高考英语语法精品学案:专题13 特殊句式
- 格式:doc
- 大小:111.00 KB
- 文档页数:18

2019高考英语:(13)二轮语法学案(独立主格结构)(练习题配解析或解析)复习独立主格结构1、独立主格结构的基本概念独立主格结构是由一个独立的名词或代词(作为该短语结构的逻辑主语),加上一个分词、形容词、副词、动词不定式或介词短语(作为该短语结构的逻辑谓语)构成。
这种结构在形式上与主句没有关系,因此,通常把它叫做独立主格结构。
该结构主要起状语作用,相当于一个状语从句,多用来表示行为、方式、伴随的情况,有时也用来表示时间、原因、条件等。
2、独立主格结构的基本构成形式及其作用如上所述,独立主格结构在句中一般作状语,其作用相当于一个状语从句。
常见的构成形式如下:(1)名词或代词主格十分词(现在分词或过去分词)eg:TheexperimentdonE、thestudentswentontotakenotesintheexperimentreport、试验结束后,同学们继续在试验报告上作记录。
(2)名词或代词主格+形容词eg:Computersbeingverysmall,wecanusethemwidely、随着电脑体积变小,我们可以广泛地使用它们。
(3)名词或代词主格+不定式eg:Thewaytogrowcropswell,thefarmershavefoundatlast、农民们最终找到了种好庄稼的办法。
(4)名词或代词主格+介词短语eg:OurEnglishteachercameintotheclassroom,papersinhanD、我们的英语老师拿着卷子走进教室。
(5)名词或代词主格+副词eg:Themeetingbeingover,ourheadmastersoonleftthemeetingroom、随着会议结束,校长很快离开了会议室。
3、独立主格结构及分词短语作状语的异同(1)独立主格结构与分词短语在句子中都可以转换为状语从句。
但是要注意,独立主格结构转换为状语从句后,它有自己的逻辑主语,与主句的主语不一致。




特殊句式一、倒装“主语+谓语”是英语句子的最基本结构。
如果把谓语放在主语之前,该句就成倒装结构。
1、完全倒装:谓语动词完全放在主语之前的句子,便(1) 在there be结构中There stands an old tree on the top of the hill.(2)在表示方位或时间的副词或介词短语,如:here, there, now, then ,up , down ,in, out, away, off, in the room,on the wall等置于句首,且以名词作主语的句子Here comes the bus. Away flew the birds.Out went the children. Now comes your turn. 现在轮到你了。
【注意】主语是代词就不用倒装,即主谓语序不变。
Away ran the thief. Away he ran.2、部分倒装只把谓语的一部分(多为助动词或情态动词)置于主语之前的句子,叫部分倒装句。
(1) 否定词(hardly, seldom, never, rarely,in no way, under no circumstances, by no means, not only,,,but also, not until…)(2) 表示否定或者半否定意义的副词,介词短语,连词等置于句首。
否定副词never, nor,not, hardly, little, seldom, scarcely, rarely及表否定意义的介词短语at no time, under/in no circumstances, in no case, by no means, on no condition等置于句首时要倒装,不在句首则用正常语序。
Never have I seen such a performance.Hardly do I think possible to finish the job before dark.= I hardly think it possible to finish the job before dark.练一练1. Never in my wildest dreams ____B___ these people are living in such poor conditions.A. I could imagineB. could I imagineC. I couldn’t imagineD. couldn’t I imagine2. Only then ___D____ how much damage had been caused.A. she realizedB. she had realizedC. had she realizedD. did she realize(3) so放在句首,So + adj. /adv…that,意为“如此……以至于……”后接表语或状语,再跟that从句,so后面的主句要倒装,而that引导的从句不倒装。

高考英语特殊句式分类汇总在高考英语中,掌握各种特殊句式是提高语言表达能力和得分的关键。
下面是对高考英语特殊句式进行详细介绍。
1. 强调句型强调句型是通过强调句子中的某个成分来突出其重要性或特殊性。
在高考英语中,常见的强调句型有两种形式:It is/was…that和What…。
(1) It is/was…that该形式中,强调句子的主语、宾语、状语等成分,一般将被强调的成分放在it后面,用that引导的从句作为原句的主句。
