C语言第十章复习题(含答案)
- 格式:pdf
- 大小:131.51 KB
- 文档页数:15



高等教育自学考试C语言程序设计(二)课程代号(05772)同步练习题班级学号姓名二O 一六年三月目录第一章C语言概述第二章基本数据类型第三章控制结构第四章运算符和表达式第五章函数第六章数组第七章字符与字符串第八章变量类别与编译预处第九章指针第十章结构体、共用体和枚举类型第十一章文件第一章C语言概述一、单项选择题1.在计算机上可以直接运行的程序是()。
A.高级语言程序B.汇编语言程序C.机器语言程序D.C语言程序2. 一个C语言程序是由()A.若干函数组成B.若干过程组成C.若干主程序组成D.若干子程序组成3. C语言不具有的特点是()A.具有结构化的控制语句B.数据类型丰富C.语法限制不太严格,程序设计自由度大D.在可移植性上,C语言比其他语言差4. 以下叙述不正确的是()A.一个C语言程序可由一个或多个函数组成B.一个C语言程序必须包含一个主函数C.C语言程序的基本组成单位是函数D.在C语言程序中,注释说明只能位于一条语句的后面5. 以下叙述正确的是()A.C语言比其他语言高级B.C语言可以不用编译就能被计算机识别和执行C.C语言以接近英语国家的自然语言和数学语言作为语言的表达形式D.C语言出现的最晚,所以具有其他语言的一切优点二、填空1. 计算机语言的发展经过了、和等阶段。
2. C语言既适合编写,也适合编写应用软件。
标准答案一、单项选择题CADDC二、填空1. 机器语言,汇编语言,高级语言2. 系统软件第二章基本数据类型一、单项选择题1.正确的C语言用户自定义标识符是()A.printB.floatC.when?D.random%22.属于C语言基本数据类型的是( )A.指针型B.无符号整型C.数组型D.结构型3.C语言的长整型数值在计算机中占用的字节个数是( )A.1B.2C.3D.44.C语言中,″\x3d″在内存中占用的字节数是( )A.1B.2C.4D.55.下列关于C语言的叙述错误的是( )A. 英文字母大小写不加以区分B. 不同类型的变量可以出现在同一个表达式中C. 在赋值表达式中赋值号两边的类型可以不同D. 某些运算符在不同的场合可以有不同的含义6.下列转义字符中错误的是( )A. ′\000′B. ′\14′C. ′\x111′D. ′\2′7.下列标识符中,不是C语言保留字的是( )A. charB. whileC. minD. default8.下列保留字中用于构成循环结构的是()A.ifB.whileC.switchD.default9. 数据-324在二进制文件和文本文件中所占的字节数分别是()A.2,2B.2,4C.4,2D.4,410. 请选出可以作为C语言用户标识符的一组标识符()A.void, define, WORD B.A3_B3, _123, abcC.FOR, -abc, Case D.2a, Do, Sizeof11.下列运算符优先级最高的是()A.关系运算符B.赋值运算符C.算术运算符D.逻辑运算符12. sizeof(float)是()A.一种函数调用B.一个不合法的表示形式C.一个整型表达式D.一个浮点表达式13. 下列叙述不正确的是()A.一个C语言程序可由一个或多个函数组成B.一个C语言程序必须包含一个main函数C.C语言程序的基本组成单位是函数D.在C语言程序中,注释说明只能位于一条语句的后面14. 编译C语言程序时,程序中的注释部分将()A.不参加编译,也不会出现在目标程序中B.参加编译,但不会出现在目标程序中C.不参加编译,但会出现在目标程序中D.参加编译,并会出现在目标程序中15. 下列字符串常量不正确的是()A.'abc' B."12'12" C."0" D." "16. 下列4个选项中,均是合法整型常量的是()A.160 -0xffff 011B.-0xcdf 01ª0xeC.-01 986,012 0668D.-0x48a 2e5 0x17. 以下选项中不属于C语言类型的是()A.signed short int B.unsigned long intC.unsigned int D.long short18. 数值029是一个()A.八进制数B.十六进制数C.十进制数D.非法数19. 在C语言中,要求运算数必须是整型的运算符是()A./ B.++ C.!=D.%20. 当c的值不为0时,以下能将c的值赋给变量a,b 的是()A.c=b=a B.(a=c) || (b=c)C.(a=c) && (b=c) D.a=c=b二、填空1. 表示空类型的保留字是_____________。

谭浩强版C语言的第十章《指针》答案第十章《指针》答案如下inc/testPtr.h#include <string.h>#include <ctype.h>#include <math.h>#include <assert.h>#define SIZE 1024int a2i(char *start, char *end){int size = 0, ret = 0;long base = 0;size = end - start + 1;base = (long)pow(10, size - 1);while(size-- > 0){ret += (*start++ - '0') * base;base /= 10;}return ret;}int extraNum(char *str, int arr[]){int ite = 0, counter = 0;char *start = NULL, *end = NULL;while(*str != '\0'){if(isdigit(*str)){start = end = str;while( isdigit(*end) && *end != '\0'){++end;}arr[ite++] = a2i(start, end-1);str = end;}else{str++;}}return ite;}int sortStr(char *arr[], int size){int ite1 = 0, ite2 = 0, minPos = 0;char *tmp;for(ite1 = 0; ite1 < size - 1; ite1++){minPos = ite1;for(ite2 = ite1 + 1; ite2 < size; ++ite2 ){if( strcmp(arr[ite2], arr[minPos]) < 0 ){minPos = ite2;}}if(minPos != ite1){tmp = arr[minPos];arr[minPos] = arr[ite1];arr[ite1] = tmp;}}return 0;}int sort(int arr[], int size){int minPos = 0, ite1 = 0, ite2 = 0, tmp = 0;for(ite1 = 0; ite1 < size - 1; ite1++){minPos = ite1;for(ite2 = ite1 + 1; ite2 < size; ite2++){if( arr[ite2] < arr[minPos] ){minPos = ite2;}}if(minPos != ite1){tmp = arr[ite1];arr[ite1] = arr[minPos];arr[minPos] = tmp;}}return 0;}int sortPtr(int arr[], int size){int minPos = 0, ite1 = 0, ite2 = 0, tmp = 0;for(ite1 = 0; ite1 < size - 1; ite1++){minPos = ite1;for(ite2 = ite1 + 1; ite2 < size; ite2++){if( *(arr + ite2) < *(arr + minPos) ){minPos = ite2;}}if(minPos != ite1){tmp = *(arr + ite1);*(arr + ite1) = *(arr + minPos);*(arr + minPos) = tmp;}}return 0;}int getMultiArr(int arr[][5], int n){int i = 0, j = 0, min = 0, tmp = 0, size = 5 * n;int *p = NULL, pos[size];/* copy */p = (int *)malloc(size * sizeof(int));assert(p != NULL);memcpy(p, arr, size * sizeof(int));/* sort */for(i = 0; i < size - 1; i++){min = i;for(j = i + 1; j < size; j++){if( *(p + j) < *(p + min)){min = j;}}if(min != i){tmp = *(p + min);*(p + min) = *(p + i);*(p + i) = tmp;}}/* move */for(i = 0; i < n; i++){for(j = 0; j < 5; j++){if( *p == arr[i][j] ){tmp = arr[i][j];arr[i][j] = arr[0][0];arr[0][0] = tmp;continue;}if( *(p + 1) == arr[i][j] ){tmp = arr[i][j];arr[i][j] = arr[0][4];arr[0][4] = tmp;continue;}if( *(p + 2) == arr[i][j] ){tmp = arr[i][j];arr[i][j] = arr[n - 1][0];arr[n - 1][0] = tmp;continue;}if( *(p + 3) == arr[i][j] ){tmp = arr[i][j];arr[i][j] = arr[n - 1][4];arr[n - 1][4] = tmp;continue;}if( *(p + size - 1) == arr[i][j] ){tmp = arr[i][j];arr[i][j] = arr[n/2][2];arr[n/2][2] = tmp;continue;}}}free(p);p = NULL;return 0;}int statStr(char *str){int