语言学期中测验
- 格式:doc
- 大小:56.50 KB
- 文档页数:10

Part One: 40’A. True/ False questions: (10’)Read the statements carefully and decide whether each of them is true (T) or false (F) in terms of linguistics.T【1 】The study of the ways in which morphemes can be combined to form words is called morphology.T【 2 】Phonetics is different from phonology in that the latter studies the combinations of the sounds to convey meaning in communication.F【3 】According to the shape of the lips, vowels can be classified into close vowels, semi-close vowels, semi-open vowels and open vowels.F【4 】Modern linguistics regards the written language as primary, not the spoken language.F【5 】English consonants can be classified in terms of place of articulation and the part of the tongue that is raised the highest.T【6 】V owel sounds can be differentiated by a number of factors: the position of tongue in the mouth, the openness of the mouth, the shape of the lips, and the length of the vowels.F【7 】A phone is a phonetic unit that distinguishes meaning.F【8 】Words are the smallest meaningful units of language.F【9 】Prefixes usually modify the part of speech of the original word, not the meaning of it.T【10 】Phonetically, the stress of a compound always falls on the first element, while the second element receives secondary stress.B. Complete each of the statements with the most likely answer: (30’)【 1 】Language is a system of arbitrary vocal symbols used for human __________.A. communicationB. contactC. relationD. community【 2 】Which of the following words is entirely arbitrary?A. treeB. typewriterC. crashD. bang【 3 】What is the most important function of language?A. Interpersonal 人际的B. Phatic 交流感情的C. Informative 教育性D. Metalingual【 4 】Who put forward the distinction between Langue and Parole?A. SaussureB. ChomskyC. HallidayD. Anonymous【 5 】According to Chomsky, which is the ideal user's internalized 内在化knowledge of his language?A. competenceB. paroleC. performanceD. langue【 6 】The function of the sentence “A nice day, isn’t it?” is__________ .A. informative 教育性的B. phaticC. directive 指示的D. performative行为语【7 】Which of the following statements about language is NOT true?A. Language is a systemB. Animals also have languageC. Language is symbolicD. Language is arbitrary【8 】The distinction between vowels and consonants lies in__________ .A. the obstruction of airstreamB. the place of articulationC. the position of the tongueD. the shape of the lips【9 】Which is the branch of linguistics which studies the characteristics of speech sounds and provides methods for their description, classification and transcription?A. PhonologyB. PhoneticsC. SemanticsD. Pragmatics【10 】Which studies the sound systems in a certain language?A. PhoneticsB. PhonologyC. SemanticsD. Pragmatics【11 】The function of the sentence “Water boils at 100 degrees Centigrade.” is ________.A. interrogative疑问句B. directiveC. informativeD. performative【12 】Usually, suprasegmental features include__________, length and pitch.音高A. phonemeB. speech soundsC. syllablesD. stress【13 】Conventionally a __________ is put in slashes (/ /).斜杠语法A. allophoneB. phoneC. phonemeD. morpheme【14 】An aspirated送气p, an unaspirated 不送气p and an unreleased不吐放的p are ________ of the p phoneme.A. analoguesB. tagmemesC. morphemesD. allophones【15 】Which studies the internal structure of words, and the rules by which words are formed?A. MorphologyB. SyntaxC. PhonologyD. Semantics【16 】Which one is different from the others according to places of articulation 发音部位?A. [m]B. [n]C. [ b ]D. [p]【17 】All words contain a __________A. root morphemeB. bound morphemeC. prefixD. suffix【18 】In English –ise and –tion are called __________.A. suffixesB. prefixesC. infixesD. stems【19 】“-s” in the word“books” is _______.A. a derivative 派生affixB. a stemC. an inflectional affixD. a root【20 】The meaning carried by the inflectional morpheme is _______.A. lexicalB. morphemicC. grammaticalD. semantic【21 】The prefixes contained in the following words are called ______: pseudo-friend假朋友, malpractice玩忽职守, mistrust.A. reversative prefixedB. negative prefixesC. locative prefixesD. pejorative轻蔑语prefixes【22 】The prefixed contained in unwrap, de-compose and disallow驳回are _________.A. reversative prefixedB. negative prefixesC. pejorative prefixesD. locative prefixes【23 】The prefixes in words bilingual, uniform and hemisphere are ________. A. number prefixes B. prefixes of degree or sizeC. pejorative prefixesD. locative prefixes【24 】Omega, Xerox and Danone are words from _________.A. names of booksB. names of placesC. names of peopleD. trade names【25 】Ex-student, foretell and post-election contain________.A. negative prefixesB. prefixes of degree or sizeC. locative prefixesD. prefixes of time and order【26 】The prefixes in words new-Nazi, autobiography and pan-European are ________.A. negative prefixesB. miscellaneous多种多样的prefixesC. prefixes of time and orderD. prefixes of degree or size【27 】A historical study of language is a ____ study of language.A. synchronicB. diachronicC. prescriptiveD. comparative【28 】 In Chinese when someone breaks a bowl or a plate the host or the people present are likely to say“碎碎(岁岁)平安”as a means of controlling the forces which they believes feel might affect their lives. Which functions does it perform? A. Performative B. Emotive C. Interpersonal D. Recreational【29 】__________ refers to the actual realization of the ideal language user’s knowledge of the rules of his language in utterances.A. PerformanceB. CompetenceC. LangueD. Parole【30 】The prefixes in the words of irresistible, nonclassical and apolitical are called _______.A. reversative prefixesB. negative prefixesC. pejorative prefixesD. locative prefixesPart Two: 20’Linguistic Analysis(20%):Comment on the following linguistic phenomena briefly.【 1 】a: Don't say X.b: People don't say X.【 2 】bkli; I apple eat.【 3 】“A rose by any other name would smell as sweet”----Shakespeare【 4 】pin-bin, bin-tin, tie-die, choke-joke, pill-bill, bill-till, till-kill.【 5 】“k b i l”a: blik, klib, bilk, kilbb: lbki, ilbk, bkil, ilkb【 6 】a: sign, design, paradigmb: signature, designation, paradigmatic【7 】/p/=[ p h ] + [ p. ] + [ p¬ ] (unreleased)/l/ = [ l ] + [ ł ]/e/ = [e]【8 】Write down all the morphemes in the word-- antidisestablishmentarianism 【9 】ion/-tion/-sion/-ation【10 】bird's eye----fish-eye, worm's-eye, cat's-eyePart Three: 40’QuestionsAnswer the following questions as comprehensively as possible. Give examples for illustration if necessary.【 1 】Why do you think speech is more basic than writing? (8’)【 2 】Why do people take duality as one of the important design features of human language? Can you tell us what language will be if it has no such design feature? (8’)【 3 】Why is it difficult to define language? (8’)【 4 】What are the differences between voiced sounds and voiceless sounds in terms of articulation? (8’)【 5 】After World War II, neologisms sweep in at a rate much faster than any other historical period. What are the main reasons for the frequent appearance of neologisms? (8’)。
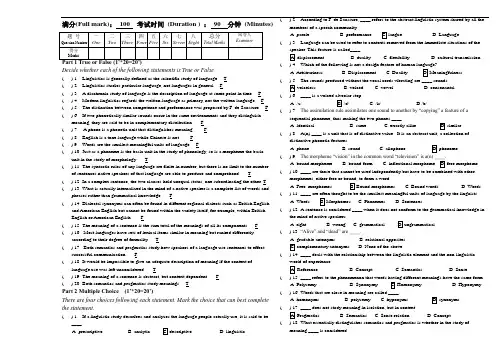
...满分(Full mark): 100 考试时间 (Duration ) : 90 分钟 (Minutes)Decide whether each of the following statements is True or False( ) 1. Linguistics is generally defined as the scientific study of language. T ( ) 2. Linguistics studies particular language, not languages in general. F( ) 3.A diachronic study of language is the description of language at some point in time. F ( ) 4. Modern linguistics regards the written language as primary, not the written language. F ( ) 5. The distinction between competence and performance was proposed by F. de Saussure. F ( ) 6. If two phonetically similar sounds occur in the same environments and they distinguishmeaning, they are said to be in complementary distribution.F ( ) 7. A phone is a phonetic unit that distinguishes meaning. F ( ) 8. English is a tone language while Chinese is not. F ( ) 9. Words are the smallest meaningful units of language. F( ) 10. Just as a phoneme is the basic unit in the study of phonology, so is a morpheme the basicunit in the study of morphology. T( ) 11. The syntactic rules of any language are finite in number, but there is no limit to the numberof sentences native speakers of that language are able to produce and comprehend. T( ) 12. In a complex sentence, the two clauses hold unequal status, one subordinating the other. T ( ) 13.What is actually internalized in the mind of a native speaker is a complete list of words andphrases rather than grammatical knowledge. F( ) 14. Dialectal synonyms can often be found in different regional dialects such as British Englishand American English but cannot be found within the variety itself, for example, within British English or American English. F( ) 15. The meaning of a sentence is the sum total of the meanings of all its components. F( ) 16. Most languages have sets of lexical items similar in meaning but ranked differentlyaccording to their degree of formality. T( ) 17. Both semantics and pragmatics study how speakers of a language use sentences to effectsuccessful communication. F( ) 18. It would be impossible to give an adequate description of meaning if the context oflanguage use was left unconsidered. T( ) 19. The meaning of a sentence is abstract, but context-dependent. F ( ) 20. Both semantics and pragmatics study meanings. TPart 2 Multiple Choice (1’*20=20’)There are four choices following each statement. Mark the choice that can best completethe statement.( ) 1. If a linguistic study describes and analyzes the language people actually use, it is said to be____.A. prescriptiveB. analytic D. linguistic( ) 2. According to F. de Saussure, ____ refers to the abstract linguistic system shared by all themembers of a speech community.A. paroleB. performance D. Language( ) 3. Language can be used to refer to contexts removed from the immediate situations of thespeaker. This feature is called____.B. dualityC. flexibilityD. cultural transmission ( ) 4. Which of the following is not a design feature of human language?A. ArbitrarinessB. Displacement( ) 5. The sounds produced without the vocal cords vibrating are ____ sounds.B. voicedC. vowelD. consonantal ( ) 6. ____ is a voiced alveolar stop.C. /k/D./b/( ) 7. The assimilation rule assimilates one sound to another by “copying” a feature of asequential phoneme, thus making the two phones ____.A. identicalB. sameC. exactly alike ( ) 8. A(n) ____ is a unit that is of distinctive value. It is an abstract unit, a collection ofdistinctive phonetic features.A. phoneB. sound( ) 9. The morpheme “vision” in the common word “television” is a(n) ____.A. bound morpheme( ) 10. ____ are those that cannot be used independently but have to be combined with othermorphemes, either free or bound, to form a word.C. Bound wordsD. Words ( ) 11. ____ are often thought to be the smallest meaningful units of language by the linguists.C. PhonemesD. Sentences( ) 12. A sentence is considered ____ when it does not conform to the grammatical knowledge inthe mind of native speakers.A. rightB. wrongC. grammatical ( ) 13. “Alive” and “dead” are ____.A. gradable antonymsB. relational opposites D. None of the above( ) 14. ____ deals with the relationship between the linguistic element and the non-linguisticworld of experience.B. ConceptC. SemanticsD. Sense ( ) 15. ____ refers to the phenomenon that words having different meanings have the same form.A. PolysemyB. Synonymy ( ) 16. Words that are close in meaning are called ____.A. homonymsB. polysemy ( ) 17. ____ does not study meaning in isolation, but in context.C. Sense relationD. Concept ( ) 18. What essentially distinguishes semantics and pragmatics is whether in the study ofmeaning ____ is considered.