[英语学习]应用化学专业英语考试必背
- 格式:ppt
- 大小:320.02 KB
- 文档页数:78

黄冈师范学院2009—2010学年度第一学期期末试卷考试课程:专业英语考核类型:考试A卷考试形式:闭卷出卷教师:杨一思考试专业:化学考试班级:应用化学200601 一、Translate the following into English(20 points)1.过滤2.浓缩3.结晶化4.吸附5. 蒸馏6.超临界的7.二氯甲烷8.热力学平衡9.亲电性10.表面张力11.共轭的12.酮13.平衡常数14.丙基15.丁基16.亚甲基18.环己酮19.同位素20.标准熵二、Translate the following into Chinese(20 points)1. methyl propanoate2. rate constant3. ethyl methyl ketone4. free energy5. radical intermediate6. isobutyl methyl ether7. 3-chloropropene8. primary radical9. n-propyl bromide10. bond energy 11. circulating electrons12. local magnetic fields13. tetramethylsilane14. mass to charge ratios15 phenylamine16 amide17. amine18. nucleophile19. perchlorate20. carbocation三、Translation the following into chinese (40 points)A卷【第1页共 3 页】1. We can see why benzene is stable: according to resonance theory, the more resonance forms a substance has, the more stable it is. Benzene, with two resonance forms of equal energy, is therefore more stable and less reactive than a typical alkene.2. Membranes can be defined essentially as barrier, which separates two phases and restricts transport of various chemicals in a selective manner. A membrane can be homogenous or heterogeneous, symmetric or asymmetric in structure, solid or liquid, can carry a positive or negative charge or be neutral or bipolar. Transport through a membrane can be effected by convection or by diffusion of individual molecules, induced by an electric field or concentration, pressure or temperature gradient. The membrane thickness may vary from as small as 100 micron to several mms.3. The most common industrial adsorbents are activated carbon, silica gel, and alumina, because they present enormous surface areas per unit weight.A surface already heavily contaminated by adsorbates is not likely to have much capacity for additional binding, but further heating will drive off these compounds to produce a surface with high adsorptive capacity.Temperature effects on adsorption are profound, and measurements are usually at a constant temperature. Graphs of the data are called isotherms. Most steps using adsorbents have little variation in temperature.A卷【第2页共 3 页】4. In the absence of peroxides, hydrogen bromide adds to peopene via the Markovnikov pathway to yield isopropyl bromide. In the presence of peroxides, however, the order of addition is reversed, and the product is n-propyl bromide; the addition in this case is said to be anti-Markovnikov. This is interpreted in terms of initiation of the addition reaction by bromine atom, rather than by a proton, as is the case for electrophilic addition.四、Translate the following paragraphs into Chinese(20 points)1.Benzene and its derivatives can be nitrated using a mixture of concentrated nitric and sulphuric acid. The temperature must be controlled to prevent more than one nitro-group going in.2. Benzene can be made to react with halogen derivatives using aluminium chloride as a catalyst. This is called a Friedel-Crafts reaction.can be sulphonated by reacting it with fuming sulphuric acid(oleum). The benzene reacts with sulphur trioxide in the oleum.benzene is converted into ethylbenzene by reacting it with ethene. The ethylbenzene (also called styrene) is used to make polystyrene.黄冈师范学院2009—2010学年度第一学期期末试卷参考答案及评分标准考试课程:专业英语考核类型:考试A卷考试形式:闭卷出卷教师:杨一思考试专业:化学考试班级:应用化学200601 一、Translate the following into English(20 points)2. concentrate 4. adsorption chlorideequilibriumtensionconstant14. propylmagneticresonanceentropy二、Translate the following into Chinese(20 points)1. 丙酸甲酯2. 速率常数3. 甲乙酮4. 自有能5. 自由基中间体6. 异丁基甲醚7. 3-氯丙烯8. 伯自由基9. 正丙基溴化10. 键能11.循环电子12. 局部电磁场13. 四甲基硅烷14. 质荷比15.苯胺16.氨基化合物17.胺18亲核试剂19.高氯酸盐20.碳正离子三、Translation the following into chinese (50 points)1.依据共振理论,物质具有的共振式越多就越稳定。



一单词短语1.Molecule 分子molecular 分子的2.chemical process 化学过程element 元素3.a t o m原子a t t r a c t i o n吸引力4.repulsion 排斥力distillation 蒸馏、n5.distill 蒸馏v rectification 精馏position 构成structure 结构7.property 性质mass 质量8.atomicweight 原子量atomic number 原子序数9.ionization energy 电离能period 周期10.g r o u p族f a m i l y族11.transition group 过渡族main group 主族12.i o n离子s u b s t i t u t i o n取代反应13.el i mi na ti on消除反应nucl eoph i l i c 亲核的14.nucleophilie 亲核试剂electrophilie亲电试剂15.alkyl 烷基的functional group 官能团16.halides 卤素的leaving group 离去基团17.transition state过渡态intermediate 中间体18.r e a c t a n t反应物p r o d u c t生成物19.concentration 浓度rate equation 速率方程20.c o n s t a n t常数e t h e r醚21.endothermic 吸热的substrate 反应底物22.mechanism 机理reagen 试剂23.alkene 烯烃exothermic 放热的24.A n i o n阴离子n i t r o g e n氮气25.Hydrocarbon 碳氢化合物carbonhydrate 碳水化合物26.Alkane 烷烃substituent 取代基27.Isomerism 同分异构现象isomer 同分异构28.V i n y l乙烯基d e r i v a t i v e s衍生物29.acid halides 酰卤acid anhydrides 酸酐30.e s t e r s酯a m i d e酰胺31.ammonia NH3 Acetic anhydride乙酸酐32.phenol 芬acid—base titration 酸碱滴定33.precipitation沉淀analyses 化学分析员34.IR 红外UV紫外MS质谱GC色相色谱HPLC高效液相色谱TLC薄层色谱X—rayX射线衍射二选词填空1、We can now easily account for many things,which were thought to be mysterious by theancients2、the acid acts on the metal and a gas is givenoff.3、you should adapt yourself to new ways oflooking at matters4、electrolytes have more pronounced effect oncolligative properties than do nonelectrolytes. 