upper = 0, lower = 0, space = 0, num = 0, other = 0;while(*str != '\0'){if(isdigit(*str)){num++;}else if (isupper(*str)){upper++;}else if (islower(*str)){lower++;}else if (isspace(*str)){space++;}else{other++;}str++;}assert(3 == upper);assert(5 == lower);assert(10 == num);assert(2 == space);assert(6 == other);return 0;}int average(int(*stu)[6], int classNum, int stuNum){int i = 0, ave = 0;for(i = 0; i < stuNum; i++){ave += (*(stu + i))[classNum];}ave /= stuNum;return ave;}int searchStu(int(*stu)[6], int stuNum){int counter = 0, i = 0, j = 1, stuCounter = 0;for (i = 0; i < stuNum; i++){counter =0;for(j = 1; j < 6; j++){if( (*(stu + i))[j] < 60 ){counter++;}}if(counter >= 2){stuCounter++;}}return stuCounter;}int moveInt(int arr[], int n, int m){int i = 0, *p = NULL;p = (int*)malloc(n * sizeof(int));assert(p != NULL);memcpy(p + m, arr, (n - m) * sizeof(int));memcpy(p, arr + n -m , m * sizeof(int));memcpy(arr, p, n * sizeof(int));free(p);p = NULL;return 0;}int myStrcmp(char *p1, char*p2){int ret = 0;while((*p1 != '\0') && (*p2 != '\0') && ( *p1 == *p2 ) ) {p1++;p2++;}if(*p1 == '\0'){ret = -1;}else if (*p2 == '\0'){ret = 1;}else{ret = (*p1 - *p2) > 0 ? 1 : -1;}return ret;}int revArr(int a[], int size){int tmp = 0, *start = NULL, *end = NULL;start = a;end = start + size - 1;size = size / 2;while(size >= 0){tmp = *(start + size);*(start + size) = *(end - size);*(end - size) = tmp;size--;}return 0;}char *getMonth(char *month[], int which) {assert(which <= 12);return ( *(month + which - 1));}int getStr(char *dest, char* src, int m) {int len = 0;len = strlen(src) + 1 - m;src = src + m - 1;memcpy(dest, src, len * sizeof(char));return 0;}int removePer3(int arr[], int size){int i = 0;for(i = 0; i < size; i++){if(((arr[i]) % 3) == 0){arr[i] = 0;}}return 0;}int getMinMax(int a[], int size){int i = 0, min = 0, max = 0, tmp = 0;min = max = 0;for(i = 0; i < size; i++){if (a[i] <= a[min]){min = i;}if(a[i] >= a[max]){max = i;}}tmp = a[0];a[0] = a[min];a[min] = tmp;tmp = a[size - 1];a[size - 1] = a[max];a[max] = tmp;}int test_10_1(){int ite = 0, iRet = 0, arr[5] = {121, 234, 456456, 543, 23};iRet = sortPtr(arr, 5);assert (23 == arr[0]);assert (121 == arr[1]);assert (234 == arr[2]);assert (543 == arr[3]);assert (456456 == arr[4]);printf("\r\nTest_10_1 Passed!");return 0;}int test_10_2(){int ite = 0, iRet = 0;char *arr[10] = { "In the IBM Rational ClearCase environment", \"An auditable history of source files and software builds is maintained in your organization", \"The efforts of your team can be coordinated into a definable"};iRet = sortStr(arr, 3);assert( strcmp(arr[0], "An auditable history of source files and software builds is maintained in your organization") == 0 );assert( strcmp(arr[1], "In the IBM Rational ClearCase environment") == 0);assert( strcmp(arr[2], "The efforts of your team can be coordinated into a definable") == 0);printf("\r\nTest_10_2 Passed!");return 0;}int test_10_3(){int ret = 0, a[10] = {7,2,3,9,1,0,7,6,5,0};ret = getMinMax(a, 10);assert(a[0] == 0);assert(a[9] == 9);printf("\r\nTest_10_3 Passed!");return 0;}int test_10_4(){int ret = 0, arr[9] = {0, 1, 2, 3, 4, 5, 6, 7, 8};ret = moveInt(arr, 9, 3);assert(6 == arr[0]);assert(7 == arr[1]);assert(8 == arr[2]);assert(0 == arr[3]);assert(1 == arr[4]);assert(2 == arr[5]);assert(3 == arr[6]);assert(4 == arr[7]);assert(5 == arr[8]);printf("\r\nTest_10_4 Passed!");return 0;}int test_10_5(){int ret = 0, i = 0, a[12] = {1,2,3,4,5,6,7,8,9,10,11,12};ret = removePer3(a, 12);assert(a[2] == 0);assert(a[5] == 0);assert(a[8] == 0);assert(a[11] == 0);printf("\r\nTest_10_5 Passed!");return 0;}int test_10_7(){int ret = 0;char s2[100] = {0}, *s1 = "hello world!";getStr(s2, s1, 7);assert( strcmp(s2, "world!") == 0);printf("\r\nTest_10_7 Passed!");return 0;}int test_10_8(){int ret = 0;char *str = "a123xABC ??#$%^ 302tab5876";ret = statStr(str);if(ret == 0){printf("\r\nTest_10_8 Passed!");}return 0;}int test_10_10(){int i = 0, j = 0, ret = 0;int arr[5][5] = { \{16, 17, 18, 19, 20}, \{11, 12, 13, 14, 15}, \{1, 2, 3, 4, 5}, \{21, 22, 23, 24, 25}, \{6, 7, 8, 9, 10}, \};ret = getMultiArr(arr, 5);assert(1 == arr[0][0] );assert(2 == arr[0][4] );assert(3 == arr[4][0] );assert(4 == arr[4][4] );assert(25 == arr[2][2] );printf("\r\nTest_10_10 Passed!");return 0;}int test_10_11(){int ite = 0, iRet = 0;char *arr[10] = { "In the", \"An aud", \"The ef", \"Proces", \"Sets o", \"Unifie", \"Out-of", \"Practi", \"Ration", \"Explor" \};iRet = sortStr(arr, 10);assert( strcmp(arr[0], "An aud") == 0 );assert( strcmp(arr[1], "Explor") == 0);assert( strcmp(arr[2], "In the") == 0);assert( strcmp(arr[3], "Out-of") == 0);assert( strcmp(arr[4], "Practi") == 0);assert( strcmp(arr[5], "Proces") == 0);assert( strcmp(arr[6], "Ration") == 0);assert( strcmp(arr[7], "Sets o") == 0);assert( strcmp(arr[8], "The ef") == 0);assert( strcmp(arr[9], "Unifie") == 0);printf("\r\nTest_10_11 Passed!");return 0;}int test_10_12(){int ite = 0, iRet = 0;char *arr[10] = { "In the IBM Rational ClearCase environment", \"An auditable history of source files and software builds is maintained in your organization", \"The efforts of your team can be coordinated into a definable", \"Process by using one of the following", \"Sets of Rational ClearCase features", \"Unified Change Management (UCM),", \"Out-of-the-box process that supports best", \"Practices for change management as described in the IBM", \"Rational Unified Process. Project managers can configure", \"Explorer. For more information about Rational ClearCase"};iRet = sortStr(arr, 10);assert( strcmp(arr[0], "An auditable history of source files and software builds is maintained in your organization") == 0 );assert( strcmp(arr[1], "Explorer. For more information about Rational ClearCase") == 0);assert( strcmp(arr[2], "In the IBM Rational ClearCase environment") == 0);assert( strcmp(arr[3], "Out-of-the-box process that supports best") == 0);assert( strcmp(arr[4], "Practices for change management as described in the IBM") == 0);assert( strcmp(arr[5], "Process by using one of the following") == 0);assert( strcmp(arr[6], "Rational Unified Process. Project managers can configure") == 0);assert( strcmp(arr[7], "Sets of Rational ClearCase features") == 0);assert( strcmp(arr[8], "The efforts of your team can be coordinated into a definable") == 0);assert( strcmp(arr[9], "Unified Change Management (UCM),") == 0);printf("\r\nTest_10_12 Passed!");return 0;}int test_10_14(){int ret = 0, a[11] = {0, 1, 2, 3, 4, 5, 6, 7, 8, 9, 10};ret = revArr(a, 11);assert(10 == a[0]);assert(9 == a[1]);assert(8 == a[2]);assert(7 == a[3]);assert(6 == a[4]);assert(5 == a[5]);assert(4 == a[6]);assert(3 == a[7]);assert(2 == a[8]);assert(1 == a[9]);assert(0 == a[10]);printf("\r\nTest_10_14 Passed!");return 0;}int test_10_15(){int ave = 0, ret = 0;int student[4][6] = { \{1, 100, 90, 80, 70, 97}, \{2, 34, 45, 56, 78, 97}, \{3, 76, 34, 68, 84, 12}, \{4, 90, 90, 90, 75, 28} \};ave = average(student, 1, 4);ret = searchStu(student, 4);assert(75 == ave);assert(2 == ret);printf("\r\nTest_10_15 Passed!");return 0;}int test_10_16(){int iRet = 0, ite = 0, arr[SIZE] = {0};char *str = "a123x456 17960? 302tab5876";iRet = extraNum(str, arr);assert(123 == arr[0]);assert(456 == arr[1]);assert(17960 == arr[2]);assert(302 == arr[3]);assert(5876 == arr[4]);printf("\r\nTest_10_16 Passed!");return 0;}int test_10_17(){int ret = 0;char *s1 = "abcd", *s2 = "abCd";ret = myStrcmp(s1, s2);assert(ret == 1);char *s3 = "aBcd", *s4 = "abCd";ret = myStrcmp(s3, s4);assert(ret == -1);char *s5 = "abcde", *s6 = "abcd";ret = myStrcmp(s5, s6);assert(ret == 1);char *s7 = "abcd", *s8 = "abcde";ret = myStrcmp(s7, s8);assert(ret == -1);char *s9 = "abcd", *s10 = "abCde";ret = myStrcmp(s9, s10);assert(ret == 1);printf("\r\nTest_10_17 Passed!");return 0;}int test_10_18(){int which = 0;char *month[12] = { \"January", \"February", \"March", \"April", \"May", \"June", \"July", \"August", \"September", \"October", \"November", \"December" \};which = 11;assert( strcmp("November", getMonth(month, which)) == 0 );which = 7;assert( strcmp("July", getMonth(month, which)) == 0 );printf("\r\nTest_10_18 Passed!");return 0;}int test_10_20(){int ite = 0, iRet = 0;char *arr[5] = { "In the IBM Rational ClearCase environment", \"An auditable history of source files and software builds is maintained in your organization", \"The efforts of your team can be coordinated into a definable", \"Process by using one of the following", \"Sets of Rational ClearCase features" \};iRet = sortStr(arr, 5);assert( strcmp(arr[0], "An auditable history of source files and software builds is maintained in your organization") == 0 );assert( strcmp(arr[1], "In the IBM Rational ClearCase environment") == 0);assert( strcmp(arr[2], "Process by using one of the following") == 0);assert( strcmp(arr[3], "Sets of Rational ClearCase features") == 0);assert( strcmp(arr[4], "The efforts of your team can be coordinated into a definable") == 0);printf("\r\nTest_10_20 Passed!");return 0;}int test_10_21(){int ite = 0, iRet = 0, arr[5] = {121, 234, 456456, 543, 23};iRet = sort(arr, 5);assert (23 == arr[0]);assert (121 == arr[1]);assert (234 == arr[2]);assert (543 == arr[3]);assert (456456 == arr[4]);printf("\r\nTest_10_21 Passed!");return 0;}int testPtr(){int iRet = 0;#if 0#endifiRet += test_10_1();iRet += test_10_2();iRet += test_10_3();iRet += test_10_4();iRet += test_10_5();iRet += test_10_7();iRet += test_10_8();iRet += test_10_10();iRet += test_10_11();iRet += test_10_12();iRet += test_10_14();iRet += test_10_15();iRet += test_10_16();iRet += test_10_17();iRet += test_10_18();iRet += test_10_20();iRet += test_10_21();return iRet;}src/#include <stdio.h>#include <stdlib.h>#include <assert.h>#include "../inc/testFile.h" #include "../inc/testBits.h" #include "../inc/testPtr.h"int main(){int iRet = 0;#if 0iRet += testFile();assert(iRet == 0);iRet += testBits();assert(iRet == 0);#endifiRet += testPtr();assert(iRet == 0);return 0;}。

第10章对文件的输入输出(2012年9月真题)(40)有以下程序#include <stdio.h>main(){ FILE *fp;int i,a[6]={1,2,3,4,5,6};fp=fopen("d2.dat","w+");for(i=0;i<6;i++) fprintf(fp,"%d\n",a[i]);rewind(fp);for(i=0;i<6;i++) fscanf(fp,"%d",&a[5-i]);fclose(fp);for(i=0;i<6;i++) printf("%d,",a[i]);}程序运行后的输出结果是A)4,5,6,1,2,3, B)1,2,3,3,2,1,C)1,2,3,4,5,6, D)6,5,4,3,2,1,答案:D(2012年3月真题)40、以下函数不能用于向文件写入数据的是A ftellB fwriteC fputcD fprintf答案:A(2011年9月真题)40.有以下程序#include<stdio.h>main(){FILE *fp; int k,n,i,a[6]={1,2,3,4,5,6};fp=fopen("d2.dat","w");for(i=0;i<6;i++)fprintf(fp,"%d\n",a[i]);fclose(fp); fp=fopen("d2.dat","r");for(i=0;i<3;i++)fscanf(fp,"%d%d",&k,&n);fclose(fp); printf("%d,%d\n",k,n); }程序运行后的输出结果是A.1,2B.3,4C.5,6D.123,456答案:C(2011年3月真题)(40)设fp已定义,执行语句fp=fopen("file","w");后,以下针对文本文件file操作叙述的选项中正确的是A)写操作结束后可以从头开始读 B)只能写不能读C)可以在原有内容后追加写 D)可以随意读和写(2010年3月真题)(40)有以下程序#include#include<stdio.h>main(){ FILE *fp;char str[10];fp=fopen("myfile.dat","w");fputs("abc",fp);fclose(fp);fopen("myfile.data","a+");fprintf(fp,"%d",28);rewind(fp);fscanf(fp,"%s",str); puts(str);fclose(fp); }程序运行后的输出结果是A)abc B) 28c C) abc28 D)因类型不一致而出错答案:B(2009年9月真题)(40)下列关于C语言文件的叙述中正确的是A)文件由一系列数据依次排列组成,只能构成二进制文件B)文件由结构序列组成,可以构成二进制文件或文本文件C)文件由数据序列组成,可以构成二进制文件或文本文件D)文件由字符序列组成,其类型只能是文本文件答案:C(2009年3月真题)40.有以下程序#include <stdio.h>main(){ FILE *f;f=fopen("filea.txt","w"); fprintf(f,"abc"); fclose(f); }若文本文件filea.txt中原有内容为:hello,则运行以上程序后,文件filea.txt的内容为A)helloabc B)abclo C)abc D)abchello答案:C(2008年9月真题)(40)有以下程序#include <stdio.h>main(){ FILE *pf;char *s1="China", *s2="Beijing";pf=fopen("abc.dat","wb+");fwrite(s2,7,1,pf);rewind(pf); /*文件位置指针回到文件开头*/fwrite(s1,5,1,pf);fclose(pf);}以上程序执行后abc.dat文件的内容是A) China B) Chinang C) ChinaBeijing D) Bei jingChina答案:B(2008年4月真题)30、下列叙述中错误的是( )。

第10章字符串三、编程题10.19请编写函数mygets和myputs,其功能与gets和puts相同,函数中用getchar 和putchar读入和输出字符。
#include <stdio.h>voidmygets(char * str){ char c;int i=0;while((c=getchar())!='\n') str[i++]=c;str[i]='\0';}voidmyputs(char * str){ int i=0;while(str[i]!='\0') putchar(str[i++]);putchar('\n');}void main(){ char c[80];mygets(c);myputs(c);}10.20编写函数,判断一个字符串是否是回文。
若是回文函数返回值为1,否则返回值为0。
回文是顺读和倒读都一样的字符串。
#include <stdio.h>#include <string.h>int judge(char * str){ char a[80];inti,len=strlen(str),j=0;for(i=len-1;i>=0;i--)a[j++]=str[i];a[j]='\0';//最后加上字符串结束标志if(strcmp(a,str)==0) return 1;else return 0;}void main(){char c[80];int n;gets(c);n=judge(c);if(n==1) printf("是回文\n");else printf("不是回文\n");}10.21请编写函数,删除字符串中指定位置(下标)上的字符。
删除成功函数返回被删字符,否则返回空值。
#include <stdio.h>#include <string.h>charfundel(char * str, int n){ char c='\0';inti,len=strlen(str);if(n>0 && n<len){ c=str[n];for(i=n;i<len;i++)str[i]=str[i+1];}return c;}void main(){char c[80],ch;int n;gets(c);//输入字符串scanf("%d",&n);//输入要删除字符的下标ch=fundel(c,n);if(ch=='\0') printf("删除失败\n");else printf("删除成功,删除后:%s\n",c); }。

明解C语⾔⼊门篇第⼗章答案练习10-1#include <stdio.h>void adjust_point(int*n) {if (*n > 100)*n = 100;if (*n < 0)*n = 0;}int main() {int x;printf("请输⼊⼀个数:");scanf("%d", &x);adjust_point(&x);printf("修改后的值是%d",x);}练习10-2void decrement_date(int* y, int* m, int* d) {*d -= 1;if (*d == 0) {*m -= 1;if (*m == 1 || *m == 3 || *m == 5 || *m == 7 || *m == 10 || *m == 8 ||* m == 0) {*d = 31;}if (*m == 2) {*d = 28;if (*y % 4 == 0) {*d = 29;}}else*d = 30;if (*m == 0) {*m = 12;*y -= 1;}}}void increment_date(int* y, int* m, int* d) {*d += 1;if ((*m == 1 || *m == 3 || *m == 5 || *m == 7 || *m == 10 || *m == 8 || *m == 12) && (*d == 32)) {*d = 1;*m += 1;}if ((*m == 4 || *m == 6 || *m == 9 || *m == 11 ) && (*d == 31)) {*d = 1;*m += 1;}if (*m == 2) {if (*d == 29&& ((*y & 4) != 0)) {*d = 1;}if (*d == 30 && ((*y & 4) == 