光纤传感器的基本知识
- 格式:ppt
- 大小:244.00 KB
- 文档页数:28

光纤传感器光纤传感器①光纤传感器的基本原理光纤传感器通过光导纤维把输⼊变量转换成调制的光信号。
光纤传感器的测量原理有两种。
(1) 物性型光纤传感器原理物性型光纤传感器是利⽤光纤对环境变化的敏感性,将输⼊物理量变换为调制的光信号。
其⼯作原理基于光纤的光调制效应,即光纤在外界环境因素,如温度、压⼒、电场、磁场等等改变时,其传光特性,如相位与光强,会发⽣变化的现象。
因此,如果能测出通过光纤的光相位、光强变化,就可以知道被测物理量的变化。
这类传感器⼜被称为敏感元件型或功能型光纤传感器。
激光器的点光源光束扩散为平⾏波,经分光器分为两路,⼀为基准光路,另⼀为测量光路。
外界参数(温度、压⼒、振动等)引起光纤长度的变化和相位的光相位变化,从⽽产⽣不同数量的⼲涉条纹,对它的模向移动进⾏计数,就可测量温度或压⼒等。
(2) 结构型光纤传感器原理结构型光纤传感器是由光检测元件(敏感元件)与光纤传输回路及测量电路所组成的测量系统。
其中光纤仅作为光的传播媒质,所以⼜称为传光型或⾮功能型光纤传感器。
图2 结构型光纤传感器⼯作原理⽰意图(3) 拾光型光纤传感器原理⽤光纤作为探头,接收由被测对象辐射的光或被其反射、散射的光。
其典型例⼦如光纤激光多普勒速度计、辐射式光纤温度传感器等。
图3 拾光型光纤传感器⼯作原理⽰意图②光纤传感器的优点与传统的各类传感器相⽐,光纤传感器⽤光作为敏感信息的载体,⽤光纤作为传递敏感信息的媒质,具有光纤及光学测量的特点,有⼀系列独特的优点。
(1) 电绝缘性能好。
(2) 抗电磁⼲扰能⼒强。
(3) ⾮侵⼊性。
(4) ⾼灵敏度。
(5) 容易实现对被测信号的远距离监控。
(6) 耐腐蚀,防爆。
(7) 光路有可挠曲性,便于与计算机联接。
(8) 结构简单,体积⼩,重量轻,耗电少等。
光纤传感器在军事、航空、医学、环境监测、⼟⽊⼯程、电⼦系统等很多领域都有⼴泛的应⽤,尤其适⽤于以下特殊环境:(1) 在⾼压、电磁感应噪⾳条件下的测试;(2) 在危险和环境恶劣条件下的测试;(3) 在机器设备内部的狭⼩间隙中的测试;(4) 在远距离的传输中的测试。


第三节光纤传感器光纤传感器是七十年代发展起来的新型传感技术,与常规传感器相比,有很多优点:①抗电磁干扰能力强。
光纤主要由电绝缘材料做成,工作时利用光子传输信息,因而不怕电磁场干扰;此外,光波易于屏蔽,外界光的干扰也很难进入光纤。
②光纤直径只有几微米到几百微米。
而且光纤柔软性好,可深入到机器内部或人体弯曲的内脏等常规传感器不宜到达的部位进行检测。
③光纤集传感与信号传输于一体,利用它很容易构成分布式传感测量。
光纤传感器的优点突出,发展极快。
自1977年以来,已研制出多种光纤传感器,被测量遍及位移、速度、加速度、液位、应变、力、流量、振动、水声、温度、电流、电压、磁场和化学物质等。
新的传感原理及应用正在不断涌现和扩大。
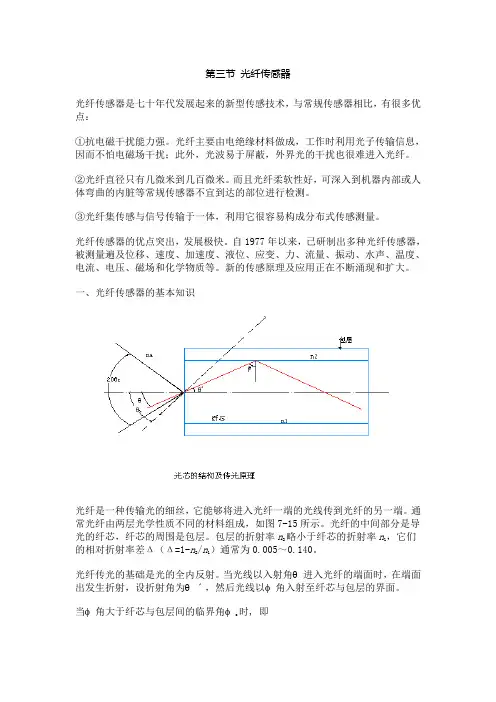
一、光纤传感器的基本知识光纤是一种传输光的细丝,它能够将进入光纤一端的光线传到光纤的另一端。
通常光纤由两层光学性质不同的材料组成,如图7-15所示。
光纤的中间部分是导光的纤芯,纤芯的周围是包层。
包层的折射率n2略小于纤芯的折射率n1,它们的相对折射率差Δ(Δ=1-n2/n1)通常为0.005~0.140。