( ) 19. Speech act theory did not come into being until ____.late 50’s of the 20the century B. in the early 1950’sC. in the late 1960’sD. in the early 21st century. ( ) 20. ____ is advanced by Paul GriceB. Politeness PrincipleC. The General Principle of Universal GrammarD. Adjacency PrinciplePart 3 Definition (5’*5=25’)Define the following terms.Classify the consonants in each word.Example: [z] voiced alveolar fricative 1. [t] voiceless alveolar stop 2. [n] voiced nasal alveolar 3. [k] voiceless velar stop 4. [θ] voiceless interdental fricative 5. [l] voiced alveolar approximantPart 5 Morphology: Word Formation Processes (1’*10=10’)Insert the words in the table according to the word formation processes.Analyze the following sentences in terms of clauses, functions and categories.Example:He missed the early bus.He – subject NP / missed – predicate VP / the early bus – object NP 1. I am writing an essay on Milton. I – Subject NP Am writing - Predicate VP An essay on Milton - Object: NP 2. Your teaching style has impressed the new Principal. Your teaching style – Subject NP has impressed Predicate VP the new Principal- Object: NPPart 7 Semantics: Sense relations (0.5’*5=2.5’)Insert the following pairs of words in the table according to their sense relations.a. pass away/ dieb. stem/ flowerc. sweets/ candies Which of the Conversational Maxims is being violated in the following conversation?A: Tom is an excellent linguist. Don ’t you think? B: He is a good cookIt may be regarded as a violation of the maxim of ___relation___.(The hearer assumes that if the speaker is cooperative, his reply must be relevant in a different sense- Tom is not a good linguistic.a. to motherb. telephonec. moteld. VOAe. UFOf. televiseg. talkingh. boyishi. greenhousej. quake。

济南外国语学校度第一学期高二期中模块考试法语试题(2023.11)说明:第I、II卷均为必做题,总分值为120分。
第I卷为第1页至第2页,第II卷为第3页至第10页。
考试时间120分钟。
第I卷(听力局部,共20分)I. Écoutez et choisissez la bonne réponse.( 15 points )Texte 11. Vous êtes en communication avec le répondeur:A. d’un cabinet médicalB. d’un cabinet d’architecteC. d’un cabinet juridique2. Le cabinet est ouvert :A. tous les matins et tous les après-midi.B. seulement le matin.C. toute la journée du lundi au vendredi et le samedi matin.3. Quel numéro devez-vous appeler en cas d’urgence?A. 02 28 18 63 29B. 22 28 18 63 29C. 02 18 28 63 29Texte 24. La scène se passe:A. au début du repas.B. au milieu du repas.C. à la fin du repas.5. La salade du pêcheur est faite avec:A. de la salade et de la viande.B. de la salade et du poisson.C. de la salade seulement.6. Paul et Hélène mangent la même chose.A. VraiB. FauxC. On ne sait pas.7. Paul et Hélène sont de bons amis.A. VraiB. FauxC. On ne sait pas.Texte 38. Mathieu et Ludovic sont voisins :A. depuis longtempsB. depuis quleques joursC. depuis hier9. L’appartement de Mathieu se compose de:A. deux chambres et un salonB. une chambres, un salon et un bureauC. une chambre, un salon et un atelier10. Mathieu habite:A. seulB. avec des amisC. avec Sophie11. Mathieu et Ludovic vont se revoir parce que :A. Mathieu invite LudovicB. Ludovic veut visiter l’appartementC. Ludovic va faire les travaux de peintureTexte 412. Quand vous entendez ce message vous êtes:A. dans un salon de coiffureB. dans un salon de beautéC. dans un salon nautique13. Le message annonce :A. l’ouverture du salon à 18hB. la fermeture du salon à 18h30C. la fermeture du salon à 19h14. Vous pouvez revenir au salon :A. entre le 6 et le 10 févrierB. entre le 10 et le 13 févrierC. jusqu’au 16 février15. Que vous demande-t-on de faire?A. d’acheter un billetB. de regagner la sortieC. de faire la queueII. Écoutez deux fois et complétez le texte.( 5 points )Le 22 se ptembre, à Paris, une grande 1._______________ du centre de la capitale sera fermée de 9 heures à 19 heures et seuls les vélos, les taxis et les transports en commun pourront circuler dans cette zone. Il y aura 900 2._______________ de métros 3._____________________ et plus d’autobus. Il 4.___________________ de la Journée sans voiture. Les habitants sont encouragés à choisir un moyen de transport plus propre et moins 5.______________________ , qui consomme moins d’6.__________________. Cette année, 99 villes française et 1 321 villes étrangères ont décidé d’y7.___________________. Avec la Journée sans voiture, l’air est moins pollué que d’habitude et les gens plus sympathiques. Mais une question8.___________________ : est-ce que cette journée a aidé à ch anger les habitudes des Français? Selon une9.__________________ en 2002, de nombreux Français pensentqu’une journée ne 10.__________________pas pour améliorer la qualité de vie, et trois quarts d’entre eux disent qu’ils préfèrent toujours leur voiture.温馨提示:听力局部选择题,请在答题卡上填涂1—15;单项选择题填涂16—35;阅读题填涂36—55。

语言学考试和答案一、单项选择题(每题2分,共20分)1. 语言是人类最重要的()。
A. 交际工具B. 思维工具C. 表达工具D. 学习工具答案:A2. 语言的最小意义单位是()。
A. 语素B. 词C. 句子D. 音节答案:A3. 语言学的主要研究对象是()。
A. 语音B. 语法C. 词汇D. 语言答案:D4. 语音学是研究()的学科。
A. 语音的物理属性B. 语音的生理属性C. 语音的感知属性D. 语音的社会属性答案:A5. 语法学是研究()的学科。
A. 语言的词汇B. 语言的语音C. 语言的结构规则D. 语言的意义答案:C6. 语义学是研究()的学科。
A. 语言的词汇B. 语言的语音C. 语言的意义D. 语言的结构规则答案:C7. 社会语言学是研究()的学科。
A. 语言的演变B. 语言与社会的关系C. 语言的语音D. 语言的语法答案:B8. 心理语言学是研究()的学科。
A. 语言的心理过程B. 语言的语音C. 语言的语法D. 语言的社会属性答案:A9. 计算语言学是研究()的学科。
A. 语言的演变B. 语言与计算机的关系C. 语言的语音D. 语言的语法答案:B10. 语言的任意性是指()。
A. 语言符号与它所指的对象之间没有必然的联系B. 语言符号与它所指的对象之间有必然的联系C. 语言符号与它所指的对象之间有偶然的联系D. 语言符号与它所指的对象之间有逻辑的联系答案:A二、多项选择题(每题3分,共15分)11. 语言的基本功能包括()。
A. 交际功能B. 思维功能C. 社会功能D. 文化功能答案:ABCD12. 语言的要素包括()。
A. 语音B. 语法C. 词汇D. 语义答案:ABCD13. 语音学的研究内容主要包括()。
A. 发音语音学B. 听觉语音学C. 声学语音学D. 社会语音学答案:ABCD14. 语法学的研究内容主要包括()。
A. 句法B. 词法C. 语义语法D. 语用语法答案:ABCD15. 语义学的研究内容主要包括()。

I.Choose the best answer. (20%) 1. Using language for the sheer joy of using it shows that language has afunction.A. recreationalB. metalingualC. informativeD. performative 2. Displacement benefits human beings by giving them the power to handleA.arbitrariness and creativityB. generalizations and abstractionsC. interpersonal relationshipsD. performative functions, the task of a linguist is to determine from 3. According tothedata of performance the underlying system of rules that has been mastered by the language user.A. Roman JacobsonB. Leonard BloomfieldC. Kenneth PikeD. Noam Chomsky4.“A person can refer to Shakespeare even though he died many years ago.”This shows that language has the design feature ofA. dualityB. creativityC. displacementD. arbitrariness5.Which of the following is not the principal suprasegmental features?A. vowelB. stressC. toneD. intonation6.Which branch of phonetics concerns the production of speech sounds?A. Acoustic phoneticsB.Articulatory phoneticsC.Auditory phoneticsD.None of the above7.Which of the following word involve “nasalization”?A. rapB. readC. runningD. close8.Which of the following word is not likely to have stress in sentences?A. aB. testC. bikeD. sun9.“Don't end a sentence with a preposition.”This is an example ofA. prescriptiveB. descriptiveC. transformationalD. functional10.Which of the following is the correct description of [v]?A. voiceless labiodental fricativeB. voiced labiodental fricativeC. voiceless labiodental stopD. voiced labiodental stopII.D ecide whether the following statements are true or false. (20%) 11. Duality is one of the characteristics of human language. It refers to the fact that languages has two levels of structures: the system of sounds and the system of meanings.12.Prescriptive linguistics is more popular than descriptive linguistics, because it can tell us how to speak correct language.13.Suprasegmental phonology refers to the study of phonological properties of units larger than the segment-phoneme,such as syllable, word and sentence.14.The air stream provided by the lungs has to undergo a number of modification to acquire the quality of a speech sound.15.Two sounds are in free variation when they occur in thesame environment and do not contrast, namely, the substitution of one for theother does not produce a different word, but merely a different pronunciation.16. All syllables must have a nucleus but not all syllables contain an onset and a coda.17. When pure vowels or monophthongs are pronounced, no vowel glides take place.18. In most cases, the number of syllables of a wordcorresponds to the number of morphemes.19. By diachronic study we mean to study the changes and development of language.20. Langue is relatively stable and systematic while parole is subject to personal and situational constraints.III. Fill in the blanks. (20%)21. The theory that language arose from instinctive emotional cries,expressive of pain or joy has been called the 22. Saussure put forward two importantconcepts. the abstract linguistic system shared by all members of a speech community.23. Linguistic potential is similar to Saussure 'lasngue and Chomsky ' s24. In phonological analysis the words fail / veil aredistinguishable simply because of the two phonemes /f/ - /v/. This is an example fortheory.refers toillustrating25. refers to the phenomenon of sounds continuallyshow theinfluence of theirneighbors.26. phonetics studies the movement of the vocalorgans ofproducing the sounds ofspeech.27. According to , when there is a choice as to where to placea consonant, it is put into the onset ratherthan the coda.28. In English there are a number of , which are produced bymoving from one vowel position to another through intervening positions.29. Speech takes place when the organs of speech move to producepatterns of sound. These movements have an effecton thecoming from thelungs.30. The fact that different sounds are used to refer to the same object indifferent languages proves the of language.IV Explain the following terms.(20%)31.Allophone32. DistinctivefeaturesV. Answer the following questions.(20%)33. What are the main design features of humanlanguage?34. Give sound segments according to the description of them in thefollowing.(1) front mid-high unrounded laxvowel(2)bilabial nasal(3)voiceless postalveolar affricate(4)voiced alveolar trill(5)palatal approximant。

于对市爱美阳光实验学校度第二学期模块考试高一期中小语种英语试题〔2021.4〕考试时间 60 分钟总分值 60分第一卷〔选择题,共40 分〕第一:听力〔共二节,总分值10分〕第一节听下面5段对话。
每段对话后有一个小题,从题中所给的A,B,C三个选项中选出最正确选项,并标在试卷的相位置。
听完每段对话后,你都有10秒钟的时间来答复有关小题和阅读下一小题。
每段对话仅读一遍。
1.What size does the man want?A. Size 12.B. Size 10.C. Size 14.2.What happened to the man?A. He broke his leg.B. He hurt his arms.C. He had a car accident.3.How many swimming classes are there this semester?A.8.B. 13.C. 5.4.What does the woman think of the sailing?A. Dangerous.B. Exciting.C.Challenging.5.What is the man doing?A. Giving advice.B. Asking for help.C. Making an invitation.第二节听下面5段对话或独白。
每段对话或独白后有几个小题,从题中所给的A,B,C三个选项中选出最正确选项,并标在试卷的相位置。
听每段对话或独白前,你将有时间阅读各个小题,每题5秒钟;听完后,各小题将给出5秒钟的作答时间。
每段对话或独白读两遍。
听第六段材料,答复第6至7题。