5、if water in these lakes evaporated at the samerate as fresh water ,both would nearly dryup in a matter of year.6、both laks evaporated very slow compared with afresh lake or even the ocean.7、a property that depends only on the relativeamounts of solute and solvent is know as acolligative property.8、for example ,both NaCl (ionic) and HCl (polarcovalent)are classified as electrolytes becausethey form ions in aqueous solution.9、when compounds such as NaCl and HCl aredissolved in water ,the effect is obvious.10、if the wires is cut ,the light goes out becausethe circuit is broken.11、when wires are attached to a charged batteryand then to a light bulb ,the light shinesbrightly.12、glass and wood as well as pure water areexamples or nonconductors of electricity.13、other substances resist the flow of electricityand are known as nonconductors orinsulators.14、it has long been known that the presence of asolute in water may affect its ability toconduct electricity.15、when the collection of papers was first broughtout,it was well received by the reviewers.16、in the same way the dozen or so mostcommon kinds of kinds of atoms can be put together in many millions of different ways tomake molecules .17、elements are made up of tiny fundamentalparticles called atoms. Fundamental, as it is usedhere ,means that they cannot be furtherdivided by any chemical metheods.18、each element has atoms that is different fromthe atoms of other elements.19、it would not be quite round; on the contraryit would consist of three parts represented byspheres.20、it is not to be summed up in a singleproduct or word ,but in an idea or basicconcept.21、the chemical symbol of an element may standthe element for.22、the rate of a chemical reaction is influencedby several factors such as temperature ,concentration of reagents , particle size ,light ,and catalyst.23、all forms of life in earth are very dependenton chemical reactions or chemical changes.24、a chemical reaction occurs when elements andcompounds react together to produce differentcompounds , or when compounds break down into simpler compounds or elements.三无机物的命名H Hydrogen Li Lithium Na Sodium K Potassium Mg Magnesium Ca CalciumMn manganese Cu copper Zn zinc Fe iron Hg mercury Ag silver Au gold C Carbon Si Silicon Pb Lead Al Aluminium F Fluorine Cl Chlorine Br Bromine I IodineO Oxygen S Sulfur N Nitrogen P Phosphorus1.直呼其名,即读其元素名称+ ion如:Na+ sodium ionK+ potassium ion2.对于有变价的金属元素,除了可用前缀来表示以外,更多采用罗马数字来表示金属的氧化态,或用后缀-ous 表示低价,-ic 表示高价如:Cu+ copper (Ⅰ) ion 或cuprous ion Cu2+ copper (Ⅱ) ion 或cupric ionFe2+ iron (Ⅱ) ion 或ferrous ionFe3+ iron (Ⅲ) ion 或ferric ion3.含氢酸根:酸根中的H读做hydrogen,氢原子的个数用希腊前缀表示:mono- di - tri- tetra - penta- hexa-hepta- octa- nona- deca-举例:CO32-carbonate ionHCO3-hydrogen carbonate ionPO43- phosphate ionHPO42hydrogencarbonate ionH2PO4- dihydrogenphosphate ion4.结晶水读做hydrate ,结晶水的个数用希腊前缀表示:mono-di - tri- tetra - penta- hexa- hepta- octa- nona- deca-CuSO4·5H2O copper(Ⅱ) sulfate pentahydrateAlCl3 ·6H2O aluminum chloride hexahydrate5.测试Mg(OH)2magnesium hydroxide AlCl3aluminum chlorideFeBr2 iron(II) bromide CaSO4calcium sulfateZnCO3zinc carbonate HF hydrofluoric acidH3PO4phosphoric acid NO2nitrogen dioxideCuO copper(II) oxide Al2O3aluminum oxideNaHSO3sodium hydrogen sulfiteKMnO4potassium permanganateNaClO sodium hypochloride四有机物的命名1)命名正烷基时,只需把烷烃的词尾“-ane换成“-yl”,加在相应的烷烃的字首后2)字母规则:Butyl>Ethyl>Isopropyl>Methyl>Neopentyl>tert-Pentyl >Propyl3)环烷烃:只需在所对应的烷烃前加上cyclo-即可4)有些结构较复杂的烷基,需添加词头5)烯烃和炔烃命名时将相应的烷烃的词尾“烷”(ane)改为“烯”(ene)或“炔”(yne),后缀前加上不饱和键的编号即可。

专业英语重点总结单词Toxic chemicals:有毒化学品 Chemical pollution:化学污染Physical property :物性 Isolate:分离Determine:测定 Synthesize:合成Fundamental principles:基本原理 Investigation:研究Utilize:利用 Catalyst 催化剂Enzyme 酶 Biosphere 生物圈Heterogeneous catalyst 非均相催化剂 Nanotechnology 纳米技术Carbon monoxide 一氧化碳 Chemical formulas:化学式anion: 阴离子 Oxidation number:氧化值sulphate: 硫酸盐 Hydrides: 氢化物Sodium:钠 cation: 阳离子Covalent bond:共价键 electroneutral: 电中性的Electronegative atom:电负性原子 trivial names:俗名Oxidation:氧化 Peroxides:过氧化物Superoxide:超氧化物 Periodic table:周期表Noble gases: 惰性气 vacant orbital:空轨道Coordination (complex) compound: 配位化合物Unshared pair of electrons:未共用电子对oxidation state:氧化态 hydroxides:氢氧化物caustic soda solution:苛性钠溶液 vacant orbital:空轨道Formula 分子式 Common name 俗名Derivative 衍生物 Acid salt 酸式盐Hydrate 水合物 Anhydrous 无水的Oxidizing agent 氧化剂 Reducing agent 还原剂Oxidation reduction reaction氧化还原反应Electrochemistry 电化学 Electrolysis 电解Strong acid 强酸 Weak base 弱碱Acid-base indicator 酸碱指示剂 Distilled water 蒸馏水Buffer solution 缓冲溶液 Common ion effect 同离子效应Equivalence point 等效点 Neutralization 中和Dissociation 离解度 Anhydride 脱水物Periodic law: 元素周期率 periods (rows):周期group (columns):族 protons:质子Valence electrons:价电子 Halogens: 卤素Atomic radius: 原子半径 alkaline earths:碱土金属attractive force: 吸引力 electronegativity: 电负性electropositive:正电性 univalent ion: 一价离子electron shell: 电子层 bonding force 结合力monatomic 单原子的 Neutrons:中子hydrogen bond 氢键 conduct electricity 导电Electrically neutral 电中性的 Electrostatic 静电的isomerism :异构现象 Reversible :可逆的Chirality :手性 Charge:电荷mirror image:镜像 mirror image:镜像Hydrocarbons:碳氢化合物 Methane: 甲烷propane :丙烷 butane :丁烷-ane:-烷 -ene:烯-yne:炔 -ol:醇-one :酮 -al:醛-aldehyde: 醛 -acetal:缩醛alkoxy-:烷氧基 -amide: 酰胺-amino:氨基的 -amine : 