例如:- It was Mary who won the first prize in the English contest.- It is the teacher who inspired me to study hard.(2) What…该形式中,强调句子的谓语动词,用what引导的名词从句位于句首。
例如:- What makes him different from others is his positive attitude towards life. - What we need to do now is to find a solution to the problem.2. 倒装句型倒装句型是指把句子的主语和谓语动词的位置颠倒过来的结构。
在高考英语中,常见的倒装句型有两种形式:完全倒装和部分倒装。
(1) 完全倒装在完全倒装句中,谓语动词位于主语之前,主语位于动词之后。
例如:- Not only did he pass the exam, but he also got a high score.- Never have I seen such a beautiful sunset.(2) 部分倒装在部分倒装句中,只有助动词、情态动词或系动词的前移。
例如:- Should you have any questions, feel free to ask.- Can you imagine how excited I was when I received the good news?3. 条件句型条件句型是指表示条件关系的句子结构。
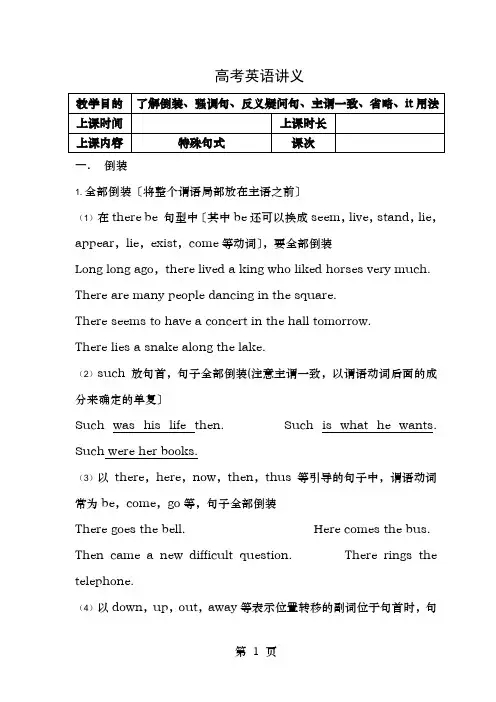
高考英语讲义一.倒装1. 全部倒装〔将整个谓语局部放在主语之前〕(1)在there be 句型中〔其中be还可以换成seem,live,stand,lie,appear,lie,exist,come等动词〕,要全部倒装Long long ago,there lived a king who liked horses very much. There are many people dancing in the square.There seems to have a concert in the hall tomorrow.There lies a snake along the lake.(2)such 放句首,句子全部倒装(注意主谓一致,以谓语动词后面的成分来确定的单复〕Such was his life then. Such is what he wants. Such were her books.(3)以there,here,now,then,thus等引导的句子中,谓语动词常为be,come,go等,句子全部倒装There goes the bell. Here comes the bus. Then came a new difficult question. There rings the telephone.(4)以down,up,out,away等表示位置转移的副词位于句首时,句子全部倒装(人称代词出现时,句子不倒装〕Up went the arrow into the sky. In came the teacher. Away ran the dog.Out rushed the people from their house when the earthquake happened.In she came. Here you are. Out it ran. (人称代词出现,不倒装〕(5)表地点的介词短语放在句首,句子要用倒装In the classroom stays a girl.On the desk lies a book.2. 局部倒装〔将谓语中的助动词,情态动词,be动词放在主语之前〕(1)only+状语〔副词,介词短语,状语从句〕放在句首,谓语动词局部倒装Only then did I realize the importance of English.Only in this way can you solve the problem.Only when I came into the house did I recognize the man.注:only修饰主语时,句子不用倒装Only you can finish the work.(2)so +be动词/助动词/情态动词+主语,句子局部倒装So did I〔我也是〕与so he does〔他确实是〕的判断方法〈1〉判断原句正负〔肯定为正,否认为负〕原句为正用so开头,原句为负用neither或nor开头〈2〉判断原句的be/助动词/情态动词〔根据时态与人称确定〕〈3〉看人称所指一致不一致人称所指一致,用正序;人称所指不一致用倒序〈4〉如果出现第三个人与前面两人的情况一样时,用it is the same with sb.如果两者情况都一样时,并且原句为否认,那么省略句还可用:主语be/助动词/情态动词+either.I went there yesterday, so did he.我昨天去那里了,他也去了。

特殊句式【课标要求】特殊句式在高考中的考点【复习任务】1.学习重点:强调句、省略句和倒装句在高考中的考点。
2.学习难点:1)强调句型用于强调not…until…句型;2)承前省略的动词不定式如果有助动词have或be,则要保留be或have。
3)在can not but, can not choose but, can not help but之后的动词不定式一般不带to; but之前有实义动词do的某个形式do, does, did, done 时,也不带to, 否则要带to。
4)表示方向的副词out, in, up, down等置于句首,要用全部倒装。