6.What is the relationship between the two speakers?A.Husband and wife.B. Coach and player.C. Doctor and patient.7.What do we know about the man?A.He had a heart attack.B.He’s on the football team.C.He used to play football very well.听第七段材料,答复第8至9题。

I. Choose the best answer. (40%)1. Pitch variation is known as _____A_____ when its patterns are imposed on sentences.A. intonationB. toneC. pronunciationD. voice2. Conventionally a _____C_____ is put in slashes (/ /).A. allophoneB. phoneC. phonemeD. morpheme3. In English –ise and –tion are called ____B______.A. prefixesB. suffixesC. infixesD. stems4. Which branch of linguistics studies the similarities and differences among languages?DA. Diachronic linguisticsB. Synchronic linguisticsC. Prescriptive linguisticsD. Comparative linguistics5. Which one is different from the others according to manners of articulation?BA. [z]B. [w]C. [θ]D. [v]6. Which one is different from the others according to places of articulation?AA. [n]B. [b]C. [m]D. [p]7. Which of the following words is entirely arbitrary?AA. treeB. typewriterC. crashD. bang8. What kind of sounds can we make when the vocal cords are vibratingB?A. V oicelessB. V oicedC. Glottal stopD. Consonant9. Which of the following word involve ―nasalization‖?CA. rapB. readC. runningD. close10. Whose Cardinal V owel system is still in use?CA. A. J. EllisB. A. M. BellC. Daniel JonesD. A. C. Gimson11. Which of the following is called schwa?DA. [a]B.[æ]C. [o]D.[ə]12. In Chinese when someone breaks a bowl or a plate the host or the people present are likely to say―碎碎(岁岁)平安‖as a means of controlling the forces which they believes feel might affect their lives. Which functions does it perform?CA. InterpersonalB. EmotiveC. PerformativeD. Recreational13. Study the following dialogue. What function does it play according to the functions of language?B—A nice day, isn’t it?— Right! I really enjoy the sunlight.A. EmotiveB. PhaticC. PerformativeD. Interpersonal14. Which branch of phonetics concerns the production of speech sounds?BA. Acoustic phoneticsB. Articulatory phoneticsC. Auditory phoneticsD. None of the above15. Which of the following is the correct description of [v]?BA. voiceless labiodental fricativeB. voiced labiodental fricativeC. voiceless labiodental stopD. voiced labiodental stop16. _________ refers to the actual realization of the ideal language user’s knowledge of the rules of his language in utterances.A. PerformanceB. CompetenceC. LangueD. Parole17. An aspirated p, an unaspirated p and an unreleased p are __________ of the p phoneme.A. analoguesB. tagmemesC. morphemesD. allophones18. The opening between the vocal cords is sometimes referred to as __________.A. glottisB. vocal cavityC. pharynxD. uvula19. The diphthongs that are made with a movement of the tongue towards the center are known as __________ diphthongs.A. wideB. closingC. narrowD. centering20. A phoneme of a group of similar sounds called __________.A. minimal pairsB. allomorphsC. phonesD. allophonesII. Fill in the blanks. (20%)21. Consonant sounds can be either __________ or __________, while all vowel sounds are ____.22. Consonant sounds can also be made when two organs of speech in the mouth are brought close together so that the air is pushed out between them, causing __________.23. The qualities of vowels depend upon the position of the __________ and the lips.24. One element in the description of vowels is the part of the tongue which is at the highest point in the mouth. A second element is the __________ to which that part of the tongue is raised.25. Consonants differ from vowels in that the latter are produced without __________.26. In phonological analysis the words fail / veil are distinguishable simply because of the two phonemes /f/ - /v/. This is an example for illustrating __________.27. In English there are a number of __________, which are produced by moving from one vowel position to another through intervening positions.28. _______ refers to the phenomenon of sounds continually show the influence of their neighbors.29. Speech takes place when the organs of speech move to produce patterns of sound. These movements have an effect on the __________ coming from the lungs.30. Saussure put forward two important concepts. __________ refers to the abstract linguistic system shared by all members of a speech community.III. Decide whether the following statements are true or false. (20%)31. Duality is one of the characteristics of human language. It refers to the fact that languages has two levels of structures: the system of sounds and the system of meanings.32. Prescriptive linguistics is more popular than descriptive linguistics, because it can tell us how to speak correct language.33. Sound [p] in the word ―spit‖ is an unaspirated stop.34. Suprasegmental phonology refers to the study of phonological properties of units larger than the segment-phoneme, such as syllable, word and sentence.35. Acoustic phonetics is concerned with the perception of speech sounds.36. In most cases, the number of syllables of a word corresponds to the number of morphemes.37. The maximal onset principle states that when there is a choice as to where to place a consonant, it is put into the coda rather than the onset.38. Base refers to the part of word that remains when all inflectional affixes are removed.39. Fore as in foretell is both a prefix and a bound morpheme.40. Two sounds are in free variation when they occur in the same environment and do not contrast, namely, the substitution of one for the other does not produce a different word, but merely a different pronunciation.41. All syllables must have a nucleus but not all syllables contain an onset and a coda.42. When pure vowels or monophthongs are pronounced, no vowel glides take place.43. According to the length or tenseness of the pronunciation, vowels can be divided into tense vs.lax or long vs. short.44. Received Pronunciation is the pronunciation accepted by most people.45. Language is a system of arbitrary, written signs which permit all the people in a given culture, or other people who have learned the system of that culture, to communicate or interact.46. Competence and performance refer respectively to a language user’s underlying knowledge about the system of rules and the actual use of language in concrete situations.47. By diachronic study we mean to study the changes and development of language.48. Langue is relatively stable and systematic while parole is subject to personal and situational constraints.49. In language classrooms nowadays the grammar taught to students is basically descriptive, and more attention is paid to the developing learner s’ communicative skills.50. Arbitrariness of language makes it potentially creative, and conventionality of language makesa language be passed from generation to generation. As a foreign language learner, the latter is more important for us.IV. Explain the following terms, using examples. (20%)51. Assimilation52. Suprasegmental feature53. Complementary distribution54. Distinctive features51. Assimilation rule assimilates one sound to another by ―copying‖a feature of a sequential phoneme, thus making the two phones similar.52. Suprasegmental feature refers to the phonemic features that occur above the level of the segments.53. Not all speech sounds occur in the same environment, when the two sounds never occur in the same environment they are said to be in complementary distribution.54. The features that a phoneme possesses, making it different from other phonemes, are its distinctive features.。

Mid-Term Exercises of Linguistics_____________________________________________________________________ I.Blank Filling1. Linguistics is the scientific systematic study of __________ .2. To many people, a linguist is the same as a ________ , one who can speak several Languages fluently.3. In professional usage, the ______ is a scholar who studies Language objectively, observing it scientifically, recording the facts of Language, and generalizing from them.4. ______ phonetics studies the movement of the vocal organs of producing the sounds of speech; _______ phonetics studies the way the sounds of speech are perceived by the human ear.5. The ancient theories of the origin of Language were of ____origin.6. The theory that primitive man made involuntary vocal noises while performing heavy work has been called the ___ theory.7. A commonly held view among the classic Greeks was that at some ancient time there was a“___ “ who gave the correct, natural name to everything.8. The theory that Language arose from instinctive emotional cries, expressive of pain or joy has been called the ___ theory.9. The theory that primitive Language was an imitation of natural sound, such as animal cries, has been called the theory .10. The symbols are said to be arbitrary because they do not ___ what they represent.11. Language is called upon not only for communication, but also for ___ and cultural ____.12. Language is an ___ system of articulated sounds made use of by a group of humans as a means of carrying on the affairs of their society.13. The earliest grammar of any Language was ___ grammar by the Hindu scholar Panini.14. The Language of Britain was ___ when the Romans invaded the land in 55 and 54BC.15. The Celtic Language was influenced by ___ during the roman occupation after AD 44.16. The three Teutonic groups established in England by the successive invasions afterAD450 were: ___, ___ and __.17. As a result of the Norman Conquest of 1066, vast quantities of ___ words were added to the English vocabulary.18. The most memorable writing in the Middle English period was ___ by Geoffrey Chaucer.19.As Samuel Johnson’s A Dictionary of the English Language established a uniform standard for ___ and word use, so Bishop Lowth’s and other grammarians’ wo rks standardized English ___.20. When sounds are produced, the air-stream sent out from the lungs passes through the ___ contained in the larynx.21. A sound which is made with the glottis wide open is called a ___ sound.22. Consonant sounds can be either ___ or ___, while all vowel sounds are ___.23. The shape of the ___ and ___ cavities can be changed, and each change producesa different sound.24. The differences between the vowel in the word tea and the vowel in the word two is that the first is made with the lips ___ and the front of the tongue humped, and the second is made with the lips ___ and the back of the tongue humped.25. The sounds /t/, /d/, /p/, and /b/ are made when the ___ in the mouth is suddenly opened and the air allowed to escape in a little puff or explosion.26. The sounds /f/ and /v /are the result of air escaping under friction between the lower ___ and upper ___.27. The qualities of vowels depend upon the position of the ___ and the lips.28. _________ sounds are produced by retracting the body of the tongue from the neutral position.29. V owels can be described by referring to the part of the tongue which is at the highest point in the mouth. If the front of the tongue is at the highest point near thehard palate, a ___ vowel is produced. If the back of the tongue is at the highest point near the soft palate, a ___ vowel is produced.30.If, in making a vowel sound, the organs of speech remain in one position without moving to