胺Aquo- 含水的 azo- 偶氮Polythene (PE): 聚乙烯 Benzene:苯Ethene:乙烯 Propene:丙烯double bond:双键 triple bond:三键Valence bond theory 价键理论 skeleton:骨架methyl:甲基 ethyl:乙基alkyl :烷基 side chains: 侧链substituent:取代基Meth-:甲 eth-:乙propyl-:丙 but-:丁Pent(a)-:戊 hex-:己hepta-:庚 oct-:辛non-:壬 deca-:葵di-:二 tri- : 三tetra- : 四 penta-: 五primary carbon:伯碳 secondary carbon:仲碳tertiary carbon:叔碳 allyl :烯丙基substitution reaction :取代反应 free radical:自由基nucleophilic substitution:亲核取代 carbocation :碳正离子electrophilic substitution:亲电取代 carbanion :碳负离子addition reaction :加成反应elimination reaction:消去反应acid anhydride:酸酐 alcohol:乙醇Thermodynamics 热力学 quantum chemistry 量子化学statistical mechanics 统计力学 Kinetics 动力学Equilibrium 平衡 deposition 沉积sublimation 升华 Condensation 冷凝evaporation 蒸发 Melting 熔化Freezing 冷冻 Work 功the states of system系统状态Irreversible 不可逆的 surrounding 环境open system 开放系统 closed system 封闭系统isolated system 孤立系统 impermeable 不可渗透的Adiabatic 绝热的 steady state稳态tap water 自来水 rinse 润洗fine chemicals 精细化学品 Buchner funnel 布氏漏斗bunsen burners 煤气喷灯 tripod supports 三角支架wash bottles 洗瓶 dropper 滴管transfer pipette 移液管 hot plate 轻便电炉wire gauzes 石棉网 test tube brush 试管刷test tube rack 试管架filter paper 滤纸ring stand with rings 带环环架iron support 铁架台utility clamp 铁试管夹 clamp holder 夹柄buret clamp 滴定管夹 extension clamp 万能夹ring clamp 环形夹子 pinchcock 弹簧夹pinch clamp 弹簧节流夹 tubing clamp 管夹hose clamp 软管夹 test tube clamp 试管夹cork stopper 软木塞 rubber stopper 橡胶塞laboratory jack 实验升降台 spatulas 刮刀beaker tongs 烧杯钳 crucible tongs 坩埚钳tweezer 镊子 watch glasses 表面皿goggles 护目镜fume hoods 通风橱capillary melting point tube 毛细熔点管 Caliper 卡尺table balance 托盘天平 analytical balance 分析天平top pan balance 市秤 magnetic stirrers 电磁搅拌器Fahrenheit thermometer 华氏温度计 celsius 摄氏度magnetic stir bar 磁搅拌子 alcohol lamp 酒精灯Spectrophotometers 分光光度计 connection tube 连接管rubber tube 橡皮管 adapter 接合器Socket 套接口 ball joint 球形接头Stopper 塞子 adaptor 转接口splash heads 防溅头 thermometer pocket温度计插孔air leak tube 空气渗漏管 distill head 蒸馏头melting point tube 熔点管 burettes 滴定管Stopcock 活塞 volumetric flask 容量瓶measuring cylinder 量筒 centrifuge tube 离心管graduated pipette刻度吸量管 filter funnel 过滤漏斗chromatography colum 层析柱dropping funnel 滴液漏斗pressure equalizing funnel 均压漏斗 separating funnel 分液漏斗rotary evaporator 旋转蒸发仪 petri dishes 培养皿spectrophotometer 分光光度计 drying tube 干燥管evaporating dishes 蒸发皿 condenser 冷凝管Reflux 回流 erlenmeyer flask 锥形烧瓶round bottom flask 圆底烧瓶 distillation flask 蒸馏烧瓶filtration flask 过滤瓶 reagent bottle 试剂瓶glass desiccator 玻璃干燥器Beaker 烧杯distilling receiver 蒸馏接收器dry tower 干燥塔vaccume dessicator 真空干燥器 extractor 萃取器无机化合物及化学式的命名·二元化合物:氧化物,盐,酸(1)阴离子元素加后缀–ide(2)多价态元素加前缀:mono-, di-, tri-, tetra-, penta-, hexa(3)低价氧化态后缀–ous,高价氧化态后缀–ic·酸:基础元素(前缀 hydro-, 后缀-ic)+ acid·氢氧化物(碱):金属元素(价态)+ hydroxide·含氧酸及其盐(1)基本元素仅有一种氧化态酸:基础元素加后缀-ic + acid盐:阳离子元素+基础元素加后缀-ate(2)基本元素有二种氧化态酸:基础元素加后缀( -ous低价态,-ic高价态) + acid盐:阳离子元素 + 基础元素加后缀( -ite低价态, -ate高价态)(3)基本元素有多种氧化态酸:最低氧化态基础元素(前缀 hypo-, 后缀-ous)+ acid较低氧化态基础元素加后缀-ous+ acid较高氧化态基础元素加后缀-ic + acid最高氧化态基础元素(前缀 per-, 后缀-ic)+ acid 盐:最低氧化态阳离子元素 + 基础元素(前缀 hypo-, 后缀-ite)较低氧化态阳离子元素 + 基础元素加后缀-ite较高氧化态阳离子元素 + 基础元素加后缀-ate最高氧化态阳离子元素 + 基础元素(前缀 per-, 后缀-ate)·不同水分子含量的酸较低水含量前缀 meta较高水含量前缀 ortho·不同基本元素形成的酸前缀 di-, pyro·含硫的酸:源于含氧酸中的氧被硫取代,使用前缀 thio·含氢盐(酸式盐):源于含有1个以上氢原子酸中的氢原子被金属离子取代,形成酸式盐,氢原子以及金属离子使用前缀 di-, (bi),tri·配位化合物的命名阳离子 + [ 配体及中心原子] (氧化数)前缀:prefix·二元化合物,原子个数前缀1—mono-(可省略);2—di-;3—tri-;4—tetra-;5—penta-;6—hexa- Eg:·Oxide-氧化物CaO:calcium oxide(quicklime-生石灰)N2O:nitrogen(Ⅰ) oxide = dinitrogen oxide = nitrous oxide(laughing gas) NO:nitrogen(Ⅱ) oxide = nitrogen oxide = nitric oxideN 2O3:nitrogen(Ⅲ) oxide = dinitrogen trioxideNO2:nitrogen(Ⅳ) oxide = nitrogen dioxideN 2O5:nitrogen(Ⅴ)oxide = dinitrogen pentaoxideCu2O: copper(Ⅰ) oxide = dicopper oxide = cuprous oxide-低价态CuO: copper(Ⅱ) oxide = cupric oxide-高价态·Salt-盐ZnF2: znic fluorideSnCl2: tin(Ⅱ) chloride = stannous chlorideHg2Cl2: mercury(Ⅰ) chloride = mercurous chloride (calomel-甘汞)HgCl2: mercury(Ⅱ) chloride = mercuric chloride (sublimate) KCN: potassium cyanide·Acids-酸HBr: hydrobromic acid (aqueous solution)HCN: hydrocyanic acidH2S: hydrosulphuric acid·Hydroxides(bases)-碱NaOH: sodium hydroxide (sodium lye, caustic soda solution) KOH: potassium (hydroxid potassium lye, caustic potash)Fe(OH)2: iron(Ⅱ) hydroxide (ferrous hydroxide)Fe(OH)3: iron(Ⅲ) hydroxide (ferric hydroxide)·Oxo acids and their salts-含氧酸及其盐H2CO3: carbonic acid Na2CO3: sodium carbonateH3BO3: boric acid K3BO3: potassium borate·The basic element is in two oxidation statesHNO2: nitrous acid NaNO2: sodium nitriteHNO3: nitric acid Co(NO3)2: cobalt(Ⅱ) nitrate = cobaltous nirate·The basic element is in more than two oxidation states HClO: hypochlorous acid KClO: potassium hypochloritaHClO2: chlorous acid KClO2: potassium chloriteHClO3: chloric acid KClO3: potassium chlorateHClO4: perchloric acid KClO4: potassium perchlorateHMnO4: permanganic acid AgMnO4:sliver permanganate·The hydrogen salt-含氢盐Na3PO4: trisodium phosphate (tertiary phosphate)Na2HPO4: disodium hydrogen phosphate (secondary phosphate)NaH2PO4: sodium dihydrogen phosphate (primary phosphate)NaHCO3: sodium hydrogen carbonate (sodium bicarbonate) ·Give formulas for the following1.ammonium sulfate: (NH4)2 SO42.barium iodide: BaI23.iron(Ⅱ) sulfate:Fe2SO44.potassium permanganate:KMnO4 5.copper(Ⅱ)oxide:CuO6.carbonic acid:H2CO3科技论文写作Introduction section-研究的是什么问题?Key sections·Materials and Methods section-这个问题是怎么研究的?·Results and Discussion sections-发现了什么?Conclusion section-这些发现意味着什么?1.ABSTRACT (摘要)研究动机、研究方法、主要结果、简要结论摘要应言简意赅,因此以上各项内容争取用一句话说明一项,每项最多不要超过三句话,即:为什么做这个研究?用了什么方法?取得了什么结果?结论是什么?这些问题逐一回答了,摘要就写完整了。