但主语是代词时部分倒装。
5)表示地点的介词短语 (如on the wall, under the tree, in front of the house,in the middle of the room等)放在句首时,要全部倒装。
【问题导学】一.强调句1.强调句型用于强调陈述句;2.强调句型用于强调一般疑问句;3.强调句型用于强调特殊疑问句;4.强调句型用于强调not…until…句型;5.强调句型与状语从句、定语从句、祈使句的混合考查。
替代: 1.do/does/did替代动词; 2.so和not分别代替肯定和否定的从句.I.强调句1.It is (was) +被强调部分+that(who)…为了强调句子的某一成分(通常是主语、宾语、或状语),常用强调结构: It is (was) +被强调部分+that(who)…表示强调的it在这种结构的句子中作主句的主语。
原始句:Last night I saw a film in the Youth Palace.强调主语:It was I that (or: who) saw a film in the Youth Palace last night.强调宾语:It was a film that I saw in the Youth Palace last night.强调地点状语:It was in the Youth Palace that I saw a film last night.强调时间状语:It was last night that I saw a film in the Youth Palace.一般讲,原句的谓语动词如果是现在或将来各种时态,用It is…that (who)…;如果原句谓语动词是过去各种时态,则用It was… that(who)…。

专题13 特殊句式【2019年高考考纲解读】特殊句式比较杂乱,掌握起来有一定的难度。
其中倒装句是高考的热点,强调句是高考的难点。
同时,祈使句与陈述句的区别、省略与替代的合理运用也是高考考查的重点项目。
近三年的高考题更加注重考查知识之间的交叉现象,如在考查强调句的同时考查定语从句,把省略、强调句与时间状语从句、地点状语从句的考查等融合在一起,考查考生综合把握语言知识的能力。
【重点、难点剖析】一、倒装句(一)完全倒装(Full Inversion)谓语动词完全放在主语之前的句子便是完全倒装句。
这类句型主要有:1.表示方式、方位的副词或介词短语,如here, there, up, down, in, away, off, out, in the room, on the wall等,置于句首,且主语是名词时。
如:In a lecture hall of a university in England sits a professor.在英格兰一所大学的讲堂里坐着一位教授。
South of the river lies a small factory.一个小型工厂坐落在河的南岸。
Out rushed the children.孩子们冲了出去。
2.such置于句首时。
如:Such was Albert Einstein, a simple man and the 20th century's greatest scientist.这就是艾伯特·爱因斯坦,一个朴实的人,也是20世纪最伟大的科②如果not until引导的是句子,until从句不可倒装,只是主句需要倒装。
(7)hardly...when...,no sooner...than...“刚……就……”等引导两个句子时,前一个句子用部分倒装,后一个句子不倒装。
Hardly/Scarcely had he heard the news when he began to cry.他一听到这个消息就哭了。

特殊句式I There beA 定义表达“某处/某时存在某人/某物”。
B 结构一般结构:There + be + 名词+ 地点将来结构:There will be + 名词+ 地点完成结构:There has been + 名词+ 地点含情态动词结构:There + 情态动词+ be + 名词+地点C 用法a. 就近原则例:There is some juice and some cakes on the table.b. 衍生结构①There be + 名词+ doing(与名词形成主动关系)例:There must be something blocking the pipe.②There be + 名词+ done(与名词形成被动关系)例:T here’s only four days left.③There be + 名词+ to do(未发生,表将要做…)例:There is still a lot of work for me to do.拓展:there be句型中,其结构中谓语动词和非谓语结构的变化·there be中的be有时可用seem to be,happen to be,is likely to be或go,remain,stand,lie,exist,follow,live,come,occur等替换例:There existed different opinions on this problem.·there be结构的非谓语形式:there to be 和there being。