another, the result is a ___ vowel. If the organs of speech start in the position for one vowel and then immed8iately glide to the position of another, the result is a ___.31. A phoneme is a group of similar sounds called___.32. An aspirated p, an unaspirated p, and an unreleased p are ___ of the p ___.33. The contrast between k and g enables us to distinguish between words which would otherwise by ___.34. Conventionally a phoneme is put in ___ while an allophone is put in ___ brackets.35. The sounds and the meaning of a word are ___.36. Morphology is the study of word ___ and the internal ___ of words.37. The most elemental grammatical units in a Language are ___.38. Some morphemes are ___ in that they must be joined to other morphemes, and are always parts of word and never words by themselves. Other morphemes are ___ in that they need not be attached to other morphemes.39. Bound morphemes may be subdivided into ___ and ___ morphemes.40. A small set of conjunctions, prepositions and pronouns belongs to “___ class’, while the largest part of noun s, verbs, adjectives and adverbs belongs to “___ class”.41. According TG grammarians, perhaps the most important fact about the sentences of human Languages is that all sentences have both a ___ structure and a ___ structure.II. Short-answer Questions:Explain each of the following linguistic views in no more than 50 words. .ment on the saying “Language is culturally-transmitted”.2.Words can form by compounding, blending ,back-formation, acronym andborrowing,etc.Give two .words for each of them.Mid-Term Exercises of LinguisticsAnswer SheetName_______________________ Student Number ________________ I.Blank filling.II.Short answer questions.12.。

2012—2013学年度第一学期《英语语言学概论》期中试卷A Mid-term Examination Paper in Introduction to English LinguisticsⅠ Multiple Choice (40%)Directions:In each question there are four choices. Decide which one would be the best answer to the question or to complete the sentence best. Mark your answer on the Answer Sheet.1. What kind of function does the sentence “How do you do?” have?A. InformativeB. EmotiveC. Recreational D Phatic communion2. ______________ has been widely accepted as father of modern linguistics.A. BloomfieldB. SaussureC. ChomskyD. Halliday3. _____________ is a voiced alveolar stop.A. /d/B. /g/C. /b/D. /z/4. Of the following sound combination, only _____________ is permissible in English.A. bkilB. kiblC. ilkbD. ilbk5. As modern linguistics aims to describe and analyze the language people actually use, and not to lay down rules for "correct" linguistic behavior, it is said to be ______________.A. prescriptiveB. sociolinguisticC. psycholinguistic D descriptive6. The process that “televise” derives from “television” is known as___________.A. blendingB. zero-derivationC. acronym D back-formation7. A historical study of language is a _____________ study of language.A. prescriptiveB. descriptiveC. diachronicD. synchronic8. In the cardinal vowel diagram, ______________ is called schwa.A. [ә]B. [a]C. [i]D. [o]9. Nouns and verbs in English belong to ______________ words.A. invariableB. closed-classC. grammaticalD. lexical10. is a process in which part of the form is native and part is borrowed, but the meaning is fullyborrowed.A. LoanshiftB. Loan translationC. LoanwordD. Loanblend11. The word “so” in “I think so.” is a _________________.A. pronounB. pro-formC. auxiliaryD. determiner12. The morpheme “-ceive” in “de ceive” is ________________.A. a derivational affixB. an inflectional affixC. a free root D a bound root13. Unlike animal communication systems, human language is_______.A. stimulus freeB. stimulus boundC. under immediate stimulus controlD. stimulated by some occurrence of communal interest14. Compound words consist of _____ morphemes.A. bound C. both bound and freeB. free D. neither free nor bound15. All syllables contain a/an______.A. nucleusB. codaC. onsetD. rhyme16. ____________refers to the fact that the forms of linguistic signs bears no relationship to their meaning.A. CreativityB. DisplacementC. DualityD. Arbitrariness17. Velum refers to_______.A. larynxB. soft palateC. alveolarD. pharynx18. A _____ is any morpheme or combination of morphemes to which an inflectional affix can be added.A. stemB. rootC. allomorphD. lexeme19. The different phones which can represent a phoneme in different phonetic environments are called the ____ of that phoneme.A. phonesB. soundsC. phonemesD. allophones20. Which of the following compounds is exocentric?A. self-controlB.eye-entertainingC.water-resistantD. cutthroatⅡ True or False Questions (20%)Directions:Decide whether the following statements are true or false. Write T for true and F for false in the bracket before each of them. Mark your answer on the Answer Sheet.21. ( ) The sound /p/ in the word “expensive” is pronounced as a aspirated consonant.22. ( ) A root is not always a free form.23. ( ) All affixes are bound morphemes.24. ( ) Macrolinguistics includes psycholinguistics, sociolinguistics, pragmatics, anthropologicallinguistics, and computational linguistics.25. ( ) “Tofu” is a direct borrowing from Chinese.26. ( ) English is a tone language.27. ( ) The words “water” and “teacher” have a common phoneme and a common morpheme as well.28. ( ) Words are the smallest meaningful units of language.29. ( ) Bound morphemes cannot occur alone.30. ( ) English is more difficult than Chinese.III Define the Following Terms (20%)31. morpheme32. duality33. articulatory phonetics34. phoneme35. diachronicIV Short Essay Questions (20%)36. Can you work out a phonological rule from the following examples? (10%)peak—speaktank—standkeep—skirt47. Illustrate the differences between inflectional affixes and derivational affixes. (10%)。

LING5502 Topics in Chinese Syntax and Semantics汉语句法及语义专题2010-11 第二学期期中考试问题:一. 我们的讨论显示,在汉语中,普通名词从NP结构内基础生成,即填入名词短语中心语N的位置,代词直接填入定指结构中心语 D 的位置。
结合Huang, Li & Li (2009,The Syntax of Chinese) 第8章中有关的结构处理,讨论并解释为何与(1) 相比,(2) 合语法,而(3) 则不合语法。
用有效的结构图支持你的论点。
(25分)(1) 他们两位老师(都住在学校附近)(2) a. 他们那两位老师(都住在学校附近)b. 那两位老师他们(都住在学校附近)(3) a.*老师两位他们(都住在学校附近)b.*他们两位老师们(都住在学校附近)c.*他们那两位老师们(都住在学校附近)d.*老师们他们两位(都住在学校附近)e.* 那两位他们老师(都住在学校附近)注:将讨论的篇幅限制在半页以内。
以上各例括号中的语料仅用来提供必要的语境在讨论范围内。
参考意见:(1) is correct:The author believes that a pronoun can be followed by number, classifier, and noun, which means the pattern [ pronoun+number+classifier+noun] is possible. The structure is [DP 他们[NumP 两[CLP 位[NP 老师]]]].(2)a is correct: And the author also mentioned that pronouns and demonstratives, which have both been claimed to occupy the D position, can occur together. The structure is :[DP [DP他们] 那[NumP 两[CLP 位[NP 老师]]]],the pronoun is the Spec of D.(2)b is correct: [DP那[Nump两[CLP位[NP老师[DP他们]]]]].(3)a is wrong:It is mentioned that common nouns are not base-generated in D or Spec of DP but they are base-generated in N. We expect the order of [noun+number+classifier] can’t be base- generated. It can’t be derived by movement of N to D because this movement is ruled out by the Head Movement Constraint which disallows movement of one head across another. And common nouns cannot be followed by demonstratives(and/or pronouns).(3)b ,(3)c and (3)e are wrong: –men is not compatible with [number+classifier]expression;-men can be suffixed to a definite expression taking the form of a proper name or a pronoun, this is not possible with the definite expression consisting of a demonstrative.(3)d and (3)e are wrong: A pronoun followed by –men can be followed by not preceded by a number phrase.二.Huang, Li & Li (2009) 在The Syntax of Chinese一书的第二章(Chapter 2) 2.1.2.节中为什么要提出汉语动补复合词中论元匹配与组合的问题?问题的实质是什么?(即与之相关的理论问题是什么?) (25分)注:将讨论的篇幅限制在半页以内。

语言学期中考试题及答案一、选择题(每题2分,共20分)1. 以下哪个选项是“语言”的正确定义?A. 一种交流的工具B. 一种数学符号C. 一种艺术形式D. 一种物理现象答案:A2. 语言的起源可以追溯到:A. 古代文明B. 史前时期C. 现代科学D. 宗教信仰答案:B3. 语言的语法规则包括:A. 词法和句法B. 词法和音位学C. 句法和音位学D. 词法和语义学答案:A4. 在语言学中,“语用学”研究的是:A. 语言的物理属性B. 语言的社会功能C. 语言的历史发展D. 语言的内在结构答案:B5. “语言习得”通常指的是:A. 学习第二语言B. 学习母语C. 学习计算机语言D. 学习任何语言答案:D6. 以下哪个选项是“方言”的正确定义?A. 一种语言的书面形式B. 一种语言的口头形式C. 一种语言的变体D. 一种语言的方言答案:C7. 语言的“词汇”包括:A. 单词和短语B. 单词和句子C. 短语和句子D. 单词和音节答案:A8. 语言的“音位学”研究的是:A. 语言的发音B. 语言的书写C. 语言的语法D. 语言的意义答案:A9. “双语者”是指:A. 同时使用两种语言的人B. 学习两种语言的人C. 只使用一种语言的人D. 无法使用任何语言的人答案:A10. 语言的“语义学”研究的是:A. 语言的发音B. 语言的意义C. 语言的语法D. 语言的使用答案:B二、填空题(每题2分,共20分)1. 语言是一种________的工具。
答案:交流2. 语言的起源可以追溯到________时期。
答案:史前3. 语言的语法规则包括词法和________。
答案:句法4. 在语言学中,“语用学”研究的是语言的________功能。
答案:社会5. “语言习得”通常指的是学习________。
答案:任何语言6. “方言”是指一种语言的________。
答案:变体7. 语言的“词汇”包括单词和________。
答案:短语8. 语言的“音位学”研究的是语言的________。
Mid-term reviewLanguage and linguistics:Descriptive, prescriptive, synchronic, diachronic, langue, parole, competence, performance ●Design features of language with examples P5中文2009-11-14Design features of languageArbitrarinessDualityCreativityDisplacementVocalInterchangeabilityCulture transmissionsystematic1Ps后四个课件有,书上没有●Functions of language with examples P71 Informative(告知功能)e.g. He went to Japan last week.I have finished my term paper.2 Interpersonal function(人际功能)e.g. dear professor/sir3 Performative (施动功能)e.g. I announce you husband and wifeI hereby name this ship “hope”.4 Emotive functione.g. What a picturesque place!5Phatic functione.g. How are you today!A fine day, isn’t it?6 Recreational function7Metalingual function (语言解释功能)●Name different linguistic branches and their field of study.Microlinguitics-- Phonetics, Phonology, Morphology, Syntax, Semantics, Pragmatics.Macrolinguistics-- Psycholinguistics, Sciolinguistics, Anthropological linguistics, Computational linguisticsPhonetics:Phonetics, phonology, vowels, co articulation, assimilation, phoneme, allophone, minimal pair, syllableminimal pair—to take a word,replace one sound by another, and see whether a different meaning results.●Terms used in manner and place of articulation (英文书p35图)●Distinctive features of vowels元音and consonants辅音whether they have the obstruction of airstream or not●The importance of stress, intonation and toneThe importance of stress1.Different place of the stress can represent different gramatical funtion of a word.Eg. In`sult (v.)--`insult (n.)2.The alternations of stress occured between compound words and phrases.Eg. Black `board--`blackboard3.In a sentence, stress is often used to express emphasis,surprise ect.The importance of intonationA difference in tone changes thte meaning of a group of words and, when this happens, it is called a difference in intonation. The rising tone at the end of the an utterance is often used for asking yes-no questions and showing politeness or surprises, whereas tha falling tone sometimes leads to rudenesss and abrupness.The importance of toneIn Chinese tone changes are used in a different way, affecting the meaning of individual words.Morphology:Morpheme, allomorph, inflection, derivation, pro-form, stempro-form:An item in a sentence, typically a pronoun, verb, or adverb, that substitutes for a constituent phrase or clause.3 general classifications of words with examples1.Variable & Invariablea.Variable words:e.g.work—works—working—workedbig—bigger—biggestcup—cupsb.Invariable wordse.g.a/an, in, on, over, under, since, because, and, but, he, I, we, our when, seldom, hello2.Grammatical words虚词vs. lexical words实词a.Grammatical words1) Those which express grammatical meanings.2) conjunctions, prepositions, articles, and pronouns are grammatical words.3) As the grammatical ones serve to link its different parts together, they are also known as function words.b.lexical words1) Those which have lexical meanings.2) Those can be used to refer to substance, action and quality, such as noun, verb, adjective.nouns, verbs, adjectives, and adverbs3) As the lexical words carry the main content of a language, it was also known as content words.Eg.He is a young man.Grammatical words—he, aLexical words—is, young, man3.Open class & closed classa.Open class pronouns,prepositions, conjunctions, articles. (auxiliary verbs which used to be ranked as open-classes, are relatively close in number)b.closed class nouns, verbs, adjectives, and many adverbs. (preposition is relativelyopen in English. )●Word class with examples P56中文1) Particle 助词,小品词,介副词Eg. to deal withThey did not come on time.look back2) Auxiliaries 助动词1) Negation否定: He will not come.2) Inversion倒装: Does he come?3) Code语码: I will come and so will Tom.4) emphasis强调: He did come.3) Pro-form 代词形式Types of Pro-form:•Pro- adjective代形容词You are right. So is he.