英译汉:1.First, electrons are added one at a time moving from left to right across a period……首先,从左向右横跨一个周期时每次增加一个电子。
当这种情况发生时,最外层电子将受到逐渐增强的核引力,所以电子将更接近原子核而受到其更紧密的束缚力。
其次,在周期表中从上向下移动一列,最外层电子受到核的束缚力将变弱。
这是因为主能级数(屏蔽最外层电子受到核的吸引)在每族向下移动时增加。
这些趋势解释了通过观察元素的原子半径、电离能、电子亲和力和电负性而得到的元素性质的周期性规律。
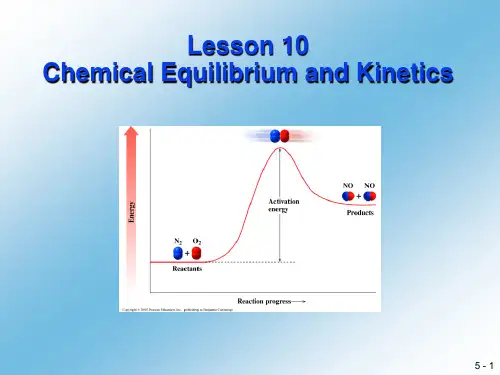
2.It is important to note that at equilibrium the rates of reaction,rate r and rate f are equilibriummixture are usually not equal……值得注意的是,在化学平衡时的反应速率,正反应速率和你反应速率相等但反应物和生成物的摩尔浓度在平衡混合态时一般不相等。
但是,事实上每种反应物和生成物在平衡时其浓度为定值,因为每种物质在一个反应中的消耗速率与其在相应你反应正的生成速率相等。
在化学平衡提出之前,这种系统被称为动力学平衡状态。
3.This is a mathematical expression of the law of chemical equilibrium which may be stated as follows:When a reversible…………这是化学平衡定律的数学表达式,它可以通过如下所述:当一个可逆反应在给定温度下达到平衡时,在方程式中箭头右边物质的摩尔浓度的积除以左边物质摩尔浓度的积(每种物质浓度的幂等于反应方程式中每种物质的分子数)为定值,4.Analytical chemistry,or the art of recognizing different substances and determining theirconstituents, takes a prominent position among分析化学或鉴定不同物质并测定其成分的技术,因为可以解决每当化学过程被用于科学的或技术性的目的是产生的问题,而在科学应用领域中占显著地位。

东华大学应用化学专业英语总结专业英语重点总结单词Toxic chemicals:有毒化学品Chemical pollution:化学污染Physical property :物性 Isolate:分离Determine:测定 Synthesize:合成Fundamental principles:基本原理 Investigation:研究Utilize:利用 Catalyst 催化剂Enzyme 酶Biosphere 生物圈Heterogeneous catalyst 非均相催化剂Nanotechnology 纳米技术Carbon monoxide 一氧化碳Chemical formulas:化学式anion: 阴离子 Oxidation number:氧化值sulphate: 硫酸盐 Hydrides: 氢化物Sodium:钠 cation: 阳离子Covalent bond:共价键electroneutral: 电中性的Electronegative atom:电负性原子 trivial names:俗名Oxidation:氧化Peroxides:过氧化物Superoxide:超氧化物Periodic table:周期表Noble gases: 惰性气vacant orbital:空轨道Coordination (complex) compound: 配位化合物Unshared pair of electrons:未共用电子对oxidation state:氧化态 hydroxides:氢氧化物caustic soda solution:苛性钠溶液vacant orbital:空轨道Formula 分子式 Common name 俗名Derivative 衍生物 Acid salt 酸式盐Hydrate 水合物 Anhydrous 无水的Oxidizing agent 氧化剂Reducing agent 还原剂Oxidation reduction reaction氧化还原反应Electrochemistry 电化学 Electrolysis 电解Strong acid 强酸 Weak base 弱碱Acid-base indicator 酸碱指示剂Distilled water 蒸馏水Buffer solution 缓冲溶液Common ion effect 同离子效应Equivalencepoint 等效点 Neutralization 中和Dissociation 离解度 Anhydride 脱水物Periodic law: 元素周期率 periods (rows):周期group (columns):族 protons:质子Valence electrons:价电子 Halogens: 卤素Atomic radius: 原子半径alkaline earths:碱土金属attractive force: 吸引力electronegativity: 电负性electropositive:正电性univalent ion: 一价离子electron shell: 电子层 bonding force 结合力monatomic 单原子的 Neutrons:中子hydrogen bond 氢键conduct electricity 导电Electrically neutral 电中性的Electrostatic 静电的isomerism :异构现象Reversible :可逆的。

unite 1. Inorganic chemistry1.1 what is chemistry(1). 重点专业词汇讲解:Chemical: adj . 化学的、化学药品Transformation: 变化,化学转变,转化Dye: n. 染料染色,或者vt. 染Charcoal: ['t ? ck??l] 木炭Cellulose : 纤维素细胞的['selj?l??z; ] Fat:n. 脂肪肥肉adj . 肥大的alkalis :碱adj . 碱性的glycerin: 甘油丙三醇alkalis: n. 碱金属alloy: 合金使成合金bronze:青铜色的n. 青铜(铜和锡的合金)brass:[br a s] n.黄铜(铜和锌)要求学生会区别黄铜及青铜的不同翻译Poison:毒物毒药t.毒害放毒下毒Proton:n. 质子Nulei: n.核(nucleus 的复数形式)['njukl ??s]Identical : adj . 同一的Chirality n.手性手征和Handeness的区别Amino acid :n. 氨基酸Ala nine: n.丙氨酸2. 课文中重点词组(phrase)Chemical change:化学变化physical change:物理变化Explore: 探险研究research investigate studyIsolate: 分离chemical bonds 化学键chemical reaction :化学反应Natural substance 天然物质Coke : 焦炭carbon monoxide 一氧化碳Carbon Dioxide 二氧化碳Chemical bond 化学键fundamental principle 基本原理The periodic table of elements :元素周期表numbers of protons 质子数atomic number 原子序数covalent bonds 共价键positive 正阳性negative 负阴性3. 课文中重点句子The first and most important principle is that chemical substances are made up of molecules in which atoms of various elements are linked in well-defined ways. 需要着重给学生讲解第一条也是最重要的原理是化学物质是有分子组成的,分子中的不同元素的原子是以一定的方式连接在一起的。

Toxic chemicals:有毒化学品Chemical pollution:化学污染Physical property :物性Natural changes: 自然变化Scientific fields:科学领域Isolate:分离Determine:测定Synthesize:合成Fundamental principles:基本原理Investigation:研究Utilize:利用化学式书写的基本规则如何写化学式命名化合物二元化合物:氧化物,盐,酸(1)阴离子元素加后缀–ide(2)多价态元素加前缀:mono-, di-, tri-, tetra-, penta-, hexa-(3)低价氧化态后缀–ous,高价氧化态后缀–ic氧化物盐酸:基础元素(前缀hydro-, 后缀-ic)+ acid氢氧化物(碱):金属元素(价态)+ hydroxide含氧酸及其盐(1)基本元素仅有一种氧化态酸:基础元素加后缀-ic + acid盐:阳离子元素+基础元素加后缀-ate(2)基本元素有二种氧化态酸:基础元素加后缀(-ous低价态,-ic高价态)+ acid盐:阳离子元素+ 基础元素加后缀(-ite低价态, -ate高价态)(3)基本元素有多种氧化态酸:最低氧化态基础元素(前缀hypo-, 后缀-ous)+ acid较低氧化态基础元素加后缀-ous+ acid较高氧化态基础元素加后缀-ic + acid最高氧化态基础元素(前缀per-, 后缀-ic)+ acid盐:最低氧化态阳离子元素+ 基础元素(前缀hypo-, 后缀-ite)较低氧化态阳离子元素+ 基础元素加后缀-ite较高氧化态阳离子元素+ 基础元素加后缀-ate最高氧化态阳离子元素+ 基础元素(前缀per-, 后缀-ate)不同水分子含量的酸较低水含量前缀meta-较高水含量前缀ortho-不同基本元素形成的酸前缀di-, pyro-含硫的酸:源于含氧酸中的氧被硫取代,使用前缀thio-含氢盐(酸式盐):源于含有1个以上氢原子酸中的氢原子被金属离子取代,形成酸式盐,氢原子以及金属离子使用前缀di-, (bi-),tri-配位化合物的命名阳离子+ [ 配体及中心原子] (氧化数)Chemical formulas:化学式anion: 阴离子Oxidation number:氧化值sulphate: 硫酸盐Sodium:钠cation: 阳离子Covalent bond:共价键electroneutral: 电中性的Electronegative atom:电负性原子mono-一Hydrogen: 氢di-二Hydrides: 氢化物tri-三Oxidation:氧化tetra- 四前缀Peroxides:过氧化物penta-五Superoxide:超氧化物hexa-六Positive:正oxidation state:氧化态Periodic table:周期表trivial names:俗名Noble gases: 惰性气sulphide: 