光纤传光的基础是光的全内反射。
当光线以入射角θ进入光纤的端面时,在端面出发生折射,设折射角为θˊ,然后光线以φ角入射至纤芯与包层的界面。
时, 即当φ角大于纤芯与包层间的临界角φc(7-10)则射入的光线在光纤的界面上发生全反射,并在光纤内部以同样的角度反复逐次反射,直至传播到另一端面。
实际工作时光纤可能弯曲,只要仍满足全反射定律,光线仍继续前进。
由于光纤具有一定柔软性,很容易使光线“转弯”,这给传感器的设计带来了极大的方便。
根据斯乃尔折射定律,(7-11)设当φ达到临界角φc 时的入射角为θc, 由式(7-10)和式(7-11)可得(7-12)式中n0sinθc是为光纤的数值孔径,用NA表示。
它表示当入射光从折射率为n0的外部介质进入光纤时,只有入射角小于θc的光才能在光纤中传播。
否则,光线会从包层中逸出而产生漏光。



目录一、引言 (1)二、光纤传感器的基本原理及特点 (1)2.1基本原理 (1)2.2 特点 (2)三、光纤传感器的发展历程 (2)四、光纤传感器的分类及应用原理 (3)4.1 分类 (3)4.2 应用原理 (4)4.2.1光强调制型 (4)4.2.2相位调制型 (5)4.2.3偏振态调制型 (6)五、光纤传感器的应用及存在问题 (6)5.1光纤温度传感器及其应用 (7)5.2光纤陀螺及其应用 (7)六、光纤传感器的发展趋势 (8)光纤传感器一、引言传感器在当代科技领域及实际应用中占有十分重要的地位,各种类型的传感器早已广泛应用于各个学科领域。
近年来,传感器朝着灵敏、精巧、适应性强、智能化和网络化方向发展。
光纤传感技术是20世纪70年代末新兴的一项技术,在全世界成了研究热门,已与光纤通信并驾齐驱。
光纤传感器作为传感器家族的一名新成员,由于其优越的性能而备受青睐,其具有体积小、质量轻、抗电磁干扰、防腐蚀、灵敏度高、测量带宽、检测电子设备与传感器可以间隔很远等优点,优良的性能使得光纤传感器具有广泛的应用前景。
本文从光纤传感器的基本原理及特点、光纤传感器的发展历程、光纤传感器的分类及应用原理、光纤传感器的应用及存在问题以及光纤传感器的发展趋势五大方面对光纤传感器进行介绍。
二、光纤传感器的基本原理及特点光纤( Optical Fiber) 是光导纤维的简称,光纤的主要成份为二氧化硅,由折射较高的纤芯、折射率较低的包层及保护层组成。
纤芯为直径大约0.1 mm 左右的细玻璃丝,把光封闭在其中并沿轴向进行传播的导波结构。
光纤传感器的发现起源于探测光纤外部扰动的实践,在实践中,人们发现当光纤受到外界环境的变化时,会引起光纤内部传输光波参数的变化,而这些变化与外界因素成一定规律,由此发展出光纤传感技术。
2.1基本原理图 1 是光纤传感器的原理结构图。
光纤传感器通常由光源、传输光纤、传感元件或调制区、光检测等部分组成。




光纤传感器的原理和应用光纤传感器是一种基于光纤技术的传感器,通过光纤的传输和延时特性来实现对物理量的测量和检测。
它具有高精度、快速响应、抗干扰能力强等优点,被广泛应用于工业、医疗、环境监测等领域。
本文将介绍光纤传感器的基本原理和常见的应用场景。
一、光纤传感器的基本原理光纤传感器是利用光纤波导结构的特性来实现物理量的测量和检测。
光纤波导是一种能够将光信号传送的导光器件,其核心部分是由折射率高于外部包层的光纤芯构成。
基于光的干涉、散射、吸收等特性,光纤传感器能够实现对温度、压力、位移、浓度等多种物理量的测量。