•Pro-verb 代动词He knows English better than she did.•Pro-adverb代副词He joined the game and I did so too.•Pro-locative代处所词Mary is sitting there, in front of the computer.●Lexical change with examples P731.invention eg. Coke, nylon2.blending eg. Smoke+ fog=smog3.abbreviation 缩写词eg. Ways of clipping1) Cutting the final partadvertisement ad2) Cutting the initial parttelephone phone3) Cutting both the initial and the final part.influenza flurefrigerator fridge4. Acronym 缩略语e.g. WTO--World Trade Organization,WB --World bank,VAT--value added tax5.Back-formation逆构词法eg.原来先有的是长的那个词语,把原词截断后,才创造了短的那个词语1.back-form from back-formationmentate from commentator3.diplomat from diplomatic4.edit from editor6.analogical creation 类推构词eg. Work 原来的分词形式是wrought, 但写错的人多了,就成了worked Wrought→worked7.Borrowing 借词i. Loanword (both form and meaning) eg. Tea Sputnikii. Loanblend (part is native, part is borrowed) eg. Chinatowniii. Loanshift ( form is native, meaning is borrowed)eg. bridgeiv. Loanshift ( form is native, meaning is borrowed) eg. Black humor (From French Translation)●Difference between English word and Chinese ZiComparison of Chinese and Englishwriting systemBasic Unit English word Chinese ZiA tight-knit unitPhonology Sound Phoneme: 1 or moreSyllable: 1 or morePhoneme: 1 to 4Syllable: 1Writing system Letter: 1 or more(usually 1 letter for1 phoneme)Square character: 1Morphology Meaning Morpheme: 1 ormoreMorpheme: 1 or lessSyntax:Syntagmatic relation, immediate constituent, endocentric, exocentric, paradigmatic relation subordination, coordination, phrase, clause, conjoining, embedding, transformational rulesparadigmatic relation--is a relation holding between elements replaceable with each other at a particular place in a structure ,or between one element present and the others present.IC analysisSementics:Referential theory-- the theory of meaning which relates the meaning of a word to the thing it refers to, or stands for.Synonymy --Two words, or expressions, which have the same semantic components Antonymy--Words with a contrasting componentHyponymy --Words which have all the semantic components of another denotation,connotation,concept means something that is abstract, which has no exitence in the materiak world and can only be sensed in our minds.reference,componential analysis--An approach to the study of meaning which analyzes a word into a set of meaning components or semantic features.entailment,syllogism(三段论)proposition(命题) P:a statement, with a truth value (true or false),●Types of meaning with examples 108中文1. Conceptual meaning 概念意义Eg. A Woman means an adult femal2.Associative meaninga.Connotative meaning 内涵意义eg. magpie means Gossip in Englishb.Social meaning 社会意义eg. The animal horse can be referred to by different words--Steed (poetic) Horse (general) Nag (slang) Gee-gee (baby language)c.Affective meaning 感情意义eg.I’m terribly sorry to interrupt, but I wonder if you would be so kind as to lower your voices a little.—showing that Iam annoyed by the noise.d.Reflected meaning 反射意义eg. hot weather → hot girle.Collocative meaning 搭配意义eg.Pretty: girl, boy, woman, flower, garden, color, village,Handsome: boy, man, car, vessel, overcoat, airliner, etc.3. Thematic meaning 主位意义Eg.Mrs. Bessie Smith donated the first prize.The first prize was donated by Mrs. Bessie Smith. 通过语序表强调。
语言学期中测试班级: 姓名:学号:I: Multiple Choice第一章语言与语言学1. Linguistics can be defined as the scientific study of ___.A. A particular languageB. The system of a particular languageC. Human languages in generalD. The English languageWilliam Shakespeare's play Romeo and Juliet, Juliet said "What's in a name That which wecall a rose by any other name would smell as sweet." This illustrates ___.A. the arbitrary nature of languageB. the big difference between human language and animal communicationC. the creative nature of languageD. the universality of language3. Which of the following features is NOT one of the design features of languageA. Productive.B. Dual.C. SymbolicD.Arbitrary4. Who put forward the distinction between langue and paroleA. HallidayB. Ferdinand de SaussureC. Noam ChomskyD. Charles Hockett5. One of the properties of language is that a language user can understand and produce sentenceshe/she has never heard before. This property of language is called ___.A. dualityB. arbitraryC. displacementD. Productivity6. The ____ function refers to the fact that language can be used for establishinga favorable atmosphere or maintaining social contact rather than for exchanging information or ideas.A. phaticB. directiveC. evocativeD. performative7. Modern linguistics is the scientific study of language. Consequently, modern linguistics emphasizes the importance of language data collected from ___.A. newspapers and magazinesB. writing by the famous writersC. the language people actually speakD. radio broadcasts8. Language is passed on from one generation to the next through teaching and learningrather than by instinct. This property of language is called ___.A. interchangeabilityB. cultural transmissionC. productivityD. arbitrarinessa linguistic study describes and analyzes the language people actually use, it is said to be ___.A. DescriptiveB. linguisticC. prescriptiveD. analytic linguistic10. Which of the following statements is NOT trueA. Language is a system.B. Animals also have language.C. Language is symbolic.D. Language is arbitrary.11. According to Noam Chomsky, which of the following is seen as the ideal user’s internalized knowledge of his languageA. Competence.B. Parole.C. PerformanceD. Langue12. Our linguistic ability is a ___ gift of the species' gene program.A. biologicalB. physicalC. scientificD. chemical13. The description of a language at some point in time is a ___ study.A. diachronicB. prescriptiveC. descriptiveD. synchronic14. One of the properties of language is that there is no logical connection between meaning and sounds. This property of language is ___.A. dualityB. productivityC. displacementD. arbitrariness15. Language can be used to refer to contexts removed from the immediate situations of the speaker. This is what we mean by ___.A. dualityB. productivityC. displacementD. arbitrariness16. Cultural transmission is one of the ____features of language.A. suprasegmentalB. pragmaticC. distinctiveD. design17. As modern linguistics aims to describe and analyze the language people actually use, and not lay down rules for "correct " linguistic behavior, it is said to be ___.A. descriptiveB. sociolinguisticC. prescriptiveD. psycholinguistic18. Which of the following is the exception to the feature of arbitrariness of languageA. Native English wordsB. Borrowed wordsC. Onomatopoeic wordsD. One-syllable words19. Saussure took a(n) ____ view of language, while Chomsky looks at language froma ___ point of view.A. sociological, psychologicalB. psychological, sociologicalC. Applied, pragmaticD. Semantic, linguistic20. Modern linguistics regards the written language as ___.A. primaryB. correctC. secondaryD. stable第二章语音学与音系学1. The tone, defined as variation, is an important suprasegmental feature of tone languages such as ____.A. ChineseB. EnglishC. Chinese and EnglishD. English and French2. According to the places of articulation, sounds in English such as /t/, /l/ and /z/ can be labeled as ____ ones.A. dentalB. bilabialC. velar D alveolar3. Of the following sound combinations, only ____ is permissible according to the sequentla1 rules in English.A. kiblB. bkil C ilkb D. ilbk4. Of all the speech organs, the ____ is the most flexible.A lip B. mouth C. vocal cord D. tongue5. The sounds produced without the vocal cords vibrating are ____ sounds.A. voicelessB. voicedC. vowelD. consonantal6. ____ is a voiced alveolar stop.A . /z / B. /d / C. /k/ D. /b/7. The assimilation rule assimilates one sound to another by "copying" a feature of a sequential phoneme, thus making the two phones ____.A. identicalB. similarC. exactly alikeD. same8. Since /p/ and /b/ are phonetically similar, occur in the same environments and they can distinguish meaning, they are said to be ____.A. in phonemic contrastB. in complementary distributionC. the allophonesD. minimal pair9. The sound /f/ is a ____.A. voiced palatal affricateB. voiced alveolar stopC. voiceless velar fricativeD. voiceless labiodentals fricativel0. A ____ vowel is one that is produced with the front part of the tongue maintaining the highest position.A. backB. centralC. frontD. middle11. Distinctive features can be found running over a sequence of two or more phonemic segments. The phonemic features that occur above the level of the segments are called ____.A. suprasegmental featuresB. immediate constituentsC. phonetic componentsD. semantic features12. A(n)____is a unit that is of distinctive value. It is an abstract unit, a collection of distinctive phonetic features.A. phoneB. soundC. allophoneD. phoneme13. The different phones which can represent a phoneme in different phonetic environments are called the ____ of that phoneme.A. phonesB. soundsC. phonemesD. allophones14. Which of the following statements about allophone is NOT correctA. Allophones are different forms of the same phoneme.B. Allophones of the same phoneme are in complementary distribution.C. Allophones distinguish meani ng·D. Allophones are language specific.15. When pitch, stress and length variations are tied to the sentence rather than to the word, they are collectively known as ____.A. intonationB. toneC. phonemeD. sentence stress16. Which of the following is also called "semivowelsA. fricativesB. liquidsC. affricatesD. glides17. In terms of place of articulation, the two consonants /f/, /v/ are ____.A. denta1B. alveolarC. palatalD. labiodental18. In terms of manners of articulation, the sounds /p/, /b/, /t/,/d/, /k/,/g/ are ____.A. bilabialB. stopsC. affricatesD. fricatives19. What is your understanding of "the Adam’s apple”A. Part of Adam’s body.B. The front part of larynx.C. The top of larynx.D. A kind of apple.20. Which of the following is NOT a velar soundA. /k/B. /ŋ/C. /v/D./g/ 第三章形态学1. ____ is a process of combining two or more words into one lexical