there to be结构可用作动词的宾语,也可用作介词for的宾语;there being可用作除for外的介词宾语或状语例:I expect there to be no argument about this.(作宾语)I have never dreamed of there being a chance to go abroad.(作宾语)There being no enough time left, we have to hurry.(独立主格结构作状语)注:·跟动名词的动词后用there being,常见的有:deny,mind,admit,imagine等·跟不定式的动词后用there to be,常见的动词有:expect,want,hope,wish,like,hate,would like,prefer,mean,intend等c. 固定句型①There is no point/sense (in) doing sth “做某事没意义”例:There is no point/sense arguing further.②There is no doubt that…“毫无疑问…”例:There is no doubt that the new technology is changing the way we work.③There is no need to do sth “没必要做某事“例;There is no need to get up early tomorrow.④There is no possibility/ chance that…“……是不可能的”例:There is no chance that he will change his mind.⑤There is no denying (the fact) that…“不可否认……”例:There is no denying (the fact) that our life has gone from bad to worse.⑥There is no difficulty/ trouble in doing sth“作某事没困难”例:There is no trouble in solving the problem.d. 区分:there be 和have①there be与have都可表示“有”,但在意义上,have表示所有关系,即“拥有”,there be则表示“客观存在”。

【高优指导】(全国通用)2021高考英语一轮复习语法专题13特殊句式新人教版Ⅰ.依照语境和括号内的提示完成句子1.(2020·江苏改编)It might have saved me some trouble (I know) the schedule.2.(2020·湖南改编)Always(keep) in mind that your main task is to get this company running smoothly.〚导学号95480027〛3.(2020·安徽江南十校联考改编) Don’t forget to put the tools back where they were after you have finished your work,you?4.(2020·湖南衡阳五校联考改编)It was not until near the end of the lettershe mentioned her own plan.〚导学号95480028〛5.(2020·福州第二次质检改编)It is not until I have got all the informationI can make further comments.6.(2020·安徽江淮十校联考改编) It was only when I watched Inception a second timeI had a better understanding of what it was talking about.7.(2020·安徽淮北二模改编)(Take) a deep breath and you will immediately feel the spring in the air.8.(2020·重庆改编)—I spent two weeks in London last summer.—Then you must have visited the British Museum during your stay,?〚导学号95480029〛9.(2020·湖南改编)It’s not doing the things we like,but liking the things we have to do makes life happy.10.(2020·福建改编)It was the culture,rather than the language, made it hard for him to adapt to the new environment abroad.Ⅱ.完成句子1.所有的英国人都通晓自己的语言,这绝不是确实。
高考英语二轮总复习第13讲特殊句式学案1、and, then, and then 意思是“就,那么,才”,表示按照祈使句说的去做,会产生顺应的结果。
2、 or, or else, otherwise 意思是“否则,要不,不然的话”,表示不按照祈使句说的去做,则会产生相反的结果。
Come early, and youll catch the first bus、→If you come early, youll catch the first bus、→Coming early, youll cat chthe first bus、→Come early, or you wont catch the first bus、反意疑问句1、反意疑问句的陈述部分含有由un, im, in, dis等否定意义的前缀构成的词语时,陈述部分要视为肯定含义,问句部分用否定形式。