硫化物Transition elements:过渡元素hydroxides:氢氧化物Ion: 离子caustic soda solution:苛性钠溶液Combining capacity:结合能力phosphorus: 磷Coordination (complex) compound: 配位化合物vacant orbital:空轨道Unshared pair of electrons:未共用电子对Ethene:乙烯Propene:丙烯butene :丁烯Single bond:单键double bond:双键triple bond:三键Benzene:苯Symmetrical:对称的Naphthalene: 萘functional group :官能团hydroxyl :羟基Carbohydrates: 碳水化合物,糖类Sucrose: 蔗糖glucose :葡萄糖alcohols:醇ether:醚ketone:酮aldehyde:醛fatty acids:脂肪酸esters:酯diethyl :二乙基hexagonal :六边的Formaldehyde: 甲醛methyl :甲基acetate :醋酸盐pentagonal :五边形的amines :胺类ammonia :氨amino acid :氨基酸methylamine :甲胺glycine :甘氨酸vitamin :维生素chlorophyll :叶绿素alkali :碱enzyme :酶-ane:-烷-ene:烯-yne:炔cyclo-:环-Meth-:甲eth-:乙propyl-:丙but-:丁Pent(a)-:戊hex-:己hepta-:庚oct-:辛non-:壬deca-:葵skeleton:骨架-yl: (烷)基methyl:甲基ethyl:乙基alkyl :烷基side chains: 侧链substituent:取代基cis and trans isomers :顺式和反式异构体enantiomers :对映异构体di-:二tri- : 三tetra- : 四penta-: 五straight-chain:直链iso-:异primary carbon:伯碳secondary carbon:仲碳tertiary carbon:叔碳allyl :烯丙基methylene :亚甲基ethylidene :亚乙基Ethylene:次乙基hybridization :杂化cycloalkane :环烷alkene :烯烃geometric isomer:几何异构体chiral carbon:手性碳clockwise direction:顺时针方向counterclockwise direction :逆时针方向Glyceraldehyde:甘油醛substitution reaction :取代反应nucleophilic substitution:亲核取代nucleophile :亲核试剂dissociate :离解carbocation :碳正离子Intermediate:中间体substrate :底物leaving group :离去基团electrophilic substitution:亲电取代carbanion :碳负离子addition reaction :加成反应addition product:加成物attacking reagent:进攻试剂free radical:自由基migration:移动elimination reaction:消去反应adjacent carbon:相邻碳rearrangement reaction:重排反应酸酐acid anhydride 酸性化物acid halide乙醇alcohol 乙醛aldehyde脂肪族aliphatic 烷烃alkane烯烃alkene 醇盐alkoxide烷基alkyl 炔烃alkyne烯丙基allyl 氨基化合物amide胺amine 氨基酸amino acid氨(络)合物ammine 芳烃arene芳香环aromatic ring 芳基aryl含氮的azo 羰基carbonyl羧酸carboxylic acid 胡萝卜素carotene螯合物chelate 手性chiral构象异构体conformer 配位数coordination number晶体场稳定化能crystal filed splitting energy右旋性的dextrorotary重氮化作用diazonium salt二氯甲烷dichloromethane 酯ester脂肪酸fatty acid 自由基free radical官能团functional group 甘油glycerol杂环的heterocyclic 高自旋配合物high spin complex 同系物homolog 烃hydrocarbon诱导效应inductive effect 酮ketone左旋的levorotatory 配体ligand低自旋配合物low spin complex 甲基methyl分子筛molecular sieve 单齿配位物monodentate辛烷octane 旋光性optical activity石蜡paraffin 苯酚phenol苯基Phenyl 多配位基的polydentate聚合物Polymer 丙烷propane外消旋的Racemic 共振效应resonance effect过氧化物superoxide互变异构体tautomer薄层分析法thin layer chromatography甘油三(酸)酯triglyceride不饱和化合物unsaturated compound水煤气water gas两性离子zwitterionbeaker 烧杯phenolphthalein indicator 酚酞指示剂Pipette 移液管acetic acid 醋酸pH meter pH计standard titration curve 标准滴定曲线benzoic acid 苯甲酸ethyl alcohol 乙醇qualitative organic analysis 定性有机分析Unambiguous 明确的characterize 表征structure determination 结构测定bunsen burners 煤气喷灯tripod supports 三角支架wash bottles 洗瓶dropper 滴管transfer pipette 移液管hot plate 轻便电炉wire gauzes 石棉网test tube brush 试管刷test tube rack 试管架ring stand with rings 带环环架filter paper 滤纸utility clamp 铁试管夹clamp holder 夹柄buret clamp 滴定管夹extension clamp 万能夹ring clamp 环形夹子pinchcock 弹簧夹pinch clamp 弹簧节流夹tubing clamp 管夹hose clamp 软管夹test tube clamp 试管夹cork borer set木塞钻孔器套件cork stopper 软木塞rubber stopper 橡胶塞laboratory jack 实验升降台spatulas 刮刀beaker tongs 烧杯钳crucible tongs 坩埚钳Forceps 医用钳tweezer 镊子watch glasses 表面皿goggles 护目镜carbon stirring rod 碳搅拌棒fume hoods 通风橱capillary melting point tube 毛细管熔点管Caliper 卡尺table balance 托盘天平analytical balance 分析天平top pan balance 市秤magnetic stirrers 电磁搅拌器Fahrenheit thermometer 华氏温度计celsius 摄氏度bulb pipettor 球形移液器magnetic stir bar 磁搅拌子Mortars 碾钵pestles 捣锤spotting plates 滴试板alcohol lamp 酒精灯Spectrophotometers 分光光度计connection tube 连接管rubber tube 橡皮管adapter 接合器Socket 套接口ball joint 球形接头Stopper 塞子adaptor 转接口splash heads 防溅头thermometer pocket温度计插孔air leak tube 空气渗漏管distill head 蒸馏头melting point tube 熔点管burettes 滴管Stopcock 活塞aspirating stopcock 吸气式移液管measuring cylinder 量筒volumetric flask 容量瓶centrifuge tube 离心管graduated 有刻度的chromatography colum 层析柱filter funnel 过滤漏斗pressure equalizing funnel 均压漏斗powder funnel 药粉漏斗separating funnel 分液漏斗dropping funnel 滴液漏斗rotary evaporator 旋转蒸发仪spectrophotometer 分光光度计crystallizing dishes with spout 带喷嘴的结晶皿petri dishes 培养皿evaporating dishes 蒸发皿drying tube 干燥管condenser 冷凝管Reflux 回流erlenmeyer flask 锥形烧瓶round bottom flask 圆底烧瓶flat bottom flask 平底烧瓶distillation flask 蒸馏烧瓶filtration flask 过滤瓶round bottom flask 圆底烧瓶weighing bottles 称量瓶reagent bottle 试剂瓶aspirator bottle 蒸馏水瓶BOD bottle 生化需氧量瓶dropping bottle 滴瓶specific gravity bottle 比重瓶glass desiccator 玻璃干燥器Beaker 烧杯extractor 萃取器dry tower 干燥塔vaccume dessicator 真空干燥器gas washing bottle 气泡吸收瓶distilling receiver 蒸馏接收器。
The Roots Of ChemistryChemistry can be broadly defines as the science of molecules and their transformations.化学可以广泛地定义为科学的分子和他们的转换。
In contrast to mathematics,chemistry is older than people. 与数学不同,化学比人类更久远。
The appearance of life and people on our planet (earth) is most probably the end result of specific chemical processes .生命的出现和人类生活在我们地球上都最可能是特殊化学过程的结果。
Chemical processes have been present in the lives of people from the dawn of history until the present time .化学过程存从古至今存在人们的生活中。
Initially ,these processes were not under our control 最初,这些过程不受我们的控制,,for instance ,the fermentation of fruit juice,the rotting of meat and fish ,and the burning of wood .例如,果汁的发酵,肉和鱼的腐烂,木材的燃烧。