0)) {*d = 1;*m += 1;}}if (*m == 13) {*y += 1;*m = 1;}}练习10-3#include<stdio.h>void swap(int* px, int*py) {int temp = *px;*px = *py;*py = temp;}void sort3(int*n1, int*n2, int*n3) {if (*n1 > *n2) {swap(n1, n2);}if (*n1 > * n3) {swap(n1, n3);}if (*n2 > * n3) {swap(n2, n3);}}int main(void) {int n1, n2, n3;printf("n1=");scanf("%d", &n1);printf("n2=");scanf("%d", &n2);printf("n3=");scanf("%d", &n3);putchar('\n');sort3(&n1, &n2, &n3);printf("%d,%d,%d", n1, n2, n3); }练习10-4#include <stdio.h>#define number 5void set_idx(int*v, int n) {int i = 0;for (i = 0; i < n; i++) {*(v + i) = i;}}int main() {int i;set_idx(x, number);for (i = 0; i < number; i++) {printf("x[%d]=%d", i,x[i] );putchar('\n');}}练习10-5会报错数组中元素会溢出,因为直接从v【2】开始赋值。

一、C 语言概述练习题选择1.一个C 程序的执行是从。
A)本程序的 main 函数开始,到 main 函数结束B)本程序文件的第一个函数开始,到本程序文件的最后一个函数结束C)本程序文件的第一个函数开始,到本程序 main 函数结束D)本程序的 main 函数开始,到本程序文件的最后一个函数结束2.以下叙述不正确的是。
A) 一个C 源程序必须包含一个main 函数B)一个C 源程序可由一个或多个函数组成C) C 程序的基本组成单位是函数D) 在C 程序中,注释说明只能位于一条语句的后面3.以下叙述正确的是。
A)在对一个 C 程序进行编译的过程中,可发现注释中的拼写错误B)在C 程序中,main 函数必须位于程序的最前面C)C 语言本身没有输入输出语句D) C 程序的每行中只能写一条语句4.一个C 语言程序是由。
A)一个主程序和若干个子程序组成B) 函数组成C) 若干过程组成D) 若干子程序组成5.计算机高级语言程序的运行方法有编译执行和解释执行两种,以下叙述中正确的是。
A) C 语言程序仅可以编译执行B) C 语言程序仅可以解释执行C) C 语言程序既可以编译执行又可以解释执行D) 以上说法都不对6.以下叙述中错误的是。
A) C 语言的可执行程序是由一系列机器指令构成的B)用C 语言编写的源程序不能直接在计算机上运行C)通过编译得到的二进制目标程序需要连接才可以运行D)在没有安装 C 语言集成开发环境的机器上不能运行 C 源程序生成的.exe文件7.以下叙述正确的是。
A) C 语言程序是由过程和函数组成的B) C 语言函数可以嵌套调用,例如:fun(fun(x))C) C 语言函数不可以单独编译 D) C 语言中除了 main 函数,其他函数不可作为单独文件形式存在二、数据类型、运算符与表达式选择.1.若x、i、j、k 都是int 型变量,则计算下面表达式后,x 的值为x=(i=4,j=16,k=32) A) 4 B) 16 C) 32 D) 522.下列四组选项中,均不是C 语言关键字的选项是。

C语言程序设计复习题(含参考答案)C语言程序设计复习题(含参考答案)一、单项选择题(本题共30小题,每小题2分,共60分)在每小题列出的四个备选项中只有一个是符合题目要求的。
1. 以下正确的C语言自定义标识符是______。
A. _1aB. 2a_C. doD. a.122、假设所有变量均为整型,则表达式(x=3,y=4,y++, y-x`)的值是______。
A.7B.1C.6D.23. 设int a, x=2; 执行语句a=x>0?3*x:x=10; 后,变量x的值是_______。
A. 1B. 2C. 6D. 104.设有以下程序段:int x=2,y=2,z=0,a;a=++x||++y&&z++;printf("%d,%d,%d\n",x,y,z);执行后输出的结果是_________。
A. 2, 2, 0B. 3, 3,1C. 3, 2, 0D. 3, 2, 15. 在C语言中,strlen("\\TOP\t\65\"")的值是_______。
A. 5 B.7C. 8D. 126. 设float x,由键盘输入:12.45, 能正确读入数据的输入语句是_________。
A. scanf("%5f",&x);B. scanf("%5d",&x);C. scanf("%f",x);D. scanf("%s",&x);7.若有int a=5;则逗号表达式a=2*6,a*3,a+5的值是_________。
A. 12B. 17C.36 D. 108. C语言程序中,整型常量的书写形式不包括_________。
A. 二进制B. 八进制C. 十进制D. 十六进制9.下面程序的输出结果是_____。
#includemain(){ float d=2.2; int x,y;x=6.2;y=(x+3.8)/5.0;printf("%f",d*y);}A. 4B. 4.4C. 2.2D. 010. 设int x;,则与计算︱x︱等价的表达式是_________。

Chapter 10PE 10-1// pelO-l.cpp#include <iostream>#include <cstring>// class declarationclass BankAccount{private:char name 140];char acctnum[25];double balance;public:BankAccount(char * client = H no one", char * num = n0u,double bal = 0.0); void show(void) const;void deposit(double cash); void withdraw(double cash);};// method definitionsBankAccount::BankAccount(char * client, char * num, double bal) {std::strncpy(name, client, 39);name[39] =std::strncpy(acctnum, num, 24);acctnum[24] =、0‘;balance = bal;}void BankAccount::show(void) const{using std::cout;using std:: endl;cout « "Client: ” « name « endl;cout «n Account Number: n « acctnum « endl;cout « "Balance: H « balance « endl;}void Bank Account: :deposit(double cash)if (cash >= 0) balance += cash;elsestd::cout « "Illegal transaction attempted";}void Bank Account: :withdraw(double cash){if (cash < 0)std::cout «n Illegal transaction attempted n;else if (cash <= balance)balance -二cash;elsestd::cout « "Request denied due to insufficient funds.\n H; }// sample useint main(){BankAccount bird;BankAccount frog(H Kermit n, "croak322n, 123.00);bird.show();frog.show();bird = BankAccount(n Chipper n, n peep8282", 214.00);bird.show();frog.deposit(20);frog.show();frog.withdraw(4000);frog.show();frog.withdraw(50);frog.showQ;PE 10-4//pel0-4.h #ifndef SALES. #define SALES namespace SALES const int QUARTERS = 4;class Salesprivate:double sales[QUARTERS];double average;double max;double min;public:// default constructorSales();// copies the lesser of 4 or n items from the array ar// to the sales member and computes and stores the// average, maximum, and minimum values of the entered items;// remaining elements of sales, if any, set to 0 Sales(const double ar[], int n);// gathers sales for 4 quarters interactively, stores them// in the sales member of object and computes and stores the// average, maximum, and minumum valuesvoid setSales();// display all information in object void showSales();};}#endif// pe 10-4a.cpp #include <iostream> #include ”pel0・4.h" int main() {using SALES::Sales;double vals[3] = {2000, 3000, 5000};Sales forFiji(va!s, 3);forFiji.showSalesQ;Sales red;hiiuil / 二O S BJOAU(0<)凹!1)到•0 = [!]SQRS(++! -snaiHvnd > i = i)」oj {:[屮E = UllU(uiui > [!]JE)J! osp t[l]jB = XBUJ(XELU v [!] JE) JT 讣屮e 二 + pno)= [l]S0|US})"J(++!