Your father is unhappy,_isnt_he?(不能用is he?)2、陈述部分用must (may, might)+ have + v、ed表示推测时,若句中带有明显的过去时间状语,问句部分动词用过去时形式。
陈述部分用must (may, might)+ have + v、ed表示推测时,若句中没有过去时间状语,问句部分动词用现在完成时形式。
H e might have forgottenhis pen in the classroom yesterday, didnt_he? (不用mightnt he?/ hasnt he?)You must have worked there a year ago, didnt_you?(不用mustnt you?/havent you?)省略句代替性省略:“so”可代替某些动词后的宾语从句,但绝不能用it或that。
这些常用的动词有believe, be afraid, expect, hope, imagine, suppose, Im sure等;not代替的是否定意义的宾语从句。
高考英语第二轮语法专题复习十三句子The Sentences知识要点:句子按使用的目的可分为四类:1、陈述句2、疑问句3、祈使句4、感叹句从结构上看句子可分为三种类型:1、简单句2、并列句3、复合句一、句子的种类(Kinds of Sentences)1、陈述句:(1)肯定句:We love our motherland. 我们热爱祖国。
(2)否定句:They don’t go to work on Sundays. 他们星期日不上班。
说明:叙述或否定一个事实或看法。
2、疑问句:(1)一般疑问句:Are you a worker? 你是个工人吗?Yes, I am. 是的,我是工人。
Haven’t you seen the film? No, I haven’t. 你没看过这部电影吗?没看过。
说明:以一个助动词,情态动词或动词be开始的问句。
回答要用yes或no。
(2)特殊疑问句:Who is the man? 这人是谁?When do you watch TV? 你什么时间看电视?What are they doing now? 他们现在正在干什么?说明:以一个疑问代词或疑问副词开头的句子一般要用倒装句语序(或称为疑问词加一般疑问句)(3)选择疑问句:Do you want tea or coffee? Either will do. 你要茶水还是要咖啡?哪种都行。
Does he learn Japanese or French? He learns French. 他学日语还是学法语?他学法语。
说明:提出两个或两个以上的情况,选择一个作为答案。
(4)反意疑问句:They are goi ng to the airport, aren’t they? 他们要去机场,是吗?You haven’t finished your homework, have you? 你没做完作业,是吗?说明:提出情况或看法问对方是否同意。
2013高考英语二轮复习精品资料专题13 特殊句式(教学案,教师版)【2013高考考纲解读】特殊句式已经成为高考的热点,而倒装句和强调句又是热点之热点。
命题者加大了对句子结构和知识面的考查,同时注重考查知识之间的交叉和语法知识的力度。
例如,高考试题中,在考查强调句的同时考查定语从句、时间状语从句、地点状语从句,强调了学生综合把握语法知识的能力。
这就要求我们在平时的复习和备考中注意总结,全面把握。
倒装句、强调句有以下十大考点:(1)含有否定意义的副词放在句首引起的部分倒装;(2)含有否定意义的连接词置于句首引起的部分倒装;(3)“so(nor, neither)+助动词 + 主语”与“so(nor, neither)+主语+助动词”之间的区别以及与“ so + 主语+ 助动词”的句式区别;(4)省略if的虚拟条件句以had / were / should开头引起的部分倒装;(5)not until置于句首引起后面句子的部分倒装;(6)only短语置于句首引起的部分倒装;(7)考查强调句式的基本结构;(8)考查含有“not…until…”句型的强调句式;(9)考查强调句式的疑问句;(10)考查强调句式的正确判断;【重点知识整合】一、完全倒装1. here, there, away, down, in, up, off, out, now, then, next等表方位的副词或时间副词放在句首,且句子主语为名词时。
Here comes the bus.公共汽车朝这儿开过来了。
【例】For a moment nothing happened Then all shouting together.A. voices had comeB. came voicesC. voices would comeD. did voices come 【答案】B【解析】考查特殊句式。
副词then位于句首,且当句子的主语是名词时,句子用全部倒装句,选B。
特殊句式(强调句型、省略、反意疑问句及其他)强调强调句的基本句型是“It is/was+被强调的部分+that/who+其他部分”。
被强调的部分可以是主语、宾语和状语等。
强调句型的使用特点主要有以下几个方面:(1)被强调的是状语或状语从句时,要用that引导从句,而不能用which,而且通常不能省略。
It was in the park that I met him.我是在公园里遇到他的。
It was in 1964 that the first telephone satellite was set up by the Group of 17 Countries.17国集团发射第一颗电话卫星是在1964年。
(2)被强调的是人时,引导词可用who,也可用that。