1. 光纤干涉型传感器光纤干涉型传感器是利用光的干涉效应来测量物理量的一种传感器。
光信号在光纤中传播时,受到温度、应变等物理量的影响,使得光的相位发生改变。
通过测量光的相位差,可以确定物理量的大小。
常见的光纤干涉型传感器有光纤布拉格光栅传感器、光纤干涉仪传感器等。
2. 光纤散射型传感器光纤散射型传感器是利用光在光纤中的散射效应来测量物理量的一种传感器。
光信号在光纤中传输时,会与光纤中的杂质或结构缺陷散射,通过测量散射光的特性来推断物理量的变化。
常见的光纤散射型传感器有光时域反射计传感器、拉曼散射光纤传感器等。
3. 光纤吸收型传感器光纤吸收型传感器是利用光在光纤中的吸收效应来测量物理量的一种传感器。
光信号在光纤中传输时,会被光纤材料吸收,通过测量吸收光的强度来判断物理量的变化。
常见的光纤吸收型传感器有红外光纤传感器、光纤化学传感器等。
二、光纤传感器的应用领域光纤传感器具有灵敏度高、抗干扰能力强等优点,被广泛应用于各个领域。
以下是几个典型的应用场景。
1. 工业自动化光纤传感器在工业自动化领域中,常用于测量温度、压力、液位等物理量,用于控制和监测生产过程。
例如,光纤温度传感器可以实时监测设备的温度变化,及时进行报警和控制;光纤压力传感器可以监测管道中的压力变化,用于流体控制和安全保护。
2. 医疗领域光纤传感器在医疗领域中,常用于生理参数的监测和诊断。
光纤传感器的原理和应用探究在现代科技日新月异的时代,光纤传感器作为一种新兴的传感器技术,其应用范围越来越广泛。
光纤传感器通过测量光的参数变化来检测环境、物理量、化学量等信息,具有响应快、抗干扰能力强、使用寿命长等优点。
本文将对光纤传感器的原理和应用进行探究。
一、光纤传感器的基本原理光纤传感器是利用光的物理特性进行测量的一种传感器。
它的基本原理是利用光纤中光的衍射、干涉、散射、吸收等现象,将周围环境产生的信号转换成光信号,通过传递、解调和处理,最终获得需要测量的物理量信息。
光纤传感器的工作原理可以分为两个部分:光纤传感部分和信号传递及处理部分。
1、光纤传感部分光纤传感部分是光纤传感器的重要组成部分,主要是通过利用光的散射、吸收等物理现象,将要测量的信号转换为光信号。
光纤传感部分主要由光源、光纤和光电器三个部分构成。
(1)光源光源是光纤传感器的初级部件,它主要是产生光信号的光波源。
在光纤传感器中,常使用激光diode LED、LED 这两种类型的光源。
它们的特点是光输出功率稳定、寿命长,对环境温度变化和机械振动等均有良好的适应性。
(2)光纤光纤是光纤传感器的核心部分,是将光信号转换为机械量或其它指标成分的传感器。
它作为光传输的介质,一般采用单模或多模光纤,常用的光纤有石英光纤和塑料光纤。
在光纤中,光信号会通过散射或吸收等方式受到外部环境作用,从而产生不同程度的衰减,物理量的变化会导致光纤中传输特性的变化,如光功率、相位和波长等。
(3)光电器光电器是光纤传感器中的一个重要组成部分,主要作用是将入射的光信号转换成电信号。
光电器一般包括光电二极管、光电倍增管和光栅等,其中光电倍增管能够把非常微弱的光信号转换成较大的电信号。
通过控制光源的强度和改变光纤的位置,光电器能够准确地检测出光强度和位置的变化,实现对环境变化量的测量。
2、信号传递及处理部分信号传递及处理部分是光纤传感器的重要组成部分,主要是将光纤传感产生的信号传递到处理器进行解调、滤波和数字化等处理,最终输出需要测量的参数值。