爼呵>1-0 = 1:【1UI• • t[O]JB 二YUIU 二UlUI(0:0 = Q S UJQAB:0 = XBUI!Q = UIUIto =回O) 9]qnop •saaiHvnd: u 右sya±Hvnd > u = uui:0 二u (0 > u) J!} (u 3ui [pre ojqnop 3Suoo)SQps-sops :[puo::pis Suisn t)noo::p)s Suisntup::p)s Suisn}sanvsoocdsouiEuuM^-0Pd u opnpui#<UIP0J)SOl> 9pn(3UI#ddo-qt-opd//{ :0 ujnjoj:()S0p?SMoqs・pai :()so[ES)os・pQiX)S0|BSMOqS-p0J Sales::Sales()min = 0;max = 0;average = 0;for (int i = 0; i < QUARTERS; i++)salesfil =0;}void Sales::setSales(){double safQUARTERS];int i;for (i = 0; i < QUARTERS; i++){cout « "Enter sales for quarter " « i + 1 «n:";cin »safi];}// create temporary object, copy to invoking object 逬his 二Sales(sa, QUARTERS);}void Sales::showSales(){cout« "SalesAn";for (int i = 0; i < QUARTERS; i++)cout « "Quarter " « i + 1 « ": $" « sales[i] « endl;cout « "Average: $" « average « endl; cout « "Minimum:$" « min « endl;cout « "Maximum: $*' « max « endl;}}PE 10-5// pelOstack.h — class definition for the stack ADT // for use with pel0-5.cpp#ifndef_STACK_H_#define STACK Hstruct customer {char fullname[35];double payment;};typedef customer Item;class Stack{private:enum {MAX =10}; // constant specific to classItem itemsfMAX]; // holds stack itemsint top; // index for top stack itempublic:Stack();bool isemptyO const;bool isfull() const;// push() returns false if stack already is full, true otherwise boolpush(const Item & item); // add item to stack// pop() returns false if stack already is empty, true otherwise bool pop(Item & item); // pop top into item};# endif// pelOstack.cpp Stack member functions // for use with pel0-5-cpp // exactly the same as stack.cpp in the text#include "pelOstack.h"Stack::Stack() // create an empty stack {top = 0;}bool Stack::isempty() const{return top == 0;}bool Stack::isfull() constreturn top == MAX;bool Stack::push(const Item & item) {if (top < MAX){items[top++]二item; return true;}elsereturn false;}bool Stack::pop(Item & item){讦(top > 0){item = itemsf—topi; return true;}elsereturn false;// pel0-5.cpp#include <iostream>#include <cctype>#include n pelOstack.h n // modified to define customer structure // link with pelOstack.cppvoid get_customer(customer & cu);int main(void){using namespace std;Stack st; // create a stack of customer structurescustomer temp;double payments = 0;char c;cout « "Please enter A to add a customerAn H«n P to process a customer, and Q to quit.\n H;while (cin » c && (c = toupper(c)) != 'Q')while (cin.get() !=、rf) continue;if(c !二A && c !二P)cout «n Please respond with A, P, or Q: continue;}switch (c)case A : if (st.isfull())cout «”stack already full\n H; else{get_customer(temp); st.push(temp);}break;case P : if (st-isemptyO)cout «n stack already empty\n H;else {st.pop(temp);payments + 二temp.payment;cout « temp.fullname «n processed. ”;cout «n Payments now total $n« payments «”\n”;}break;default : cout « "Whoops! Programming error!\n u;cout «n Please enter A to add a customer,\n n«n P to process a customer, and Q to quit.\n n; } cout« "Done!\n";return 0;}void get_customer(customer & cu){using namespace std;cout « "Enter customer name: n;cin.getline(cu.fullname,35);cout «H Enter customer payment: H;cin » cu.payment;while (cin.get() != '\n f)continue;PE 10-8// pel0-8arr.h — header file for a simple list class#ifndef SIMPLEST.#define SIMPLEST,// program-specific declarationsconst int TSIZE = 45; // size of array to hold titlestruct film{char title[TSIZEJ;int rating;};// general type definitionstypedef struct film Item;const int MAXLIST = 10;class simplist{private:Item items [MAXLIST];int count;public:simplist(void);bool isempty(void);bool isfull(void);int itemcount();bool additem(Item item);void transverse( void (*pfun)(Item item));};#endif// pel0-8arr.cpp —functions supporting simple list operations #include ”pel0・8arr.h” simplist: :simplist( void)count = 0;bool simplist::isempty(void){return count == 0;}bool simplist::isfull(void){return count == MAXLIST;}int simplist:: itemcount(){return count;}bool simplist::additem(Item item){if (count == MAXLIST)return false;elseitems [count++] = item;return true;}void simplist::transverse( void (*pfun)(Item item)){for (int i = 0; i < count; i++) (*pfun)(items[i]);}// pel0-8.cpp — using a class definition#include <iostream>#include <cstdlib> // prototype for exit()#include n pel0-8arr.h n // simple list class declaration// array versionvoid showmovies(Item item); // to be used by transverse()int main(void)using namespace std;simplist movies; // creates an empty listItem temp;if (movies.isfullO) // invokes isfull() member function {cout «H No more room in list! Bye!