Was it you that/who let out the secret to her?是你把这个秘密泄露给她的吗?注意:当被强调的是主语时,代词要用主格形式。
It was I who put forward the theory first.是我最先提出这个理论的。
(3)被强调的不管是单数还是复数名词,主句的be动词都用单数is或was。
It was Madame Curie and her husband who discovered radium.是居里夫人和她的丈夫发现了镭。
It is the PLA men who/that are safeguarding our country day and night.是解放军战士日夜保卫着我们的祖国。
(4)对not...until时间状语从句进行强调时,其句型是:It is/was not until...that从句,即not和until在强调句中总是紧挨着的。
注意习惯上不用not till,而且从句不能用when引导。
It was not until the last operation was finished that Bethune left the battle hospital.直到做完最后一个手术白求恩才离开战地医院。
特殊句式在近几年高考题中所占分量居中,各套试题中至少有一道小题考查特殊句式。
主要考查倒装句、省略替代、强调句以及感叹句和反意疑问句。
一、倒装口诀速记:副词开头要倒装,人称代词则如常。
only修饰副介状,位于句首半倒装。
否定意义副连词,“既不……也不”需倒装。
表语前置主语长,衔接自然常倒装。
such代词作表语,引起主谓要倒装。
not only开头句,前一分句需倒装。
had,were,should虚拟句,省略if半倒装。
倒装分两类:全部倒装和部分倒装。
全部倒装是将句子中的谓语动词全部置于主语之前。
实义动词、情态动词或be 动词放在主语之前。
部分倒装是指将谓语的一部分如助动词或情态动词倒装至主语之前。
如果句中的谓语没有助动词或情态动词,则需添加助动词do, does 或did,并将其置于主语之前。
1.全部倒装的情况2. 部分倒装的情况二、省略在英语中,有时为了避免结构上或内容上的重复,并使上下文紧密连接;有时因为语法的客观要求,句子中的一个或几个成分不需要表达出来,这种现象称为省略。
英语中的省略要求不破坏语法结构,要保持句子意义的准确无误。
省略有词法上的省略,也有句法上的省略,还有一种替代省略。
省略部分的成分和含义可从上下文或具体语言环境中找到而且是有章可循的,英语的省略大致有以下几种情况:1.介词的省略一些与动词、名词或形容词一起搭配的介词常省略,而保留其后的动名词。
常见的句型有:spend some time (in) doing sth.;be busy (in) doing sth.;have difficulty (in) doing sth.;stop/prevent sb. (from) doing sth.2.连词that 的省略I believe (that) he will e here.It's a pity (that) he will leave this city.3.定语从句与名词性从句中的省略(1) 在限制性定语从句中,作宾语用的关系代词whom, which, that可省略。
如:The teacher (who/whom/that) I talked with was Mr. Meng.(2) 在与suggest, request, order, advise等词相关的名词性从句中,应用虚拟语气形式“should +动词原形”,should可以省略。
如:She suggests that we (should) go at once.4.动词不定式省略,只保留to的场合。
不定式作某些动词的宾语时,常见的动词有expect, refuse, mean, like, love, hope,want等。
如:He went home that day though he didn't want to.三、反意疑问句1.陈述部分含有must的反意疑问句当must作“必须”讲时,其反意疑问部分用needn't;当含有mustn't(不允许、禁止)时,其反意疑问部分用must;当must表示推测,作“一定,准是”讲时,反意疑问部分的动词形式根据must后面的动词形式确定。
如:You must go now, needn't you?你现在必须走,是不是?You mustn't smoke here, must you?你不能在这里吸烟,是吧?You must have watched that football match last night, didn't you? 你昨晚一定是看足球比赛了,是吧?2.陈述部分含有used to的反意疑问句陈述部分含有used to时,其反意疑问部分用usedn't或didn't均可。
如:You used to play football, usedn't/didn't you?你过去常常踢足球,是吗?3.陈述部分含有ought to的反意疑问句其反意疑问部分用oughtn't或shouldn't均可。
如:He ought to attend the meeting, oughtn't/shouldn't he?他应该参加会议,是不是?4.否定词或半否定词的反意疑问句当陈述部分带有seldom, hardly, scarcely, never, few, little, nothing, nobody等否定词或半否定词时,疑问部分的动词用肯定形式。
如:He could hardly get up, could he?他几乎起不来了,是不是?5.陈述部分含有表示“否定”意义的前缀构成的词,其反意疑问部分一般用否定式。