unit.A. DerivationB. BlendingC. AbbreviationD. Compounding2. Words such as "telex " and "workfare "are created through ____.A. blendingB. compoundingC. conversionD. affixation3. According to the morphological analysis, the underlined part in the word “internationali sm” should be referred to as a ____.A. rootB. stemC. prefixD. suffix4. Which of the following words is made up of bound morphemes onlyA. Happiness.B. Television.C. Ecology.D. Teacher.5. Which of the following words is a derivativeA. Able.B. Pet.C. Dusty.D. Change.6. How many morphemes are there in the word “d i sarmed”A. 2.B. 3.C. 4D. 57. When "-ing" in "gangling" is removed to get a verb "gangle", we call this way of creating words ____.A. suffixingB. compoundingC. back-formationD. acronymy8. The phoneme "vision" in the common word “television” is a(n) ____.A. bound morphemeB. bound formC. inflectional morphemeD. free morpheme9. As is known ____ are often thought to be the smallest meaningful units of language.A. wordsB. sentencesC. phonemesD. morphemes10. “-s” in the word "books" is ____.A. a derivative affixB. a stemC. an inflectional affixD. a root11. The meaning carried by the inflectional morpheme is ____.A. lexicalB. morphemicC. grammaticalD. semantic12. The compound word "bookstore" is the place where books are sold. This indicates that themeaning of a compound____.A. is the sum total of the meaning of its componentsB. can always be worked out by looking at the meanings of morphemesC. is the same as the meaning of a free phraseD. none of the above13. Bound morphemes are those that ____.A. have to be used independentlyB. cannot be combined with other morphemesC. have to be combined with other morphemesD. can either be free or bound14. As one of the affixes, a prefix is ____.A. below the stemB. after the stemC. before the stemD. in the middle of the stem15. ____ is a branch of grammar which studies the internal structure of words and the rules by which words are formed.A. syntaxB. grammarC. morphologyD. morpheme16. Which one of the following is NOT a suffix for adjectivesA. -ous .B. -nessC. -al17. ____ modify the meaning of the stem, but usually do not change the part of speech of the original word.A. PrefixesB. SuffixesC. RootsD. Affixes18. The stem of the word “d isengagements” is ____.A. engagementB. disengageC. engageD. disengagement19. Which of the following words is a derivational oneA. CocktailB. ReadsC. EstablishmentD. Kids20. ____ and ____ can constitute a compound.A. A stem, an affixB. A free morpheme; a free morphemeC. A root, an affixD. A prefix, a suffixII: Define the following terms2. parole3. competence4. performance5. synchronic study6. diachronic study7. IPA8. phonetics 229. narrow transcription10. phonology11. phoneme12. phone13. allophone14. assimilation rules15. suprasegmental features16. morpheme17. morph18. allomorph19. free morpheme20. bound morpheme21. inflectional morpheme22. derivational morpheme23 compounding24. conversion25. derivation语言学期中测试班级: 姓名:学号:I: Multiple Choice第一章语言与语言学1. Linguistics can be defined as the scientific study of ___.A. A particular languageB. The system of a particular languageC. Human languages in generalD. The English languageWilliam Shakespeare's play Romeo and Juliet, Juliet said "What's in a name That which wecall a rose by any other name would smell as sweet." This illustrates ___.A. the arbitrary nature of languageB. the big difference between human language and animal communicationC. the creative nature of languageD. the universality of language3. Which of the following features is NOT one of the design features of languageA. Productive.B. Dual.C. SymbolicD.Arbitrary4. Who put forward the distinction between langue and paroleA. HallidayB. Ferdinand de SaussureC. Noam ChomskyD. Charles Hockett5. One of the properties of language is that a language user can understand and produce sentenceshe/she has never heard before. This property of language is called ___.A. dualityB. arbitraryC. displacementD. Productivity6. The ____ function refers to the fact that language can be used for establishinga favorable atmosphere or maintaining social contact rather than for exchanging information or ideas.A. phaticB. directiveC. evocativeD. performative7. Modern linguistics is the scientific study of language. Consequently, modern linguistics emphasizes the importance of language data collected from ___.A. newspapers and magazinesB. writing by the famous writersC. the language people actually speakD. radio broadcasts8. Language is passed on from one generation to the next through teaching and learning rather than by instinct. This property of language is called ___.A. interchangeabilityB. cultural transmissionC. productivityD. arbitrarinessa linguistic study describes and analyzes the language people actually use, it is said to be ___.A. DescriptiveB. linguisticC. prescriptiveD. analytic linguistic10. Which of the following statements is NOT trueA. Language is a system.B. Animals also have language.C. Language is symbolic.D. Language is arbitrary.11. According to Noam Chomsky, which of the following is seen as the ideal user’s internalized knowledge of his languageA. Competence.B. Parole.C. PerformanceD. Langue12. Our linguistic ability is a ___ gift of the species' gene program.A. biologicalB. physicalC. scientificD. chemical13. The description of a language at some point in time is a ___ study.A. diachronicB. prescriptiveC. descriptiveD. synchronic14. One of the properties of language is that there is no logical connection between meaning and sounds. This property of language is ___.A. dualityB. productivityC. displacementD. arbitrariness15. Language can be used to refer to contexts removed from the immediate situations of the speaker. This is what we mean by ___.A. dualityB. productivityC. displacementD. arbitrariness16. Cultural transmission is one of the ____features of language.A. suprasegmentalB. pragmaticC. distinctiveD. design17. As modern linguistics aims to describe and analyze the language people actually use, and not lay down rules for "correct " linguistic behavior, it is said to be ___.A. descriptiveB. sociolinguisticC. prescriptiveD. psycholinguistic18. Which of the following is the exception to the feature of arbitrariness of languageA. Native English wordsB. Borrowed wordsC. Onomatopoeic wordsD. One-syllable words19. Saussure took a(n) ____ view of language, while Chomsky looks at language froma ___ point of view.A. sociological, psychologicalB. psychological, sociologicalC. Applied, pragmaticD. Semantic, linguistic20. Modern linguistics regards the written language as ___.A. primaryB. correctC. secondaryD. stable第二章语音学与音系学1. The tone, defined as variation, is an important suprasegmental feature of tone languages such as ____.A. ChineseB. EnglishC. Chinese and EnglishD. English and French2. According to the places of articulation, sounds in English such as /t/, /l/ and /z/ can be labeled as ____ ones.A. dentalB. bilabialC. velar D alveolar3. Of the following sound combinations, only ____ is permissible according to the sequentla1 rules in English.A. kiblB. bkil C ilkb D. ilbk4. Of all the speech organs, the ____ is the most flexible.A lip B. mouth C. vocal cord D. tongue5. The sounds produced without the vocal cords vibrating are ____ sounds.A. voicelessB. voicedC. vowelD. consonantal6. ____ is a voiced alveolar stop.A . /z / B. /d / C. /k/ D. /b/7. The assimilation rule assimilates one sound to another by "copying" a feature of a sequential phoneme, thus making the two phones ____.A. identicalB. similarC. exactly alikeD. same8. Since /p/ and /b/ are phonetically similar, occur in the same environments and they can distinguish meaning, they are said to be ____.A. in phonemic contrastB. in complementary distributionC. the allophonesD. minimal pair9. The sound /f/ is a ____.A. voiced palatal affricateB. voiced alveolar stopC. voiceless velar fricativeD. voiceless labiodentals fricativel0. A ____ vowel is one that is produced with the front part of the tongue maintaining the highest position.A. backB. centralC. frontD. middle11. Distinctive features can be found running over a sequence of two or more phonemic segments. The phonemic features that occur above the level of the segments are called ____.A. suprasegmental featuresB. immediate constituentsC. phonetic componentsD. semantic features12. A(n)____is a unit that is of distinctive value. It is an abstract unit, a collection of distinctive phonetic features.A. phoneB. soundC. allophoneD. phoneme13. The different phones which can represent a phoneme in different phonetic environments are called the ____ of that phoneme.A. phonesB. soundsC. phonemesD. allophones14. Which of the following statements about allophone is NOT correctA. Allophones are different forms of the same phoneme.B. Allophones of the same phoneme are in complementary distribution.C. Allophones distinguish meani ng·D. Allophones are language specific.15. When pitch, stress and length variations are tied to the sentence rather than to the word, they are collectively known as ____.A. intonationB. toneC. phonemeD. sentence stress16. Which of the following is also called "semivowelsA. fricativesB. liquidsC. affricatesD. glides17. In terms of place of articulation, the two consonants /f/, /v/ are ____.A. denta1B. alveolarC. palatalD. labiodental18. In terms of manners of articulation, the sounds /p/, /b/, /t/,/d/, /k/,/g/ are ____.A. bilabialB. stopsC. affricatesD. fricatives19. What is your understanding of "the Adam’s apple”A. Part of Adam’s body.B. The front part of larynx.C. The top of larynx.D. A kind of apple.20. Which of the following is NOT a velar soundA. /k/B. /ŋ/C. /v/D./g/ 第三章形态学1. ____ is a process of combining two or more words into one lexical unit.A. DerivationB. BlendingC. AbbreviationD. Compounding2. Words such as "telex " and "workfare "are created through ____.A. blendingB. compoundingC. conversionD. affixation3. According to the morphological analysis, the underlined part in the word “internationalism” should be referred to as a ____.A. rootB. stemC. prefixD. suffix4. Which of the following words is made up of bound morphemes onlyA. Happiness.B. Television.C. Ecology.D. Teacher.5. Which of the following words is a derivativeA. Able.B. Pet.C. Dusty.D. Change.6. How many morphemes are there in the word “disarmed”A. 2.B. 3.C. 4D. 57. When "-ing" in "gangling" is removed to get a verb "gangle", we call this way of creating words ____.A. suffixingB. compoundingC. back-formationD. acronymy8. The phoneme "vision" in the common word “television” is a(n) ____.A. bound morphemeB. bound formC. inflectional morphemeD. free morpheme9. As is known ____ are often thought to be the smallest meaningful units of language.A. wordsB. sentencesC. phonemesD.morphemes10. “-s” in the word "books" is ____.A. a derivative affixB. a stemC. an inflectional affixD. a root11. The meaning carried by the inflectional morpheme is ____.A. lexicalB. morphemicC. grammaticalD. semantic12. The compound word "bookstore" is the place where books are sold. This indicates that themeaning of a compound____.A. is the sum total of the meaning of its componentsB. can always be worked out by looking at the meanings of morphemesC. is the same as the