\n n; exit(l);}cout « "Enter first movie title:\n n;while (cin.getline(temp.title,TSIZE) && temp.title[O] != '\0') {cout « "Enter your rating <0・10>:”;cin »temp.rating;while(cin.get() != '\n*)continue;if (movies.additem(temp) == false){cout« "List already is full!\n";break;}if (movies.isfull()){cout « "You have filled the listAn";break;}cout « "Enter next movie title (empty line to stop):\n"; } if (movies.isemptyO)cout « "No data entered.else{cout « "Here is the movie list:\n"; movies.transverse(showmovies);}cout« "Bye!\n";return 0;}void showmovies(Item item){std::cout « "Movie: ” « item.title «” Rating:"« item.rating « std::endl;。
C语言习题级答案10 10 选择题 1:若有以下说明: int a={1,2,3,4,5,6,7,8,9,10,11,12}; char c='a',d,g; 则数值为4的表达式是() A、a B、a['d'-'c'] C、a['d'-c] D、a[g-c] 答案C 2:若有说明:int a;则对a数组元素的 正确引用是()。 A、a(5) B、a C、a[3,5] D、a[10-10] 答案D 3:下列定义不正确的是()。 A、int max(x,y); intx,y; { } B、static char c; C、#define S3 45 D、#define PI 3.***** 答案A 4:结构化程序由三种基本结构组成, 由这三种基本结构组成的算法 A、只能完成一些简单的任务 B、只能完成部分复杂的任务 C、可以完成任何复杂的任务 D、只能完成符合结构化的任务 答案D 5:设变量定义为\执行下列语句时, 输入_____,则a和b的值都是10. scanf(\ A、a=10 b=10 B、10 10 C、10, 10 D、a=10, b=10 答案D 6:以下所列的函数\首部\中,正确的是() A、void play(a as int,b as int) B、void play(inta,int b) C、void play(a:int,b:int) D、void play(inta,b) 答案B 7:以下程序段的输出结果是。 int n=10; while(n7) { n--; Printf(“%d”, n ); } A、1098 B、***** C、987 D、9876 答案C 8:下列四个选项中,均是C语言关键字的选 项是()。 A、if struct type B、switch typedef continue C、signed union scanf D、auto enum include 答案B 9:C语言中,double类型数据占()。 A、4个字节 B、8个字节 C、1个字节 1 D、2个字节 答案B 10:以下数值中,不正确的八进制数或十六进制数 是()。 14:在一个C程序中()。 A、main函数必须出现在固定位置 B、main函数必须出现在所有函数之前 C、main函数可以在任何地方出现 D、main函数必须出现在所有函数之后 答案C 15:若有以下说明和定义,则对fun函数的正 A、-16 B、0x16 C、16 D、0xaaaa 答案A 11:以下标识符中,不能作为合法的C用户定义标 识符的是()。 A、signed B、_if C、to D、answer 答案A 12:为了避免在嵌套的条件语句if-else中产生二 义性,C语言规定:else总与( )配对 确调用语句是 main() { int (*a)( int ), *b(), w, c; … } fun( int *c ) { … } A、a = fun; (*a)( B、b = fun; *b( w ) C、fun(b); D、a = fun; a( w ) 答案A 16:下面四个选项中,均是不合法的浮点数 A、同一行上的if B、其之后最近的if C、其之前最近的未配对的if D、缩排位置相同的if 答案C 13:已知指针p的指向,则表达式++*p的值 的选项是()。 A、160. 0.12 e3 B、123 2e4.2 .e5 C、-.18 123e4 0.0 D、-e3 .234 1e3 答案B 17:根据以下定义,能输出字母M的语句是。 是 A、30 B、20 C、21 D、31 答案:C struct person { char name; Int age; }; struct person class={{“John”,17},{“Paul”,19},{“Mary”,18},{“Adam”,16}}; A、printf(“%c\\n”,class.name); 2 B、printf(“%c\\n”,class.name); C、printf(“%c\\n”,class.name); D、printf(“%c\\n”,class.name); 答案B 18:执行下列程序段后,m的值是________. int w=2,x=3,y=4,z=5,m; m=(wm="(m pritnf(“%d\\n”, k); } A、108 B、68 C、60 D、99 答案C 22:下列标识符中,不合法的C语言用户自定义标 识符是()。 A、printf B、sin C、enum D、_ 答案C 23:C语言执行程序的开始执行点是()。 A、程序中第一个函数 B、程序中的main函数 C、程序中第一条可以执行语言 D、包含文件中的第一个函数 答案B 24:下列叙述中不正确的是 A、C程序的main函数可以没有参数 B、C程序的main函数若有参数时,第一个参数的值最少是1 C、C程序的main函数可以有参数 D、main函数的第一个参数必须是整数,其名字必须是argc;第二个参数可以定义成:char *argv[],名字必须是argv。 答案D 25:若a为int类型,且其值为3,则执行完 A、4 B、2 C、3 D、5 答案B 19:下列选项中,合法的C语言关键字是()。 A、cher B、integer C、VAR D、default 答案D 20:以下对一维整型数组a的正确说明是()。 A、#define SIZE 10 (换行) int a[SIZE]; B、int a(10); C、int n; scanf(\D、int n=10,a[n]; 答案A 21:以下程序的输出结果是 main() { int a = {1, 3, 5, 7, 9, 11, 13, 15, 17, 19, 21, 23}; int (*p) = a, i, j, k = 0; for(i = 0; i i++) for(j =0; j j++) k += *(*(p + i) + j); 3 表达式a+=a-=a*a后,a的值是()。 A、6 B、-3 C、-12 D、9 答案C 26:有一个命名为C001.C的C语言源程序,当正常执行后,在当前目录下不存在的文件是 A、C001.OBJ B、C001.C C、C001.EXE D、C001.DAT 答案D 27:在调用函数时,如果实参是简单变量,它与对 应形参之间的数据 传递方式是()。 A、4 B、19 C、20 D、5 答案C A、传递方式由用户指定 B、地址传递 C、由实参传给形参,再由形参传回实参 D、单向值传递 答案D 28:设变量a是整型,f是实型,i是双精度型,则 表达式10+'a'+i*f值的 数据类型为()。 A、不确定 B、double C、int D、float 答案B 29:以下叙述中不正确的是()。 A、以下是正确的宏定义 #define IBM_PC B、在程序中凡是以#号开始的语句行都是预处理命令行 C、C程序在执行过程中对预处理命令行进行处理 D、预处理命令行都必须以#号开始 答案C 30:static char array=\数组元 素个数为( ) 4 判断题 1:语句 printf(\输出为 0.*****。 F 2:假设有int a, *p;则p=a与p=a等价 T 3:若有定义 char a;则能正确表示数字字符的表达式为(a='0'a='9')。 T 4:若定义:int x=11; 则表达式(x++ * 1/3)的值是4。 F 5:参加位运算的数据可以是任何类型的数据。 F 6:\的长度为9。 T 7:若有定义和语句: int a;char c;float f;scanf(\若通过键盘输入: 10,A,12.5,则a=10,c='A',f=12.5. T 8:如果想使一个数组中全部元素的值为0,可以写成 int a={0*10}; F 9:如果想使一个数组中全部元素的值为0,可以写成 int a={0*10}; F 10:在C程序中 , 函数既可以嵌套定义 , 也可以嵌套调用 F 程序设计题 题1: /*------------------------------------------------------- 【程序设计】 --------------------------------------------------------- 题目:分别统计字符串中字母、数字、空格和其他字符出现的 次数(字符长度小于80)。 -------------------------------------------------------*/ #include void bky(); /*-全局变量,a用于保存字母个数、num用于保存数字个数 b用于保存空格个数、other用于保存其他字符字数*/ int a=0,num=0,b=0,other=0; void count(char c[]) { /**********Begin**********/ int i; for(i=0;c[i]!='\\0';i++) if((c[i]='A'c[i]='Z')||(c[i]='a'c[i]='z')) a=a+1; else if (c[i]='0'c[i]='9') num=num+1; else if (c[i]==' ') b=b+1; else other=other+1; 5
