评估程序,以了解被审计单位及其环境:[1]询问管理层和被审计单位内部其他相关人员;[2]分析程序;[3]观察和检查。
In order to understand the entity and its environment, procedures of risk assessment are as follows: [1]Inquiries;[2]Analytical procedures; [3]Observation and inspection.注册会计师了解被审计单位及其环境,包括其内部控制,目的是识别和评估在财务报表层面和认定层面,由于舞弊或者错误而存在的重大错报风险,并在此基础上设计和实施应对的措施。
The objective of the auditor is to identify and assess the risk of material misstatement, whether due to fraud or error, at the financial statementThe CPA understands the entity and its environment, includes its internal control, in order to identify and assess the risk of material misstatement at the financial statement and assertion levels due to fraud or error, and designs and implements responses to the assessed risks of material misstatement on this basis and assertion levels, through understanding the entity and itsenvironment, including the entity’s internal control, thereby providing a basis for designing and implementing responses to the assessed risks of material misstatement.注册会计师应当从下列方面了解被审计单位及其环境:[1]相关行业状况、法律环境与监管环境及其他外部因素;[2]被审计单位的性质;[3]被审计单位对会计政策的选择和运用;[4]被审计单位的目标、战略以及可能导致重大错报风险的相关经营风险;[5]对被审计单位财务业绩的衡量和评价;[6]被审计单位的内部控制。
The auditor should understand the entity and its environment as follows : [1]Related industry status, legal and regulatory environment and other external factors; [2]The nature of theentity;[3]The selection and application of accounting policy;[4]The objectives, strategy and business risk that can lead to material misstatement risks;[5]Measurement and evaluation of financial performance;[6]The internal control.注册会计师通过询问、观察、检查和穿行测试了解被审计单位的内部控制,以评价内部控制设计的是否合理以及是否得到执行。
Auditors understand the internal controls of the entity by inquiries, observation, inspection and walk-through test to evaluate whether the internal controls are designed reasonably and implemented effectively.内部控制存在固有局限性,无论如何设计和执行,只能对财务报告的可靠性提供合理保证。
No matter how to be designed and implemented, any internal control system can only provide auditor with reasonable assurance because of inherent limitations.内部控制包括下列五个要素:[1]控制环境;[2]风险评估过程;[3]与财务报告相关的信息系统与沟通;[4]控制活动;[5]对控制的监督。
Internal control has five elements:[1]The control environment;[2]The process of risk assessment;[3]The information system and communication;[4]Control activities;[5]Supervision of controls.relevant to/ associated with financial reportingMonitoringThe entity’s risk assessment process(2)风险应对Responding to the risk assessmenta.针对财务报表层次重大错报风险注册会计师应当针对评估的财务报表层次重大错报风险确定下列总体应对措施:Overall responses to the risks of material misstatements at the financial statement level will include the following :[1]向项目组强调保持职业怀疑的必要性;Emphasize to the audit team on the necessity to maintain the professional skepticism;[2]指派更有经验或具有特殊技能的审计人员,或利用专家的工作;Appoint auditors with more experience and special skills, or use the expert’s work.[3]提供更多的督导;Provide more monitoring;[4]在选择拟实施的进一步审计程序时融入更多的不可预见的因素。