meaning of a free phraseD. none of the above13. Bound morphemes are those that ____.A. have to be used independentlyB. cannot be combined with other morphemesC. have to be combined with other morphemesD. can either be free or bound14. As one of the affixes, a prefix is ____.A. below the stemB. after the stemC. before the stemD. in the middle of the stem15. ____ is a branch of grammar which studies the internal structure of words and the rules by which words are formed.A. syntaxB. grammarC. morphologyD. morpheme16. Which one of the following is NOT a suffix for adjectivesA. -ous .B. -nessC. -al17. ____ modify the meaning of the stem, but usually do not change the part of speech of the original word.A. PrefixesB. SuffixesC. RootsD. Affixes18. The stem of the word “disengagements” is ____.A. engagementB. disengageC. engageD. disengagement19. Which of the following words is a derivational oneA. CocktailB. ReadsC. EstablishmentD. Kids20. ____ and ____ can constitute a compound.A. A stem, an affixB. A free morpheme, a free morphemeC. A root, an affixD. A prefix, a suffixII: Define the following terms1. langue2. parole3. competence4. performance5. synchronic study6. diachronic study7. IPA8. phonetics 229. narrow transcription10. phonology11. phoneme12. phone13. allophone14. assimilation rules15. suprasegmental features16. morpheme17. morph18. allomorph19. free morpheme20. bound morpheme21. inflectional morpheme22. derivational morpheme23 compounding24. conversion25. derivation南京师范大学联办生学士学位课程考试英语专业《英语语言学》课程考试卷I. Multiple Choice ( 20x1)Directons: You are supposed to choose the best out of the four choices and write theletter of the answer you have chosen in the corresponding space in the TABLE.1. What are the dual structures of languageA. Sounds and letters.B. Sounds and meaningC. Letters and meaningD. Sounds and symbols.2. Which of the following is NOT a compound wordA. LandladyB. GreenhouseC. UpliftD. Unacceptable3. Which of the following statements about language is NOT trueA. Language is a system.B. Language is symbolic.C. Animals also have languageD. Language is arbitrary4. Who put forward the distinction between Langue and ParoleA. SaussureB. ChomskyC. HallidayD. Anonymous5. According to Chomsky, which is the ideal user's internalized knowledge of his languageA. competenceB. paroleC. performanceD. langue6. The study of the way listeners perceive the sounds is called ____.A. acoustic phoneticsB. auditory phoneticsC. articulatory phoneticsD. phonology7. The distinction between vowels and consonants lies in ____.A. the place of articulationB. the obstruction of airstreamC. the position of the tongueD. the shape of the lips8. Which is the branch of linguistics which studies the characteristics of speech sounds and provides methods for their description, classification and transcriptionA. Phonetics.B. Phonology.C. Semantics.D. Pragmatics.9. Which studies the sound systems in a certain languageA. PhoneticsB. PhonologyC. SemanticsD. Pragmatics10. Which studies the internal structure of words, and the rules by which words are formedA. MorphologyB. SyntaxC. PhonologyD. Semantics11. ______ does not study meaning in isolation, but in context.A. PragmaticsB. SemanticsC. Sense relationD. Concept12. ______is the act performed by or resulting from saying something; it is the consequence of or the change brought about by the utterance.A. A locutionary actB. An illocutionary actC. A perlocutionary actD. A performative act13. Historical linguistics explores __________.A. the nature of language changeB. the causes that lead to language changeC. the relationship between languagesD. all of the above14. Language change is essentially a matter of change _____.A. in collocationsB. in meaningC. in grammarD. in usages15. The most distinguishable linguistic feature of a regional dialect is its _____.A. use of wordsB. use of structuresC. accentD. morphemes16. ______ in a person's speech or writing usually ranges on a continuum from casual or colloquial to formal or polite according to the type of communicative situation.A. Regional variationB. Changes in emotionsC. Variation in connotationsD. Stylistic variation17. Human linguistic ability largely depends on the structure and dynamics of______.A. human brainB. human vocal cordsC. human memoryD. human18. Linguistic _____ is the brain's neurological specialization for language.A. fossilizationB. performanceC. competenceD. lateralization19. In first language acquisition, imitation plays _____.A. a minor roleB. a significant roleC. a basic roleD. no rule20. In general, a good second language learner is an adolescent_____.A. who has a strong and well-defined motivation to learnB. who seeks out all chances to interact with the inputC. who is willing to identify himself with the culture of the target language communityD. all the aboveII. Define the following terms (6x5)Directions: You are supposed to write each of the following definitions in the corresponding space.1. productivity2. context3. sentence and utterance4. regional dialect and sociolect5. psycholinguistics6. interlanguageIll. Decide whether the statements are true or false (10x1)Directions: You are supposed to put your answer T (true) or F (false) for each sentence into the corresponding space in the TABLE.1. A sentence cannot be a word or a fragment in strict sense, but an utterance can be a word or a fragment of a sentence.2. A stem first of all refers to any morpheme or combination of morphemes, but an affix can be added to it.3. Every word in a language can find at least one referent in the objective world.4. In most cases, lexicon means vocabulary and is related to the analysis and creation of words, idioms and collocations.5. The use of the term 'implicature' is different from 'implication' in that it usually indicates a rather narrowly denned logical relationship between two propositions.6. The defining properties of human language that distinguish it from any animal system of communication are termed design features.7. There are other channels, besides language, for communicating our thoughts, so language is only one aspect of semiotics.8. Modem linguistics regards the spoken language as primary, written language as secondary.9. Descriptive linguistics aims to lay down rules for 'correct' language use, ., to tell people what they should say and what should not say.10. Phonology is the branch of linguistics which studies the characteristics of speech sounds and their patterns.IV. Answer the following questions (4x10).Directions: You are supposed to answer each of the following questions in the corresponding space.1. What are the possible causes of language change2. Draw a tree diagram for the following sentence to show its syntactic structure They knew that the senator would win the election.3. What is arbitrariness Illustrate it with examples4. What do you think of Sapir-Whorf hypothesis Give examples or proof to support your point of view. ^。
语言学考试试卷和答案**语言学考试试卷**一、选择题(每题2分,共20分)1. 语言学是研究什么的科学?A. 语言的物理属性B. 语言的社会功能C. 语言的结构和规律D. 语言的历史发展2. 以下哪个选项不是语言学的分支?A. 语音学B. 句法学C. 社会语言学D. 数学3. 语言的最小意义单位是什么?A. 音素B. 词汇C. 词组D. 句子4. 语言的任意性是指什么?A. 语言符号的任意性B. 语言符号的固定性C. 语言符号的象似性D. 语言符号的规律性5. 以下哪个选项是语言的双重性质?A. 工具性和象征性B. 符号性和工具性C. 符号性和象征性D. 工具性和象征性6. 语言的同质性是指什么?A. 所有语言在结构上都相同B. 所有语言在功能上都相同C. 所有语言在形式上都相同D. 所有语言在结构和功能上都具有相似性7. 以下哪个选项是语言的变异性?A. 语言的同质性B. 语言的稳定性C. 语言的动态性D. 语言的不变性8. 语言的任意性原则是由哪位学者提出的?A. 索绪尔B. 乔姆斯基C. 布隆菲尔德D. 皮尔士9. 以下哪个选项是语言的交际功能?A. 认知功能B. 表达功能C. 审美功能D. 教育功能10. 语言的符号性是指什么?A. 语言符号与其所指对象之间的直接联系B. 语言符号与其所指对象之间的任意联系C. 语言符号与其所指对象之间的必然联系D. 语言符号与其所指对象之间的固定联系**答案**1. C2. D3. A4. A5. A6. D7. C8. A9. B10. B二、填空题(每题2分,共20分)1. 语言的______性是指语言符号与其所指对象之间没有必然的、自然的联系。
2. 语言的______性是指语言符号与其所指对象之间的联系是任意的。
3. 语言的______性是指语言符号与其所指对象之间的联系是约定俗成的。
4. 语言的______性是指语言符号与其所指对象之间的联系是固定的。
装订线满分(Full mark): 100 考试时间 (Duration ) : 90 分钟 (Minutes)Decide whether each of the following statements is True or False( ) 1. Linguistics is generally defined as the scientific study of language. T ( ) 2. Linguistics studies particular language, not languages in general. F ( ) 3.A diachronic study of language is the description of language at some point in time. F ( ) 4. Modern linguistics regards the written language as primary, not the written language. F ( ) 5. The distinction between competence and performance was proposed by F. de Saussure. F ( ) 6. If two phonetically similar sounds occur in the same environments and they distinguish meaning, they are said to be in complementary distribution.F( ) 7. A phone is a phonetic unit that distinguishes meaning. F ( ) 8. English is a tone language while Chinese is not. F ( ) 9. Words are the smallest meaningful units of language. F( ) 10. Just as a phoneme is the basic unit in the study of phonology, so is a morpheme the basic unit in the study of morphology. T ( ) 11. The syntactic rules of any language are finite in number, but there is no limit to the number of sentences native speakers of that language are able to produce and comprehend. T ( ) 12. In a complex sentence, the two clauses hold unequal status, one subordinating the other. T ( ) 13.What is actually internalized in the mind of a native speaker is a complete list of words and phrases rather than grammatical knowledge. F ( ) 14. Dialectal synonyms can often be found in different regional dialects such as British English and American English but cannot be found within the variety itself, for example, within British English or American English. F ( ) 15. The meaning of a sentence is the sum total of the meanings of all its components.F( ) 16. Most languages have sets of lexical items similar in meaning but ranked differentlyaccording to their degree of formality. T( ) 17. Both semantics and pragmatics study how speakers of a language use sentences to effectsuccessful communication. F( ) 18. It would be impossible to give an adequate description of meaning if the context oflanguage use was left unconsidered.T( ) 19. The meaning of a sentence is abstract, but context-dependent. F ( ) 20. Both semantics and pragmatics study meanings. TPart 2 Multiple Choice (1’*20=20’)There are four choices following each statement. Mark the choice that can best completethe statement.