Department of Automation School of Information Science & Engineering Central South University Changsha, Hunan, 410083, China
1
Contents
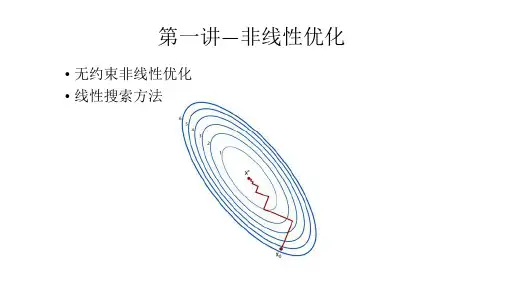
Chapter 1 Introduction
According to the principle of optimality, if the N -stage decision VN [ x (0)] is optimal,
then the ( N − 1)-stage decision VN −1 [ x(1) ] , regarding the x(1) resulting from x(0)
Recurrently solving from final state:
V (F ) = 0
⎧V (a3 ) = 4 ⎪ ⎨V (b3 ) = 6 ⎪V (c ) = 8 ⎩ 3
⎧V (a2 ) = min { L ( a2 → V (a3 ) ) , L ( a2 → V (b3 ) ) , L ( a2 → V (c3 ) )} = 10 ⎪ ⎪ ⎨V (b2 ) = min { L ( b2 → V (a3 ) ) , L ( b2 → V (b3 ) ) , L ( b2 → V (c3 ) )} = 9 ⎪ ⎪V (c2 ) = min { L ( c2 → V (a3 ) ) , L ( c2 → V (b3 ) ) , L ( c2 → V (c3 ) )} = 8 ⎩
7
V ( S ) = min {L ( S → V ( a1 ) ) , L ( S → V (b1 ) ) , L ( S → V ( c1 ) )} = 12