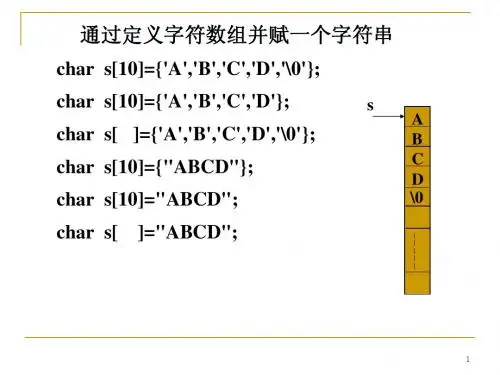
智慧树知到程序设计基础(C语言)测试第十章单元测试参考答案•总题数: 101【单选题】 (10分)若给出下列定义:char x[]="abcdefg";char y[]={'a','b','c','d','e','f','g'};则正确的叙述为( )。
A.数组y的定义是错的B.数组x的长度大于数组y 的长度C.数组x和数组y的长度相同D.数组x的长度小于数组y的长度正确本题总得分10分2【单选题】 (10分)有下列程序,程序运行后的输出结果是()。
#include <stdio.h>int main(){char ch[7]={ "65ab21"};int i,s=0;for (i=0;ch[i]>= '0'&&ch[i]<='9';i+=2)s=10*s+ch[i]- '0';printf("%d\n",s);return 0;}A.62B.6C.6521D.12ba56正确本题总得分10分3【单选题】 (10分)设有如下的程序段:char s[]="girl", *t; t=s;则下列叙述正确的是()。
A.t指向s数组首元素B.数组s中的内容和指针变量t中的内容相等C.*t与&s[0]相等D.s数组长度和t长度相等正确本题总得分10分4【单选题】 (10分)有下列程序段,程序段运行后的输出结果是()。
char b1[8]="abcdefg", b2[8], *pb=b1+3;while( --pb>=b1) strcpy(b2, pb);printf("%d", strlen(b2));A.7B.1C.8D.3正确本题总得分10分5【单选题】 (10分)有下列程序,程序运行后的输出结果是()。
目录- 1 -目录第一章C语言基础知识参考答案 ................................................................................ - 2 - 第二章顺序结构参考答案.......................................................................................... - 5 - 第三章选择结构参考答案.............................................................................................. - 7 - 第四章循环结构参考答案............................................................................................ - 11 - 第五章函数参考答案................................................................................................ - 15 - 第六章指针参考答案.................................................................................................... - 18 - 第七章一维数组参考答案............................................................................................ - 21 - 第八章二维数组参考答案.......................................................................................... - 28 - 第九章字符串参考答案.......................................................................................... - 31 - 第十章对C语言的深入讨论参考答案 ....................................................................... - 33 - 第十一章结构体与共用体参考答案............................................................................ - 34 - 第十二章文件参考答案........................................................................................ - 35 -全国计算机等级考试二级教程C 语言习题集参考答案- 2 - 第一章C语言基础知识参考答案一,选择题1 C2 D3 A4 C5 A6 D7 C 分析:C答案以数字开头了8 D 分析:int 是关键字9 C 10 D 11 B12 D 分析:Visual C++6.0中int类型的变量占的字节数为4。
第十章和十一章习题作业10-5解:#include<stdio.h>#include<stdlib.h>typedef struct list{int data;struct list *next;}linklist;int main(){int n,m,k,i=1;linklist head,*p,*q,*l;printf("enter n:\n");scanf("%d",&n);printf("enter m:\n",&m);scanf("%d",&m);printf("enter k:\n",&k);scanf("%d",&k);l=&head;p=l;for(;i<=n;i++){q=(linklist *)malloc(sizeof(head));p->next=q;q->data=i;p=q;}p->next=l->next; /*创建循环表*/p=l->next;for(i=1;i<m;i++) /*找到m的位置*/p=p->next;while(p->data!=p->next->data){for(i=1;i<k-1;i++)p=p->next;q=p->next;printf("%3d",q->data);p->next=q->next;p=q->next; /*p指向第k+1个人的位置*/free(q); /*释放空间*/}printf("%3d\n",p->data);free(l);free(p);}10-12解:#include <iostream>#include <cstdlib>#include <ctime>using namespace std;int main(){int r[100],s[10],i;for (i=0;i<10;++i){s[i]=0;}srand(time(NULL));//初始化随机数种子,产生不同随机数序列 for (i=0;i<100;++i){r[i]=rand()%10;//产生一个随机数++s[r[i]];}for (i=0;i<10;++i){cout<<i<<' '<<s[i]<<endl;}}11—7解://1 保存现在的格式化参数设置,以便将来恢复这些设置;//2 把对齐方式由缺省的右对齐改为左对齐;//3 把输出域的宽度由缺省值0改为10;//4 消除对齐方式的设置;//5 更改浮点数的显示设置;//6 恢复原来的格式化参数设置。
《全国计算机等级考试二级教程—— C 语言程序设计》习题分析与详细解答第一章程序设计基本概念习题分析与解答1. 1【参考答案】 EXE1. 2【参考答案】[1] .C[2] .OBJ [3] .EXE1. 3【参考答案】[ 1]顺序结构[2]选择结构[ 3]循环结构第二章 C 程序设计的初步知识习题分析与解答一、选择题2. 1【参考答案】 B)2. 2【参考答案】 D)2. 3【参考答案】 B)2. 4【参考答案】 A)2. 5【参考答案】 C)2. 6【参考答案】 A)2. 7【参考答案】 B)2. 8【参考答案】 B)2. 9【参考答案】 D)2. 10 【参考答案】 C)2. 11 【参考答案】 B)2. 12 【参考答案】 B)2. 13 【参考答案】 A)二、填空题2. 14【参考答案】[1] 11[2] 122. 15【参考答案】[ 1] 4.2[2] 4.22. 16【参考答案】[1] {[2] }[3]定义[4]执行2. 17【参考答案】[ 1]关键字[ 2]用户标识符2. 18【参考答案】[ 1] int[2] float[3] double2. 19【参考答案】float a1=1.0, a2=1.0;或 float a1=1, a2=1;( 系统将自动把 1 转换为 1.0)2. 20 【参考答案】存储单元2. 21【参考答案】 3.52. 22【参考答案】[ 1] a*b/c[2] a/c*b[3] b/c*a2. 23【参考答案】把 10 赋给变量 s2. 24【参考答案】[1]位[2] 1 位二进制数据 (0 或 1)2. 25【参考答案】[ 1] 8 [ 2] 127 [3]01111111 [4]-128 [ 5 ] 10000000 2. 26【参考答案】[ 1] 32767[2] -32768[3] 000002. 27【参考答案】[1]十[2]八[3]十六三、上机改错题2. 28【分析与解答】第 1 行的错误:(1) include是一个程序行,因此在此行的最后不应当有分号(;) 。