如:Mary dislikes sports, doesn't she?玛丽不喜欢体育运动,不是吗?6.含有宾语从句的反意疑问句当陈述部分带有宾语从句时,疑问部分的主语应和主句的主语保持一致。
但当主句是:I think,I believe, I suppose, I expect, I imagine等结构时,疑问部分的主语和谓语动词均应和宾语从句的主语和谓语保持一致。
如:He said that he would e here on time, didn't he?I don't think he will e here on time, will he?7.祈使句的反意疑问句祈使句后加附加问句,不表示反意,而表示一种语气。
其结构为:否定祈使句,+will you?肯定祈使句,+will/won't you? Let's…,+shall we? Let us…,+will you?如:Open the door, will you?Let's go out for a walk, shall we?Let us go to school, will you?注意:(1) 反意疑问句的回答不要看汉语如何翻译,只看所提到的事情是否发生。
如果发生了,用肯定回答,否则用否定回答。
如:当对方问你“You aren't a teacher, are you?”或“You are a teacher, aren't you?”时,如果你是老师,回答“Yes, I am. ”否则,回答“No, I am not. ”(2)反意疑问句的主语和陈述部分的主语在人称、数上需要注意的几种情况四、强调句一个句子中除谓语外的任何成分均可借助It be…that…予以强调,被强调部分置于be 之后。
无论被强调的是人﹑物﹑时间﹑地点还是方式一律用that, 只有强调人时也可用who。
被强调的人称代词主格或宾格如I /me,其形式不可变动,即被强调的任何成分必须原封不动地放到be之后。
一个句子,如果将其中的It is/was…that去掉,在不加减任何词语的情况下,语序稍作调整能构成一个完整正确的句子,便可以认定为强调句,否则就不是强调句。
1.【误】Did he begin to learn English only when he was 30 years old.【正】He began to learn English only when he was 30 years old.【解析】当only和所修饰的状语位于句首时引起部分倒装,如果不在句首时,则不倒装,此外,当only用于修饰名词或代词时,也不倒装,如:Only the grown-ups are allowed to see the film.2.【误】Not only can he repair bikes but can he repair televisions.【正】Not only can he repair bikes but he can repair televisions.【解析】not only…but (also)…的部分倒装,其结构为:not only+倒装语序,but also +语序不变。
此外,当not only…but also…位于句首连接两个并列的主语时,主谓也不倒装,如:Not only I but also she will get married next year.3.【误】—I seldom watch TV, but listen to the radio a lot.—So do I.【正】—I seldom watch TV, but listen to the radio a lot.—So it is with me.【解析】若前面为两个或两个以上的分句,表示不同的主语与前面有关的各种情况相同,往往用:so it is/was with +主语或者是it is/was the same with +主语。
4.【误】A child as/though he is, he is very brave.【正】Child as/though he is, he is very brave.【解析】由as/though引导的表示“虽然,尽管”的让步状语从句用倒装语序,把从句的表语或状语等放在as/though的前面,但是如果从句中的表语是名词,其名词前不加任何冠词。
5.【误】—Are you a sailor?—No, but I used to.【正】—Are you a sailor? —No, but I used to be.【解析】动词不定式的省略:在同一句或联系紧密的对话里,常把不定式符to后内容相同的部分省略,只保留to,但如果省略的不定式内容有作助动词用的have或be的任何形式时,to后要保留原形have 或be。
6.【误】—Are you and Jane getting married?—We hope.【正】—Are you and Jane getting married?—We hope to.【解析】动词不定式在like, love, care, want, hope, expect, prefer, refuse, decide, mean, intend, try, promise等动词后作宾语时,为了避免重复,常承前省略不定式后的内容,但要保留不定式符to。
7.【误】I came not to scold but praise you.【正】I came not to scold but to praise you.【解析】在并列结构中为了避免重复,后一个to常省略,但两个不定式有对照或对比的意义时,则后一个to不能省略。