( ) 1. If a linguistic study describes and analyzes the language people actually use, it is said to be____.A. prescriptiveB. analytic D. linguistic( ) 2. According to F. de Saussure, ____ refers to the abstract linguistic system shared by all themembers of a speech community.A. paroleB. performance D. Language( ) 3. Language can be used to refer to contexts removed from the immediate situations of thespeaker. This feature is called____.B. dualityC. flexibilityD. cultural transmission ( ) 4. Which of the following is not a design feature of human language?A. ArbitrarinessB. Displacement( ) 5. The sounds produced without the vocal cords vibrating are ____ sounds.B. voicedC. vowelD. consonantal ( ) 6. ____ is a voiced alveolar stop.C. /k/D./b/( ) 7. The assimilation rule assimilates one sound to another by “copying” a feature of asequential phoneme, thus making the two phones ____.A. identicalB. sameC. exactly alike ( ) 8. A(n) ____ is a unit that is of distinctive value. It is an abstract unit, a collection ofdistinctive phonetic features.A. phoneB. sound( ) 9. The morpheme “vision” in the common word “television” is a(n) ____.A. bound morphemeB. bound formC. inflectional morpheme( ) 10. ____ are those that cannot be used independently but have to be combined with othermorphemes, either free or bound, to form a word.C. Bound wordsD. Words ( ) 11. ____ are often thought to be the smallest meaningful units of language by the linguists.C. PhonemesD. Sentences( ) 12. A sentence is considered ____ when it does not conform to the grammatical knowledge inthe mind of native speakers.A. rightB. wrongC. grammatical ( ) 13. “Alive” and “dead” are ____.A. gradable antonymsB. relational opposites D. None of the above( ) 14. ____ deals with the relationship between the linguistic element and the non-linguisticworld of experience.B. ConceptC. SemanticsD. Sense( ) 15. ____ refers to the phenomenon that words having different meanings have the same form.A. PolysemyB. Synonymy ( ) 16. Words that are close in meaning are called ____.A. homonymsB. polysemyC. hyponyms ( ) 17. ____ does not study meaning in isolation, but in context.C. Sense relationD. Concept装 订 线( ) 18. What essentially distinguishes semantics and pragmatics is whether in the study ofmeaning ____ is considered.A. referenceB. speech actC. practical usage ( ) 19. Speech act theory did not come into being until ____.late 50’s of the 20the centuryB. in the early 1950’sC. in the late 1960’sD. in the early 21st century. ( ) 20. ____ is advanced by Paul GriceB. Politeness PrincipleC. The General Principle of Universal GrammarD. Adjacency PrinciplePart 3 Definition (5’*5=25’)Define the following terms.Classify the consonants in each word.Example: [z] voiced alveolar fricative 1. [t] voiceless alveolar stop 2. [n] voiced nasal alveolar 3. [k] voiceless velar stop 4. [θ] voiceless interdental fricative 5. [l] voiced alveolar approximantPart 5 Morphology: Word Formation Processes (1’*10=10’)Insert the words in the table according to the word formation processes.Analyze the following sentences in terms of clauses, functions and categories.Example:He missed the early bus.He – subject NP / missed – predicate VP / the early bus – object NP 1. I am writing an essay on Milton.I – Subject NP Am writing - Predicate VP An essay on Milton - Object: NP 2. Your teaching style has impressed the new Principal. Your teaching style – Subject NP has impressed Predicate VP the new Principal- Object: NPPart 7 Semantics: Sense relations (0.5’*5=2.5’)Insert the following pairs of words in the table according to their sense relations.a. pass away/ dieb. stem/ flowerc. sweets/ candies Which of the Conversational Maxims is being violated in the following conversation?A: Tom is an excellent linguist. Don ’t you think? B: He is a good cookIt may be regarded as a violation of the maxim of ___relation___.(The hearer assumes that if the speaker is cooperative, his reply must be relevant in a different sense- Tom is not a good linguistic.a. to motherb. telephonec. moteld. VOAe. UFOf. televiseg. talkingh. boyishi. greenhousej. quake。
屯溪一中08-09学年高二下学期期中考试英语试题Class ________ Name ________ Score ________I. 听力(一共两节,满分是30分)第一节(一共5小题;每一小题1.5分,满分是7.5分)请听下面5段对话,选出最正确选项。
1.What are the speakers probably doing?A. Resting on the hillB. Picnicking on the hillC. Climbing a hill2. How much is the man’s bag?A. $2.5B. $4C. $53. Where does the conversation probably take place?A. In a shopping center.B. In a hotel.C. In a restaurant.4. Why doesn’t the man like to go to Canana for his vacation?A. It’s too cold there.B. He has been there before.C. He prefers to go to Mexico.5. What impressed the man most in Australia?A. The sea.B. The seaside cities.C. The beautiful beaches. 第二节(一共15小题;每一小题1.5分,满分是22.5分)请听下面5段对话或者独白,选出最正确选项。
请听第6段材料,答复第6、7题。
6. When will the man come back from the trip?A. On Nov. 13th.B. On Nov. 16th.C. On Nov. 21st.7. Why is the man so excited?A. He likes the weather there.B. It is his first time to go abroad.C. He can go on a trip with the woman.请听第7段材料,答复第8至10题。
1. The study of language as a whole is often called ________ linguistics.A. particularB. generalC. ordinaryD. generative2. Traditional grammar regards the ________ form of language as primary, not the spoken form.A. oralB. writtenC. writingD. vocal3. Who put forward the distinction between Langue and Parole?A.Saussure B.Chomsky C.Halliday D.Anonymous 4. According to F. de Saussure, ________ refers to the abstract linguistic system shared by all the members of a speech community.A. paroleB. performanceC. langueD. Language5. Language is arbitrary in that there is no logical connection between meanings and ________.A. wordsB. soundsC. objectsD. ideas6. Which of the following isn’t the design features of human language?A. arbitrarinessB. performanceC. dualityD. displacement7. The core of linguistics excludes ________.A. semanticsB. morphologyC. phoneticsD. psycholinguistics8. Morphology refers to the ________ of words.A. scienceB. formC. historyD. system9. The smallest meaningful unit of language is ________.A. morphemeB. phoneC. phonemeD. allomorpheme10. The word “boyish” contains two ________.A. phonemesB. morphsC. morphemesD. allomorphs11. ________ morphemes are those that cannot be used independently but have to be combined with other morphemes, either free or bound, to form a word.A. FreeB. BoundC. RootD. Affix12. Morphemes that represent “tense”, “number”, “gender”, “case” and so forth are called ________ morphemes.A. inflectionalB. independentC. freeD. derivational13. ________ modify the meaning of the stem, but usually do not change the part of speech of the original word.A. PrefixesB. SuffixesC. RootsD. Affixes14. In English “-ise” and “-tion” are called ________.A. prefixesB. suffixesC. infixesD. free morphemes15. There are rules that govern which affix can be added to what type of ________ to form a new word.A. rootB. affixC. stemD. word16. The words such as “lab” and “doc” are ________.A. formed by blendingB. acronymsC. coined by back-formationD. clipped words17. Chinese, the most popular language of the world, belongs to the ________ family.A. Indo-EuropeanB. Sino-TibetanC. AustronesianD. Afroasiatic18. An important set of extensive sound changes affecting vowels, known as the Great V owel Shift, occurred at the end of the ________.A. Old English periodB. Middle English periodC. Modern English periodD. Middle ages19. The most widely-spread morphological changes in the historical development of English are the loss and addition of ________.A. prefixesB. suffixesC. affixesD. case markings20. The most dramatic morphological loss concerns the loss of ________.A. gender markingsB. case markingsC. tense markingsD. both A and B21. The most vigorous and on-going change in the historical development of a language is the change in its ________.A. soundB. vocabularyC. morphological systemD. syntax22. The most obvious way in which Modern English differs lexically from Old English is in the number of borrowed words from other languages, particular from ________.A. LatinB. FrenchC. GreekD. German23. The word “Motel”comes from “motor+hotel”. This is an example of in morphology.A.BackformationB. conversionC. blendingD. acronym24. Which of the following features is NOT one of the design features of language?A.Symbolic B.Dual C.Productive D.Arbitrary 25. What is the most important function of language?A.Interpersonal B.Phatic C.Informative D.Metalingual26. The description of a language at some point in time is a ________ study.A. synchronicB. diachronicC. historicalD. comparative27. According to Chomsky, which is the ideal user's internalized knowledge of his language?A.competence B.parole C.performance D.langue28. The function of the sentence "A nice day, isn't it?" is .A.informative B.phatic C.directive D.performative29. Language is the tool of communication. The symbol “Highway Closed” on a highway serves .A.an expressive functionB.an informative functionC.a performative functionD.a persuasive function31. When a speaker expresses his intention of speaking, such as asking someone to open the window, he is performingA.an illocutionary actB. a perlocutionary actC. a locutionary actD. none of the above32. The study of the mental process of language comprehension and production isA.corpus linguisticsB. sociolinguisticsC.theoretical linguisticsD. psycholinguistics33. Which is the smallest unit of language in terms of relationship between expression and content?A.Word B.Morpheme C.Allomorph D.Root 34. Which studies the internal structure of words, and the rules by which words are formed?A.Morphology B.Syntax C.Phonology D.Semantics35. The phenomenon that words having different meanings have the same form is calledA.hyponymyB. synonymyC. polysemyD. homonymy36. All words contain a ___________.A.root morpheme B.bound morpheme C.prefix D.suffix 37. The relationship between "fruit" and "apple" is ___________.A.homonymy B.hyponymy C.polysemy D.synonymy 38. The part of the grammar that represents a speaker's knowledge of the structure of phrases and sentences is called___________.A.lexicon B.morphology C.syntax D.semantics 39. The pair of words "lend" and "borrow" are ___________.A.gradable opposites B.converse oppositesC.co-hyponyms D.synonyms40. "Big" and "Small" are a pair of___________ opposites.A.complementary B.gradable C.complete D.converse41. What essentially distinguishes semantics and pragmatics is the notion ofA.referenceB.meaningC.antonymyD.context42. What type of sentence is “Mark likes fiction, but Tim is interested in poetry.”?A.a simple sentenceB.a coordinate sentenceC.a complex sentenceD.none of the above43. The word tail once referred to “the tail of a horse”, but now it is used to mean “the tail of any animal”. This is an example ofA.widening of meaningB.narrowing of meaningC.meaning of shiftD.loss of meaning44. The words kid, child, offspring are examples ofA.dialectal synonymsB.stylistic synonymsC.emotive synonymsD.collocational synonyms45. In the following conversation:- Beirut is in Peru, isn't it?- And Rome is in Romania, I suppose.The second person violates the ___________.A.Quantity MaximB.Quality MaximC.Relation MaximD.Manner Maxim46. The maxim of requires that a participant's contribution be relevant to the conversation.A.quantity B.quality C.manner D.relation 47. Which of the following italicized parts is an inflectional morpheme?A Un lockB Govern mentC Go esD Off-stage48. ____ is a language phenomenon in which words sound like what they refer to.A OnomatopoeiaB CollocationC DenotationD Assimilation49. The sentence “Close your book and listen to me carefully”performs a(n) _____ function.A interrogativeB informativeC performativeD directive50. The speech act theory was first put forward byA.John SearleB.John AustinC.Noam ChomskyD.M.A.K. HollidayDivide the following words into their separate morphemes by placing a “+” between each morpheme and the next.Example: microfilm: micro + filmmanuallydictationhomosexualperspectivebiologyIn what ways are the following expressions ambiguous? Explain them by two different tree diagrams and translate them into Chinese:The parents of the bride and the groom were waiting.He hit the boy with the steak.Write down the ten ways of forming new words and illustrate them with examples.。