Later on we learned to control chemical processes and to use them to prepare a variety of different products such as food ,metals ,ceramics and leather .后来,我们学着控制化学过程,用它们来准备一系列不同的产品例如食物。
应用化学专业英语Cu—copper Fe—iron Hg—mercury Na—sodium K—potassium Ag—silverNaOH—sodium hydroxide KOH—potassium hydroxide Fe(OH)2—iron(Ⅱ)hydroxide Fe(OH)3—iron(Ⅲ)hydroxide NH4OH—ammonium hydroxideK3[Fe(CN)6]—potassium hexacyanoferrate(Ⅲ)K4[Fe(CN)6]—potassium hexacyanoferrate(Ⅱ)Ⅰ.Name the following1.(NH4)2CO3Ammonium carbonate2.N2O Nitrous Oxide3.H2SO4Sulfuric acid4.P4O6Phosphorus(Ⅲ)trioxide5.Al2O3Aluminium oxide6.SnCl4Tin(IV)chloride7.KHSO4Potassium hydrogen sulfate8.Cu2S Copper(Ⅰ)sulfide9.HClO4Perchloric acid10.BaCl2Barium chloride11.P4O10Phosphorus(Ⅴ)pentoxide12.NaH Sodium hydride13.Ca(MnO4)2Calcium permanganate14.PF5Phosphorus pentafluoride15.(NH4)2HPO4Diammonium hydrogen phosphateⅡ.Give formulas for the following1.ammonium sulfate(NH4)2SO42.barium iodide BaI23.iron(Ⅱ)sulfate Fe2SO44.potassium permanganate KMnO45.copper(Ⅱ)oxide CuO6.carbonic acid H2CO3Melting point 熔点boiling point 沸点1.Which particles play the most active role in chemical bonding?(a)electrons (b)neutrons (c)protons (d)valence electrons2.An ionic bond is formed when electrons are:(a)completely destroyed (b)compeltely transferred (c)divied (d)equally shared3.Due to the that Ionic compounds have strong intermolecular forces they are at room temperature.(a)bonded covalently (b)gases (c)liquids(d)solids 1-butene trans -2-butenecis -2-butene iso -butene (E )-2-butene (Z )-butene 2-methylpropene1.Draw structure that correspond to the following names.(a)2,2-dimethylpentane (b)4-isobutyl-2,5-dimethylheptane (c)(Z)-3-menthyl-2-octene (d)(2R,3S)-2,3-pentanediol2.Give the IUPAC name for each of the following structures.(e)(f)(E)-1-methyl-4-ethylcyclohexane(g)(h)(S)-2-chloro-butyraldehyde (2R,3R)-2,3-dichlorobutyric acid补充:(E)-2-chloro-3-methyl-2-octene Nucleophile亲核试剂carbocation碳阳离子Compressible可压缩的incompressible不可压缩的1.A chemical system can be studied from either a or a(n)viewpiont.(A)physical...chenical(B)molecual...atomic (C)Microscopic...macroscopic(D)Mechanic...kinetic2.Is a macroscopic science that studies the interrelationships between the various equilibrium properties of a stystem.(A)Kinetics(B)Thermodynamics (C)Statistical mechanics(D)Quantum chenistry3.In,the molecular and macroscopic levels are related to each other.(A)quantum(B)statistical(C)thermodynamics(D)kinetics4.thermodynamics studies.(A)heat,work,energy,and the changes they produce in the states of systems(B)The relationships between the molecules of a system(C)heat,work,temperature,and the energy they produce in the states of systems(D)heat,energy,and work5.For a(n)system,neither matter nor energy can be transferred between system and surroundings.(A)closed(B)open(C)isolated(D)none of the aboveⅠ.Translate the following from English into Chinese.(1)pollution of the atmosphere(2)nondegradable pollutant大气污染不可降解污染物(3)harmless pollutant(4)interacting chemicals无害污染物相互作用的化学物质(5)threshold level(6)sound pressure level限定值,阈值声压水平(7)speech interference(8)transmission path 语音干扰传输途径Translate the following from Chinese into English.(1)定性分析qualitative analysis (2)分析物analyte (3)准确度accuracy (5)反应速率reaction-rate (5)解吸附作用deserption (6)吸附absorption conduction 热传导convection 对流radiation 辐射Balance and classify each of the following chemical equations as a (1)combination reactions ,(2)decomposition reaction ,(3)displacement reaction ,or (4)partner-exchange reaction.(a))()(2243l O H s Fe H O Fe +→+)(4)(342243l O H s Fe H O Fe +→+displacement reaction 置换反应(b))()()(23g O s KCl s KClO +→)(3)(2)(223g O s KCl s KClO +→decomposition reaction 分解反应(c)steam and hot carbon react to form gasecous hyfrogen and gaseous carbon monoxide.)()()()(22g CO g H s C l O H +→+displacement reaction 置换反应(d))()()(4272aq HClO g O H g O Cl →+)(2)()(4272aq HClO g O H g O Cl →+combination reactions 化合反应(e))()()(22aq HBrO aq HBr O H l Br +→+)()()(22aq HBrO aq HBr O H l Br +→+decomposition reaction 分解反应(f))()()()()(43442243aq PO H s CaSO aq SO H s PO Ca +→+)(2)(3)(3)()(43442243aq PO H s CaSO aq SO H s PO Ca +→+partner-exchange reaction 复分解反应(g)Potassium reacts with water to give aqueous potassium hydroxide and gaseous hydroxide.)()(2)(2)(222g H aq KOH l O H s K +→+displacement reaction 置换反应(h)Solid magnesium carbonate decomposes to form solid magnesium oxide and gaseous carbon monoxide.)()()(23g CO s MgO s MgCO +→decomposition reaction 分解反应Abstract 摘要Results and discussion 结果与讨论Experimental实验References参考文献E-factor影响因素Journal of the American Chemical Society美国化学会志Journal of the Chemical Society化学会志Journal of Organic Chemistry有机化学杂志Tetrahedron四面体'\.._/ ( Wb川ache mical reaction?Acherr山al react i on occurs when subs'孟忘"(tlie reactants) collide (碰撞) with enough energy to rearrange to form different compounds (由e produc时. η1e change in energy由at occurs when a reaction take place is described by thermodynamics (热力学) and the rate or speed at which a reaction occ u rs is described by kfaetics (动力学) . Reactions in which the reactants and produc臼coexist are considered to be in equ山brium (处于平衡). A chemical equation consists of the chemical formula (化学式) of the reactants,且目the chemical formula of the products. The two are separated by an 一一- usually read as ”yielas·’and each chemical formula is separated from others by a plus sign (加号) . Sometimes a triangle is drawn over the arrow symbol to denote energy must be added to the substances for the reaction to begin. Each chemical formula may be preceded by a scalar (数量的) coefficient ind i cating the proportion (比例) of that substance necessary to produce the reaction in formula. For instance, the formula for the burning of methane (C比+ 202 →C02 + 2H20) indicates that twice as much 02 as C比is needed, and when they react, twice as much H20 as C02 will be produced.η1is is because during the reaction, each atom of carbon needs exactly two atoms of oxygen to combine with, to produce the C02, and every two atoms of hydrogen need an atom of oxygen to combine with to produce the H20. If the proportions of t he reactants are not respected, when they are forced to react, either not all of the substanc e used will participate in the react i on, or the react i on that will take p l ace will be different from the one noted in the equation.。
Unit 1 The Rootsof Chemis tryI. Compre hensi on.1.It can be inferred from this articl e whichone of the followi ng itemsi s not mainly basedon practi c al use C. Greekchemis try2. It was B. Empedo cless who firsti ntrod ucedthe idea that all things are not formed from just one elemen t.3. In the develo pment of Greekchemis t ry, D. Democri tus was the first one defini tingthe ultimatelyconsti tuent s of matter?4. Accord i ng to Plato, thereare B. 4 ―elemen ts‖ whosefacesare consti tuted by regula r polygons.5. In the last paragraph,authors thinkthat experi ment DD.can deal with the reacti ons by whichone substa n ce is converted into anothe rII. Make a senten ce out of each item by rearra nging the wordsin bracke ts.1.The purifi catio n of an organi c compou nd is usuall y a matter of consid erabl e diffic ulty, and itis necess ary to employ variou s method s for this purpos e.2.Scienc e is an ever-increa singbody of accumu lated and system atize d knowle dge and is also anactivi ty by whichknowle dge is genera ted.3.Life, afterall, is only chemis try, in fact, a smallexampl e of chemis try observ ed on a si nglemundan e planet.4.People are made of molecul es; some of the molecul es in people are rather simple wherea sothers are highly comple x.5.Chemist ry is ever presen t in our livesfrom birthto deathbecause withou t chemis t ry therei sneithe r life nor death.6.Mathem atics appears to be almost as humanki nd and also permea tes all aspect s of humanlife,althou gh many of us are not fullyawareof this.III. Transl ation.1.(a)化学过程;(b)自然科学;(c)蒸馏技术(a) chemic al proces s (b) natura l science (c) the techni que of distil latio n2.正是原子构成铁、水、氧等。
Aabscissa[æbˈsɪsə] n. 横座标 abundance n. 丰富, 充裕acceptor n. 接受体accumulator n. 储料器 acetic acid n. 醋酸, 乙酸 acknowledge v. &n. 致谢activation n. 活化acylation ['æsil] n. 酰化addition [əˈdiʃən] n. 加成反应adhesive [ædˈhisɪv, -zɪv] n. 粘合剂advancement n. 进展,增长advantageous adj. 有利的aerosol[ˈeərəˌsɔ:l, -ˌsɔl] n. 烟雾affinity [əˈfɪnɪti:] n. 亲合力agent [ˈeidʒənt] n. 试剂aldehyde [ˈældəˌhaɪd]n. 醛aldol[ˈældəul]n. 醛醇aliphatic acid [ˌæliˈfætik]n. 脂肪酸alkaline[ˈælkəlɪn, -ˌlaɪn] adj. 碱的alkaloid[ˈæl kəlɔid] n. 生物碱alkane[ˈælˌken]n. 烷烃alkene[ˈælki:n]n. 烯烃alkylation [ˌælkiˈleiʃ(ə)n]n. 烃化, 烷基化alkyl halide[ˈælkil][ˈhælaid]n. 烷基卤, 卤烷alkyne n. 炔alphabetic adj. 依字母顺序ambiguity n. 模糊, 意义不明确amide n. 酰胺amine n. 胺amino acid n. 氨基酸amorphous adj. 无定形analogue n. 类似物anhydride n. 酸酐aniline n. 苯胺anion n. 阴离子anomaly n. 异常,反常antibiotics n. 抗菌素antifreezing agent n. 抗冻剂antioxidant n. 抗氧剂appreciable adj. 可估计的architect n. 建筑师, 设计师arene n. 芳烃aromatic adj. 芳香的aromatization n. 芳构化asymmetric adj. 不对称的autooxidation n. 自氧化awarenness n, 意识azeotrope n.共沸混合物azo dye n. 偶氮染料Bbackup n. /adj 备用设备base n. 碱, 基, 底beaker n. 烧杯benzene n. 苯biological degradation n. 生物降解biosynthesis vt. 生物合成bleach vt. 漂白bond n. 键branched chain n. 支链budget n. & v. 预算bubble-cap tower n. 泡罩塔buffer n. 缓冲,缓冲剂Ccarbanion n. 负碳离子, 阴碳离子carbene n. 碳烯, 卡宾carbide n. 碳化物, 碳化钙carbocation n. 正碳离子, 阳碳离子carbonyl group n. 羰基carboxy group n. 羧基carboxylic acid n. 羧酸carcinogenic adj. 致癌的β-carotene n. β胡萝卜素carrier n. 载体cartridge n. 软片暗盒catalysis n. 催化(作用) cation n. 阳离子cellulose n. 纤维素ceramic adj/n. 陶瓷(的) chemical shift n. 化学位移chirality n. 手性chlorination n. 氯化作用chlorohydrocarbon n. 氯代烃chromophore n. 发色团cis-trans isomer n. 顺反异构体classic adj. 经典的, 传统的cluster n. 蔟,一串,一束coherent adj. 黏附的,相干的(光学) coil n. 蛇管colorant n. 颜料,着色剂commodity n. 用品compensation n. 补偿competitive n. 竞争的complementary n. 补充的complex n. 络合物complication n. 复杂concerted reaction n. 协同反应condensation n. 缩合反应condiment n. 调味品conformation n. 构象conjugation n. 共轭construction n. 建设, 建筑consultant n. 顾问consumer n. 消耗container n. 容器containment n. 抑制cooler n. 冷却器corporate adj. 共同的correlate n. 相关的事物cosmetic n. 化妆品counteract vt. 抵消,抵抗coupling reaction n. 偶合反应covalent bond n. 共价键critical adj. 临界的cumulative adj. 累积的,累加的customary adj. 通常的, 常例的cycloparaffin n. 环烷烃Ddecolorant n. 脱色剂decolorize v. 脱色degradation n.降解dehydration n. 脱水作用dehydrogenation n. 脱氢作用delocalization n. 离域作用denatured alcohol n. 变性酒精denominator n. 分母derivation n. 衍生,由来derivative n. 衍生物desorption n. 解吸作用destructive distillation 分解蒸馏detergent n. 洗涤剂developer n. 显影剂dextrorotary adj. 右旋的diazonium salt n. 重氮盐diazotization n. 重氮化作用dielectric adj.不导电的,n.电介质dipole n. 偶极directory n. 地址录disclose vt. 揭露, 揭发discrete adj. 离散的,不连续的disposal vt. 排出, 处理director n. 定位基dissolve v.溶解distillation n. 蒸馏dominant adj. 支配的,统治的donor n. 给体drastic n. 激烈的, 猛烈的droplet n. 液滴dyestuff n. 染料Eelectrophilic reagent n. 亲电试剂electrophobic adj 疏电子的electronegative adj 电负性的electron withdrawing group n. 吸电子基electrostatic adj. 静电的elimination n. 消除反应emulsion n. 乳剂endothermic adj. 吸热的enantiomer n. 对映体enzyme n. 酶epoxy adj. 环氧化的essential oil n. (香)精油ester n. 酯esterification n. 酯化作用ethanol n. 乙醇ether n. 醚, 乙醚ethyl n. 乙基ethylene n. 乙烯ethynyl n. 乙炔基evaluation n. 评价,估价evaporation n. 蒸发excitation n. 激发态exothermic adj. 放热的extract vt. 萃取extrapolation n. 推断Ffermentation n. 发酵fiber n. 纤维filament n. 细丝,丝状体filter n.过滤器,滤色片flare v. & n. 闪耀, 闪烁flavoring n. 香剂, 调味剂fluorescent n. 荧光fore adj. 先时的, 前部的formaldehyde n. 甲醛fossil n. 化石fractional distillation n. 分馏free radical n. 自由基fumigant n. 熏蒸(消毒)剂functional group n. 官能团furan n. 呋喃Ggeneralization n. 一般(性), 普遍(性) genetic code n. 遗传密码geological adj. 地质(学)的geomatrical adj. 几何学的glacial acetic acid n. 冰醋酸glucose n. 葡萄糖glycerol n. 甘油, 丙三醇graphics n. 图,制图法Hhabituation n. 习惯作用, 毒瘾halogenation n. 卤化hazardous adj. 危险的, 有危害的herbicide n.除草剂heterocyclic compound n.杂环化合物heterogeneous adj. 非均相的, 多相的hexagon n. 六边形highlight n. 光线明亮处hold-up n. 塔储量, 容纳量homologous series n. 同系列hormone n. 激素humectant n. 润湿剂hybrid n. 杂化hydration n. 水合作用hydrogenation n. 氢化作用hydrolysis n. 水解hydrophobic adj. 疏水的hydroxyl group n. 羟基Iidealize vt. 理想化inasmuch as adv. 因为, 由于indicator n. 指示剂indiscriminate adj. 不加选择的indol n. 吲哚inductive effect n. 诱导效应ineffective adj. 无效的, 低效率的infrared spectroscopy n. 红外光谱ingenious adj. 坦率的, 天真的ingestion n. 吸收, 吸入inlet n. 进口, 入口insecticide n. 杀虫剂insulin n. 胰岛素integrate vt. 积分,使...一体化interchangeable adj. 可互换的intermediate n. 中间体ion n. 离子isoelectric point n. 等电点isomer n. 异构体Jjacket n. 套, 夹套justification n. 认为正当, 正当的理由Kketone n. 酮Llactic acid n. 乳酸leakage n. 泄漏lesser adj. 较小的, 更少的lime n. 石灰lining n. 衬里, 衬料, 衬套link vt. 连接,键合liquefy vt. 液化lubricating grease n. 润滑脂Mmanipulation n. 操作, 操纵manuscript n. 稿子, 手稿mass spectroscopy n. 质谱mechanism n. 机理, 历程medium n. 介质, 培养基metallurgical adj. 冶金(学)的methane n. 甲烷methnol n. 甲醇methodology n. 方法论micelle n. 胶粒microorganism n. 微生物migrate vi. 迁移miscible adj. 可溶混的modification n. 修饰monomer n. 单体monosaccharide n. 单糖multiplet n. 多重峰multiplicity n 多重性Nnaphthalene n. 萘nitration n. 硝化作用nitric acid n. 硝酸nitrile n. 腈noble adj. 贵重的, 惰性的nomenclacture n. 命名法noteworthy adj. 显著的nucleophile n. 亲核试剂nucleic acid n. 核酸neutralization n. 中和numerator n. (数学上) 分子nutrient n. 营养素, 养分Oobservable a. 可观察到的octane number n. 辛烷值olefin n. 烯烃optical activity n. 旋光性optics n. 光学optimum n. 最佳条件orbital n. 轨道organometallic compound 金属有机化合物originate vi./vt. 起源outermost adj. 最外层的,远离中心的overhead n. 塔顶馏出物overheat vt. 过热overlap vt. 重叠oxidation n. 氧化作用ozonide n. 臭氧化合物ozonolysis n. 臭氧分解Pparaffin n. 链烷烃, 石蜡peptide n. 肽perfume n. 香料peroxide n. 过氧化合物persistence n. 坚持, 固执pesticide n. 杀虫剂pharmaceuticals n. 药物phenol n. 苯酚phenoxide n. (苯)酚盐phenylsulfonic acid n. 苯磺酸phosphoric acid n. 磷酸photochemical reaction n. 光化学反应photochromism n. 光致变色photoconductivity n. 光电导性pigment n. 颜料pink n. 粉红色polyamide n. 聚酰胺polarization n. 极化作用polyhydric alcohol n. 多元醇polymerization n. 聚合作用precipitate vi. /n. 沉淀preservative n. 防腐剂prolong vt. 延长, 拖延propellant n. 推进剂prospective adj. 预期的, 有希望的protecting group n. 保护基purity n. 纯度pyridine n. 吡啶pyrolysis n. 热解pyrrole n. 吡咯Qquantify vt. 使量化,确定数量quaternary ammonium salt n. 季铵盐quench vt. 淬灭quinoline n. 喹啉Rracemization n. 外消旋作用reagent n. 试剂realization n. 实现recover vt. 回收recrystallization n. 重结晶rectifier n. 精馏器reduction n. 还原(作用) reflux n. 回流refract vt. 折射refrigerant n. 冷冻剂remainder n. 剩余物, 残余部分的replica n. 复制品,拷贝resolution n. 分辨, 拆开restrictive adj. 限制性的ribonucleic acid n. 核糖核酸(RNA) rigorous adj. 严厉(格)的Ssaccharin n. 糖精saponification n. 皂化(作用) screen n. 筛子, 屏幕seal n. 密封(垫) segment n. 部分, 链段selectivity n. 选择性settle vt. (使)沉淀, 澄清setup vt. 装置, 装配sewage n. 污水silica gel n. 硅胶singlet n. 单重峰skeleton n. 骨架solubility n. 溶解度solvant n. 溶剂化物solvent n. 溶剂, 有溶解力的sophistication n. 复杂spectroscopy n. 光谱spin-spin coupling n. 自旋-自旋偶合stabilization n. 稳定作用stereoisomerism n. 立体异构现象steric factors n. 位阻因素, 空间因素still pot n.蒸馏釜stoichiometric adj. 化学计算的straightforward adj.一直向前, 正直的substituent n. 取代基substitution reaction n. 取代反应sucrose n. 蔗糖sulfa drug n. 磺胺药sulfonation n.磺化作用sulfuric acid n. 硫酸supervisor n. 导师, 监督人, 主管人suspension n. 悬浮液sweetener n. 增甜剂symmetry n. 对称性symposium n. 座谈会syn addition n. 顺式加成Ttar n. 焦油(沥青)tartaric acid n. 酒石酸tautomerism n. 互变异构现象terpene n. 萜烯tertiary adj. 叔的, 第三的tetrahedron n. 四面体thiazole n. 噻唑thiophene n. 噻吩toluene n. 甲苯toxicity n. 毒性transesterification n. 酯交换反应transition state n. 过渡状态tray n. 盘, 分馏塔盘triplet n. 三重峰trivial adj. 轻微的Uultraviolet-visible spectroscopy n. 紫外-可见光谱unify vt. 统一urea n. 尿素Vvalidate vt. 使生效vaporize vt.蒸发versatile adj. 多方面的vice versa adj. 反之也然vinegar n. 醋violate vt. 破坏,侵害Wwhereas conj. 而, 却, 鉴于withdraw vt. 拉, 提取, 取出withdrawal n. 收回,撤回Xxerography n. 静电复印法Yyeast n. 酵母Zzymochemistry n. 酶化学。